
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
The NASA spacecraft MAVEN entered into orbit around Mars to study the planet's atmosphere.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.

MAVEN is an American spacecraft orbiting Mars to study the loss of its atmospheric gases to space, providing insight into the history of the planet's climate and water. The spacecraft name is an acronym for "Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution" and also a word that means "a person who has special knowledge or experience; an expert". MAVEN was launched on an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, on 18 November 2013 UTC and went into orbit around Mars on 22 September 2014 UTC. The mission is the first by NASA to study the Mars atmosphere. The probe is analyzing the planet's upper atmosphere and ionosphere to examine how and at what rate the solar wind is stripping away volatile compounds.

Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos.

The atmosphere of Mars is the layer of gases surrounding Mars. It is primarily composed of carbon dioxide (95%), molecular nitrogen (2.8%), and argon (2%). It also contains trace levels of water vapor, oxygen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and noble gases. The atmosphere of Mars is much thinner than Earth's. The average surface pressure is only about 610 pascals (0.088 psi) which is less than 1% of the Earth's value. The currently thin Martian atmosphere prohibits the existence of liquid water on the surface of Mars, but many studies suggest that the Martian atmosphere was much thicker in the past. The higher density during spring and fall is reduced by 25% during the winter when carbon dioxide partly freezes at the pole caps. The highest atmospheric density on Mars is equal to the density found 35 km (22 mi) above the Earth's surface and is ≈0.020 kg/m3. The atmosphere of Mars has been losing mass to space since the planet's core slowed down, and the leakage of gases still continues today.
Two suicide bombers attacked a church in Peshawar, Pakistan.
On 22 September 2013, a twin suicide bombing took place at All Saints Church in Peshawar, Pakistan, in which 127 people were killed and more than 250 injured. It was the deadliest attack on the Christian minority in the history of Pakistan.

Peshawar is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is the capital of the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where it is the largest city. Peshawar is primarily populated by Pashtuns, who comprise the second-largest ethnic group in the country. Situated in the Valley of Peshawar, a broad area situated east of the historic Khyber Pass, Peshawar's recorded history dates back to at least 539 BCE, making it one of the oldest cities in South Asia. Peshawer is among the oldest continuously inhabited cities of the country.
At least 75 people are killed in a suicide bombing at a Christian church in Peshawar, Pakistan.
On 22 September 2013, a twin suicide bombing took place at All Saints Church in Peshawar, Pakistan, in which 127 people were killed and more than 250 injured. It was the deadliest attack on the Christian minority in the history of Pakistan.

Peshawar is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is the capital of the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where it is the largest city. Peshawar is primarily populated by Pashtuns, who comprise the second-largest ethnic group in the country. Situated in the Valley of Peshawar, a broad area situated east of the historic Khyber Pass, Peshawar's recorded history dates back to at least 539 BCE, making it one of the oldest cities in South Asia. Peshawer is among the oldest continuously inhabited cities of the country.
Twenty-three people were killed in a maglev train collision in Lathen, Germany.

Maglev, is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of electromagnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage of the lack of friction. Such trains rise approximately 10 centimetres (3.9 in) off the track. There are both high speed, intercity maglev systems, and low speed, urban maglev systems being built and under construction and development.
On 22 September 2006, a Transrapid magnetic levitation train collided with a maintenance vehicle near Lathen, Germany, killing 23 people. It was the first fatal accident involving a maglev train.

Lathen is a municipality in the Emsland district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the location of the Emsland Transrapid Test facility, a testing site for Transrapid maglev trains.

Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
An E-3B AWACS crashes outside Elmendorf Air Force Base, Alaska after multiple bird strikes to two of the four engines soon after takeoff; all 24 on board are killed.

The Alaska Boeing E-3 Sentry accident was the September 22, 1995 crash of a United States Air Force Boeing E-3 Sentry airborne early warning aircraft with the loss of all 24 crewmembers on board. The aircraft, serial number 77-0354 with callsign Yukla 27, hit birds on departure from Elmendorf Air Force Base in Alaska, United States. With the loss of thrust from both of the left engines the aircraft crashed into a wooded area less than a mile from the end of the runway.
The Nagerkovil school bombing is carried out by the Sri Lanka Air Force in which at least 34 die, most of them ethnic Tamil schoolchildren.
The Nager Kovil school bombing refers to an airstrike that took place on September 22, 1995, when the Sri Lankan Air Force bombed the Nagar Kovil Maha Vidyalayam school in Jaffna, resulting in the death of, by varying accounts, 34-71 Sri Lankan Tamil civilians, primarily schoolchildren and the injury of many more. Sri Lankan Defense Spokesman admitted the incident but claimed that it was a LTTE facility and most of the dead were LTTE cadres. Journalists and human rights organizations reported the imposition of censorship and the airstrike took place about 12 hours after the Government imposed press censorship on reporting military events.
The Nordhordland Bridge, crossing Salhusfjorden between Klauvaneset and Flatøy in Vestland, and Norway's second-longest bridge, officially opened.

The Nordhordland Bridge is a combined cable-stayed and pontoon bridge which crosses Salhusfjorden between Klauvaneset and the island of Flatøy in Vestland county, Norway. It is 1,614 meters (5,295 ft) long, of which the pontoon section is 1,246 meters (4,088 ft) long. The cable-stayed section consists of a single 99-meter (325 ft) tall H-pylon which has a length of 368 meters (1,207 ft) and a main span of 172 meters (564 ft). This allows for a clearance of 32 meters (105 ft).

Salhusfjorden is a 4-kilometer (2.5 mi) long fjord and sound between Bergen Municipality and Alver Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. To the west, it starts between the villages of Salhus and Frekhaug, where the Byfjorden meets the Herdlefjorden. To the east, the fjord ends between the village of Knarvik and the Hordvikneset peninsula, where the Osterfjorden runs northeast, the Sørfjorden runs southeast, and the Radfjorden runs north. The fjord is up to 500 meters (1,600 ft) deep. It acts as one of the borders between the districts of Midhordland to the south and Nordhordland to the north. The islands of Holsnøy and Flatøy lie along the northern side of the fjord.

Klauvaneset is a small peninsula in the northern part of Åsane in Bergen Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is the site of the southern part of the Nordhordland Bridge.
Flatøy is an island in Alver Municipality in Vestland county, Norway. The 2.2-square-kilometre (0.85 sq mi) island lies in the district of Nordhordland, just north of the city of Bergen. The main village on the island is Krossneset on the southern part of the island. The northern part of the island, on the southwest shore of Kvernafjord, is very sparsely inhabited. Historically, the island was one of the two main islands of the old Meland Municipality.

Vestland is a county in Norway established on 1 January 2020. The county is located in Western Norway and it is centred around the city of Bergen, Norway's second largest city. The administrative centre of the county is the city of Bergen, where the executive and political leadership is based, but the County Governor is based in Hermansverk. The county is one of two counties in Norway that have Nynorsk as their official written language form.
A tugboat towing a barge collided with a rail bridge in Mobile, Alabama, U.S., deforming the tracks and causing the derailment of a passenger train eight minutes later, which killed 47 people and injured an additional 103.
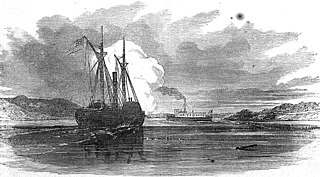
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they can or should not move under their own power, such as in crowded harbour or narrow canals, or cannot move at all, such as barges, disabled ships, log rafts, or oil platforms. Some are ocean-going, some are icebreakers or salvage tugs. Early models were powered by steam engines, long ago superseded by diesel engines. Many have deluge gun water jets, which help in firefighting, especially in harbours.

Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. The term barge has a rich history, and therefore there are many other types of barges.

Mobile is a city and the county seat of Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population within the city limits was 187,041 at the 2020 census, down from 195,111 at the 2010 United States Census. It is the fourth-most-populous city in Alabama, after Huntsville, Birmingham, and Montgomery.

On September 22, 1993, an Amtrak train derailed on the CSX Transportation Big Bayou Canot Bridge near Mobile, Alabama, United States. It was caused by displacement of a span and deformation of the rails when a tow of heavy barges collided with the rail bridge eight minutes earlier. Forty-seven people were killed and 103 more were injured. To date, it is both the deadliest train wreck in Amtrak's history and the worst rail disaster in the United States since the 1958 Newark Bay rail accident in which 48 people died.
A barge strikes a railroad bridge near Mobile, Alabama, causing the deadliest train wreck in Amtrak history. Forty-seven passengers are killed.

On September 22, 1993, an Amtrak train derailed on the CSX Transportation Big Bayou Canot Bridge near Mobile, Alabama, United States. It was caused by displacement of a span and deformation of the rails when a tow of heavy barges collided with the rail bridge eight minutes earlier. Forty-seven people were killed and 103 more were injured. To date, it is both the deadliest train wreck in Amtrak's history and the worst rail disaster in the United States since the 1958 Newark Bay rail accident in which 48 people died.
A Transair Georgian Airlines Tu-154 is shot down by a missile in Sukhumi, Georgia.

From 20 to 23 September 1993, during the Sukhumi massacre, separatists in Sukhumi, Abkhazia blocked Georgian troops' overland supply routes as part of the war in Abkhazia. In response, the Georgian government used Sukhumi Babushara Airport to ferry supplies to troops stationed in Sukhumi. Abkhaz forces attacked the airport in an attempt to further block the supply routes.
The Dead Sea Scrolls are made available to the public for the first time.

The Dead Sea Scrolls are ancient Jewish and Hebrew religious manuscripts discovered between 1946 and 1956 at the Qumran Caves in what was then Mandatory Palestine, near Ein Feshkha in the West Bank, on the northern shore of the Dead Sea. Dating from the 3rd century BCE to the 1st century CE, the Dead Sea Scrolls are considered to be a keystone in the history of archaeology with great historical, religious, and linguistic significance because they include the oldest surviving manuscripts of entire books later included in the biblical canons, along with deuterocanonical and extra-biblical manuscripts which preserve evidence of the diversity of religious thought in late Second Temple Judaism. At the same time they cast new light on the emergence of Christianity and of Rabbinic Judaism. Most of the scrolls are held by Israel in the Shrine of the Book at the Israel Museum, but their ownership is disputed by Jordan due to the Qumran Caves' history: following the End of the British Mandate for Palestine in 1947, Jordan occupied the area in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, and Israel captured both the area and several Scrolls from Jordan in the 1967 Six Day War. However, some of the scrolls are still in Jordan and are now displayed at The Jordan Museum in Amman. Ownership of the scrolls is also contested by the State of Palestine.
Iraq invades Iran, sparking the nearly eight year Iran–Iraq War.

The Iraqi invasion of Iran refers to the Iraqi military campaign against neighbouring Iran in 1980, when the Iraqi Armed Forces crossed the international border and invaded the country, sparking the protracted Iran–Iraq War. The initial invasion was launched on 22 September 1980 and lasted until 7 December of that same year. Contrary to Iraqi expectations of a disorganized and poor response from Iran in light of the turmoil caused by the 1979 Islamic Revolution, the invasion stalled severely in the face of fierce Iranian resistance, but not before Iraq had captured more than 15,000 km2 of Iranian territory.

The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598 by both sides. Iraq's primary rationale for the attack against Iran cited the need to prevent Ruhollah Khomeini—who had spearheaded Iran's Islamic Revolution in 1979—from exporting the new Iranian ideology to Iraq; there were also fears among the Iraqi leadership of Saddam Hussein that Iran, a theocratic state with a population predominantly composed of Shia Muslims, would exploit sectarian tensions in Iraq by rallying Iraq's Shia majority against the Baʽathist government, which was officially secular and dominated by Sunni Muslims. Iraq also wished to replace Iran as the power player in the Persian Gulf, which was not seen as an achievable objective prior to the Islamic Revolution as Pahlavi Iran boasted colossal economic and military strength as well as close relationships with the United States and Israel.
An American Vela satellite detected an unidentified flash of light near the Prince Edward Islands in the Indian Ocean, thought to be a nuclear weapons test.
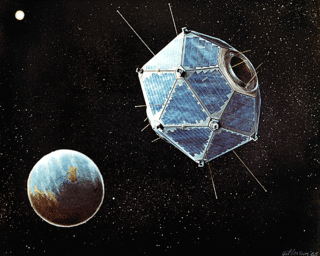
Vela was the name of a group of satellites developed as the Vela Hotel element of Project Vela by the United States to detect nuclear detonations to monitor compliance with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty by the Soviet Union.
The Vela incident was an unidentified double flash of light detected by an American Vela Hotel satellite on 22 September 1979 near the South African territory of Prince Edward Islands in the Indian Ocean, roughly midway between Africa and Antarctica. Today, most independent researchers believe that the flash was caused by a nuclear explosion—an undeclared joint nuclear test carried out by South Africa and Israel.

The Prince Edward Islands are two small uninhabited islands in the sub-Antarctic Indian Ocean that are part of South Africa. The islands are named Marion Island and Prince Edward Island.

Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test.
A bright flash, resembling the detonation of a nuclear weapon, is observed near the Prince Edward Islands. Its cause is never determined.
The Vela incident was an unidentified double flash of light detected by an American Vela Hotel satellite on 22 September 1979 near the South African territory of Prince Edward Islands in the Indian Ocean, roughly midway between Africa and Antarctica. Today, most independent researchers believe that the flash was caused by a nuclear explosion—an undeclared joint nuclear test carried out by South Africa and Israel.

The Prince Edward Islands are two small uninhabited islands in the sub-Antarctic Indian Ocean that are part of South Africa. The islands are named Marion Island and Prince Edward Island.
Sara Jane Moore attempted to assassinate U.S. president Gerald Ford, but failed due to unfamiliarity with her weapon.
Sara Jane Moore is an American criminal who attempted to assassinate U.S. President Gerald Ford in 1975. She was given a life sentence for the attempted assassination and was released from prison on December 31, 2007, after serving 32 years. Moore and Lynette "Squeaky" Fromme are the only two women to have attempted to assassinate an American president; both of their attempts were on Gerald Ford and both took place in California within three weeks of one another.

Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected to the office of president or vice president. He previously served as the leader of the Republican Party in the House of Representatives, and was appointed to be the 40th vice president in 1973. When President Richard Nixon resigned in 1974, Ford succeeded to the presidency, but was defeated for election to a full term in 1976.
Sara Jane Moore tries to assassinate U.S. President Gerald Ford, but is foiled by the Secret Service.
Sara Jane Moore is an American criminal who attempted to assassinate U.S. President Gerald Ford in 1975. She was given a life sentence for the attempted assassination and was released from prison on December 31, 2007, after serving 32 years. Moore and Lynette "Squeaky" Fromme are the only two women to have attempted to assassinate an American president; both of their attempts were on Gerald Ford and both took place in California within three weeks of one another.
Twenty-four people are killed when Ansett-ANA Flight 149 crashes in Winton, Queensland, Australia.

On 22 September 1966 a Vickers Viscount departed from Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia for a 73-minute flight to Longreach. Forty-four minutes after takeoff a fire started in one of the engines. The crew were unable to extinguish the fire or feather the propeller so made an emergency descent with the intention of landing at Winton, a small town along the route. The fire spread to the fuel tank and weakened the wing structure so that a large part of the left wing broke away and the aircraft crashed. All twenty-four occupants were killed. The accident remains the fifth-worst in Australia's civil aviation history.

Winton is a town and locality in the Shire of Winton in Central West Queensland, Australia. It is 177 kilometres (110 mi) northwest of Longreach. The main industries of the area are sheep and cattle raising. The town was named in 1876 by postmaster Robert Allen, after his place of birth, Winton, Dorset. Winton was the first home of the airline Qantas.

Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of 7,617,930 square kilometres (2,941,300 sq mi), Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east, and mountain ranges in the south-east.
The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 between India and Pakistan over Kashmir, ends after the United Nations calls for a ceasefire.

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 or the Second Kashmir War was a culmination of skirmishes that took place between April 1965 and September 1965 between Pakistan and India. The conflict began following Pakistan's Operation Gibraltar, which was designed to infiltrate forces into Jammu and Kashmir to precipitate an insurgency against Indian rule. It became the immediate cause of the war. The seventeen-day war caused thousands of casualties on both sides and witnessed the largest engagement of armored vehicles and the largest tank battle since World War II. Hostilities between the two countries ended after a ceasefire was declared through UNSC Resolution 211 following a diplomatic intervention by the Soviet Union and the United States, and the subsequent issuance of the Tashkent Declaration. Much of the war was fought by the countries' land forces in Kashmir and along the border between India and Pakistan. This war saw the largest amassing of troops in Kashmir since the Partition of India in 1947, a number that was overshadowed only during the 2001–2002 military standoff between India and Pakistan. Most of the battles were fought by opposing infantry and armoured units, with substantial backing from air forces, and naval operations.
The Sudanese Republic is renamed Mali after the withdrawal of Senegal from the Mali Federation.

The Mali Federation was a federation in West Africa linking the French colonies of Senegal and the Sudanese Republic for two months in 1960. It was founded on 4 April 1959 as a territory with self-rule within the French Community and became independent after negotiations with France on 20 June 1960. Two months later, on 19 August 1960, the Sudanese Republic leaders in the Mali Federation mobilized the army, and Senegal leaders in the federation retaliated by mobilizing the gendarmerie ; this resulted in a tense stand-off, and led to the withdrawal from the federation by Senegal the next day. The Sudanese Republic officials resisted this dissolution, cut off diplomatic relations with Senegal, and defiantly changed the name of their country to Mali. For the brief existence of the Mali Federation, the premier was Modibo Keïta, who would later become the first President of Mali, and its government was based in Dakar, the eventual capital of Senegal.
François "Papa Doc" Duvalier (pictured) was elected President of Haiti as a populist before consolidating power and ruling as a dictator for the rest of his life.

François Duvalier, also known as Papa Doc, was a Haitian politician of French Martiniquan descent who served as the President of Haiti from 1957 to 1971. He was elected president in the 1957 general election on a populist and black nationalist platform. After thwarting a military coup d'état in 1958, his regime rapidly became more autocratic and despotic. An undercover government death squad, the Tonton Macoute, indiscriminately killed Duvalier's opponents; the Tonton Macoute was thought to be so pervasive that Haitians became highly fearful of expressing any form of dissent, even in private. Duvalier further sought to solidify his rule by incorporating elements of Haitian mythology into a personality cult.

General elections were held in Haiti on 22 September 1957. Former Minister of Labour François Duvalier won the presidential election running under the National Unity Party banner, defeating Louis Déjoie, as well as independent moderate Clement Jumelle, who had dropped out on election day in a cloud of suspicions that the army was monitoring the election in favour of Duvalier. Former head of state Daniel Fignolé, considered a champion of poor blacks, was considered ineligible as he had been forcibly exiled months before the election, allegedly kidnapped.

Populism refers to a range of political stances that emphasize the idea of "the people" and often juxtapose this group against "the elite". It is frequently associated with anti-establishment and anti-political sentiment. The term developed in the late 19th century and has been applied to various politicians, parties and movements since that time, often as a pejorative. Within political science and other social sciences, several different definitions of populism have been employed, with some scholars proposing that the term be rejected altogether.
In Haiti, François Duvalier is elected president.

François Duvalier, also known as Papa Doc, was a Haitian politician of French Martiniquan descent who served as the President of Haiti from 1957 to 1971. He was elected president in the 1957 general election on a populist and black nationalist platform. After thwarting a military coup d'état in 1958, his regime rapidly became more autocratic and despotic. An undercover government death squad, the Tonton Macoute, indiscriminately killed Duvalier's opponents; the Tonton Macoute was thought to be so pervasive that Haitians became highly fearful of expressing any form of dissent, even in private. Duvalier further sought to solidify his rule by incorporating elements of Haitian mythology into a personality cult.
Led by Gail Halvorsen, the United States Air Force began Operation "Little Vittles", delivering candy to children as part of the Berlin Airlift.

COL Gail Seymour "The Candy Bomber" Halvorsen was a senior officer and command pilot in the United States Air Force. He is best known as the "Berlin Candy Bomber" or "Uncle Wiggly Wings" and gained fame for dropping candy to German children during the Berlin Airlift from 1948 to 1949.

The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control.

The Berlin Blockade was one of the first major international crises of the Cold War. During the multinational occupation of post–World War II Germany, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies' railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control. The Soviets offered to drop the blockade if the Western Allies withdrew the newly introduced Deutsche Mark from West Berlin.
Gail Halvorsen officially starts parachuting candy to children as part of the Berlin Airlift.

The Berlin Blockade was one of the first major international crises of the Cold War. During the multinational occupation of post–World War II Germany, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies' railway, road, and canal access to the sectors of Berlin under Western control. The Soviets offered to drop the blockade if the Western Allies withdrew the newly introduced Deutsche Mark from West Berlin.
Israeli-Palestine conflict: The All-Palestine Government is established by the Arab League.

The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is one of the world's most enduring conflicts, beginning in the mid-20th century. Various attempts have been made to resolve the conflict as part of the Israeli–Palestinian peace process, alongside other efforts to resolve the broader Arab–Israeli conflict. Public declarations of claims to a Jewish homeland in Palestine, including the First Zionist Congress of 1897 and the Balfour Declaration of 1917, created early tensions in the region. Following World War I, the Mandate for Palestine included a binding obligation for the "establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people". Tensions grew into open sectarian conflict between Jews and Arabs. The 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was never implemented and provoked the 1947–1949 Palestine War. The current Israeli-Palestinian status quo began following Israeli military occupation of the Palestinian territories in the 1967 Six-Day War.

The All-Palestine Government was established on 22 September 1948, during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, to govern the Egyptian-controlled territory in Gaza, which Egypt had on the same day declared as the All-Palestine Protectorate. It was confirmed by the Arab League and recognised by six of the then seven Arab League members, with Transjordan being the exception. Though it claimed jurisdiction over the whole of the former Mandatory Palestine, its effective jurisdiction was limited to the All-Palestine Protectorate (which came to be called the Gaza Strip. The President of the protectorate was Hajj Amin al-Husseini, former chairman of the Arab Higher Committee, and the Prime Minister was Ahmed Hilmi Pasha. The legislative body was the All-Palestine National Council.

The Arab League, formally the League of Arab States, is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, Eastern Africa, and Western Asia. The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945, initially with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined as a member on 5 May 1945. Currently, the League has 22 members, but Syria's participation has been suspended since November 2011.
The Holocaust in Ukraine: On the Jewish New Year Day, the German SS murders 6,000 Jews in Vinnytsia, Ukraine. Those are the survivors of the previous killings that took place a few days earlier in which about 24,000 Jews were executed.

The Holocaust in Ukraine took place in the Reichskommissariat Ukraine, the General Government, the Crimean General Government and some areas which were located to the East of Reichskommissariat Ukraine, in the Transnistria Governorate and Northern Bukovina and Carpathian Ruthenia during World War II. The listed areas are currently parts of Ukraine. Between 1941 and 1944, more than a million Jews living in the Soviet Union, almost all from Ukraine and Belarus, were murdered by Nazi Germany's "Final Solution" extermination policies and with the help of local Ukrainian collaborators. Most of them were killed in Ukraine because most pre-WWII Soviet Jews lived in the Pale of Settlement, of which Ukraine was the largest part. The major massacres against Jews mainly occurred during the first phase of the occupation, although they continued until the return of the Red Army of the Soviet Union.

Vinnytsia is a city in west-central Ukraine, located on the banks of the Southern Bug.
A joint military parade by the troops of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union took place in Brest-Litovsk to celebrate their partition of Poland.

The German–Soviet military parade in Brest-Litovsk was an official ceremony held by the troops of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union on September 22, 1939, during the invasion of Poland in the city of Brest-Litovsk. It marked the withdrawal of German troops to the demarcation line secretly agreed to in the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, and the handover of the city and its fortress to the Soviet Red Army.

Brest, formerly Brest-Litovsk, Brest-on-the-Bug, is a city in Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the Polish city of Terespol, where the Bug and Mukhavets rivers meet, making it a border town. It is the capital city of the Brest Region.

The invasion of Poland was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign or 1939 defensive war and known in Germany as the Poland campaign.
World War II: A joint German–Soviet military parade in Brest-Litovsk is held to celebrate the successful invasion of Poland.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

The German–Soviet military parade in Brest-Litovsk was an official ceremony held by the troops of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union on September 22, 1939, during the invasion of Poland in the city of Brest-Litovsk. It marked the withdrawal of German troops to the demarcation line secretly agreed to in the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, and the handover of the city and its fortress to the Soviet Red Army.
One of Britain's worst mining accidents took place when an explosion at Gresford Colliery in Wales killed 266 men.

The Gresford disaster occurred on 22 September 1934 at Gresford Colliery, near Wrexham, Denbighshire, when an explosion and underground fire killed 266 men. Gresford is one of Britain's worst coal mining disasters: a controversial inquiry into the disaster did not conclusively identify a cause, though evidence suggested that failures in safety procedures and poor mine management were contributory factors. Further public controversy was caused by the decision to seal the colliery's damaged sections permanently, meaning that only eleven of those who died were recovered.

Gresford Colliery was a coal mine located a mile from the North Wales village of Gresford, near Wrexham.
The Gresford disaster in Wales kills 266 miners and rescuers.

The Gresford disaster occurred on 22 September 1934 at Gresford Colliery, near Wrexham, Denbighshire, when an explosion and underground fire killed 266 men. Gresford is one of Britain's worst coal mining disasters: a controversial inquiry into the disaster did not conclusively identify a cause, though evidence suggested that failures in safety procedures and poor mine management were contributory factors. Further public controversy was caused by the decision to seal the colliery's damaged sections permanently, meaning that only eleven of those who died were recovered.
After nine days, the great fire of Smyrna was extinguished , having caused at least ten thousand deaths.

The burning of Smyrna destroyed much of the port city of Smyrna in September 1922. Eyewitness reports state that the fire began on 13 September 1922 and lasted until it was largely extinguished on 22 September. It began four days after the Turkish military captured the city on 9 September, effectively ending the Greco-Turkish War, more than three years after the landing of Greek army troops at Smyrna on 15 May 1919. Estimated Greek and Armenian deaths resulting from the fire range from 10,000 to 125,000.
The steel strike of 1919, led by the Amalgamated Association of Iron and Steel Workers, begins in Pennsylvania before spreading across the United States.

The Steel Strike of 1919 was an attempt by the American Federation of Labor to organize the leading company, United States Steel, in the American steel industry. The AFL formed a coalition of 24 unions, all of which had grown rapidly during World War I. In the lead role would be the Amalgamated Association of Iron, Steel and Tin Workers (AA) with a five-member steering committee. The strike began on September 22, 1919, and finally collapsed on January 8, 1920. The opposition led by Elbert H. Gary, president of U.S. Steel had triumphed.
First World War: The German submarine U-9 sank three Royal Navy cruisers, resulting in approximately 1,450 deaths.

World War I or the First World War, often abbreviated as WWI or WW1, and referred to by some Anglophone authors as the "Great War" or the "War to End All Wars", was a global conflict which lasted from 1914 to 1918, and is considered one of the deadliest conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war.
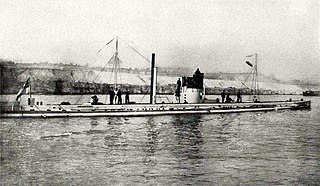
SM U-9 was a German Type U 9 U-boat. She was one of 329 submarines serving in the Imperial German Navy, and engaged in commerce raiding (Handelskrieg) during World War I.

The Action of 22 September 1914 was an attack by the German U-boat U-9 that took place during the First World War. Three obsolete Royal Navy cruisers, of the 7th Cruiser Squadron, manned mainly by Royal Naval Reserve part-time reservists and sometimes referred to as the Live Bait Squadron, were sunk by U-9 while patrolling the southern North Sea.

The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service.
World War I: German naval forces bombarded Papeete in French Polynesia.

World War I or the First World War, often abbreviated as WWI or WW1, and referred to by some Anglophone authors as the "Great War" or the "War to End All Wars", was a global conflict which lasted from 1914 to 1918, and is considered one of the deadliest conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war.

The Bombardment of Papeete occurred in French Polynesia when German warships attacked on 22 September 1914, during World War I. The German armoured cruisers SMS Scharnhorst and Gneisenau entered the port of Papeete on the island of Tahiti and sank the French gunboat Zélée and freighter Walküre before bombarding the town's fortifications. French shore batteries and a gunboat resisted the German intrusion but were greatly outgunned. The main German objective was to seize the coal piles stored on the island, but these were destroyed by the French at the start of the action.

French Polynesia is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) in the South Pacific Ocean. The total land area of French Polynesia is 3,521 square kilometres (1,359 sq mi), with a population of 299,356.
A German submarine sinks three British cruisers over a seventy-minute period, killing almost 1500 sailors.

The Action of 22 September 1914 was an attack by the German U-boat U-9 that took place during the First World War. Three obsolete Royal Navy cruisers, of the 7th Cruiser Squadron, manned mainly by Royal Naval Reserve part-time reservists and sometimes referred to as the Live Bait Squadron, were sunk by U-9 while patrolling the southern North Sea.
The Duke of York's Picture House opens in Brighton, now the oldest continually operating cinema in Britain.

The Duke of York's Picture House is an art house cinema in Brighton, England, which lays claim to being the oldest cinema in continuous use in Britain. According to cinema historian Allen Eyles, the cinema "deserves to be named Britain's oldest cinema".
Queen Victoria surpasses her grandfather King George III as the longest reigning monarch in British history.

Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and seven months was longer than that of any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India.
Lindal Railway Incident, providing inspiration for "The Lost Special" by A.C. Doyle and the TV serial Lost.

The Lindal railway incident happened on Thursday 22 September 1892 near Lindal-in-Furness, a village lying between the Cumbria towns of Ulverston and Dalton-in-Furness. A locomotive shunting at sidings disappeared into the ground after a large, deep hole opened up beneath it. The locomotive was never recovered and still lies buried beneath the railway, though the depth remains a source of speculation.
The first hydropower plant of Finland was commissioned along the Tammerkoski rapids in Tampere, Pirkanmaa.

Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower. Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. However, when constructed in lowland rainforest areas, where part of the forest is inundated, substantial amounts of greenhouse gases may be emitted.

Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland across Estonia to the south. Finland covers an area of 338,455 square kilometres (130,678 sq mi) with a population of 5.6 million. Helsinki is the capital and largest city, forming a larger metropolitan area with the neighbouring cities of Espoo, Kauniainen, and Vantaa. The vast majority of the population are ethnic Finns. Finnish, alongside Swedish, are the official languages. Swedish is the native language of 5.2% of the population. Finland's climate varies from humid continental in the south to the boreal in the north. The land cover is primarily a boreal forest biome, with more than 180,000 recorded lakes.

Tammerkoski is a channel of rapids in Tampere, Finland. The city of Tampere is located between two lakes, Näsijärvi and Pyhäjärvi. The difference in altitude between these two is 18 metres (59 ft) and the water flows from Näsijärvi to Pyhäjärvi through the Tammerkoski rapids. The banks of the Tammerkoski are among the oldest industrial areas in Finland. There was a busy marketplace in the 17th century. Tampere was founded on the banks of the rapids, as the rushing water provided a great deal of power for the needs of industry.

Tampere is a city in the Pirkanmaa region, located in the western part of Finland. Tampere is the most populous inland city in the Nordic countries. It has a population of 244,029; the urban area has a population of 341,696; and the metropolitan area, also known as the Tampere sub-region, has a population of 393,941 in an area of 4,970 km2 (1,920 sq mi). Tampere is the second-largest urban area and third most-populous individual municipality in Finland, after the cities of Helsinki and Espoo, and the most populous Finnish city outside the Greater Helsinki area. Today, Tampere is one of the major urban, economic, and cultural hubs in the whole inland region.
Pirkanmaa, also known as Tampere Region in government documents, is a region of Finland. It borders the regions of Satakunta, South Ostrobothnia, Central Finland, Päijät-Häme, Kanta-Häme and Southwest Finland. Most of the water area in the Kokemäki River watershed is located in the Pirkanmaa region, although Lake Vanajavesi is partly in the Kanta-Häme region. The region got its name from Pirkkala, which in the Middle Ages comprised most of present-day Pirkanmaa. Tampere is the regional center and capital of Pirkanmaa, and at the same time the largest city in the region.
Lord Randolph Churchill makes a speech in Ulster in opposition to the Irish Home Rule movement.

Lord Randolph Henry Spencer-Churchill was a British statesman. Churchill was a Tory radical and coined the term 'Tory democracy'. He inspired a generation of party managers, created the National Union of the Conservative Party, and broke new ground in modern budgetary presentations, attracting admiration and criticism from across the political spectrum. His most acerbic critics were in his own party, among his closest friends; but his disloyalty to Lord Salisbury was the beginning of the end of what could have been a glittering career. His elder son was Winston Churchill, who wrote a biography of him in 1906.

The Irish Home Rule movement was a movement that campaigned for self-government for Ireland within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It was the dominant political movement of Irish nationalism from 1870 to the end of World War I.
Das Rheingold, the first of four operas in Der Ring des Nibelungen by the German composer Richard Wagner (pictured), was first performed in Munich.

Das Rheingold, WWV 86A, is the first of the four music dramas that constitute Richard Wagner's Der Ring des Nibelungen. It was performed, as a single opera, at the National Theatre Munich on 22 September 1869, and received its first performance as part of the Ring cycle at the Bayreuth Festspielhaus, on 13 August 1876.

Der Ring des Nibelungen, WWV 86, is a cycle of four German-language epic music dramas composed by Richard Wagner. The works are based loosely on characters from Germanic heroic legend, namely Norse legendary sagas and the Nibelungenlied. The composer termed the cycle a "Bühnenfestspiel", structured in three days preceded by a Vorabend. It is often referred to as the Ring cycle, Wagner's Ring, or simply The Ring.

Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas. Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the music for each of his stage works. Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works in the romantic vein of Carl Maria von Weber and Giacomo Meyerbeer, Wagner revolutionised opera through his concept of the Gesamtkunstwerk, by which he sought to synthesise the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, with music subsidiary to drama. He described this vision in a series of essays published between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised these ideas most fully in the first half of the four-opera cycle Der Ring des Nibelungen.
The Battle of Curupayty is Paraguay's only significant victory in the Paraguayan War.

The Battle of Curupayty was a key battle in the Paraguayan War. On the morning on 22 September 1866, the joint force of Brazilian, Argentine, and Uruguayan armies attacked Paraguayan fortified trenches on Curupayty. The Paraguayans were led by general José Eduvigis Díaz. This position was held by 5,000 men and 49 cannons, some of them in hidden places out of the attackers view. The Imperial Brazilian Navy gave support to the 20,000 assailants, but the ships had to keep some distance from the guns at the fortress of Humaitá, which led to the lack of accuracy and impact of the ship's fire. The navy's failure was crucial at the later ground battle result.

The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadliest and bloodiest inter-state war in Latin American history. Paraguay sustained large casualties, but the approximate numbers are disputed. Paraguay was forced to cede disputed territory to Argentina and Brazil. The war began in late 1864, as a result of a conflict between Paraguay and Brazil caused by the Uruguayan War. Argentina and Uruguay entered the war against Paraguay in 1865, and it then became known as the "War of the Triple Alliance".
A preliminary version of the Emancipation Proclamation is released by Abraham Lincoln.

The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the Civil War. The Proclamation changed the legal status of more than 3.5 million enslaved African Americans in the secessionist Confederate states from enslaved to free. As soon as slaves escaped the control of their enslavers, either by fleeing to Union lines or through the advance of federal troops, they were permanently free. In addition, the Proclamation allowed for former slaves to "be received into the armed service of the United States."
The Russian warship Lefort capsizes and sinks during a storm in the Gulf of Finland, killing all 826 aboard.

Lefort was an Imperatritsa Aleksandra–class ship of the line of the Imperial Russian Navy, rated at 84 guns but actually armed with 94 guns. Her keel was laid in 1833 at Saint Petersburg and she was launched 9 August [O.S. 28 July] 1835 in the presence of Nicholas I. She was named after Admiral Franz Lefort, the head of the Russian Navy from 1695 to 1696.
Joseph Smith claims to have found the golden plates after being directed by God through the Angel Moroni to the place where they were buried.

Joseph Smith Jr. was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, he had attracted tens of thousands of followers and founded a religion that continues to the present with millions of global adherents.

According to Latter Day Saint belief, the golden plates are the source from which Joseph Smith translated the Book of Mormon, a sacred text of the faith. Some witnesses described the plates as weighing from 30 to 60 pounds, gold in color, and composed of thin metallic pages engraved with hieroglyphics on both sides and bound with three D-shaped rings.
Primidi Vendémiaire of year one of the French Republican Calendar as the French First Republic comes into being.

Vendémiaire was the first month in the French Republican calendar. The month was named after the Occitan word vendemiaire.
The office of United States Postmaster General is established.

The United States Postmaster General (PMG) is the chief executive officer of the United States Postal Service (USPS). The PMG is responsible for managing and directing the day-to-day operations of the agency.
Battle of Rymnik: Alexander Suvorov's Russian and allied army defeats superior Ottoman Empire forces.

The Battle of Rymnik on September 22, 1789 took place in Wallachia, near Râmnicu Sărat, during the Russo-Turkish War of 1787–1792. The Russian general Alexander Suvorov, acting together with the Habsburg general Prince Josias of Coburg, attacked the main Ottoman army under Grand Vizier Cenaze Hasan Pasha. The result was a crushing Russo-Austrian victory.
Nathan Hale is hanged for spying during the American Revolution.

Nathan Hale was an American Patriot, soldier and spy for the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He volunteered for an intelligence-gathering mission in New York City but was captured by the British and executed. Hale is considered an American hero and in 1985 was officially designated the state hero of Connecticut.
George III and Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz are crowned King and Queen, respectively, of the Kingdom of Great Britain.

George III was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until his death in 1820. He was the longest-lived and longest-reigning king in British history. He was concurrently Duke and Prince-elector of Brunswick-Lüneburg ("Hanover") in the Holy Roman Empire before becoming King of Hanover on 12 October 1814. He was a monarch of the House of Hanover but, unlike his two predecessors, he was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language and never visited Hanover.

Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz was Queen of Great Britain and of Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which she was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until her death in 1818. As George's wife, she was also Electress of Hanover until becoming Queen of Hanover on 12 October 1814, when the electorate became a kingdom. Charlotte was Britain's longest-serving queen consort.
The Tuscarora War begins in present-day North Carolina.

The Tuscarora War was fought in North Carolina from September 10, 1711 until February 11, 1715 between the Tuscarora people and their allies on one side and European American settlers, the Yamassee, and other allies on the other. This was considered the bloodiest colonial war in North Carolina. The Tuscarora signed a treaty with colonial officials in 1718 and settled on a reserved tract of land in Bertie County, North Carolina. The war incited further conflict on the part of the Tuscarora and led to changes in the slave trade of North and South Carolina.
The last hanging of those convicted of witchcraft in the Salem witch trials; others are all eventually released.

The Salem witch trials were a series of hearings and prosecutions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts between February 1692 and May 1693. More than 200 people were accused. Thirty people were found guilty, 19 of whom were executed by hanging. One other man, Giles Corey, was pressed to death after refusing to enter a plea, and at least five people died in jail.
Eighty Years' War: Spanish forces defeated an Anglo-Dutch army at the Battle of Zutphen.

The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, taxation, and the rights and privileges of the nobility and cities. After the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed his armies and regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic- and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent, but the general rebellion failed to sustain itself. Despite Governor of Spanish Netherlands and General for Spain, the Duke of Parma's steady military and diplomatic successes, the Union of Utrecht continued their resistance, proclaiming their independence through the 1581 Act of Abjuration, and establishing the Protestant-dominated Dutch Republic in 1588. In the Ten Years thereafter, the Republic made remarkable conquests in the north and east against a struggling Spanish Empire, and received diplomatic recognition from France and England in 1596. The Dutch colonial empire emerged, which began with Dutch attacks on Portugal's overseas territories.

The Battle of Zutphen was fought on 22 September 1586, near the village of Warnsveld and the town of Zutphen, the Netherlands, during the Eighty Years' War. It was fought between the forces of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, aided by the English, against the Spanish. In 1585, England signed the Treaty of Nonsuch with the States-General of the Netherlands and formally entered the war against Spain. Robert Dudley, Earl of Leicester, was appointed as the Governor-General of the Netherlands and sent there in command of an English army to support the Dutch rebels. When Alessandro Farnese, Duke of Parma and commander of the Spanish Army of Flanders, besieged the town of Rheinberg during the Cologne War, Leicester, in turn, besieged the town of Zutphen, in the province of Gelderland and on the eastern bank of the river IJssel.
The Battle of Zutphen is a Spanish victory over the English and Dutch.

The Battle of Zutphen was fought on 22 September 1586, near the village of Warnsveld and the town of Zutphen, the Netherlands, during the Eighty Years' War. It was fought between the forces of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, aided by the English, against the Spanish. In 1585, England signed the Treaty of Nonsuch with the States-General of the Netherlands and formally entered the war against Spain. Robert Dudley, Earl of Leicester, was appointed as the Governor-General of the Netherlands and sent there in command of an English army to support the Dutch rebels. When Alessandro Farnese, Duke of Parma and commander of the Spanish Army of Flanders, besieged the town of Rheinberg during the Cologne War, Leicester, in turn, besieged the town of Zutphen, in the province of Gelderland and on the eastern bank of the river IJssel.
The Treaty of Basel concludes the Swabian War.
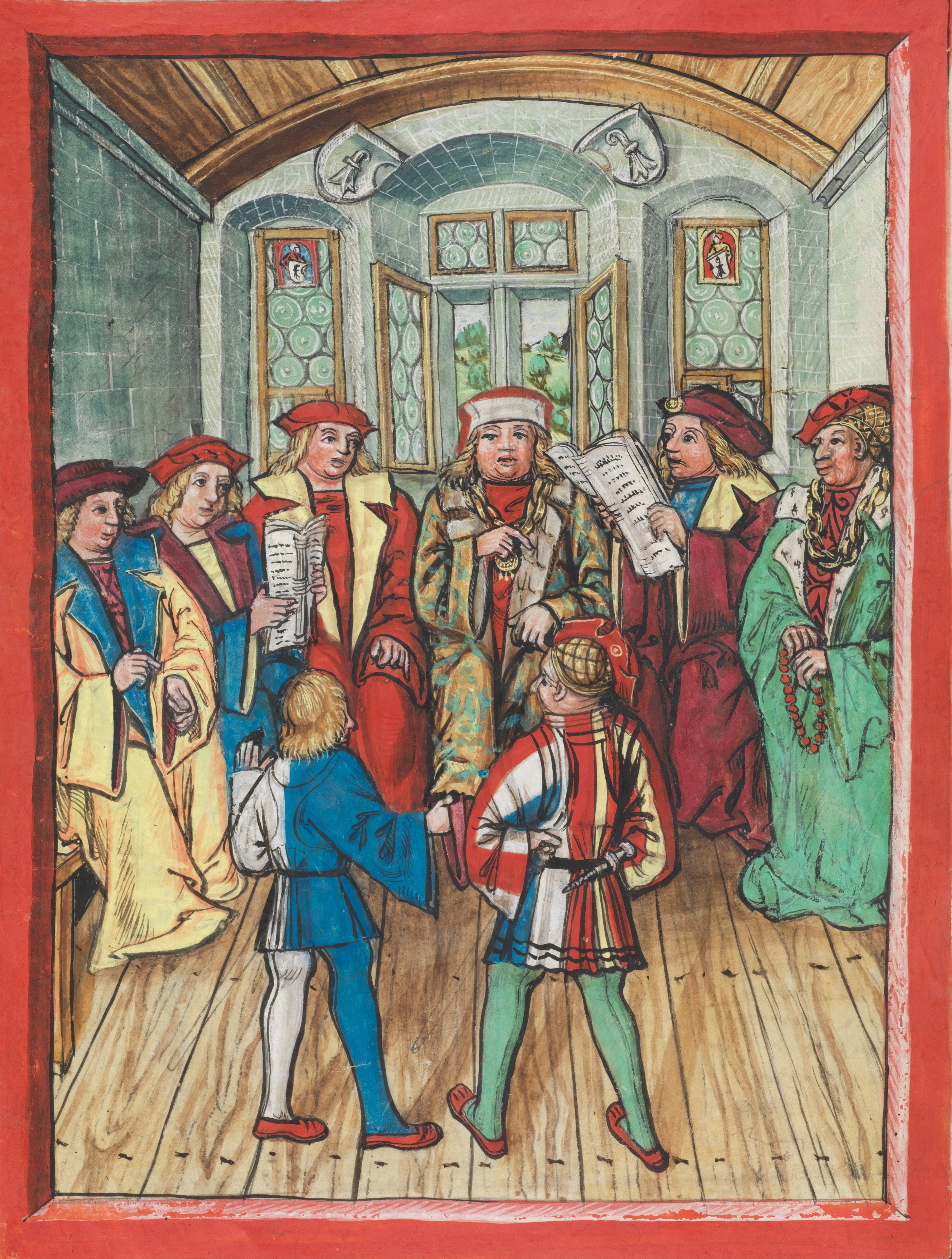

The Treaty of Basel of 22 September 1499 was an armistice following the Battle of Dornach, concluding the Swabian War, fought between the Swabian League and the Old Swiss Confederacy.

The Swabian War of 1499 was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of Habsburg. What had begun as a local conflict over the control of the Val Müstair and the Umbrail Pass in the Grisons soon got out of hand when both parties called upon their allies for help; the Habsburgs demanding the support of the Swabian League, while the Federation of the Three Leagues of the Grisons turning to the Swiss Eidgenossenschaft. Hostilities quickly spread from the Grisons through the Rhine valley to Lake Constance and even to the Sundgau in southern Alsace, the westernmost part of the Habsburg region of Further Austria.
Livonian Crusade: The Livonian Brothers of the Sword were soundly defeated by pagan Samogitian and Semigallian troops at the Battle of Saule.

The Livonian crusade refers to the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – in what is now Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal-sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was conducted mostly by the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Denmark. It ended with the creation of Terra Mariana and the Danish duchy of Estonia. The lands on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea were one of the last parts of Europe to be Christianised.
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword was a Catholic military order established in 1202 during the Livonian Crusade by Albert, the third bishop of Riga. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204 for the second time. The membership of the crusading order comprised warrior monks, mostly from northern Germany, who fought Baltic and Finnic "pagans" in the area of modern-day Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Alternative names of the Order include Christ Knights, Swordbrothers, Sword Brethren, Order of the Brothers of the Sword, and The Militia of Christ of Livonia. The seal reads: +MAGISTRI ETFRM MILICIE CRI (Christi) DE LIVONIA.

Samogitians are an ethnographic group of Lithuanians of the Samogitia region, an ethnographic region of Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian language, which in Lithuania is mostly considered a dialect of the Lithuanian language together with the Aukštaitian dialect. The Samogitian language differs the most from the standard Lithuanian language.

Semigallians were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania. They are noted for their long resistance (1219–1290) against the German crusaders and Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades. Semigallians had close linguistic and cultural ties with Samogitians.

The Battle of Saule was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Between 48 and 60 knights were killed, including the Livonian Master, Volkwin. It was the earliest large-scale defeat suffered by the orders in Baltic lands. The Sword-Brothers, the first Catholic military order established in the Baltic lands, was soundly defeated and its remnants accepted incorporation into the Teutonic Order in 1237. The battle inspired rebellions among the Curonians, Semigallians, Selonians, Oeselians, tribes previously conquered by the Sword-Brothers. Some thirty years' worth of conquests on the left bank of Daugava were lost. To commemorate the battle, in 2000 the Lithuanian and Latvian parliaments declared 22 September to be the Baltic Unity Day.
The Samogitians defeat the Livonian Brothers of the Sword in the Battle of Saule.

The Battle of Saule was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Between 48 and 60 knights were killed, including the Livonian Master, Volkwin. It was the earliest large-scale defeat suffered by the orders in Baltic lands. The Sword-Brothers, the first Catholic military order established in the Baltic lands, was soundly defeated and its remnants accepted incorporation into the Teutonic Order in 1237. The battle inspired rebellions among the Curonians, Semigallians, Selonians, Oeselians, tribes previously conquered by the Sword-Brothers. Some thirty years' worth of conquests on the left bank of Daugava were lost. To commemorate the battle, in 2000 the Lithuanian and Latvian parliaments declared 22 September to be the Baltic Unity Day.
The warlord Zhu Quanzhong kills Emperor Zhaozong, the penultimate emperor of the Tang dynasty, after seizing control of the imperial government.

Emperor Taizu of Later Liang (後梁太祖), personal name Zhu Quanzhong (朱全忠), né Zhu Wen (朱溫), name later changed to Zhu Huang (朱晃), nickname Zhu San, was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician. He was a Jiedushi and warlord who in 907 overthrew the Tang dynasty and established the Later Liang as its emperor, ushering in the era of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms. The last two Tang emperors, Emperor Zhaozong of Tang and Emperor Ai of Tang, who "ruled" as his puppets from 903 to 907, were both murdered by him.

Emperor Zhaozong of Tang, né Li Jie, name later changed to Li Min and again to Li Ye, was the penultimate emperor of the Tang dynasty of China. He reigned from 888 to 904. Zhaozong was the seventh son of Emperor Yizong of Tang and younger brother of Emperor Xizong of Tang. Later Li Jie was murdered by Zhu Wen, the Later Liang ruler who overthrew the Tang dynasty.
Hilary Mantel, British author (b. 1952) deaths

Dame Hilary Mary Mantel was a British writer whose work includes historical fiction, personal memoirs and short stories. Her first published novel, Every Day Is Mother's Day, was released in 1985. She went on to write 12 novels, two collections of short stories, a personal memoir, and numerous articles and opinion pieces.
Neil Brannon, American politician (b. 1940) deaths
Neil Brannon was an American politician who served in the Oklahoma House of Representatives from the 3rd district from 2002 to 2010.
Chas Hodges, English musician and singer (b. 1943) deaths

Charles Nicholas Hodges was an English musician and singer who was the lead vocalist of musical duo Chas & Dave.
Edna Molewa, South African politician (b. 1957) deaths

Bomo Edith Edna Molewa was a South African politician and member of the African National Congress. Molewa became the Minister of Water and Environmental Affairs of South Africa on 31 October 2010, as part of a cabinet reshuffle by President Jacob Zuma. On 25 May 2014 her Ministry has been divided and she was appointed Minister of Environmental Affairs. She succeeded Buyelwa Sonjica. Prior to her death, Molewa was studying towards a Bachelor's of Arts Honours in Developmental Studies through the University of South Africa.
Mike Labinjo, Canadian football player (b. 1980) deaths
Michael Labinjo was a Canadian professional gridiron football player who played as a defensive end. He was a member of the Calgary Stampeders, Philadelphia Eagles, Indianapolis Colts and Miami Dolphins.
Yogi Berra, American baseball player, coach, and manager (b. 1925) deaths

Lawrence Peter "Yogi" Berra was an American professional baseball catcher who later took on the roles of manager and coach. He played 19 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB), all but the last for the New York Yankees. He was an 18-time All-Star and won 10 World Series championships as a player—more than any other player in MLB history. Berra had a career batting average of .285, while hitting 358 home runs and 1,430 runs batted in. He is one of only six players to win the American League Most Valuable Player Award three times. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest catchers in baseball history and was elected to the Baseball Hall of Fame in 1972.
James David Santini, American lawyer and politician (b. 1937) deaths

James David Santini was an American attorney, politician and lobbyist who served as the U.S. representative for Nevada's at-large congressional district from 1975 to 1983. He was a member of the Democratic Party until 1986, when he joined the Republican Party.
Richard G. Scott, American engineer and religious leader (b. 1928) deaths
Richard Gordon Scott was an American scientist and religious leader who served as a member of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Phyllis Tickle, American author and academic (b. 1934) deaths

Phyllis Natalie Tickle was an American author and lecturer whose work focuses on spirituality and religion issues. After serving as a teacher, professor, and academic dean, Tickle entered the publishing industry, serving as the founding editor of the religion department at Publishers Weekly, before then becoming a popular writer. She is well known as a leading voice in the emergence church movement. She is perhaps best known for The Divine Hours series of books, published by Doubleday Press, and her book The Great Emergence- How Christianity Is Changing and Why. Tickle was a member of the Episcopal Church, where she was licensed as both a lector and a lay eucharistic minister. She has been widely quoted by many media outlets, including Newsweek, Time, Life, The New York Times, USA Today, CNN, C-SPAN, PBS, The History Channel, the BBC and VOA. It has been said that "Over the past generation, no one has written more deeply and spoken more widely about the contours of American faith and spirituality than Phyllis Tickle." A biography of Tickle, written by Jon M. Sweeney, was published in February 2018. Phyllis Tickle: A Life, has been widely reviewed.
Fernando Cabrita, Portuguese footballer and manager (b. 1923) deaths
Fernando da Silva Cabrita was a Portuguese football forward and manager.
Sahana Pradhan, Nepalese politician, Nepalese Minister of Foreign Affairs (b. 1927) deaths

Sahana Pradhan was a Nepalese politician from a Newar family in Kathmandu. She resigned as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nepal on April 16, 2008. She also served as Deputy Prime Minister of Nepal within the coalition government of Prime Minister Girija Prasad Koirala from 2007 to 2008.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MoFA; Nepali: परराष्ट्र मन्त्रालय) is responsible for conducting external affairs of the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal. Ministry of Foreign Affairs represents other line ministries and the Government of Nepal while dealing with other states.
Erik van der Wurff, Dutch pianist, composer, and conductor (b. 1945) deaths

Erik van der Wurff was a Dutch pianist, composer, arranger, producer and conductor. He worked mainly on soundtracks and as a composer for many movies and television shows. He also made acting appearances in two Dutch-German television shows in 1977 and 1980. He was the regular pianist and composer on the Herman van Veen shows. He composed music for many theater productions, musicals, movies and for the comic series Alfred Jodokus Kwak which was aired in various countries.
Hans E. Wallman, Swedish director, producer, and composer (b. 1936) deaths

Hans E. Wallman, in Sweden known as Hasse Wallman, né Hans Erik Wallman in Stockholm, was a Swedish entrepreneur, impresario, composer, director, author, producer and entertainment executive. At his own venues in Stockholm he has presented acts like the Beatles (1963), Rolling Stones and Lill-Babs.
Gary Brandner, American author and screenwriter (b. 1930) deaths

Gary Phil Brandner was an American horror fiction author best known for his werewolf themed trilogy of novels, The Howling. The first book of the series was adapted loosely as a motion picture in 1981. Brandner's second and third Howling novels, published in 1979 and 1985 respectively, have no association with the film series, though he was involved with writing the screenplay for the second Howling film, Howling II: Your Sister Is a Werewolf. The fourth film of the Howling series, Howling IV: The Original Nightmare, is actually the closest adaptation of Brandner's original novel, though this too varies to some degree.
Jane Connell, American actress and singer (b. 1925) deaths

Jane Sperry Connell was an American actress and singer.
David H. Hubel, Canadian-American neurophysiologist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1926) deaths

David Hunter Hubel was a Canadian American neurophysiologist noted for his studies of the structure and function of the visual cortex. He was co-recipient with Torsten Wiesel of the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, for their discoveries concerning information processing in the visual system. For much of his career, Hubel worked as the Professor of Neurobiology at Johns Hopkins University and Harvard Medical School. In 1978, Hubel and Wiesel were awarded the Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize from Columbia University. In 1983, Hubel received the Golden Plate Award of the American Academy of Achievement.

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
Álvaro Mutis, Colombian-Mexican author and poet (b. 1923) deaths

Álvaro Mutis Jaramillo was a Colombian poet, novelist, and essayist. His best-known work is the novel sequence The Adventures and Misadventures of Maqroll, which revolves around the character of Maqroll el Gaviero. He won the 1991 International Nonino Prize in Italy. He was awarded the 2001 Miguel de Cervantes Prize and the 2002 Neustadt International Prize for Literature.
Hans Erich Slany, German industrial designer, founded TEAMS Design (b. 1926) deaths
Hans Erich Slany was a German designer considered by many to have been the first industrial designer to design plastic housings for power tools. Slany is also thought of as one of the icons of design in Germany. He founded TEAMS Design GmbH, was a Professor of Industrial Design (ID) for more than 20 years and helped found the Verband Deutscher Industrie Designer e. V. in 1959. He then helped the VDID with their entry into the International Council of Societies of Industrial Design (ICSID).
Hector Abhayavardhana, Sri Lankan theorist and academic (b. 1919) deaths

Hector Abhayavardhana was a Sri Lankan Trotskyist theoretician, a long-standing member of the Lanka Sama Samaja Party (LSSP) and a founder-member of the Bolshevik-Leninist Party of India, Ceylon and Burma.
Irving Adler, American mathematician, author, and academic (b. 1913) deaths

Irving Adler was an American author, mathematician, scientist, political activist, and educator. He was the author of 57 books about mathematics, science, and education, and the co-author of 30 more, for both children and adults. His books have been published in 31 countries in 19 different languages. Since his teenaged years, Adler was involved in social and political activities focused on civil rights, civil liberties, and peace, including his role as a plaintiff in the McCarthy-era case Adler vs. Board of Education that bears his name.
Juan H. Cintrón García, Puerto Rican businessman and politician, 126th Mayor of Ponce (b. 1919) deaths

Juan Herminio Cintrón García was a Puerto Rican politician and Mayor of Ponce, Puerto Rico, from 1968 to 1972. Under his administration the city of Ponce saw the construction of the Coliseo Juan "Pachín" Vicéns and the Centro Gubernamental de Ponce on Avenida Las Americas.
This is a list of mayors of Ponce, Puerto Rico's southern economic center, the island's second largest and second most important city.
Grigory Frid, Russian pianist and composer (b. 1915) deaths

Grigory Samuilovich Frid also known as Grigori Fried was a Russian composer of music written in many different genres, including chamber opera.
Jan Hendrik van den Berg, Dutch psychiatrist and academic (b. 1914) deaths
Jan Hendrik van den Berg was a Dutch psychiatrist notable for his work in phenomenological psychotherapy and metabletics, or "psychology of historical change." He is the author of numerous articles and books, including A different existence and The changing nature of man.
Knut Steen, Norwegian sculptor (b. 1924) deaths

Knut Steen was a Norwegian sculptor. Steen lived in Sandefjord for most of his life and dedicated works such as the Whaler's Monument to the city. Many of his sculptures may also be seen at Midtåsen Sculpture Park, a park dedicated to Steen at the former villa of Anders Jahre in Sandefjord.
Eddie Fisher, American singer (b. 1928) deaths

Edwin Jack Fisher was an American singer and actor. He was one of the most popular artists during the 1950s, selling millions of records and hosting his own TV show, The Eddie Fisher Show. Actress Elizabeth Taylor was best friends with Fisher's first wife, actress Debbie Reynolds. After Taylor's third husband, Mike Todd, was killed in a plane crash, Fisher divorced Reynolds and he and Taylor married that same year. The scandalous affair that Fisher and Taylor had been having while each were already married was widely reported and brought unfavorable publicity to both Fisher and Taylor. Approximately five years later, he and Taylor divorced and he later married Connie Stevens. Fisher is the father of Carrie Fisher and Todd Fisher, whose mother is Reynolds, and the father of Joely Fisher and Tricia Leigh Fisher, whose mother is Stevens.
Vyacheslav Tsaryov, Russian footballer (b. 1971) deaths
Vyacheslav Vyacheslavovich Tsaryov was a Russian professional footballer.
Edward Delaney, Irish sculptor (b. 1930) deaths

Edward Delaney (1930–2009) was an Irish sculptor born in Claremorris in County Mayo in 1930. His best known works include the 1967 statue of Wolfe Tone and famine memorial at the northeastern corner of St Stephen's Green in Dublin and the statue of Thomas Davis in College Green, opposite Trinity College Dublin. These are both examples of lost-wax bronze castings, his main technique during the 1960s and early 1970s.
Thomas Dörflein, German zookeeper (b. 1963) deaths

Thomas Dörflein was a German zookeeper at the Berlin Zoological Garden for 26 years. After the baby polar bear Knut was abandoned by his mother shortly after his birth in 2006, Dörflein—who cared for both the zoo's wolves and the bears—was assigned as the cub's caretaker. As a result of the zoo's decision to raise Knut by hand, and the resultant close relationship between keeper and animal, Dörflein became a reluctant celebrity.
Petrus Schaesberg, German painter, historian, and educator (b. 1967) deaths
Petrus Graf Schaesberg was a German art historian, artist, editor, and teacher.
ʻAlí-Muhammad Varqá, last Hand of the Cause of God in the Baháʼí Faith (b. 1911) deaths
ʻAlí-Muhammad Varqá was a prominent adherent of the Baháʼí Faith. He was the longest surviving Hand of the Cause of God, an appointed position in the Baháʼí Faith whose main function is to propagate and protect the religion on the international level.
Hand of the Cause was a title given to prominent early members of the Baháʼí Faith, appointed for life by the religion's founders. Of the fifty individuals given the title, the last living was ʻAlí-Muhammad Varqá who died in 2007. Hands of the Cause played a significant role in propagating the religion, and protecting it from schism.

The Baháʼí Faith is a relatively new religion teaching the essential worth of all religions and the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the Middle East, where it has faced ongoing persecution since its inception. The religion is estimated to have 5–8 million adherents, known as Baháʼís, spread throughout most of the world's countries and territories.
Marcel Marceau, French mime and actor (b. 1923) deaths

Marcel Marceau was a French actor and mime artist most famous for his stage persona, "Bip the Clown". He referred to mime as the "art of silence", and he performed professionally worldwide for over 60 years. As a Jewish youth, he lived in hiding and worked with the French Resistance during most of World War II, giving his first major performance to 3,000 troops after the liberation of Paris in August. Following the war, he studied dramatic art and mime in Paris.
Edward Albert, American actor (b. 1951) deaths

Edward Laurence Albert was an American actor. The son of actor Eddie Albert and Mexican actress Margo, he starred opposite Goldie Hawn in Butterflies Are Free (1972), a role for which he won a Golden Globe Award for New Star of the Year. He was nominated for Best Actor in a Motion Picture - Musical or Comedy. Albert starred in more than 130 films and television series, including Midway, The Greek Tycoon, Galaxy of Terror, The House Where Evil Dwells, The Yellow Rose, Falcon Crest and Power Rangers Time Force.
Carla Benschop, Dutch basketball player and educator (b. 1950) deaths
Carla Ida Benschop-de Liefde was a Dutch basketball player.
Pete Schoening, American mountaineer (b. 1927) deaths
Peter Kittilsby Schoening was an American mountaineer. Schoening and Andrew Kauffman was two Americans to first successfully climb the Pakistani peak Gasherbrum I in 1958, and was one of the first to summit Mount Vinson in Antarctica in 1966.
Ray Traylor Jr., American professional wrestler better-known as the Big Boss Man (b. 1963) deaths

Ray Washington Traylor Jr. was an American professional wrestler best known for his appearances with the World Wrestling Federation (WWF) under the ring name Big Boss Man, as well as for his appearances with World Championship Wrestling (WCW) as The Boss, The Man, The Guardian Angel, and Big Bubba Rogers. During his appearances with the WWF, Big Boss Man held the WWF World Tag Team Championship once and the WWF Hardcore Championship four times.
Gordon Jump, American actor (b. 1932) deaths

Alexander Gordon Jump was an American actor best known as the clueless, yet occasionally wise, radio station manager Arthur "Big Guy" Carlson in the TV series WKRP in Cincinnati and the incompetent Chief of Police Tinkler in the sitcom Soap. Jump guest starred on a two-part episode of the 1980s sitcom Diff'rent Strokes, in which he portrayed a pedophile who tries to molest main characters Arnold and his friend, Dudley. He also played the "Maytag Repairman" in commercials for Maytag brand appliances, from 1989 until his retirement from the role in July 2003.
Hugo Young, English journalist and author (b. 1938) deaths
Hugo John Smelter Young was a British journalist and columnist and senior political commentator at The Guardian.
Jan de Hartog, Dutch-American author and playwright (b. 1914) deaths

Jan de Hartog was a Dutch playwright, novelist and occasional social critic who moved to the United States in the early 1960s and became a Quaker.
Isaac Stern, Polish-Ukrainian violinist and conductor (b. 1920) deaths

Isaac Stern was an American violinist.
Saburō Sakai, Japanese lieutenant and pilot (b. 1916) deaths

Saburō Sakai was a Japanese naval aviator and flying ace of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Sakai had 28–64 aerial victories, including shared ones, according to official Japanese records, but his autobiography, Samurai!, which was co-written by Martin Caidin and Fred Saito, claims 64 aerial victories.
Kim Yo-han, South Korean singer and actor births

Kim Yo-han, also known by the mononym Yohan, is a South Korean singer and actor. He is a member of the boy group WEi and a former member of boy group X1, finishing first on Produce X 101. He made his solo debut with the digital single "No More" on August 25, 2020. He debuted in acting through A Love So Beautiful.
George C. Scott, American actor, director, and producer (b. 1927) deaths

George Campbell Scott was an American actor, director, and producer who had a celebrated career on both stage and screen. With a gruff demeanor and commanding presence, Scott became known for his portrayal of stern, but complex, authority figures such as prosecutor Claude Dancer in Anatomy of a Murder, General Buck Turgidson in Stanley Kubrick's Dr. Strangelove, Herbert Bock in The Hospital, Ebenezer Scrooge in A Christmas Carol, Lt. Kinderman in The Exorcist III, and General George S. Patton in the biopic Patton, which won him the Academy Award for Best Actor. Described by The Guardian as "a battler and an actor of rare courage", his performances won him widespread recognition and numerous other accolades, including a Golden Globe, a Genie Award, and two Primetime Emmys.
Ludmilla Chiriaeff, Latvian-Canadian ballerina, choreographer, and director (b. 1924) deaths
Ludmilla Chiriaeff was a Latvian-Canadian ballet dancer, choreographer, teacher, and company director.
Dorothy Lamour, American actress and singer (b. 1914) deaths

Dorothy Lamour was an American actress and singer. She is best remembered for having appeared in the Road to... movies, a series of successful comedies starring Bing Crosby and Bob Hope.
Im Nayeon, South Korean singer births

Im Na-yeon, known mononymously as Nayeon, is a South Korean singer. She became a member of the South Korean girl group Twice, under JYP Entertainment, in 2015 as a winning contestant of the reality survival television show Sixteen.
Carlos Correa, Puerto Rican-American baseball player births

Carlos Javier Correa Oppenheimer Jr. is a Puerto Rican professional baseball shortstop who is a free agent. He has played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Houston Astros, who selected him first overall in the 2012 MLB draft, and for the Minnesota Twins.
Leonard Feather, English-American pianist, composer, producer, and journalist (b. 1914) deaths

Leonard Geoffrey Feather was a British-born jazz pianist, composer, and producer, who was best known for his music journalism and other writing.
Maurice Abravanel, Greek-American pianist and conductor (b. 1903) deaths

Maurice Abravanel was an American classical music conductor. He is remembered as the conductor of the Utah Symphony Orchestra for over 30 years.
Philip Hindes, English track cyclist births

Philip Hindes MBE is a British track cyclist, specialising in sprints. He holds dual nationality, having been born in Germany to a British father. Having initially competed for Germany at a junior level, in 2010 he switched to the British Cycling programme. At the 2012 Summer Olympics he won the gold medal in the Men's team sprint, and again at the 2016 Summer Olympics he won the gold medal in the Men's team sprint.
Aurelio López, Mexican baseball player (b. 1948) deaths

Aurelio Alejandro López Rios was a Mexican professional baseball player. After pitching for several years in the Mexican League, he spent eleven seasons with four teams in Major League Baseball — a majority of it spent with the Detroit Tigers. He acquired the nickname "Señor Smoke" in Detroit, while he was known as "El Buitre de Tecamachalco" in Mexico. López was discovered in his hometown by Mexican League scouts and converted from a starting pitcher to a relief pitcher.
Kenny Bromwich, New Zealand rugby league player births

Kenneath Bromwich is a New Zealand professional rugby league footballer who plays as a second-row forward for the Dolphins in the National Rugby League (NRL), and New Zealand at international level.
Denard Robinson, American football player births

Denard Xavier Robinson is currently the Assistant Director of Player Personnel for the University of Michigan football program. Robinson is also a former American football running back who played for four seasons in the National Football League (NFL). He was drafted by the Jacksonville Jaguars in the fifth round of the 2013 NFL Draft. Robinson was the starting quarterback in all 26 games for the 2010 and 2011 Michigan Wolverines football teams and played at the same position as a senior for the 2012 team as well as running back and wide receiver in the second half of the season.
Jon Bass, American actor births
Jon Bass is an American actor, known for his roles in She-Hulk: Attorney at Law, Super Pumped, Baywatch, and the comedy series Big Time in Hollywood, FL.
Kim Hyo-yeon, South Korean singer, dancer, and actress births

Kim Hyo-yeon, referred to as Hyoyeon or DJ Hyo, is a South Korean singer, dancer, DJ, and television personality. She debuted as a member of the girl group Girls' Generation in August 2007, which went on to become one of the best-selling artists in South Korea and one of the most popular K-pop groups worldwide. She has since participated in other SM Entertainment projects, including Girls' Generation-Oh!GG and Got the Beat. Since 2016, she has also released singles as a solo artist.
Sabine Lisicki, German tennis player births

Sabine Katharina Lisicki is a German professional tennis player.
Ambrose Folorunsho Alli, Nigerian academic and politician (b. 1929) deaths

Ambrose Folorunsho Alli was a Nigerian medical professor who served as Executive Governor of the defunct Nigerian state of Bendel State between 1979 and 1983. He was the first civilian governor.
Irving Berlin, Russian-born American composer and songwriter (b. 1888) deaths

Irving Berlin was a Russian-American composer, songwriter and lyricist. His music forms a large part of the Great American Songbook.
Nikita Andreyev, Russian footballer births

Nikita Yevgenyevich Andreyev is a former Russian footballer who played as a striker.
Rais Amrohvi, Pakistani psychoanalyst, scholar, and poet (b. 1914) deaths

Rais Amrohvi, whose real name was Syed Muhammad Mehdi (1914-1988) was a Pakistani scholar, Urdu poet, paranormal investigator, and psychoanalyst and elder brother of Jaun Elia. He was known for his style of qatanigari. He wrote quatrains for Pakistani newspaper Jang for several decade. He promoted the Urdu language and supported the Urdu-speaking people of Pakistan. His family is regarded as family of poets.
Derick Brassard, Canadian ice hockey player births

Derick Brassard is a Canadian professional ice hockey centre currently playing for the Ottawa Senators of the National Hockey League. He previously played in the NHL for the Columbus Blue Jackets, New York Rangers, Pittsburgh Penguins, Florida Panthers, Colorado Avalanche, New York Islanders, Arizona Coyotes, Philadelphia Flyers and the Edmonton Oilers. The Blue Jackets selected him in the first round, sixth overall, of the 2006 NHL Entry Draft.
Stefan Denifl, Austrian cyclist births

Stefan Denifl is an Austrian former professional cyclist, who rode professionally between 2006 and 2018 for seven different professional teams. In 2019, Denifl confessed to doping during a five-year period in his career, and was given a four-year ban from the sport; as a consequence of this, Denifl received a two-year sentence in 2021 for serious commercial fraud.
Tom Felton, English actor births

Thomas Andrew Felton is an English actor best known for playing Draco Malfoy in the film adaptations of the Harry Potter fantasy novels by J. K. Rowling.
Zdravko Kuzmanović, Serbian footballer births

Zdravko Kuzmanović is a Serbian footballer who plays as a defensive or central midfielder. He last played for FC Basel. He represented Serbia in the 2010 FIFA World Cup.
Hákun Djurhuus, Faroese educator and politician, 4th Prime Minister of the Faroe Islands (b. 1908) deaths

Hákun Djurhuus was the prime minister of the Faroe Islands from 1963 to 1967. He was born in Tórshavn.

The prime minister of the Faroe Islands is the head of government of the Faroe Islands
Dan Rowan, American actor, comedian, and producer (b. 1922) deaths

Daniel Hale Rowan was an American actor and comedian. He was featured in the television show Rowan & Martin's Laugh-In, wherein he played straight man to Dick Martin and won the 1969 Emmy for Outstanding Variety or Musical Series.
Matteo Cavagna, Italian footballer births
Matteo Sergio Cavagna is an Italian footballer who plays as a midfielder for Albese.
Faris Haroun, Belgian footballer births

Faris Haroun is a Belgian footballer who plays as a defensive midfielder for Royal Antwerp in the Belgian First Division A. He has also played for the Belgian national football team.
Jamie Mackie, Scottish footballer births

James Charles Mackie is a former professional footballer who played as a striker or winger, most notably for Queens Park Rangers, Plymouth Argyle, and Oxford United. Born in England, Mackie played for Scotland.
Tatiana Maslany, Canadian actress births

Tatiana Gabriele Maslany is a Canadian actress. She rose to prominence for playing multiple characters in the science fiction thriller television series Orphan Black (2013–2017), which won her a Primetime Emmy Award (2016), two Critics' Choice Awards, and five Canadian Screen Awards (2014–18). Maslany is the first Canadian to win an Emmy in a major dramatic category for acting in a Canadian series.
Ibragim Todashev, Russian-American mixed martial artist (d. 2013) births

Ibragim Todashev was a Chechen-born former mixed martial artist, former amateur boxer and friend of Boston Marathon bomber Tamerlan Tsarnaev. At his apartment in Orlando, Florida, he was shot dead by FBI agent Aaron McFarlane during a police interview on May 22, 2013. He had allegedly attacked the agent, with a pipe or stick, while writing a statement about the Boston Marathon bombings and a triple homicide that took place in Waltham, Massachusetts, on September 11, 2011. The investigators involved in the incident said that Todashev had implicated both himself and Tamerlan Tsarnaev in the Waltham murders before he was killed.
Ross Jarman, English drummer and songwriter births

Ross Anthony Jarman is a British drummer who is a member of the rock band The Cribs.
Thiago Silva, Brazilian footballer births

Thiago Emiliano da Silva is a Brazilian professional footballer who plays as a centre-back for Premier League club Chelsea and captains the Brazil national team. Considered one of the greatest defenders of all time, he is known for his defensive prowess, discipline, and leadership.
Kyla, British singer births
Kyla Reid is a British house music singer in the UK funky subgenre. She is best known for the song "Do You Mind" which was later sampled on Drake's 2016 international hit "One Dance".
Glenn Loovens, Dutch professional footballer births

Glenn Loovens is a Dutch former professional footballer who played as a centre-back.
Petr Tatíček, Czech professional ice hockey births

Petr Tatíček is a Czech professional ice hockey centre who is currently an unrestricted free agent. He most recently played for ERC Ingolstadt of the Deutsche Eishockey Liga (DEL). He has previously played for the Florida Panthers of the National Hockey League (NHL).
Tommy Thelin, Swedish footballer births
Tommy Thelin is a retired Swedish footballer. His brother Jimmy is a former footballer and the current manager of Elfsborg.
Domenic Cassisi, Australian footballer births
Domenic Cassisi is a former premiership winning Australian rules footballer with the Port Adelaide Football Club, and was the club's 62nd captain from 2009 to 2012. He was recruited in the 2000 AFL Draft with pick 50, and is a member of Port Adelaide's 2004 premiership side.
Billie Piper, English actress and singer births

Billie Paul Piper is an English actress and former singer. She initially gained recognition as a singer after releasing her debut single "Because We Want To" at age 15, which made her the youngest woman to ever enter at number one on the UK Singles Chart. Her follow-up single "Girlfriend" also entered at number one. In 1998, Piper released her debut studio album, Honey to the B, which was certified platinum by the British Phonographic Industry. Her second studio album, Walk of Life, was released in 2000 and spawned her third number one single, "Day & Night". In 2003, Piper announced that she had abandoned her music career to focus on an acting career.
Maarten Stekelenburg, Dutch footballer births

Maarten Stekelenburg is a Dutch professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for Eredivisie club Ajax.
Alexei Ramírez, Cuban baseball player births

Alexei Fernando Ramírez Rodriguez is a Cuban former professional baseball shortstop. He has played for the Chicago White Sox, San Diego Padres and Tampa Bay Rays in MLB and Pinar del Rio of the Cuban National Series. His nickname, given to him by former White Sox manager Ozzie Guillén, is "The Cuban Missile" due to his tall, slim physique and combination of speed, power, and strong throwing arm. Ramírez batted and threw right-handed.
Subaru Shibutani, Japanese singer-songwriter births
Subaru Shibutani is a Japanese singer, actor and lyricist. He was also the main vocalist of Japanese male idol group Kanjani Eight, which debuted with modern enka, before he left the group in 2018. His first solo album Nisai was released in October 2019. Shibutani was already a singer in his own right before the group's debut, immensely popular among Johnny's Jr. fans as the top Kansai Jr. of his time.
Ingrid Vetlesen, Norwegian soprano births
Ingrid Vetlesen is a Norwegian soprano.
Harry Warren, American composer and songwriter (b. 1893) deaths

Harry Warren was an American composer and the first major American songwriter to write primarily for film. He was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Original Song eleven times and won three Oscars for composing "Lullaby of Broadway", "You'll Never Know" and "On the Atchison, Topeka and the Santa Fe". He wrote the music for the first blockbuster film musical, 42nd Street, choreographed by Busby Berkeley, with whom he would collaborate on many musical films.
Francesco D'Isa, Italian painter and journalist births
Francesco D'Isa is an Italian artist, writer, journalist and art curator. He has worked consistently in the field of erotic art, and also works on comics and a blog.
Svenja Weidemann, German tennis player births
Svenja Weidemann is a German tennis player. She won two singles titles on the ITF tour and on 12 April 2010 reached a singles ranking high of world number 496.
Emilie Autumn, American singer-songwriter, violinist, and poet births

Emilie Autumn Liddell is an American singer-songwriter, poet, author and violinist. Autumn's musical style is described by her as "Fairy Pop", "Fantasy Rock" or "Victoriandustrial". It is influenced by glam rock and from plays, novels, and history, particularly the Victorian era. Performing with her all-female backup dancers The Bloody Crumpets, Autumn incorporates elements of classical music, cabaret, electronica, and glam rock with theatrics, and burlesque.
Phil Waugh, Australian rugby player births

Phillip Waugh is a retired Australian rugby union footballer who played 136 matches in Super Rugby for the NSW Waratahs, and in 79 Test matches for the Wallabies. His usual position was openside flanker.
Abul A'la Maududi, Pakistani theologian, Islamic scholar and jurist (b. 1903) deaths

Abul A'la al-Maududi was an Islamic scholar, Islamist ideologue, Muslim philosopher, jurist, historian, journalist, activist and scholar active in British India and later, following the partition, in Pakistan. Described by Wilfred Cantwell Smith as "the most systematic thinker of modern Islam", his numerous works, which "covered a range of disciplines such as Qur’anic exegesis, hadith, law, philosophy and history", were written in Urdu, but then translated into English, Arabic, Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Burmese, Malayalam and many other languages. He sought to revive Islam, and to propagate what he understood to be "true Islam". He believed that Islam was essential for politics and that it was necessary to institute sharia and preserve Islamic culture similar to reign of the Rashidun and abandon immorality, from what he viewed as the evils of secularism, nationalism and socialism, which he understood to be the influence of Western imperialism.
Harry Kewell, Australian footballer and coach births

Harry Kewell is an Australian association football coach, manager and former player. His most recent role as a club manager was at English National League side Barnet, and he is currently a first team coach at Celtic F.C. As a player, Kewell represented Leeds United, Liverpool, Galatasaray, Melbourne Victory, Al-Gharafa and Melbourne Heart. While at Leeds he was named the PFA Young Player of the Year in 2000. Internationally, he received 58 caps, and scored 17 goals while playing for Australia. A left winger also capable of playing as an attacking midfielder or second striker, he is often regarded within the media as "Australia's finest football export", despite his career being blighted with injury. In 2012, Kewell was named Australia's greatest footballer in a vote by Australian fans, players and media.
David Berkeley, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births

David Berkeley is an American singer and songwriter.
Mo Collins, American football player and coach (d. 2014) births
Damon Jamal Collins, nicknamed Mo Collins, was an American college and professional football player who was an offensive lineman in the National Football League (NFL) for six seasons during the 1990s and early 2000s. Collins played college football for the University of Florida, and was a member of a national championship team. The Oakland Raiders selected him in the first round of the 1998 NFL Draft, and he played his entire professional career for the Raiders.
Ethan Moreau, Canadian ice hockey player and scout births

Ethan Byron Moreau is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player. Moreau was selected in the first round of the 1994 NHL Entry Draft, 14th overall, by the Chicago Blackhawks of the National Hockey League (NHL). He also played with the Edmonton Oilers, Columbus Blue Jackets and the Los Angeles Kings of the NHL. He recently served as an assistant coach for Niagara University. Currently, Moreau is the Director of Hockey at Athol Murray College of Notre Dame in Wilcox, Saskatchewan.
Jenn Colella, American actress and singer births

Jenn Colella is an American actress and singer. She began her career as a comedian and then branched out into musical theater. In her New York debut in Urban Cowboy, she earned a 2003 Outer Critics Circle Award nomination. More recently, she landed a Tony Award nomination, and won the Drama Desk Award, Outer Critics Circle Award, and three regional theater awards for her portrayal of Annette/Beverley Bass in Come from Away. She received a Grammy Award in January 2018 for her role for the Dear Evan Hansen original cast album. See: Awards and nominations
Kostas Kaiafas, Cypriot footballer and manager births

Kostas Kaiafas is Cypriot former football player and manager.
Yoo Chae-yeong, South Korean singer-songwriter and actress (d. 2014) births

Yoo Chae-yeong was a South Korean singer, actress, and radio host.
Stéfan Louw, South African tenor and producer births

Stéfan Louw is a South African operatic tenor, regarded as one of South Africa's leading tenors. He has been performing opera since 1995.
Bob Sapp, American wrestler births

Robert Malcolm Sapp is an American mixed martial artist, kickboxer, professional wrestler, actor, and former American football player. He is currently under contract with Rizin Fighting Federation. Sapp has a combined fight record of 24–39–1, mostly fighting in Japan. He is well known in Japan, where he has appeared in numerous commercials, television programs, and various other media, and has released a music CD, Sapp Time. He is known there as a gaijin tarento. He is currently working sporadically for various MMA promotions in the U.S., Japan, and Europe.
Paul van Zeeland, Belgian lawyer, economist, and politician, 38th Prime Minister of Belgium (b. 1893) deaths

Paul Guillaume, Viscount van Zeeland was a Belgian lawyer, economist, Catholic politician, and statesman born in Soignies.

The Prime Minister of Belgium or the Premier of Belgium is the head of the federal government of Belgium, and the most powerful person in Belgian politics.
Elizabeth Bear, American author and poet births

Sarah Bear Elizabeth Wishnevsky is an American author who works primarily in speculative fiction genres, writing under the name Elizabeth Bear. She won the 2005 John W. Campbell Award for Best New Writer, the 2008 Hugo Award for Best Short Story for "Tideline", and the 2009 Hugo Award for Best Novelette for "Shoggoths in Bloom". She is one of a small number of writers who have gone on to win multiple Hugo Awards for fiction after winning the John W. Campbell Award for Best New Writer.
Toomas Krõm, Estonian footballer births
Toomas Krõm is a former professional footballer from Estonia, playing as a forward. Born in Tallinn, he twice became topscorer of the Premier Estonian League, named Meistriliiga: in 1999 and 2000. Krõm obtained a total number of 11 caps for the Estonia national football team during his career.
Luther Reigns, American actor and wrestler births

Matthew Robert Wiese is an American former professional wrestler and actor. He is best known for his tenure in WWE, where he performed on its SmackDown brand under the ring name Luther Reigns.
Gladys Berejiklian, Australian politician, 45th Premier of New South Wales births

Gladys Berejiklian is an Australian former politician who served as the 45th premier of New South Wales and the leader of the New South Wales division of the Liberal Party from 2017 to 2021.

The premier of New South Wales is the head of government in the state of New South Wales, Australia. The Government of New South Wales follows the Westminster Parliamentary System, with a Parliament of New South Wales acting as the legislature. The premier is appointed by the governor of New South Wales, and by modern convention holds office by his or her ability to command the support of a majority of members of the lower house of Parliament, the Legislative Assembly.
Mike Matheny, American baseball player and manager births

Michael Scott Matheny is an American former professional baseball player and former manager of the St. Louis Cardinals and Kansas City Royals of Major League Baseball (MLB). He played in MLB for 13 seasons as a catcher for the Milwaukee Brewers, Toronto Blue Jays, St. Louis Cardinals, and San Francisco Giants. Matheny later spent seven seasons as the manager of the Cardinals. One of the most accomplished defensive players of his era, he won four Rawlings Gold Glove Awards. As manager, Matheny's teams won one National League (NL) pennant and three NL Central division titles.
Mystikal, American rapper and actor births

Michael Lawrence Tyler, better known by his stage name Mystikal, is an American rapper.
Hitro Okesene, New Zealand rugby player and coach births
John Haitrosene "Hitro" Okesene, also known by the nickname of "Nitro", is a former professional rugby league footballer who played in the 1990s and 2000s and represented three countries; Western Samoa, American Samoa and New Zealand.
Rupert Penry-Jones, English actor births

Rupert William Penry-Jones is a British actor, known for his performances as Adam Carter in Spooks, Clive Reader in Silk, DI Joseph Chandler in Whitechapel, and Mr Quinlan in the American horror series The Strain.
Emmanuel Petit, French footballer births

Emmanuel Laurent Petit is a French former professional footballer who played as a defensive midfielder at club level for Arsenal, Barcelona, Monaco, and Chelsea. He represented France at international level in two FIFA World Cups and two UEFA European Championships; he scored the third goal in France's 3–0 victory in the 1998 FIFA World Cup Final and was also a member of the French squad that won UEFA Euro 2000.
Nicole Bradtke, Australian tennis player and sportscaster births
Nicole Bradtke is a retired professional tennis player from Australia.
Tuomas Kantelinen, Finnish composer and conductor births
Tuomas Kantelinen is a Finnish composer. He studied composition at the Sibelius Academy with Eero Hämeenniemi. He is best known for his scores for films such as Rukajärven tie, Äideistä parhain, Mindhunters and Mongol. He has also composed the opera Paavo the Great. Great Race. Great Dream, chamber music and orchestral works as well as music for television shows and commercials.
Sue Perkins, English comedian, actress, and radio host births
Susan Elizabeth Perkins is an English actress, broadcaster, comedian, presenter and writer. Originally coming to prominence through her comedy partnership with Mel Giedroyc in Mel and Sue, she has since become best known as a radio broadcaster and television presenter, notably of The Great British Bake Off (2010–2016), Insert Name Here (2016–2019) and Just a Minute on BBC Radio 4.
Matt Sharp, American singer-songwriter and bass player births

Matthew Kelly Sharp is an American songwriter and musician. Until 1998, he was the bassist for the alternative rock band Weezer, which he cofounded in 1992. He appears on their first two albums, the Blue Album (1994) and Pinkerton (1996). In 1994, Sharp founded the Rentals, who have released four albums. Sharp has also released an EP and an album as a solo artist.
Adolfo López Mateos, Mexican politician, 48th President of Mexico (b. 1909) deaths

Adolfo López Mateos was a Mexican politician who served as President of Mexico from 1958 to 1964.

The president of Mexico, officially the president of the United Mexican States, is the head of state and head of government of Mexico. Under the Constitution of Mexico, the president heads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the Mexican Armed Forces. The current president is Andrés Manuel López Obrador, who took office on 1 December 2018.
Matt Besser, American actor, director, producer, and screenwriter births

Matthew Gregory Besser is an American actor, comedian, director, producer, and writer, best known as one of the four founding members of the Upright Citizens Brigade sketch comedy troupe, who had their own show on Comedy Central from 1998 to 2000. He currently hosts the improvisation-based podcast Improv4humans on the Earwolf podcasting network.
Super Delfin, Japanese wrestler births

Hiroto Wakita is a Japanese professional wrestler who currently runs Kaisen Puroresu and is also working as a wrestler there. He is better known by his stage name Super Delfin .
Brian Keene, American novelist births
Brian Keene is an American author and podcaster, primarily known for his work in horror, dark fantasy, crime fiction, and comic books. He has won the 2014 World Horror Grandmaster Award and two Bram Stoker Awards. In addition to his own original work, Keene has written for media properties such as Doctor Who, Hellboy, Alien, Masters of the Universe, and The X-Files.
Ian Mortimer, English historian and novelist births
Ian James Forrester Mortimer, is a British historian and writer of historical fiction. He is best known for his book The Time Traveller's Guide to Medieval England, which became a Sunday Times bestseller in paperback in 2010.
Rickard Rydell, Swedish race car driver births

Rickard Rydell is a retired Swedish racing driver. He won the 1998 British Touring Car Championship, the 2011 Scandinavian Touring Car Championship, and has also been a frontrunner in the European/World Touring Car Championship.
Félix Savón, Cuban boxer births

Félix Savón Fabre is a retired Cuban amateur boxer, who competed from 1980 to 2000. Considered one of the all-time greatest amateur boxers, he became three-time Olympic gold medalist, and the World Champion six times in a row, all in the heavyweight division. In 1988, when he was favored by many to win the gold medal at the 1988 Summer Olympics, Cuban government boycotted the event. Savón is particularly known for having rejected numerous multimillion-dollar offers to defect, leave Cuba permanently to fight Mike Tyson as a professional.
Ruth Jones, Welsh actress, producer, and screenwriter births

Ruth Alexandra Elisabeth Jones is a Welsh actress, comedian, writer and producer. She co-wrote and co-starred in the award-winning BBC sitcom Gavin & Stacey.
Mike Richter, American ice hockey player births

Michael Thomas Richter is an American former professional ice hockey goaltender. He played his entire career with the New York Rangers organization, and led the team to the Stanley Cup in 1994. He also represented the United States in international play on several occasions. Richter was named to the U.S. Hockey Hall of Fame, alongside his former Rangers and U.S. teammate Brian Leetch, in 2008.
Michael Shank, American racing team owner births

Michael Shank is an American race car team owner and former race car driver born in Columbus, Ohio. Before leaving driving to concentrate on car ownership, he ran one race in the 1996–97 Indy Racing League season, the 1997 Las Vegas 500K at Las Vegas Motor Speedway. He started racing in 1989, winning SCCA Ohio Valley Region's Novice Driver of the Year. He also won the 1996 Player’s/Toyota Atlantic C2 championship.
Dan Bucatinsky, American actor, director, producer, and screenwriter births

Daniel Bucatinsky is an American actor, writer and producer, best known for his role as James Novak in the Shonda Rhimes drama series Scandal, for which he won the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Guest Actor in a Drama Series in 2013. In 2014, Bucatinsky starred on NBC's Marry Me, as well as the newly revived HBO series The Comeback, which he also executive produces.
Andrii Deshchytsia, Ukrainian politician and diplomat, Ukrainian Minister of Foreign Affairs births

Andrii Bohdanovych Deshchytsia is a Ukrainian diplomat and politician.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Ukraine is the ministry of the Ukrainian government that oversees the foreign relations of Ukraine. The head of the ministry is the Minister of Foreign Affairs.
Mark Guthrie, American baseball player births

Mark Andrew Guthrie is a former Major League Baseball relief pitcher who played for several teams between 1989 and 2003 and was a member of the 1991 World Series Champion Minnesota Twins.
Robert Satcher, American physician, engineer, and astronaut births

Robert Lee "Bobby" Satcher Jr. is an American physician, chemical engineer, and former NASA astronaut. He participated in 2 spacewalks during STS-129, accumulating 12hrs 19min of EVA time. Satcher holds two doctorates and has received numerous awards and honors as a surgeon and engineer.
Juha Turunen, Finnish lawyer and politician births
Juha Turunen is a Finnish criminal and former SDP city council candidate living in Turku, who confessed to a kidnapping in 2009.
Ken Vandermark, American saxophonist and composer births

Ken Vandermark is an American composer, saxophonist, and clarinetist.
Martin Crowe, New Zealand cricketer and sportscaster (d. 2016) births

Martin David Crowe was a New Zealand cricketer, Test and ODI captain as well as a commentator. He played for the New Zealand national cricket team between 1982 and 1995, and is regarded as one of the country's greatest batsmen.
Vince Coleman, American baseball player births

Vincent Maurice Coleman is an American former Major League Baseball (MLB) player, best known for his years with the St. Louis Cardinals. Primarily a left fielder, Coleman played from 1985 to 1997 and set a number of stolen base records. He was a switch hitter and threw right-handed.
Liam Fox, Scottish physician and politician, Secretary of State for Defence births

Liam Fox is a British politician who served as Secretary of State for International Trade from 2016 to 2019 and Secretary of State for Defence from 2010 to 2011. A member of the Conservative Party, Fox has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for North Somerset, formerly Woodspring, since 1992.

The secretary of state for defence, also referred to as the defence secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with overall responsibility for the business of the Ministry of Defence. The incumbent is a member of the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, sixth in the ministerial ranking.
Bonnie Hunt, American actress, producer, and talk show host births

Bonnie Lynn Hunt is an American actress, comedian, director, producer, writer and television host. Her film roles include Rain Man, Beethoven, Beethoven's 2nd, Jumanji, Jerry Maguire, The Green Mile, Cheaper by the Dozen, and Cheaper by the Dozen 2.
Diane Lemieux, Canadian lawyer and politician births

Diane Lemieux is a politician, feminist and Quebec administrator.
Catherine Oxenberg, American actress births

Catherine Oxenberg is an American actress. She is best known for her role as Amanda Carrington on the 1980s prime time soap opera Dynasty. Oxenberg is the daughter of Princess Elizabeth of Yugoslavia and Howard Oxenberg. She twice played Diana, Princess of Wales on screen, in The Royal Romance of Charles and Diana (1982) and Charles and Diana: Unhappily Ever After (1992) and has appeared in many other films.
Michael Torke, American composer births
Michael Torke is an American composer who writes music influenced by jazz and minimalism.
Marion Davies, American actress and comedian (b. 1897) deaths

Marion Davies was an American actress, producer, screenwriter, and philanthropist. Educated in a religious convent, Davies fled the school to pursue a career as a chorus girl. As a teenager, she appeared in several Broadway musicals and one film, Runaway Romany (1917). She soon became a featured performer in the Ziegfeld Follies. While performing in the 1916 Follies, the nineteen-year-old Marion met the fifty-three-year-old newspaper tycoon, William Randolph Hearst, and became his mistress. Hearst took over management of Davies' career and promoted her as a film actress.
Scott Baio, American actor births

Scott Vincent James Baio is an American actor. He is known for playing Chachi Arcola on the sitcom Happy Days (1977–1984) and its spin-off Joanie Loves Chachi (1982–1983), the title character on the sitcom Charles in Charge (1984–1990), Dr. Jack Stewart in the medical-mystery-drama series Diagnosis: Murder (1993–1995), and the titular role of the musical film Bugsy Malone (1976), his onscreen debut. Baio has guest-starred on various television programs, appeared in several independent films, and starred on the Nickelodeon sitcom See Dad Run (2012–2015).
Tai Babilonia, American figure skater and talk show host births

Tai Reina Babilonia is an American former pair skater. Together with Randy Gardner, she won the 1979 World Figure Skating Championships and five U.S. Figure Skating Championships (1976–1980). The pair qualified for the 1976 and 1980 Winter Olympics.
Saul Perlmutter, American astrophysicist, astronomer, and academic, Nobel Prize Laureate births

Saul Perlmutter is a U.S. astrophysicist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and a professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley. He is a member of both the American Academy of Arts & Sciences and the American Philosophical Society, and was elected a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2003. He is also a member of the National Academy of Sciences. Perlmutter shared the 2006 Shaw Prize in Astronomy, the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics, and the 2015 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics with Brian P. Schmidt and Adam Riess for providing evidence that the expansion of the universe is accelerating. Since 2021, he has been a member of the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST).

The Nobel Prize in Physics is a yearly award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901, the others being the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Physics is traditionally the first award presented in the Nobel Prize ceremony.
Andrea Bocelli, Italian singer-songwriter and producer births

Andrea Bocelli is an Italian tenor and multi-instrumentalist. He was born visually impaired, with congenital glaucoma, and at the age of 12, Bocelli became completely blind, following a brain hemorrhage resulting from a football accident. After performing evenings in piano bars and competing in local singing contests, Bocelli signed his first recording contract with the Sugar Music label. He rose to fame in 1994, winning the 44th Sanremo Music Festival performing "Il mare calmo della sera".
Beth Catlin, American autistic savant births
Elizabeth "Beth" Catlin is an autistic savant who sends birthday cards to people whom she has met. Using only her memory, Catlin can recall the names, birthdates, and addresses of the people she has met. As of July 2009, Catlin sends birthday cards each year to 3,834 people.
Neil Cavuto, American journalist and author births

Neil Patrick Cavuto is an American television news anchor, executive, commentator, and business journalist for Fox News. He hosts three television programs: Your World with Neil Cavuto and Cavuto Live, both on Fox News, and Cavuto: Coast to Coast on sister channel Fox Business Network.
Joan Jett, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, producer, and actress births

Joan Jett is an American singer, guitarist, record producer, and actress. Jett is best known for her work as the frontwoman of her band Joan Jett and the Blackhearts, and for earlier founding and performing with the Runaways, which recorded and released the hit song "Cherry Bomb". With The Blackhearts, Jett is known for her rendition of the song "I Love Rock 'n Roll" which was number-one on the Billboard Hot 100 for seven weeks in 1982. Jett's other notable songs include "Bad Reputation", "Light of Day", "I Hate Myself for Loving You" and her covers of "Crimson and Clover", "Do You Wanna Touch Me " and "Dirty Deeds".
Steve Carney, English footballer (d. 2013) births
Stephen Carney was an English professional footballer who played in the Football League as a defender for Newcastle United, Carlisle United, Darlington, Rochdale and Hartlepool United.
Nick Cave, Australian singer-songwriter, author, and actor births

Nicholas Edward Cave is an Australian singer, songwriter, poet, lyricist, author, screenwriter, composer and occasional actor. Known for his baritone voice and for fronting the rock band Nick Cave and the Bad Seeds, Cave's music is generally characterised by emotional intensity, a wide variety of influences and lyrical obsessions with death, religion, love and violence.
Johnette Napolitano, American singer-songwriter and bass player births
Johnette Napolitano is an American singer, songwriter and bassist best known as the lead vocalist, songwriter, and bassist for the alternative rock group Concrete Blonde.
Giuseppe Saronni, Italian cyclist and manager births
Giuseppe Saronni, also known as Beppe Saronni, is an Italian former racing cyclist. He had remarkable success riding in the Giro d'Italia. In 1980 he won 7 stages and finished 7th overall, in 1981 he won 3 stages and finished 3rd overall. In 1979 and 1983 he would win the Giro d'Italia and all total for his career win 24 stages in this race.
Soemu Toyoda, Japanese admiral (b. 1885) deaths
Soemu Toyoda was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy in World War II.
Debby Boone, American singer, actress, and author births

Deborah Anne Boone is an American singer, author, and actress. She is best known for her 1977 hit, "You Light Up My Life", which spent ten weeks at No. 1 on the Billboard Hot 100 chart and led to her winning the Grammy Award for Best New Artist the following year. Boone later focused her music career on country music, resulting in the 1980 No. 1 country hit "Are You on the Road to Lovin' Me Again". In the 1980s, she recorded Christian music which garnered her four top 10 Contemporary Christian albums as well as two more Grammys. Throughout her career, Boone has appeared in several musical theater productions and has co-authored many children's books with her husband Gabriel Ferrer.
Doug Wimbish, American singer-songwriter and bass player births

Douglas Arthur Wimbish is an American bass player, primarily known for being a member of rock band Living Colour and funk/dub/hip hop collective Tackhead, and as a session musician with artists such as Sugarhill Gang, Grandmaster Flash and the Furious Five, The Rolling Stones, Mick Jagger, Depeche Mode, James Brown, Annie Lennox, and Barrington Levy.
Ibrahim Shema, Nigerian lawyer, politician births
Ibrahim Shehu Shemapronunciation (help·info) is a Nigerian lawyer and politician who was elected Governor of the north western State of Katsina during the 2007 general elections. He was re-elected for another four-year term on 28 April 2011, running on the People's Democratic Party (PDP) platform. His second four-year term ended on 29 May 2015 after which he handed over to Aminu Bello Masari, elected governor on the platform of All Progressives Congress.
Frederick Soddy, English chemist and economist, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1877) deaths

Frederick Soddy FRS was an English radiochemist who explained, with Ernest Rutherford, that radioactivity is due to the transmutation of elements, now known to involve nuclear reactions. He also proved the existence of isotopes of certain radioactive elements. In 1921 he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for his contributions to our knowledge of the chemistry of radioactive substances, and his investigations into the origin and nature of isotopes". Soddy was a polymath who mastered chemistry, nuclear physics, statistical mechanics, finance and economics.

The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation, and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences on proposal of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry which consists of five members elected by the Academy. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death.
Jeffrey Leonard, American baseball player and coach births

Jeffrey Leonard is an American former professional baseball left fielder. He played 14 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) from 1977 to 1990 for the Los Angeles Dodgers, Houston Astros, San Francisco Giants, Milwaukee Brewers, and Seattle Mariners.
Richard Fairbrass, English singer-songwriter, musician and producer births

Richard Peter John Fairbrass is an English singer, bassist and television presenter, best known as lead singer of the pop group Right Said Fred, which achieved two hits in the early 1990s with the singles "I'm Too Sexy" and "Deeply Dippy". He and his band have won two Ivor Novello Awards. Worth over 50 million dollars in record sales.
Ségolène Royal, French politician births

Marie-Ségolène Royal is a French politician, who was the Socialist Party candidate for the Presidency of France in the 2007 election.
Bob Goodlatte, American lawyer and politician births

Robert William Goodlatte is an American politician, attorney, and lobbyist who served in the United States House of Representatives representing Virginia's 6th congressional district for 13 terms. A Republican, he was also the Chair of the House Judiciary Committee, which has jurisdiction over legislation affecting the federal courts, administrative agencies, and federal law enforcement entities. Goodlatte's district covered Roanoke and also included Lynchburg, Harrisonburg, and Staunton.
Sukhumbhand Paribatra, Thai political scientist and politician, 15th Governor of Bangkok births

Mom Rajawongse Sukhumbhand Paribatra is a Thai politician belonging to the Democrat Party. From 2009 to 2016 he was the Governor of Bangkok. He was removed from the post in October 2016 by Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha who used Section 44 of the interim charter to remove the elected official. The reason given for his ouster was "...because he was involved in many legal cases." He was replaced by Police General Aswin Kwanmuang.

The Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (BMA) is the local government of Bangkok, which includes the capital of the Kingdom of Thailand. The government is composed of two branches: the executive and the legislative. The administration's roles are to formulate and implement policies to manage Bangkok. Its purview includes transport services, urban planning, waste management, housing, roads and highways, security services, and the environment.
Américo Rocca, Mexican wrestler births
Javier Hernández Padilla is a semi-retired Mexican Luchador, or professional wrestler best known under the ring name Américo Rocca. Hernández also worked as the enmascarado (masked) Ponzoña from 1990 until 1994, and as Ninja Samurai for a brief time in 1994. Hernández is a former holder of the Mexican National Lightweight Championship and a three-time holder of both the Mexican National Welterweight Championship and the NWA World Welterweight Championship all promoted by the professional wrestling promotion Empresa Mexicana de Lucha Libre (EMLL).
Kaarlo Juho Ståhlberg, Finnish lawyer, judge, and politician, 1st President of Finland (b. 1865) deaths

Kaarlo Juho Ståhlberg was a Finnish jurist and academic, which was one of the most important pioneers of republicanism in the country. He was the first president of Finland (1919–1925) and a liberal nationalist.

The president of the Republic of Finland is the head of state of Finland. Under the Constitution of Finland, executive power is vested in the Finnish Government and the president, with the latter possessing only residual powers. The president is directly elected by universal suffrage for a term of six years. Since 1994, no president may be elected for more than two consecutive terms. The president must be a natural-born Finnish citizen. The presidential office was established in the Constitution Act of 1919. The incumbent president is Sauli Niinistö. He was elected for the first time in 2012 and was re-elected in 2018.
David Coverdale, English singer-songwriter births

David Coverdale is an English rock singer best known for his work with Whitesnake, a hard rock band he founded in 1978. Before Whitesnake, Coverdale was the lead singer of Deep Purple from 1973 to 1976, after which he established his solo career. A collaboration with ex-Led Zeppelin guitarist Jimmy Page resulted in a '"Coverdale-Page'" studio album in 1993 that was subsequently certified platinum.
Mike Graham, American wrestler and promoter (d. 2012) births

Edward Michael Gossett, better known as Mike Graham, was an American professional wrestler who was the son of Eddie Graham.
Doug Somers, American wrestler (d. 2017) births
Douglas Duane Somerson was an American professional wrestler known by his ring name "Pretty Boy" Doug Somers. He worked in the American Wrestling Association (AWA) in the mid-1980s as part of a tag team with "Playboy" Buddy Rose, managed by Sherri Martel, and twice held the AWA World Tag Team Championship.
James Cartwright, American general births

James Edward "Hoss" Cartwright is a retired United States Marine Corps four-star general who last served as the eighth vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff from August 31, 2007, to August 3, 2011. He previously served as the Commander, U.S. Strategic Command, from September 1, 2004, to August 10, 2007, and as Acting Commander, U.S. Strategic Command from July 9, 2004, to September 1, 2004. He retired from the Marine Corps on August 3, 2011, after nearly 40 years of service.
Jim McGinty, Australian lawyer and politician, Attorney-General of Western Australia births
James Andrew McGinty is an Australian former politician. He was a Labor member of the Western Australian Legislative Assembly from 1990 to 2009, representing the district of Fremantle. He was Labor Party leader and Leader of the Opposition from 1994 to 1996. He served as a minister, most notably as Attorney-General, in the governments of Carmen Lawrence, Geoff Gallop and Alan Carpenter.

The Attorney-General of Western Australia is the member of the Government of Western Australia responsible for maintenance and improvement of Western Australia's system of law and justice. Before the advent of representative government in 1870, the title was Advocate-General of Western Australia. The Attorney-General must be a qualified legal practitioner. When there are none in the cabinet, a lay person is sometimes appointed to the office of Minister for Justice.
Denis Burke, Australian soldier and politician, 6th Chief Minister of the Northern Territory births
Denis Gabriel Burke is a former Australian politician. A former Australian Army officer, he served as a Country Liberal Party member of the Northern Territory Legislative Assembly from 1994 to 2005. He spent two years as Chief Minister after succeeding Shane Stone, but oversaw the CLP's defeat at the 2001 election, ending 27 years of continuous CLP government in the Northern Territory. Burke later served as Opposition Leader from 2001 to 2003 before being toppled, but was re-elected as leader in 2005. He subsequently took the party to its largest-ever defeat at the 2005 election, culminating in the shock loss of his own seat.

The chief minister of the Northern Territory is the head of government of the Northern Territory. The office is the equivalent of a state premier. When the Northern Territory Legislative Assembly was created in 1974, the head of government was officially known as majority leader. This title was used in the first parliament (1974–1977) and the first eighteen months of the second. When self-government was granted the Northern Territory in 1978, the title of the head of government became chief minister.
Mark Phillips, English equestrian, trainer, and journalist births

Captain Mark Anthony Peter Phillips is an English Olympic gold medal-winning horseman for Great Britain and the first husband of Anne, Princess Royal, with whom he has two children. He remains a leading figure in British equestrian circles, a noted eventing course designer, and a columnist for Horse & Hound magazine.
Jo Beverley, English-Canadian author (d. 2016) births

Mary Josephine Beverley was a prolific English-Canadian writer of historical and contemporary romance novels from 1988 to 2016.
David Drewry, English glaciologist and geophysicist births
David John Drewry is a glaciologist and geophysicist who was described in the conferring of an honorary degree by Anglia Ruskin University in 1998 as having an "outstanding reputation as an eminent scientist of international repute". Drewry has also received several awards for his work. Since 1 July 2015 he is the vice-president of the European University Association.
Norma McCorvey, American activist (d. 2017) births

Norma Leah Nelson McCorvey, also known by the pseudonym "Jane Roe", was the plaintiff in the landmark American legal case Roe v. Wade in which the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in 1973 that individual state laws banning abortion were unconstitutional.
Robert Morace, American author and academic births
Robert Morace is an American writer.
King Sunny Adé, Nigerian singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Chief Sunday Adeniyi Adegeye, known professionally as King Sunny Adé, is a Nigerian jùjú singer, songwriter and multi-instrumentalist. He is regarded as one of the first African pop musicians to gain international success, and has been called one of the most influential musicians of all time.
Larry Dierker, American baseball player and manager births

Lawrence Edward Dierker is a former Major League Baseball pitcher, manager, and broadcaster. During a 14-year baseball career as a pitcher, he pitched from 1964 to 1977 for the Houston Colt .45s/Astros and the St. Louis Cardinals.
Brian Gibson, English director, producer, and screenwriter (d. 2004) births

Brian Gibson was an English film director.
Toni Basil, American singer-songwriter, dancer, and actress births

Antonia Christina Basilotta, better known by her stage name Toni Basil, is an American singer, choreographer, dancer, actress, and director. Her song "Mickey" topped the charts in the US, Canada and Australia and hit the top ten in several other countries.
Barry Cable, Australian footballer and coach births
Barry Thomas Cable MBE is a former Australian rules footballer and coach. Considered one of the greatest rovers in the sport's history, he played in 379 premiership games in the Western Australian Football League (WAFL) and the Victorian Football League (VFL), and later coached in both competitions.
Paul Hoffert, American keyboard player, composer, and academic births

Paul Matthew Hoffert, LLD, CM is a recording artist, performer, media music composer, author, academic, and corporate executive. He studied mathematics and physics at the University of Toronto. He later studied music composition with Gordon Delamont. In 1969 the 26-year-old Hoffert co-founded Lighthouse, a rock group that sold millions of records and earned three Juno Awards as one of Canada's leading pop bands. His film music earned him a San Francisco Film Festival and three SOCAN Film Composer of the Year awards, and included films such as: The Proud Rider (1971), The Groundstar Conspiracy (1972), Outrageous! (1977), High-Ballin' (1978), The Shape of Things to Come (1979), Wild Horse Hank (1979), Mr. Patman (1980), Deadly Companion (1981), Paradise (1982), Fanny Hill (1983), Bedroom Eyes (1984) and Mr. Nice Guy (1987).
Ole Anderson, American wrestler births
Alan Robert Rogowski, better known by the ring name Ole Anderson, is an American retired professional wrestler, referee, manager, and promoter. Part of the Anderson family, Anderson was a founding member of the influential stable The Four Horsemen.
Candida Lycett Green, Anglo-Irish journalist and author (d. 2014) births

Candida Rose Lycett Green was a British author who wrote sixteen books including English Cottages, Goodbye London, The Perfect English House, Over the Hills and Far Away and The Dangerous Edge of Things. Her television documentaries included The Englishwoman and the Horse, and The Front Garden. Unwrecked England, based on a regular column of the same name she wrote for The Oldie from 1992, was published in 2009.
Rubén Salazar Gómez, Colombian cardinal births

Jesús Rubén Darío Salazar Gómez is a Colombian prelate of the Catholic Church who was Metropolitan Archbishop of Bogotá from 2010 to 2020. He was made a cardinal in 2012. He was Metropolitan Archbishop of Barranquilla from 1999 to 2010.
David Stern, American lawyer and businessman (d. 2020) births

David Joel Stern was an American lawyer and business executive who was the commissioner of the National Basketball Association (NBA) from 1984 to 2014. Stern oversaw NBA basketball's growth into one of the world's most popular sports during the 1990s and 2000s. He is credited with developing and broadening the NBA's audience, especially internationally by setting up training camps, playing exhibition games, and recruiting more international players. In addition, with Stern's guidance the NBA opened 12 offices in cities outside the United States, and broadcast to over 200 territories in over 40 languages. Stern also helped found the Women's National Basketball Association and the NBA G League, the NBA's development league. Under Stern, the NBA launched their digital presence with NBA.com, NBA TV, and NBA League Pass. He also established the NBA's social responsibility program, NBA Cares.
Jeremiah Wright, American pastor and theologian births

Jeremiah Alvesta Wright Jr. is a pastor emeritus of Trinity United Church of Christ in Chicago, a congregation he led for 36 years, during which its membership grew to over 8,000 parishioners. Following retirement, his beliefs and preaching were scrutinized when segments of his sermons about terrorist attacks on the United States and government dishonesty were publicized in connection with the 2008 presidential campaign of Barack Obama.
Anna Karina, Danish-French actress, director, and screenwriter (d. 2019) births

Anna Karina was a Danish-French film avant garde actress, director, writer, and singer. She was French New Wave director Jean-Luc Godard's collaborator in the 1960s, performing in several of his films, including The Little Soldier, A Woman Is a Woman, My Life to Live, Bande à part, Pierrot le Fou and Alphaville. For her performance in A Woman Is a Woman, Karina won the Silver Bear Award for Best Actress at the Berlin Film Festival.
Bogdan Baltazar, Romanian economist and engineer (d. 2012) births
Bogdan Baltazar was a leading Romanian banker and the first spokesman of the Romanian government following the fall of the communist regime. He was also a significant financial and banking advisor.
Deborah Lavin, South African-English historian and academic births
Deborah Margaret Lavin, FRSA, is a South African academic and historian, resident in the United Kingdom for most of her career.
Gilbert E. Patterson, American bishop (d. 2007) births
Gilbert Earl Patterson was an American Holiness Pentecostal leader and minister who served as the National Presiding Bishop and Founder of the Bountiful Blessings Ministries and Chief Apostle of the Church of God in Christ (COGIC), Incorporated. Bishop Patterson was the second youngest person to ever be elected Presiding Bishop of COGIC at the age 60 in 2000, second to his predeceased uncle Bishop J. O. Patterson, Sr who was 56 when he was elected Presiding Bishop in 1968.
Junko Tabei, Japanese mountaineer (d. 2016) births

Junko Tabei was a Japanese mountaineer, author and a teacher. She was the first woman to reach the summit of Mount Everest and the first woman to ascend the Seven Summits, climbing the highest peak on every continent.
Gene Mingo, American football player births

Eugene L. Mingo is a former professional American football player from Akron, Ohio, who played several positions including halfback, placekicker, and return specialist. He is widely recognized as the first African American placekicker in American football.
Don Rutherford, English rugby player (d. 2016) births
Donald Rutherford was an England international rugby union player and administrator. He was the first ever Technical Director of the Rugby Football Union at Twickenham, becoming Director of Rugby where he served with distinction from 1969 – 1999.
Maurice Evans, English footballer and manager (d. 2000) births
Maurice George Evans was a football player with Reading Football Club, and later manager of Shrewsbury, Reading and Oxford United.
Elliott Lewis, Australian politician, 19th Premier of Tasmania (b. 1858) deaths

Sir Neil Elliott Lewis, Australian politician, was Premier of Tasmania on three occasions. He was also a member of the first Australian federal ministry, led by Edmund Barton.

The premier of Tasmania is the head of the executive government in the Australian state of Tasmania. By convention, the leader of the party or political grouping which has majority support in the House of Assembly is invited by the governor of Tasmania to be premier and principal adviser.
Jack McGregor, American captain, lawyer, and politician births
Jack Edwin McGregor is a former Pennsylvania State Senator from Pittsburgh and the founder of the National Hockey League's Pittsburgh Penguins. He currently resides in Bridgeport, Connecticut where he serves as counsel to Cohen and Wolf, P.C. as an advisor to companies looking to create business opportunities in the Bridgeport region. He also serves as a consultant to existing companies wishing to expand their market share in the area.
Lute Olson, American basketball player and coach (d. 2020) births

Robert Luther "Lute" Olson was an American basketball coach, who was inducted into both the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame and the National Collegiate Basketball Hall of Fame. He was the head coach of the Arizona Wildcats men's team for 25 years. He was also head coach for the Iowa Hawkeyes for nine years and Long Beach State 49ers for one season. Known for player development and great recruiting, many of his former players have gone on to have impressive careers in the NBA. On October 23, 2008, Olson announced his retirement from coaching. Olson died on August 27, 2020, in Tucson, Arizona. He was 85 years old.
T. Somasekaram, Sri Lankan geographer and politician, 37th Surveyor General of Sri Lanka (d. 2010) births

Sri Lanka Sikhamani Thamotharam Somasekaram was a leading Sri Lankan Tamil geographer and Surveyor General.
Surveyor General of Sri Lanka is the head of Department of Survey of Sri Lanka. The post was established on 2 August 1800 with the formation of the Surveyor General's Department by a proclamation of Governor Frederick North at Galle. Joseph Jonville was appointed as the Colonial Surveyor General, residing principally in Colombo and receiving orders directly from the government. Under him five principal surveyors were appointed and the land divided among them in the following manner. "One shall superintend the survey from the River of Chilaw to the Calanie Ganga, one from the Calanie Ganga to the River of Galle, one from the River of Galle to the North Easterly extremity of the Mahagampatto: to the Nothern extremity of the District of Mulletivoe, and the remaining one from the Northern extremity of the District of Mulletivoe to the River of Chilaw, and shall be thus distinguished, the Surveyor of Negombo, of Colombo, of Matara, of Trincomalee, of Jaffna-Patam." The post of Surveyor General was often combined with that of Civil Engineer and Commissioner of Roads. The department, during the first fifty years, was mainly engaged in the survey of scattered allotments of land for sale to private parties. The first title plan was issued by the new department on 20 August 1800 surveyed by C. Schneider.
Cecil Chubb, English barrister and one time owner of Stonehenge (b. 1876) deaths

Sir Cecil Herbert Edward Chubb, 1st Baronet, was the last private owner of Stonehenge prehistoric monument, Wiltshire, which he donated to the British government in 1918.

Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, two miles (3 km) west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around 13 feet (4.0 m) high, seven feet (2.1 m) wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connecting horizontal lintel stones. Inside is a ring of smaller bluestones. Inside these are free-standing trilithons, two bulkier vertical sarsens joined by one lintel. The whole monument, now ruinous, is aligned towards the sunrise on the summer solstice. The stones are set within earthworks in the middle of the densest complex of Neolithic and Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred tumuli.
Leonardo Balada, Spanish-American composer and educator births
Leonardo Balada Ibáñez is a Catalan American classical composer, who is noted for his operas and orchestral works.
T. Cullen Davis, American businessman births
Thomas Cullen Davis is an American former oil tycoon who is best known for being acquitted of murder and attempted murder in two high-profile trials during the 1970s. At the time of his first trial, Davis was believed to be the wealthiest man to have stood trial for murder in the United States.
Carmelo Simeone, Italian-Argentinian footballer (d. 2014) births

Carmelo "Cholo" Simeone, was an Argentine football defender who won three league championships with Boca Juniors and played for the Argentina national team. Nicknamed "Cholo", he was known for his energetic playing style.
Jesco von Puttkamer, German-American engineer (d. 2012) births

Jesco Hans Heinrich Max Freiherr von Puttkamer was a German-American aerospace engineer, senior manager at NASA, and a pulp science fiction writer.
Sime Silverman, American journalist and newspaper publisher (b. 1873) deaths
Simon J. Silverman was an American journalist and newspaper publisher. He was the founder of the weekly newspaper Variety in New York City in 1905, which gave theatre and vaudeville reviews and the Hollywood-based Daily Variety magazine in 1933, focusing on the emerging motion picture film industry.
Algirdas Brazauskas, Lithuanian politician, 2nd President of Lithuania (d. 2010) births

Algirdas Mykolas Brazauskas was the first President of a newly re-independent post-Soviet Lithuania from 1993 to 1998 and Prime Minister from 2001 to 2006.

The President of the Republic of Lithuania is the head of state of Lithuania. The officeholder has been Gitanas Nausėda since 12 July 2019.
Ingemar Johansson, Swedish boxer (d. 2009) births

Jens Ingemar "Ingo" Johansson was a Swedish professional boxer who competed from 1952 to 1963. He held the world heavyweight title from 1959 to 1960, and was the fifth heavyweight champion born outside the United States. Johansson won the title by defeating Floyd Patterson via third-round stoppage, after flooring him seven times in that round. For this achievement, Johansson was awarded the Hickok Belt as top professional athlete of the year—the only non-American in its entire 27-year first run—and was named the Associated Press Male Athlete of the Year and Sports Illustrated Sportsman of the Year.
Fay Weldon, English author and playwright births

Fay Weldon CBE, FRSL is an English author, essayist and playwright.
George Younger, 4th Viscount Younger of Leckie, Scottish banker and politician, Secretary of State for Defence (d. 2003) births

George Kenneth Hotson Younger, 4th Viscount Younger of Leckie, Baron Younger of Prestwick,, was a British Conservative Party politician and banker.

The secretary of state for defence, also referred to as the defence secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with overall responsibility for the business of the Ministry of Defence. The incumbent is a member of the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, sixth in the ministerial ranking.
Joni James, American singer (d. 2022) births

Giovanna Carmella Babbo, known professionally as Joni James, was an American singer of traditional pop music.
T. S. Sinnathuray, Judge of the High Court of Singapore (d. 2016) births

Thirugnana Sampanthar Sinnathuray, known professionally as T. S. Sinnathuray and to his friends as Sam Sinnathuray, was a judge of the High Court of Singapore. Educated at University College London and called to the bar at Lincoln's Inn, he practised for a few years in a law firm before beginning a career with the Singapore Legal Service, serving with the Attorney-General's Chambers as Crown Counsel and deputy public prosecutor (1960–1963), and senior state counsel (1966–1967); with the Subordinate Courts as a magistrate (1956–1959), first district judge (1967–1970), and senior district judge (1971–1978); and with the Supreme Court as deputy registrar and sheriff (1959–1960), and registrar (1963–1966). In 1978 he was elevated to the office of Judge of the High Court of Singapore, and served until his retirement in 1997.

The High Court of Singapore is the lower division of the Supreme Court of Singapore, the upper division being the Court of Appeal. It consists of the chief justice and the judges of the High Court. Judicial Commissioners are often appointed to assist with the Court's caseload. There are two specialist commercial courts, the Admiralty Court and the Intellectual Property Court, and a number of judges are designated to hear arbitration-related matters. In 2015, the Singapore International Commercial Court was established as part of the Supreme Court of Singapore, and is a division of the High Court. The other divisions of the high court are the General Division, the Appellate Division, and the Family Division. The seat of the High Court is the Supreme Court Building.
Serge Garant, Canadian composer and conductor (d. 1986) births

Albert Antonio Serge Garant, was a Canadian composer, conductor, music critic, professor of music at the University of Montreal and radio host of Musique de notre siècle on Radio-Canada. In 1966, he with Jean Papineau-Couture, Maryvonne Kendergi, Wilfrid Pelletier and Hugh Davidson co-founded the Société de musique contemporaine du Québec. In 1979, he was made an Officer of the Order of Canada. The Prix Serge-Garant was created in his honor by the Fondation Émile Nelligan. Among his notable pupils were Ginette Bellavance, Walter Boudreau, Marcelle Deschênes, Denis Gougeon, Richard Grégoire, Anne Lauber, Michel Longtin, Myke Roy, and François Tousignant.
Carlo Ubbiali, Italian motorcycle racer (d. 2020) births

Carlo Ubbiali was an Italian nine-time World Champion motorcycle road racer. In the 1950s, he was a dominant force in the smaller classes of Grand Prix motorcycle racing, winning six 125cc and three 250cc world titles.
Eric Broadley, English engineer and businessman, founded Lola Cars (d. 2017) births
Eric Harrison Broadley MBE was a British entrepreneur, engineer, and founder and chief designer of Lola Cars, the motor racing manufacturer and engineering company. He was arguably one of the most influential automobile designers of the post-war period, and over the years Lola was involved with many high-profile projects in Formula One, IndyCar, and sports car racing. Broadley sold Lola to Martin Birrane in 1999.
Lola Cars International Ltd. was a British race car engineering company in operation from 1958 to 2012. The company was founded by Eric Broadley in Bromley, England, before moving to new premises in Slough, Buckinghamshire and finally Huntingdon, Cambridgeshire, and endured for more than fifty years to become one of the oldest and largest manufacturers of racing cars in the world. Lola Cars started by building small front-engined sports cars, and branched out into Formula Junior cars before diversifying into a wider range of sporting vehicles. Lola was acquired by Martin Birrane in 1998 after the unsuccessful MasterCard Lola attempt at Formula One.
James Lawson, American activist, author, and academic births

James Morris Lawson Jr. is an American activist and university professor. He was a leading theoretician and tactician of nonviolence within the Civil Rights Movement. During the 1960s, he served as a mentor to the Nashville Student Movement and the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee. He was expelled from Vanderbilt University for his civil rights activism in 1960, and later served as a pastor in Los Angeles for 25 years.
Eugene Roche, American actor (d. 2004) births

Eugene Harrison Roche was an American actor and the original "Ajax Man" in 1970s television commercials.
Johnny Valentine, American wrestler (d. 2001) births

John Theodore Wisniski, better known by his ring name Johnny Valentine, was an American professional wrestler with a career spanning almost three decades. He has been inducted into four halls of fame for his achievements in wrestling. Wisniski is the father of professional wrestler Greg "The Hammer" Valentine.
Vitthalrao Gadgil, Indian politician (d. 2001) births
Vitthalrao Gadgil was a leader of Indian National Congress. He served as union minister of information and broadcasting during Rajeev Gandhi era.
Gordon Astall, English footballer and coach (d. 2020) births
Gordon Astall was an English professional footballer. He played as an outside right, and represented the Football League, the England B team and the full England side. At club level he made 456 appearances in the Football League and scored 111 goals.
Tommy Lasorda, American baseball player, coach, and manager (d. 2021) births

Thomas Charles Lasorda was an American professional baseball pitcher and manager. He managed the Los Angeles Dodgers of Major League Baseball (MLB) from 1976 through 1996. He was inducted into the National Baseball Hall of Fame as a manager in 1997.
Bill Smith, American clarinet player and composer (d. 2020) births
William Overton Smith was an American clarinetist and composer. He worked extensively in modern classical music, third stream and jazz, and was perhaps best known for having played with pianist Dave Brubeck intermittently from the 1940s to the early 2000s. Smith frequently recorded jazz under the name Bill Smith, but his classical compositions are credited under the name William O. Smith.
Virginia Capers, American actress and singer (d. 2004) births

Eliza "Virginia" Capers was an American actress. She won the Tony Award for Best Lead Actress in a Musical in 1974 for her performance as Lena Younger in Raisin, a musical version of Lorraine Hansberry's play A Raisin in the Sun.
Leila Hadley, American author (d. 2009) births
Leila Hadley was an American travel writer and socialite. Her books include Give Me the World (1958) and A Journey with Elsa Cloud (1997).
Bernard Gauthier, French cyclist (d. 2018) births
Bernard Gauthier was a French road racing cyclist, who was professional from 1947 to 1961. He won the Bordeaux–Paris road race on four occasions.
Charles Keeping, English author and illustrator (d. 1988) births

Charles William James Keeping was an English illustrator, children's book author and lithographer. He made the illustrations for Rosemary Sutcliff's historical novels for children, and he created more than twenty picture books. He also illustrated the complete works of Charles Dickens for the Folio Society.
Rosamunde Pilcher, English author (d. 2019) births
Rosamunde Pilcher, OBE was a British writer of romance novels, mainstream fiction, and short stories, from 1949 until her retirement in 2000. Her novels sold over 60 million copies worldwide. Early in her career she was also published under the pen name Jane Fraser. In 2001, she received the Corine Literature Prize's Weltbild Readers' Prize for Winter Solstice.
Charles Waterhouse, American painter, sculptor, and illustrator (d. 2013) births

Charles H. Waterhouse was an American painter, illustrator and sculptor renowned for using United States Marine Corps historical themes as the motif for his works. His art spans subjects from Tun Tavern, the birthplace of the U. S. Marines to present day topics. Throughout his career, he created over 500 pieces for the Marine Corps art collection.
J. William Middendorf, American soldier and politician, 14th United States Secretary of the Navy births

John William Middendorf II is a former Republican United States diplomat and Secretary of the Navy.

The secretary of the Navy is a statutory officer and the head of the Department of the Navy, a military department within the United States Department of Defense.
Ray Wetzel, American trumpet player and composer (d. 1951) births

Ray Wetzel was an American jazz trumpeter. Critic Scott Yanow described him as "greatly admired by his fellow trumpeters".
Dannie Abse, Welsh physician, poet, and author (d. 2014) births

Daniel Abse CBE FRSL was a Welsh poet and physician. His poetry won him many awards. As a medic, he worked in a chest clinic for over 30 years.
David Sive, American environmentalist and lawyer (d. 2014) births

David Sive was an American attorney, environmentalist, and professor of environmental law, who has been recognized as a pioneer in the field of United States environmental law.
Will Elder, American illustrator (d. 2008) births

William Elder was an American illustrator and comic book artist who worked in numerous areas of commercial art but is best known for a frantically funny cartoon style that helped launch Harvey Kurtzman's Mad comic book in 1952.
Eric Baker, English activist, co-founded Amnesty International (d. 1976) births
Eric Baker was a British activist and one of the founders of the human rights group Amnesty International, and the second Secretary-General of the organization. He was also a founder of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND).

Amnesty International is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and supporters around the world. The stated mission of the organization is to campaign for "a world in which every person enjoys all of the human rights enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and other international human rights instruments." The organization has played a notable role on human rights issues due to its frequent citation in media and by world leaders.
Anders Lassen, Danish-English soldier, Victoria Cross recipient (d. 1945) births

Anders Frederik Emil Victor Schau Lassen, VC, MC & Two Bars was a highly decorated Danish soldier, who was the only non-Commonwealth recipient of the British Victoria Cross in the Second World War. He was posthumously awarded the United Kingdom's highest gallantry award for his actions during Operation Roast on 8 April 1945 at Lake Comacchio in Italy in the final weeks of the Italian campaign.

The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously awarded by countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, most of which have established their own honours systems and no longer recommend British honours. It may be awarded to a person of any military rank in any service and to civilians under military command. No civilian has received the award since 1879. Since the first awards were presented by Queen Victoria in 1857, two-thirds of all awards have been personally presented by the British monarch. The investitures are usually held at Buckingham Palace.
Bob Lemon, American baseball player and manager (d. 2000) births

Robert Granville Lemon was an American right-handed pitcher and manager in Major League Baseball (MLB). Lemon was elected to the National Baseball Hall of Fame in 1976.
William H. Riker, American political scientist and academic (d. 1993) births
William Harrison Riker was an American political scientist who is prominent for applying game theory and mathematics to political science. He helped to establish University of Rochester as a center of behavioral revolution in political science.
Alajos Gáspár, Hungarian-Slovene author and poet (b. 1848) deaths
Alajos Gáspár was a Hungarian Slovene writer.
Hans Scholl, German activist (d. 1943) births

Hans Fritz Scholl was, along with Alexander Schmorell, one of the two founding members of the White Rose resistance movement in Nazi Germany. The principal author of the resistance movement's literature, he was found guilty of high treason for distributing anti-Nazi material and was executed by the Nazi regime in 1943 during World War II.
Henryk Szeryng, Mexican violinist and educator (d. 1988) births

Henryk Szeryng was a Polish violinist.
Grigory Frid, Russian pianist and composer (d. 2012) births

Grigory Samuilovich Frid also known as Grigori Fried was a Russian composer of music written in many different genres, including chamber opera.
Alain-Fournier, French soldier and author (b. 1886) deaths

Alain-Fournier was the pseudonym of Henri-Alban Fournier, a French author and soldier. He was the author of a single novel, Le Grand Meaulnes (1913), which has been filmed twice and is considered a classic of French literature. The book is based partly on his childhood.
Lillian Chestney, American painter and illustrator (d. 2000) births
Lillian Chestney was an American illustrator and painter. She studied in New York City and illustrated children's books, comic books, and magazine and book covers at a time when few women held artist positions in the industry.
Herbert Mataré, German physicist and academic (d. 2011) births

Herbert Franz Mataré was a German physicist. The focus of his research was the field of semiconductor research. His best-known work is the first functional European transistor, which he developed and patented together with Heinrich Welker in the vicinity of Paris in 1948, independent from the Bell Labs engineers who had developed the first transistor shortly before. The final 20 years of his life Mataré split time between his homes in Hückelhoven, Germany and Malibu, California. He was born in Aachen.
Martha Scott, American actress (d. 2003) births

Martha Ellen Scott was an American actress. She was featured in major films such as Cecil B. DeMille's The Ten Commandments (1956), and William Wyler's Ben-Hur (1959), playing the mother of Charlton Heston's character in both films. She originated the role of Emily Webb in Thornton Wilder's Our Town on Broadway in 1938 and later recreated the role in the 1940 film version, for which she was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actress.
György Faludy, Hungarian poet and author (d. 2006) births

György Faludy, sometimes anglicized as George Faludy, was a Hungarian poet, writer and translator.
John Engstead, American photographer and journalist (d. 1983) births
John Engstead was an American photographer. Engstead was born in California, and began his career in 1926, when he was hired as an office boy by Paramount Pictures' head of studio publicity, Harold Harley.
Esphyr Slobodkina, Russian-American author and illustrator (d. 2002) births

Esphyr Slobodkina was a Russian Empire-born American artist, author, and illustrator, best known for her classic children's picture book Caps for Sale. Slobodkina was a celebrated avant garde artist and feminist in the middle part of the 20th century.
Maurice Blanchot, French philosopher and author (d. 2003) births

Maurice Blanchot was a French writer, philosopher and literary theorist. His work, exploring a philosophy of death alongside poetic theories of meaning and sense, bore significant influence on post-structuralist philosophers such as Gilles Deleuze, Michel Foucault, Jacques Derrida and Jean-Luc Nancy.
Philip Fotheringham-Parker, English race car driver (d. 1981) births
Philip Fotheringham-Parker was a racing driver from England. He was born in Beckenham, Kent.
Hermann Schlichting, German engineer and academic (d. 1982) births
Hermann Schlichting was a German fluid dynamics engineer.
Ilse Koch, German war criminal (d. 1967) births

Ilse Koch was a German war criminal who was an overseer at Nazi concentration camps run by her husband, commandant Karl-Otto Koch. Working at Buchenwald (1937–1941) and Majdanek (1941–1943), Koch became infamous for her sadistic, brutal treatment of prisoners. In 1947, she became one of the first prominent Nazis tried by the U.S. military.
Haakon Lie, Norwegian lawyer and politician (d. 2009) births

Haakon Steen Lie was a Norwegian politician who served as party secretary for the Norwegian Labour Party from 1945 to 1969. Coming from humble origins, he became involved in the labour movement at an early age, and quickly rose in the party system. After actively working for the resistance movement and the exiled government during World War II, he was elected to the second-highest position in the party after the war, and his years in office were the most successful in the party's history.
Eugen Sänger, Czech-Austrian engineer (d. 1964) births

Eugen Sänger was an Austrian aerospace engineer best known for his contributions to lifting body and ramjet technology.
John Houseman, Romanian-American actor and producer (d. 1988) births

John Houseman was a Romanian-born British-American actor and producer of theatre, film, and television. He became known for his highly publicized collaboration with director Orson Welles from their days in the Federal Theatre Project through to the production of Citizen Kane and his collaboration, as producer of The Blue Dahlia, with writer Raymond Chandler on the screenplay. He is perhaps best known for his role as Professor Charles W. Kingsfield in the film The Paper Chase (1973), for which he won the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor. He reprised his role as Kingsfield in the 1978 television series adaptation.
Nadezhda Alliluyeva, second wife of Joseph Stalin (d. 1932) births

Nadezhda Sergeyevna Alliluyeva was the second wife of Joseph Stalin. She was born in Baku to a friend of Stalin, a fellow revolutionary, and was raised in Saint Petersburg. Having known Stalin from a young age, she married him when she was 18, and they had two children. Alliluyeva worked as a secretary for Bolshevik leaders, including Vladimir Lenin and Stalin, before enrolling at the Industrial Academy in Moscow to study synthetic fibres and become an engineer. She had health issues, which had an adverse impact on her relationship with Stalin. She also suspected he was unfaithful, which led to frequent arguments with him. On several occasions, Alliluyeva reportedly contemplated leaving Stalin, and after an argument, she fatally shot herself early in the morning of 9 November 1932.

Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1922–1952) and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (1941–1953). Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, he consolidated power to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically adhering to the Leninist interpretation of Marxism, he formalised these ideas as Marxism–Leninism, while his own policies are called Stalinism.
Charles Brenton Huggins, Canadian-American physician and physiologist, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1997) births

Charles Brenton Huggins was a Canadian-American physician, physiologist and cancer researcher at the University of Chicago specializing in prostate cancer. He was awarded the 1966 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for discovering in 1941 that hormones could be used to control the spread of some cancers. This was the first discovery that showed that cancer could be controlled by chemicals.

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
Paul Hugh Emmett, American chemist and engineer (d. 1985) births

Paul Hugh Emmett was an American chemist best known for his pioneering work in the field of catalysis and for his work on the Manhattan Project during World War II. He spearheaded the research to separate isotopes of uranium and to develop a corrosive uranium gas. Emmett also made significant contributions to BET Theory which explains the relationship between surface area and gas adsorption. He served on the faculty of Johns Hopkins University for 23 years throughout his scientific career.
William Spratling, American-Mexican silversmith and educator (d. 1967) births

William Spratling was an American-born silver designer and artist, best known for his influence on 20th century Mexican silver design.
Elsie Allen, Native American Pomo basket weaver (d. 1990) births

Elsie Comanche Allen was a Native American Pomo basket weaver from the Cloverdale Rancheria of Pomo Indians of California in Northern California, significant as for historically categorizing and teaching Californian Indian basket patterns and techniques and sustaining traditional Pomo basketry as an art form.
Uri Zvi Greenberg, Ukrainian-Israeli poet and journalist (d. 1981) births

Uri Zvi Greenberg was an acclaimed Israeli poet, journalist and politician who wrote in Yiddish and Hebrew. Widely regarded among the greatest poets in the country's history, he was awarded the Israel Prize in 1957 and the Bialik Prize in 1947, 1954 and 1977, all for his contributions to fine literature. Following Israeli independence in 1948, he also served in the first Knesset as a member of Menachem Begin's Herut Party. Greenberg's Revisionist orientation had an important influence on both his writings and his politics. Greenberg is considered to be the most significant representative of Expressionism in Hebrew and Yiddish literature.
Henry Segrave, American-English race car driver (d. 1930) births

Sir Henry O'Neal de Hane Segrave was an early British pioneer in land speed and water speed records. Segrave, who set three land and one water record, was the first person to hold both titles simultaneously and the first person to travel at over 200 miles per hour (320 km/h) in a land vehicle. He died in an accident in 1930 shortly after setting a new world water speed record on Windermere in the Lake District, England. The Segrave Trophy was established to commemorate his life.
Paul Muni, Ukrainian-born American actor (d. 1967) births

Paul Muni was an American stage and film actor who grew up in Chicago. Muni was a five-time Academy Award nominee, with one win. He started his acting career in the Yiddish theater. During the 1930s, he was considered one of the most prestigious actors at the Warner Bros. studio and was given the rare privilege of choosing which parts he wanted.
Elisabeth Rethberg, German soprano (d. 1976) births

Elisabeth Rethberg was a German operatic soprano singer who was active from the period of the First World War through the early 1940s.
Billy West, American actor, director, and producer (d. 1975) births

Billy West was a film actor, producer, and director. Active during the silent film era, he is best known as a semi-successful Charlie Chaplin impersonator. Beyond acting, he also directed shorts in the 1910s and 20s, as well as produced films. West ultimately retired in 1935.
Alma Thomas, American painter and educator (d. 1978) births

Alma Woodsey Thomas was an African-American artist and teacher who lived and worked in Washington, D.C., and is now recognized as a major American painter of the 20th century. Thomas is best known for the "exuberant", colorful, abstract paintings that she created after her retirement from a 35-year career teaching art at Washington's Shaw Junior High School.
Hooks Dauss, American baseball player (d. 1963) births

George August "Hooks" Dauss, born George August Daus, was an American professional baseball player from 1909 to 1926. He played 15 seasons of Major League Baseball as a right-handed pitcher for the Detroit Tigers from 1912 to 1926. He was given the nickname "Hooks", because his curveball was hard to hit. He compiled a career record of 223–182 with a 3.30 earned run average (ERA). His best years were 1915 when he had a 24–13 record, 1919 with a 21–9 record, and 1923 with a 21–13 record. Dauss continues to hold the Detroit Tigers franchise record for most wins by a pitcher with 223.
Bhaurao Patil, Indian educator and activist (d. 1959) births

Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil, born in Kumbhoj, Kolhapur, was a social activist and educator in Maharashtra, India. A strong advocate of mass education, he founded the Rayat Education Society. Bhaurao played an important role in educating backward castes and low income people by coining the philosophy earn and learn. He was a prominent member of Satyashodhak Samaj, founded by Mahatma Jyotirao Phule. The people of Maharashtra honoured him with the sobriquet Karmaveer and the Government of India awarded him with Padma Bhushan in 1959 in India.
Gunnar Asplund, Swedish architect and academic, designed the Stockholm Public Library (d. 1940) births

Erik Gunnar Asplund was a Swedish architect, mostly known as a key representative of Nordic Classicism of the 1920s, and during the last decade of his life as a major proponent of the modernist style which made its breakthrough in Sweden at the Stockholm International Exhibition (1930). Asplund was professor of architecture at the Royal Institute of Technology from 1931. His appointment was marked by a lecture, later published under the title "Our architectonic concept of space." The Woodland Crematorium at Stockholm South Cemetery (1935-1940) is considered his finest work and one of the masterpieces of modern architecture.

Stockholm Public Library is a library building in Stockholm, Sweden, designed by Swedish architect Gunnar Asplund, and one of the city's most notable structures. The name is today used for both the main library itself as well as the municipal library system of Stockholm.
Ben Chifley, Australian engineer and politician, 16th Prime Minister of Australia (d. 1951) births

Joseph Benedict Chifley was an Australian politician who served as the 16th prime minister of Australia from 1945 to 1949. He held office as the leader of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) from 1945, following the death of John Curtin on 5 July, until his own death in 1951.

The prime minister of Australia is the head of government of the Commonwealth of Australia. The prime minister heads the executive branch of the federal government of Australia and is also accountable to federal parliament under the principles of responsible government. The current prime minister is Anthony Albanese of the Australian Labor Party, who became prime minister on 23 May 2022.
Erich von Stroheim, Austrian-American actor, director, and screenwriter (d. 1957) births

Erich Oswald Hans Carl Maria von Stroheim was an Austrian-American director, actor and producer, most noted as a film star and avant-garde, visionary director of the silent era. His 1924 film Greed is considered one of the finest and most important films ever made. After clashes with Hollywood studio bosses over budget and workers' rights problems, Stroheim found it difficult to find work as a director and subsequently became a well-respected character actor, particularly in French cinema.
Ferenc Oslay, Hungarian-Slovene historian and author (d. 1932) births

Ferenc Oslay was a Hungarian-Slovene historian, writer, Trianon irredentist, and propagandist.
Frank George Woollard, English engineer (d. 1957) births

Frank George Woollard, was a British mechanical engineer who worked for nearly three decades in the British motor industry in various roles in design, production, and management. He was a pioneer in what is today called "Lean management," but whose work has been forgotten.
Wilhelm Keitel, German field marshal (d. 1946) births

Wilhelm Bodewin Johann Gustav Keitel was a German field marshal and war criminal who held office as chief of the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (OKW), the high command of Nazi Germany's Armed Forces, during the Second World War. In that capacity, Keitel signed a number of criminal orders and directives that led to numerous war crimes.
Solomon L. Spink, American lawyer and politician (b. 1831) deaths

Solomon Lewis Spink was an American lawyer who served as a delegate for the Dakota Territory in the United States House of Representatives.
Christabel Pankhurst, English activist, co-founded the Women's Social and Political Union (d. 1958) births

Dame Christabel Harriette Pankhurst, was a British suffragette born in Manchester, England. A co-founder of the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU), she directed its militant actions from exile in France from 1912 to 1913. In 1914, she supported the war against Germany. After the war, she moved to the United States, where she worked as an evangelist for the Second Adventist movement.

The Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) was a women-only political movement and leading militant organisation campaigning for women's suffrage in the United Kingdom from 1903 to 1918. Known from 1906 as the suffragettes, its membership and policies were tightly controlled by Emmeline Pankhurst and her daughters Christabel and Sylvia; Sylvia was eventually expelled.
Shigeru Yoshida, Japanese politician and diplomat, 51st Prime Minister of Japan (d. 1967) births

Shigeru Yoshida was a Japanese diplomat and politician who served as prime minister of Japan from 1946 to 1947 and from 1948 to 1954. Yoshida was one of the longest-serving Japanese prime ministers, and is the third-longest serving prime minister of post-occupation Japan.

The prime minister of Japan is the head of government of Japan. The prime minister chairs the Cabinet of Japan and has the ability to select and dismiss its Ministers of State. The prime minister also serves as the civilian commander-in-chief of the Japan Self Defence Forces and as a sitting member of the House of Representatives. The individual is appointed by the emperor of Japan after being nominated by the National Diet and must retain the nomination of the lower house and answer to parliament to remain in office.
André Tardieu, French journalist and politician, 67th Prime Minister of France (d. 1945) births

André Pierre Gabriel Amédée Tardieu was three times Prime Minister of France and a dominant figure of French political life in 1929–1932. He was a moderate conservative with a strong intellectual reputation, but became a weak prime minister at the start of the worldwide Great Depression.

The prime minister of France, officially the prime minister of the French Republic, is the head of government of the French Republic and the leader of the Council of Ministers.
Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis, Lithuanian painter and composer (d. 1911) births

Mikalojus Konstantinas Čiurlionis was a Lithuanian painter, composer and writer.
Friedrich Frey-Herosé, Swiss lawyer and politician (b. 1801) deaths

Friedrich Frey-Herosé was a Swiss politician.
Vladimir Dal, Russian lexicographer and linguist (b. 1801) deaths

Vladimir Ivanovich Dal was a noted Russian-language lexicographer, polyglot, Turkologist, and founding member of the Russian Geographical Society. During his lifetime he compiled and documented the oral history of the region that was later published in Russian and became part of modern folklore.
Charlotte Cooper, English-Scottish tennis player (d. 1966) births

Charlotte "Chattie" Cooper Sterry was an English female tennis player who won five singles titles at the Wimbledon Championships and in 1900 became Olympic champion. In winning in Paris on 11 July 1900, she became the first female Olympic tennis champion as well as the first individual female Olympic champion.
Arthur Pryor, American trombonist, composer, and bandleader (d. 1942) births

Arthur Willard Pryor was a trombone virtuoso, bandleader, and soloist with the Sousa Band. He was a prolific composer of band music, his best-known composition being "The Whistler and His Dog". In later life, he became a Democratic Party politician from New Jersey, who served on the Monmouth County Board of Chosen Freeholders during the 1930s.
Louise McKinney, Canadian educator and politician (d. 1931) births

Louise McKinney was a Canadian politician, temperance advocate, and women's rights activist. She was the first woman elected into the Legislative Assembly of Alberta and the first woman to serve in a legislature in the British Empire. She served in the Alberta legislature from 1917 to 1921 as a member of the Non-Partisan League. Later she was one of the Famous Five who campaigned successfully for the right of Canadian women to be appointed to the Senate. A former schoolteacher and temperance organizer, she came to Alberta in 1903 as a homesteader.
Anastasios Charalambis, Greek lieutenant and politician, Prime Minister of Greece (d. 1949) births

Anastasios Charalambis was a Greek Lieutenant General and interim Prime Minister of Greece for one day in 1922.

The prime minister of the Hellenic Republic, colloquially referred to as the prime minister of Greece, is the head of government of the Hellenic Republic and the leader of the Greek Cabinet. The incumbent prime minister is Kyriakos Mitsotakis, who took office on 8 July 2019 from Alexis Tsipras.
William Tierney Clark, English engineer, designed Hammersmith Bridge (b. 1783) deaths

William Tierney Clark FRS FRAS was an English civil engineer particularly associated with the design and construction of bridges. He was among the earliest designers of suspension bridges.

Hammersmith Bridge is a suspension bridge that crosses the River Thames in west London. It links the southern part of Hammersmith in the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, on the north side of the river, and Barnes in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, on the south side of the river. The current bridge, which is Grade II* listed and was designed by civil engineer Sir Joseph Bazalgette, is the second permanent bridge on the site, and has been attacked three times by Irish republicans.
Andrejs Pumpurs, Latvian soldier and poet (d. 1902) births

Andrejs Pumpurs was a poet who penned the Latvian epic Lāčplēsis and a prominent figure in the Young Latvia movement. Working in the land before volunteering to fight in Serbia against the Ottoman Empire in 1876, he became a loyal officer in the Russian army and also a staunch promoter of the Latvian culture.
Alexander Potebnja, Ukrainian linguist and philosopher (d. 1891) births

Alexander (Oleksandr) Potebnja was a Ukrainian linguist, philosopher and panslavist of Ukrainian Cossack descent, who was a professor of linguistics at the Imperial University of Kharkiv. He is well known as a specialist in the evolution of Russian phonetics.
Stephen D. Lee, American general and academic (d. 1908) births

Stephen Dill Lee was an American officer in the Confederate Army, politician and first president of Mississippi State University from 1880 to 1899. He served as lieutenant general of the Confederate States Army in the Eastern and Western theaters of the American Civil War.
Tự Đức, Vietnamese emperor (d. 1883) births

Tự Đức was the fourth emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty of Vietnam; he ruled from 1847 to 1883.
Shaka Zulu, Zulu chieftain and monarch of the Zulu Kingdom (b. 1787) deaths

Shaka kaSenzangakhona, also known as Shaka Zulu and Sigidi kaSenzangakhona, was the king of the Zulu Kingdom from 1816 to 1828. One of the most influential monarchs of the Zulu, he ordered wide-reaching reforms that re-organized the military into a formidable force.

The Zulu Kingdom, sometimes referred to as the Zulu Empire or the Kingdom of Zululand, was a monarchy in Southern Africa that extended along the coast of the Indian Ocean from the Tugela River in the south to Pongola River in the north.
Wilhelm Wattenbach, German historian and academic (d. 1897) births

Wilhelm Wattenbach, was a German historian.
Bernardino António Gomes, Portuguese physician and naturalist (d. 1877) births

Bernardino António Gomes was a Portuguese physician and scientist. He is perhaps most widely remembered for his pioneering work in Portugal in the field of anaesthesiology, as the first physician in the country to use chloroform in a surgical procedure ; he is also credited with the popularization of the use of creosote and of the first ether inhalers.
Michael Faraday, English physicist and chemist (d. 1867) births

Michael Faraday was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis.
Theodore Hook, English composer and educator (d. 1841) births

Theodore Edward Hook was an English man of letters and composer and briefly a civil servant in Mauritius. He is best known for his practical jokes, particularly the Berners Street hoax in 1809. The world's first postcard was received by Hook in 1840; he likely posted it to himself.
John Bartram, American botanist and explorer (b. 1699) deaths

John Bartram was an American botanist, horticulturist, and explorer, based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for most of his career. Swedish botanist and taxonomist Carl Linnaeus said he was the "greatest natural botanist in the world." Bartram corresponded with and shared North American plants and seeds with a variety of scientists in England and Europe.
Nathan Hale, American soldier (b. 1755) deaths

Nathan Hale was an American Patriot, soldier and spy for the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He volunteered for an intelligence-gathering mission in New York City but was captured by the British and executed. Hale is considered an American hero and in 1985 was officially designated the state hero of Connecticut.
Pope Clement XIV (b. 1705) deaths

Pope Clement XIV, born Giovanni Vincenzo Antonio Ganganelli, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 May 1769 to his death in September 1774. At the time of his election, he was the only Franciscan friar in the College of Cardinals, having been a member of OFM Conventual. To date, he is the last pope to take the pontifical name of "Clement" upon his election.
Paolo Ruffini, Italian mathematician and philosopher (d. 1822) births

Paolo Ruffini was an Italian mathematician and philosopher.
Elizabeth Simcoe, English-Canadian painter and author (d. 1850) births

Dame Elizabeth Posthuma Simcoe was an English artist and diarist in colonial Canada. Her husband, John Graves Simcoe, was the first Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada. Her diary gives an effective account of Canadian life.
Abu l-Hasan Ali I, ruler of Tunisia (b. 1688) deaths

Abu l-Hasan Ali I, also known as Ali Pasha and Ali Bey I,) was the second leader of the Husainid Dynasty and the ruler of Tunisia from 1735 to 1756.
Quintin Craufurd, Scottish author (d. 1819) births

Quintin Craufurd was a British author born at Kilwinning, Scotland.
Peter Simon Pallas, German zoologist and botanist (d. 1811) births

Peter Simon Pallas FRS FRSE was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810.
Jean-Étienne Guettard, French mineralogist and botanist (d. 1786) births

Jean-Étienne Guettard, French naturalist and mineralogist, was born at Étampes, near Paris.
Vincenzo Viviani, Italian mathematician and physicist (b. 1622) deaths

Vincenzo Viviani was an Italian mathematician and scientist. He was a pupil of Torricelli and a disciple of Galileo.
Philip Stanhope, 4th Earl of Chesterfield, English politician, Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (d. 1773) births

Philip Dormer Stanhope, 4th Earl of Chesterfield, was a British statesman, diplomat, and man of letters, and an acclaimed wit of his time.

Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, or more formally Lieutenant General and General Governor of Ireland, was the title of the chief governor of Ireland from the Williamite Wars of 1690 until the Partition of Ireland in 1922. This spanned the Kingdom of Ireland (1541–1800) and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922). The office, under its various names, was often more generally known as the Viceroy, and his wife was known as the vicereine. The government of Ireland in practice was usually in the hands of the Lord Deputy up to the 17th century, and later of the Chief Secretary for Ireland.
Martha Corey, American woman accused of witchcraft (b. 1620) deaths

Martha Corey was accused and convicted of witchcraft during the Salem witch trials, on September 9, 1692, and was hanged on September 22, 1692. Her second husband, Giles Corey, was also accused.

Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have attacked their own community, and often to have communed with evil beings. It was thought witchcraft could be thwarted by protective magic or counter-magic, which could be provided by cunning folk or folk healers. Suspected witches were also intimidated, banished, attacked or killed. Often they would be formally prosecuted and punished, if found guilty or simply believed to be guilty. European witch-hunts and witch trials in the early modern period led to tens of thousands of executions. In some regions, many of those accused of witchcraft were folk healers or midwives. European belief in witchcraft gradually dwindled during and after the Age of Enlightenment.
Barthold Heinrich Brockes, German poet (d. 1747) births

Barthold Heinrich Brockes was a German poet.
John Biddle, English minister and theologian (b. 1615) deaths
John Biddle or Bidle was an influential English nontrinitarian, and Unitarian. He is often called "the Father of English Unitarianism".
Alessandro Allori, Italian painter and educator (b. 1535) deaths

Alessandro di Cristofano di Lorenzo del Bronzino Allori was an Italian painter of the late Mannerist Florentine school.
Li Zicheng, Chinese emperor (d. 1645) births

Li Zicheng, born Li Hongji, also known by the nickname, Dashing King, was a Chinese peasant rebel leader who overthrew the Ming dynasty in 1644 and ruled over northern China briefly as the emperor of the short-lived Shun dynasty before his death a year later.
Anne of Austria, Queen and regent of France (d. 1666) births

Anne of Austria was an infanta of Spain who became Queen of France as the wife of King Louis XIII from their marriage in 1615 until Louis XIII died in 1643. She was also Queen of Navarre until that kingdom was annexed into the French crown in 1620. After her husband's death, Anne was regent to her son Louis XIV, during his minority, until 1651. During her regency, Cardinal Mazarin served as France's chief minister. Accounts of French court life of Anne's era emphasize her difficult marital relations with her husband, her closeness to her son, and her disapproval of her son's marital infidelity to her niece and daughter-in-law Maria Theresa.
Gabriel Spenser, English actor (b. c.1578) deaths

Gabriel Spenser, also spelt Spencer, was an Elizabethan actor. He is best known for episodes of violence culminating in his death in a duel at the hands of the playwright Ben Jonson.
Matthäus Merian, Swiss-German engraver and cartographer (d. 1650) births

Matthäus Merian der Ältere was a Swiss-born engraver who worked in Frankfurt for most of his career, where he also ran a publishing house. He was a member of the patrician Basel Merian family.
Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex (b. 1541) deaths

Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex, KG, was an English nobleman and general. From 1573 until his death he fought in Ireland in connection with the Plantations of Ireland, most notably the Rathlin Island massacre. He was the father of Robert, 2nd Earl of Essex, who was Elizabeth I's favourite during her later years.
Johannes Agricola, German theologian and academic (b. 1494) deaths
Johann or Johannes Agricola was a German Protestant Reformer during the Protestant Reformation. He was a follower and friend of Martin Luther, who became his antagonist in the matter of the binding obligation of the law on Christians.
Francisco Vázquez de Coronado, Spanish explorer (b. 1510) deaths

Francisco Vázquez de Coronado y Luján was a Spanish conquistador and explorer who led a large expedition from what is now Mexico to present-day Kansas through parts of the southwestern United States between 1540 and 1542. Vázquez de Coronado had hoped to reach the Cities of Cíbola, often referred to now as the mythical Seven Cities of Gold. His expedition marked the first European sightings of the Grand Canyon and the Colorado River, among other landmarks. His name is often Anglicized as Vasquez de Coronado or just Coronado.
Philipp Nicodemus Frischlin, German philologist, mathematician, astronomer, and poet (d. 1590) births

Philipp Nicodemus Frischlin was a German philologist, poet, playwright, mathematician, and astronomer, born at Erzingen, today part of Balingen in Württemberg, where his father was parish minister.
Guru Nanak, Sikh religious leader, founded Sikhism (b. 1469) deaths

Gurū Nānak, also referred to as Bābā Nānak, was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated worldwide as Guru Nanak Gurpurab on Katak Pooranmashi, i.e. October–November.
Sikhism, also known as Sikhi or Sikh Dharma, is an Indian religion that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, around the end of the 15th century CE. It is the most recently founded major organized faith and stands at fifth-largest worldwide, with about 25–30 million adherents as of the early 21st century.
Louise of Savoy, French regent (b. 1476) deaths

Louise of Savoy was a French noble and regent, Duchess suo jure of Auvergne and Bourbon, Duchess of Nemours, and the mother of King Francis I. She was politically active and served as the regent of France in 1515, in 1525–1526 and in 1529.
Selim I, Ottoman sultan (b. 1465) deaths

Selim I, known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite lasting only eight years, his reign is notable for the enormous expansion of the Empire, particularly his conquest between 1516 and 1517 of the entire Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt, which included all of the Levant, Hejaz, Tihamah and Egypt itself. On the eve of his death in 1520, the Ottoman Empire spanned about 3.4 million km2 (1.3 million sq mi), having grown by seventy percent during Selim's reign.
Anne of Cleves, Queen consort of England (d. 1557) births

Anne of Cleves was Queen of England from 6 January to 12 July 1540 as the fourth wife of King Henry VIII. Not much is known about Anne before 1527, when she became betrothed to Francis, Duke of Bar, son and heir of Antoine, Duke of Lorraine, although their marriage did not proceed. In March 1539, negotiations for Anne's marriage to Henry began, as Henry believed that he needed to form a political alliance with her brother, William, who was a leader of the Protestants of western Germany, to strengthen his position against potential attacks from Catholic France and the Holy Roman Empire.
Philibert I, Duke of Savoy (b. 1465) deaths

Philibert I, surnamed the Hunter, was the son of Amadeus IX, Duke of Savoy and Yolande of Valois. Philibert was Duke of Savoy from 1472 to 1482.
Peter II, Duke of Brittany (b. 1418) deaths

Peter II (1418–1457), was Duke of Brittany, Count of Montfort and titular earl of Richmond, from 1450 to his death. He was son of Duke John VI and Joan of France, and a younger brother of Francis I.
John VII Palaiologos, Byzantine Emperor (b. 1370) deaths

John VII Palaiologos or Palaeologus was Byzantine emperor for five months in 1390, from 14 April to 17 September. A handful of sources suggest that John VII sometimes used the name Andronikos (Ἀνδρόνικος), possibly to honour the memory of his father, Andronikos IV Palaiologos, though he reigned under his birth name.

This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors (symbasileis) who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title.
Thomas de Mowbray, 1st Duke of Norfolk, English politician, Earl Marshal of The United Kingdom (b. 1366) deaths

Thomas de Mowbray, 1st Duke of Norfolk, KG was an English peer. As a result of his involvement in the power struggles which led up to the fall of King Richard II, he was banished and died in exile in Venice.

Earl marshal is a hereditary royal officeholder and chivalric title under the sovereign of the United Kingdom used in England. He is the eighth of the great officers of State in the United Kingdom, ranking beneath the lord high constable and above the lord high admiral. The dukes of Norfolk have held the office since 1672.
Thomas le Despenser, 1st Earl of Gloucester (d. 1400) births

Thomas le Despenser, 2nd Baron Despenser, 1st Earl of Gloucester KG was the son of Edward le Despenser, 1st Baron le Despencer, whom he succeeded in 1375.
Henry, 3rd Earl of Lancaster, English politician, Lord High Steward (b. 1281) deaths

Henry, 3rd Earl of Leicester and Lancaster was a grandson of King Henry III of England (1216–1272) and was one of the principals behind the deposition of King Edward II (1307–1327), his first cousin.

The Lord High Steward is the first of the Great Officers of State in England, nominally ranking above the Lord Chancellor.
Dōgen, Japanese monk and philosopher (b. 1200) deaths

Dōgen Zenji, also known as Dōgen Kigen (道元希玄), Eihei Dōgen (永平道元), Kōso Jōyō Daishi (高祖承陽大師), or Busshō Dentō Kokushi (仏性伝東国師), was a Japanese Buddhist priest, writer, poet, philosopher, and founder of the Sōtō school of Zen in Japan.
Ibn Khallikan, Iraqi scholar and judge (d. 1282) births
Aḥmad bin Muḥammad bin Ibrāhīm bin Abū Bakr ibn Khallikān, better known as Ibn Khallikān, was a 13th century Shafi'i Islamic scholar who compiled the celebrated biographical encyclopedia of Muslim scholars and important men in Muslim history, Wafayāt al-Aʿyān wa-Anbāʾ Abnāʾ az-Zamān.
Uchtred, Lord of Galloway (b. c. 1120) deaths
Uhtred mac Fergus was Lord of Galloway from 1161 to 1174, ruling jointly with his brother Gille Brigte (Gilbert). They were sons of Fergus of Galloway; it was believed that they were half brothers, but Duncan of Carrick was addressed as cousin by the English King, as was Uchtred.. Their mother's name is not known for sure, but she must have been one of the many illegitimate daughters of Henry I of England, most likely Elizabeth Fitzroy.
Otto of Freising, German bishop and chronicler (b. c. 1114) deaths

Otto of Freising was a German churchman of the Cistercian order and chronicled at least two texts which carries valuable information on the political history of his own time. He was Otto I Bishop of Freising as from 1138. Otto participated in the Second Crusade; he lived through the journey and reached Jerusalem, and later returned to Bavaria in the late 1140s, living for another decade back in Europe.
Ouyang Xiu, Chinese historian, poet, and politician (b. 1007) deaths

Ouyang Xiu, courtesy name Yongshu, also known by his art names Zuiweng (醉翁) and Liu Yi Jushi (六一居士), was a Chinese historian, calligrapher, epigrapher, essayist, poet, and politician of the Song dynasty. He was a renowned writer among his contemporaries and is considered the central figure of the Eight Masters of the Tang and Song. He revived the Classical Prose Movement and promoted it in imperial examinations, paving the way for future masters like Su Shi and Su Zhe.
Richeza of Poland, Queen of Hungary (d. 1075) births

Richeza of Poland was Queen Consort of Hungary by marriage to Béla I of Hungary.
Wichmann II, Frankish nobleman deaths
Wichmann II the Younger was a member of the Saxon House of Billung. He was a son of Count Wichmann the Elder and his wife Frederuna, a niece of Queen Matilda. The cousin of Emperor Otto I became known as a fierce enemy of the ruling Ottonian dynasty.
Zhao Zong, emperor of the Tang Dynasty (b. 867) deaths

Emperor Zhaozong of Tang, né Li Jie, name later changed to Li Min and again to Li Ye, was the penultimate emperor of the Tang dynasty of China. He reigned from 888 to 904. Zhaozong was the seventh son of Emperor Yizong of Tang and younger brother of Emperor Xizong of Tang. Later Li Jie was murdered by Zhu Wen, the Later Liang ruler who overthrew the Tang dynasty.

The Tang dynasty, or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty.
Pope Felix IV deaths

Pope Felix IV was the bishop of Rome from 12 July 526 to his death. He was the chosen candidate of Ostrogoth King Theodoric the Great, who had imprisoned Felix's predecessor, John I.
He Jin, Chinese general and regent (b. 135) deaths
He Jin, courtesy name Suigao, was a Chinese military general and politician. He was the military Grand Marshal and regent of the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was an elder half-brother of Empress He, the empress consort of Emperor Ling, and a maternal uncle of Emperor Shao. In 189, he and his sister shared power as regents when the young Emperor Shao was put on the throne following Emperor Ling's death. During the time, the conflict between He Jin and the influential eunuch faction intensified. The eunuch faction lured He Jin into a trap in the imperial palace and assassinated him. While He Jin's subordinates slaughtered the eunuch faction in revenge, the warlord Dong Zhuo took advantage of the power vacuum to enter the imperial capital Luoyang and seize control of the Han central government. The subsequent breakdown of central command brought forth the beginning of massive civil wars which led to the end of the Han dynasty and the start of the Three Kingdoms period.
American Business Women's Day (United States)
American Business Women's Day is an American holiday, nationally recognized on September 22.
Christian feast days: Candidus

Saint Candidus was a commander of the Theban Legion. The Theban Legion was composed of Christians from Upper Egypt. He is venerated as a Christian saint and martyr.
Christian feast days: Digna and Emerita

Saints Digna and Emerita are venerated as saints by the Catholic Church. They were Roman maidens seized and put to the torture as Christians in the persecution of Valerian at Rome.
Christian feast days: Emmeram of Regensburg

Saint Emmeram of Regensburg was a Christian bishop and a martyr born in Poitiers, Aquitaine. Having heard of idolatry in Bavaria, Emmeram travelled to Ratisbon (Regensburg) some time after the year 649 to the court of Theodo I, Duke of Bavaria. He supposedly travelled up the Loire, crossed through the Black Forest and then followed the Danube to Regensburg. Theodo welcomed Emmeram to his court, where he laboured for three years carrying out missionary work. During this time, he gained a reputation as a pious man. He died circa 652 and is buried in St. Emmeram's in Regensburg, Germany. His feast day in the Catholic Calendar of saints is September 22.
Christian feast days: Felix and Constantia
Saints Felix and Constanza were a brother and sister from the Roman city of Nuceria Alfaterna, and were martyred by the emperor Nero in 68 AD.
Christian feast days: Ignatius of Santhià (Lorenzo Maurizio Belvisotti)
Ignatius of Santhià, born Lorenzo Maurizio Belvisotti, was an Italian Roman Catholic priest and a professed member of the Order of Friars Minor Capuchin.
Christian feast days: Laud of Coutances

Saint Laud of Coutances was the fifth bishop of Coutances and is venerated as a saint in the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches.
Christian feast days: Maurice (Western Christianity)

Saint Maurice was an Egyptian military leader who headed the legendary Theban Legion of Rome in the 3rd century, and is one of the favorite and most widely venerated saints of that martyred group. He is the patron saint of several professions, locales, and kingdoms.

Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity. Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic Church, Independent Catholicism and Restorationism.
Christian feast days: Paul Chong Hasang (one of The Korean Martyrs)

Paul Chong Hasang was one of the Korean Martyrs. His feast day is September 22, and he is also venerated along with the rest of the 103 Korean martyrs on September 20.
The Korean Martyrs were the victims of religious persecution against Catholics during the nineteenth century in Korea. Between 8,000–10,000 Korean Christians were killed during this period. 103 Catholics were canonized en masse in May 1984, including the first Korean Catholic priest, Andrew Kim Taegon, who was executed by sword in 1846.
Christian feast days: Phocas (the Gardener, or of Sinope)

Saint Phocas, sometimes called Phocas the Gardener (Greek:Φωκᾶς), is venerated as a martyr by the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches. His life and legend may have been a fusion of three men with the same name: a Phocas of Antioch, a Phocas the Gardener and Phocas, Bishop of Sinope.
Christian feast days: Phocas, Bishop of Sinope

Hieromartyr Phocas was born in the city of Sinope in northern Turkey. During his adult years he became Bishop of Sinope. At the time of persecution against Christians under the emperor Trajan (98–117), the governor demanded that the saint renounce Christ. After fierce torture they enclosed St Phocas in a hot bath, where he died a martyr's death in the year 117.
Christian feast days: Sadalberga

Sadalberga was the daughter of Gundoin, Duke of Alsace and his wife Saretrude. Sadalberga founded the Abbey of St John at Laon. She is the subject of a short hagiography, the Vita Sadalbergae.
Christian feast days: Saintin (Sanctinus) de Meaux

Saint Sanctinus of Meaux was a French bishop and missionary, traditionally named as the first bishop of Meaux and also of Verdun. He was supposedly a pupil of Saint Denis. His tooth is preserved as a relic in Verdun Cathedral. His feast day is celebrated on 22 September.
Christian feast days: Septimius of Iesi (this date since 1623)

Saint Septimius of Iesi was the first bishop of Iesi, a martyr, and a saint.
Christian feast days: Theban Legion

The Theban Legion figures in Christian hagiography as a Roman legion from Egypt—"six thousand six hundred and sixty-six men"—who converted en masse to Christianity and were martyred together in 286, according to the hagiographies of Saint Maurice, the chief among the Legion's saints. Their feast day is held on September 22.
Christian feast days: Thomas of Villanova

Thomas of Villanova, born Tomás García y Martínez, was a Spanish friar of the Order of Saint Augustine who was a noted preacher, ascetic and religious writer of his day. He became an archbishop who was famous for the extent of his care for the poor of his see.
Christian feast days: Philander Chase (Episcopal Church)

Philander Chase was an Episcopal Church bishop, educator, and pioneer of the United States western frontier, especially in Ohio and Illinois.
The veneration of saints in the Episcopal Church is a continuation of an ancient tradition from the early Church which honors important and influential people of the Christian faith. The usage of the term saint is similar to Roman Catholic and Orthodox traditions. Episcopalians believe in the communion of saints in prayer and as such the Episcopal liturgical calendar accommodates feasts for saints.
Christian feast days: September 22 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)

September 21 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar - September 23
Earliest date for the autumnal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere and the vernal equinox in the Southern Hemisphere: Autumnal Equinox Day (Japan)
Autumnal Equinox Day is a public holiday in Japan that usually occurs on September 22 or 23, the date of Southward equinox in Japan Standard Time. Due to the necessity of recent astronomical measurements, the date of the holiday is not officially declared until February of the previous year. Autumnal Equinox Day became a public holiday in 1948. In 1947 and before, it was the date of Shūki kōreisai (秋季皇霊祭), an event relating to Shintoism. Like other holidays, this holiday was repackaged as a non-religious holiday for the sake of separation of religion and state in Japan's postwar constitution.
Earliest date for the autumnal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere and the vernal equinox in the Southern Hemisphere: Mabon in the Northern Hemisphere, Ostara in the Southern Hemisphere. (Neopagan Wheel of the Year)
The Wheel of the Year is an annual cycle of seasonal festivals, observed by many modern pagans, consisting of the year's chief solar events and the midpoints between them. While names for each festival vary among diverse pagan traditions, syncretic treatments often refer to the four solar events as "quarter days", with the four midpoint events as "cross-quarter days". Differing sects of modern paganism also vary regarding the precise timing of each celebration, based on distinctions such as lunar phase and geographic hemisphere.

Ēostre is a West Germanic spring goddess. The name is reflected in Old English: *Ēastre, Old High German: *Ôstara, and Old Saxon: *Āsteron. By way of the Germanic month bearing her name, she is the namesake of the festival of Easter in some languages. The Old English deity Ēostre is attested solely by Bede in his 8th-century work The Reckoning of Time, where Bede states that during Ēosturmōnaþ, pagan Anglo-Saxons had held feasts in Ēostre's honour, but that this tradition had died out by his time, replaced by the Christian Paschal month, a celebration of the resurrection of Jesus.

Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism and neopaganism, is a term for a religion or family of religions influenced by the various historical pre-Christian beliefs of pre-modern peoples in Europe and adjacent areas of North Africa and the Near East. Although they share similarities, contemporary pagan movements are diverse, and do not share a single set of beliefs, practices, or texts. Scholars of religion may characterise these traditions as new religious movements. Some academics who study the phenomenon treat it as a movement that is divided into different religions while others characterize it as a single religion of which different pagan faiths are denominations. Because of these different approaches there is disagreement on when or if the term pagan should be capitalized, though specialists in the field of pagan studies tend towards capitalisation.
Earliest date for the autumnal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere and the vernal equinox in the Southern Hemisphere: The first day of Miķeļi (Latvia)
Miķeļi nav gadskārta ([miceʎi]) or Miķeļdiena is a Latvian autumn equinox and annual harvest festival and market. Latvian Miķeļi dainas referred to good and rich husbands as bread fathers, who are associated with the autumn harvest ripening. In different regions, the Miķeļi celebration was also called Mīkaļiem or Mīklāli, but it is also known to other households as Sila Miķelis, Miega Miķelis, and Miega Mača. According to an old calendar, this holiday is celebrated around autumn equinox time, when the duration of night is same as the duration of day.

Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the Baltic states; and is bordered by Estonia to the north, Lithuania to the south, Russia to the east, Belarus to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi), with a population of 1.9 million. The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Riga. Latvians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts; and speak Latvian, one of the only two surviving Baltic languages. Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population.
Independence Day, celebrates the independence of Bulgaria from the Ottoman Empire in 1908.
The official public holidays in Bulgaria are listed in the table below.

Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of 110,994 square kilometres (42,855 sq mi), and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas.

The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror.
Independence Day, celebrates the independence of Mali from France in 1960.
This is a list of public holidays in Mali.

Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali is the eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over 1,240,000 square kilometres (480,000 sq mi). The population of Mali is 21.9 million. 67% of its population was estimated to be under the age of 25 in 2017. Its capital and largest city is Bamako. The sovereign state of Mali consists of eight regions and its borders on the north reach deep into the middle of the Sahara Desert. The country's southern part is in the Sudanian savanna, where the majority of inhabitants live, and both the Niger and Senegal rivers pass through. The country's economy centres on agriculture and mining. One of Mali's most prominent natural resources is gold, and the country is the third largest producer of gold on the African continent. It also exports salt.
Resistance Fighting Day (Estonia)

Resistance Fighting Day also known as Otto Tief Government Day is a public holiday in Estonia which takes on 22 September. It honors the Estonian commander Otto Tief's attempt to restore Estonian independence in 1944. The holiday is a date of remembrance, commemorating the victims of the subsequent re-establishment of Soviet rule in Estonia following the Nazi rule, and the resulting sovietisation of the republic from 1944–1950. It falls under the cultural symbols designed to recognize the Occupation of the Baltic states until 1991. It was known in the former Estonian SSR, as well as today by the Russian Federation and pro-Russian forces in Estonia as the Day of the Liberation of Tallinn from Nazi Invaders, celebrating the Soviet Tallinn Offensive by the Red Army's 2nd Shock and 8th Armies and the Baltic Fleet against the Wehrmacht.

Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of 45,339 square kilometres (17,505 sq mi). The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the autochthonous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language.