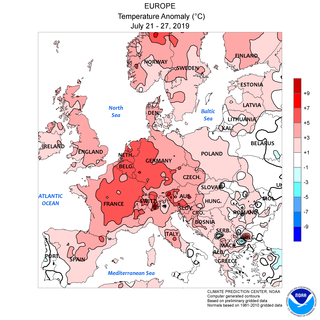
2019 European heat waves
In late June and late July 2019 there were two temporally distinct European heat waves, which set all-time high temperature records in Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom.
National extreme heat records set this day in the UK, Belgium, The Netherlands and Germany during the July 2019 European heat wave.

In late June and late July 2019 there were two temporally distinct European heat waves, which set all-time high temperature records in Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom.
As-Suwayda attacks: Coordinated attacks occur in Syria.

The 2018 As-Suwayda attacks were a string of suicide bombings and gun attacks that took place in and around As-Suwayda, Syria on 25 July, killing at least 258 people and injuring 180 others. The attacks were committed by the Islamic State and largely targeted Syria's Druze minority.
WikiLeaks published 75,000 classified documents about the War in Afghanistan in one of the largest leaks in U.S. military history.

WikiLeaks is an international non-profit organisation that publishes news leaks and classified media provided by anonymous sources. Its website stated in 2015 that it had released online 10 million documents since beginning in 2006 in Iceland. Julian Assange, an Australian Internet activist, is generally described as its founder and director and is currently fighting extradition to the United States over his work with WikiLeaks. Since September 2018, Kristinn Hrafnsson has served as its editor-in-chief.
The Afghan War documents leak, also called the Afghan War Diary, is the disclosure of a collection of internal U.S. military logs of the War in Afghanistan, which were published by WikiLeaks on 25 July 2010. The logs consist of over 91,000 Afghan War documents, covering the period between January 2004 and December 2009. Most of the documents are classified secret. As of 28 July 2010, only 75,000 of the documents have been released to the public, a move which WikiLeaks says is "part of a harm minimization process demanded by [the] source". Prior to releasing the initial 75,000 documents, WikiLeaks made the logs available to The Guardian, The New York Times and Der Spiegel in its German and English online edition, which published reports in line with an agreement made earlier the same day, 25 July 2010.
The United States government classification system is established under Executive Order 13526, the latest in a long series of executive orders on the topic beginning in 1951. Issued by President Barack Obama in 2009, Executive Order 13526 replaced earlier executive orders on the topic and modified the regulations codified to 32 C.F.R. 2001. It lays out the system of classification, declassification, and handling of national security information generated by the U.S. government and its employees and contractors, as well as information received from other governments.

The War in Afghanistan was an armed conflict in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2021. It began when an international military coalition, led by the United States, launched an invasion of Afghanistan, subsequently toppling the Taliban-ruled Islamic Emirate and establishing the internationally recognized Islamic Republic three years later. The nearly 20-year-long conflict ultimately ended with the 2021 Taliban offensive, which overthrew the Islamic Republic, and re-established the Islamic Emirate. It was the longest war in the military history of the United States, surpassing the length of the Vietnam War (1955–1975) by approximately six months.
WikiLeaks publishes classified documents about the War in Afghanistan, one of the largest leaks in U.S. military history.

WikiLeaks is an international non-profit organisation that publishes news leaks and classified media provided by anonymous sources. Its website stated in 2015 that it had released online 10 million documents since beginning in 2006 in Iceland. Julian Assange, an Australian Internet activist, is generally described as its founder and director and is currently fighting extradition to the United States over his work with WikiLeaks. Since September 2018, Kristinn Hrafnsson has served as its editor-in-chief.
The Afghan War documents leak, also called the Afghan War Diary, is the disclosure of a collection of internal U.S. military logs of the War in Afghanistan, which were published by WikiLeaks on 25 July 2010. The logs consist of over 91,000 Afghan War documents, covering the period between January 2004 and December 2009. Most of the documents are classified secret. As of 28 July 2010, only 75,000 of the documents have been released to the public, a move which WikiLeaks says is "part of a harm minimization process demanded by [the] source". Prior to releasing the initial 75,000 documents, WikiLeaks made the logs available to The Guardian, The New York Times and Der Spiegel in its German and English online edition, which published reports in line with an agreement made earlier the same day, 25 July 2010.
Pratibha Patil was sworn in as the first female president of India.

Pratibha Devisingh Patil is an Indian politician and lawyer who served as the 12th president of India spanning from 2007 to 2012. She is the first woman to become the president of India. A member of the Indian National Congress, she previously served as the Governor of Rajasthan from 2004 to 2007, and was a member of Lok Sabha from 1991 to 1996.

The president of India is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murmu is the 15th and current president, having taken office from 25 July 2022.
Pratibha Patil is sworn in as India's first female president.

Pratibha Devisingh Patil is an Indian politician and lawyer who served as the 12th president of India spanning from 2007 to 2012. She is the first woman to become the president of India. A member of the Indian National Congress, she previously served as the Governor of Rajasthan from 2004 to 2007, and was a member of Lok Sabha from 1991 to 1996.
Air France Flight 4590, a Concorde en route from Paris to New York, crashed in Gonesse, France, killing all 109 passengers on board and four people on the ground.

On 25 July 2000, Air France Flight 4590, a Concorde passenger jet on an international charter flight from Paris to New York, crashed shortly after takeoff, killing all 109 people on board and four on the ground. It was the only fatal Concorde accident during its 27-year operational history.

The Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde is a Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC). Studies started in 1954, and France and the UK signed a treaty establishing the development project on 29 November 1962, as the programme cost was estimated at £70 million . Construction of the six prototypes began in February 1965, and the first flight took off from Toulouse on 2 March 1969. The market was predicted for 350 aircraft, and the manufacturers received up to 100 option orders from many major airlines. On 9 October 1975, it received its French Certificate of Airworthiness, and from the UK CAA on 5 December.

Gonesse is a commune in the Val-d'Oise department, in the north-eastern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located 16.5 km (10.3 mi) from the centre of Paris.
Concorde Air France Flight 4590 crashes at Paris Charles de Gaulle airport, killing 113 people.

The Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde is a Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC). Studies started in 1954, and France and the UK signed a treaty establishing the development project on 29 November 1962, as the programme cost was estimated at £70 million . Construction of the six prototypes began in February 1965, and the first flight took off from Toulouse on 2 March 1969. The market was predicted for 350 aircraft, and the manufacturers received up to 100 option orders from many major airlines. On 9 October 1975, it received its French Certificate of Airworthiness, and from the UK CAA on 5 December.

On 25 July 2000, Air France Flight 4590, a Concorde passenger jet on an international charter flight from Paris to New York, crashed shortly after takeoff, killing all 109 people on board and four on the ground. It was the only fatal Concorde accident during its 27-year operational history.

Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport or Roissy Airport, is the principal airport serving the French capital, Paris, and the largest international airport in France. Opened in 1974, it is in Roissy-en-France, 23 km (14 mi) northeast of Paris and is named after statesperson Charles de Gaulle (1890–1970).
In a military coup in Burundi, Pierre Buyoya deposes Sylvestre Ntibantunganya.
The 1996 Burundian coup d'état was a military coup d'état that took place in Burundi on 25 July 1996. In the midst of the Burundi Civil War, former president Pierre Buyoya deposed Hutu President Sylvestre Ntibantunganya. According to Amnesty International, in the weeks following the coup, more than 6,000 people were killed in the country. This was Buyoya's second successful coup, having overthrown Jean-Baptiste Bagaza in 1987.

Pierre Buyoya was a Burundian army officer and politician who served two terms as President of Burundi in 1987 to 1993 and 1996 to 2003 as de facto military dictator. He was the second-longest serving president in Burundian history.

Sylvestre Ntibantunganya is a Burundian politician. He was President of the National Assembly of Burundi from 23 December 1993 to 30 September 1994, and President of Burundi from 6 April 1994 to 25 July 1996.
A gas bottle explodes in Saint Michel station of line B of the RER (Paris regional train network). Eight are killed and 80 wounded.

The 1995 France bombings were a series of attacks that targeted public transport systems in Paris and Lyon, as well as a school in Villeurbanne. They were carried out by the Armed Islamic Group of Algeria (GIA), who sought to expand the Algerian Civil War to France. The attacks killed eight people, all during the first attack on 25 July 1995. The attack also injured 190 people.

The Réseau Express Régional, commonly abbreviated RER, is a hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit system serving Paris and its suburbs. It acts as a combined city-centre underground rail system and suburbs-to-city-centre commuter rail. In the city centre it acts much like the Paris Métro, though faster, having fewer stops. This has made it a model for proposals to improve transit within other cities.
Israel and Jordan sign the Washington Declaration, that formally ends the state of war that had existed between the nations since 1948.

Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the northeast, Syria to the north, and the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea to the west. It has a 26 km (16 mi) coastline on the Gulf of Aqaba in the Red Sea to the southwest. The Gulf of Aqaba separates Jordan from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as its economic, political, and cultural centre.

The Israel–Jordan peace treaty, sometimes referred to as the Wadi Araba Treaty, is an agreement that ended the state of war that has existed between the two countries since the 1948 Arab–Israeli War and established mutual diplomatic relations. In addition to establishing peace between the two countries, the treaty also settled land and water disputes, provided for broad cooperation in tourism and trade, and obligated both countries to prevent their territory being used as a staging ground for military strikes by a third country.
Israel launches a massive attack against Lebanon in what the Israelis call Operation Accountability, and the Lebanese call the Seven-Day War.

Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lies to its west across the Mediterranean Sea; its location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has contributed to its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious diversity. It is part of the Levant region of the Middle East. Lebanon is home to roughly six million people and covers an area of 10,452 square kilometres (4,036 sq mi), making it the second smallest country in continental Asia. The official language of the state is Arabic, while French is also formally recognized; the Lebanese dialect of Arabic is used alongside Modern Standard Arabic throughout the country.
On July 25, 1993, Israeli forces launched a week-long attack against Lebanon named Operation Accountability in Israel and the Seven-Day War in Lebanon. Israel specified three purposes to the operation, to strike directly at Hezbollah, to make it difficult for Hezbollah to use southern Lebanon as a base for striking Israel, and to displace refugees in the hopes of pressuring the Lebanese government to intervene against Hezbollah. The affected civilian population included both Lebanese and Palestinian refugees.
The Saint James Church massacre occurs in Kenilworth, Cape Town, South Africa.
The Saint James Church massacre was a massacre perpetrated on St James Church of England in South Africa in Kenilworth, Cape Town, South Africa, on 25 July 1993 by four members of the Azanian People's Liberation Army (APLA). Eleven members of the congregation were killed and 58 wounded. In 1998 the attackers were granted amnesty for their acts by the Truth and Reconciliation Commission.
Salyut 7 cosmonaut Svetlana Savitskaya becomes the first woman to perform a space walk.

Salyut 7 was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including 12 crewed and 15 uncrewed launches in total. Supporting spacecraft included the Soyuz T, Progress, and TKS spacecraft.

An astronaut is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists.

Svetlana Yevgenyevna Savitskaya is a Russian former aviator and Soviet cosmonaut who flew aboard Soyuz T-7 in 1982, becoming the second woman in space. On her 1984 Soyuz T-12 mission she became the first woman to fly to space twice, and the first woman to perform a spacewalk.

Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. Absent a breathable Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environmental support. EVA includes spacewalks and lunar or planetary surface exploration. In a stand-up EVA (SEVA), an astronaut stands through an open hatch but does not fully leave the spacecraft. EVA has been conducted by the Soviet Union/Russia, the United States, Canada, the European Space Agency and China.
Black July: Thirty-seven Tamil political prisoners at the Welikada high security prison in Colombo are massacred by the fellow Sinhalese prisoners.

Black July was an anti-Tamil pogrom that occurred in Sri Lanka during July 1983. The pogrom was premeditated, and was finally triggered by a deadly ambush on 23 July 1983, which caused the death of 13 Sri Lanka Army soldiers, by the Tamil militant group Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). Although initially orchestrated by members of the ruling UNP, the pogrom soon escalated into mass violence with significant public participation.

Sri Lankan Tamils, also known as Ceylon Tamils or Eelam Tamils, are Tamils native to the South Asian island state of Sri Lanka. Today, they constitute a majority in the Northern Province, live in significant numbers in the Eastern Province and are in the minority throughout the rest of the country. 70% of Sri Lankan Tamils in Sri Lanka live in the Northern and Eastern provinces.

Colombo is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo metropolitan area has a population of 5.6 million, and 752,993 in the Municipality. It is the financial centre of the island and a tourist destination. It is located on the west coast of the island and adjacent to the Greater Colombo area which includes Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, the legislative capital of Sri Lanka, and Dehiwala-Mount Lavinia. Colombo is often referred to as the capital since Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is itself within the urban/suburban area of Colombo. It is also the administrative capital of the Western Province and the district capital of Colombo District. Colombo is a busy and vibrant city with a mixture of modern life, colonial buildings and monuments.
The Welikada Prison Massacre took place during the 1983 Black July pogrom against Sri Lankan Tamil minority in Colombo, Sri Lanka. Fifty-three prisoners were killed inside a high-security prison. No one has been convicted of crimes relating to these incidents.

Sinhalese people are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the island of Sri Lanka. They were historically known as Hela people. They constitute about 75% of the Sri Lankan population and number more than 16.2 million. The Sinhalese identity is based on language, cultural heritage and nationality. The Sinhalese people speak Sinhala, an insular Indo-Aryan language, and are predominantly Theravada Buddhists, although a minority of Sinhalese follow branches of Christianity and other religions. Since 1815, they were broadly divided into two respective groups: The 'Up-country Sinhalese' in the central mountainous regions, and the 'Low-country Sinhalese' in the coastal regions; although both groups speak the same language, they are distinguished as they observe different cultural customs.
In accord with the Egypt–Israel peace treaty, Israel begins its withdrawal from the Sinai Peninsula.

The Egypt–Israel peace treaty was signed in Washington, D.C., United States on 26 March 1979, following the 1978 Camp David Accords. The Egypt–Israel treaty was signed by Egyptian president Anwar Sadat and Israeli prime minister Menachem Begin, and witnessed by United States president Jimmy Carter.
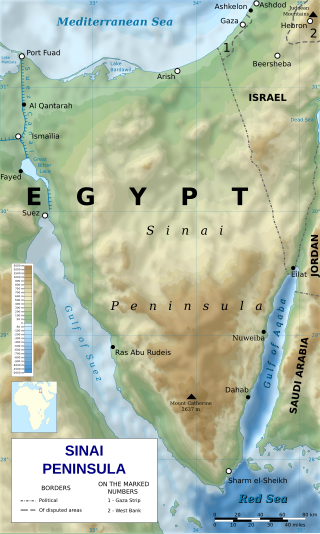
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai, is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north.
Two Puerto Rican independence activists were killed in a police ambush at Cerro Maravilla in Ponce.

Throughout the history of Puerto Rico, its inhabitants have initiated several movements to obtain independence for the island, first from the Spanish Empire from 1493 to 1898 and since then from the United States.
The Cerro Maravilla murders, also known as the Cerro Maravilla massacre, occurred on July 25, 1978, at Cerro Maravilla, a mountain in Ponce, Puerto Rico, wherein two young Puerto Rican pro-independence activists, Carlos Enrique Soto-Arriví (1959–1978) and Arnaldo Darío Rosado-Torres (1953–1978), were murdered in a Puerto Rico Police ambush. The event sparked a series of political controversies where, in the end, the police officers were found guilty of murder and several high-ranking local government officials were accused of planning and/or covering up the incident.

Cerro Maravilla is Puerto Rico's fourth highest peak at 1,205 meters (3,953 ft). It is located on the northern edge Barrio Anón in Ponce, close to the border with the municipality Jayuya, and is part of the Cordillera Central. It is known as El Cerro de los Mártires and characterized as the most infamous peak in Puerto Rico, due to the 1978 Cerro Maravilla murders which took place here.

Ponce is both a city and a municipality on the southern coast of Puerto Rico. The city is the seat of the municipal government.
Puerto Rican police shoot two nationalists in the Cerro Maravilla murders.

Puerto Rico, officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Caribbean island and unincorporated territory of the United States. It is located in the northeast Caribbean Sea, approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Miami, Florida, between the Dominican Republic and the U.S. Virgin Islands, and includes the eponymous main island and several smaller islands, such as Mona, Culebra, and Vieques. It has roughly 3.2 million residents, and its capital and most populous city is San Juan. Spanish and English are the official languages of the executive branch of government, though Spanish predominates.
The Cerro Maravilla murders, also known as the Cerro Maravilla massacre, occurred on July 25, 1978, at Cerro Maravilla, a mountain in Ponce, Puerto Rico, wherein two young Puerto Rican pro-independence activists, Carlos Enrique Soto-Arriví (1959–1978) and Arnaldo Darío Rosado-Torres (1953–1978), were murdered in a Puerto Rico Police ambush. The event sparked a series of political controversies where, in the end, the police officers were found guilty of murder and several high-ranking local government officials were accused of planning and/or covering up the incident.
Birth of Louise Joy Brown, the first human to have been born after conception by in vitro fertilisation, or IVF.
Louise Joy Brown is an English woman who was the first human to have been born after conception by in vitro fertilisation experiment (IVF). Her birth, following a procedure pioneered in Britain, has been lauded among "the most remarkable medical breakthroughs of the 20th Century".
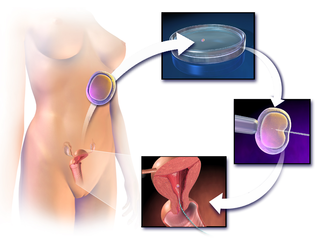
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro. The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova from their ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
The orbiting spacecraft Viking 1 took a photograph of an apparent face on Mars in a classic example of pareidolia.

Viking 1 was the first of two spacecraft, along with Viking 2, each consisting of an orbiter and a lander, sent to Mars as part of NASA's Viking program. The lander touched down on Mars on July 20, 1976, the first successful Mars lander in history. Viking 1 operated on Mars for 2307 days or 2245 Martian solar days, the longest Mars surface mission until the record was broken by the Opportunity rover on May 19, 2010.

Cydonia is a region on the planet Mars that has attracted both scientific and popular interest. The name originally referred to the albedo feature that was visible from earthbound telescopes. The area borders the plains of Acidalia Planitia and the highlands of Arabia Terra. The region includes the named features Cydonia Mensae, an area of flat-topped mesa-like features; Cydonia Colles, a region of small hills or knobs; and Cydonia Labyrinthus, a complex of intersecting valleys. As with other albedo features on Mars, the name Cydonia was drawn from classical antiquity, in this case from Kydonia, a historic polis on the island of Crete. Cydonia contains the "Face on Mars", located about halfway between the craters Arandas and Bamberg.

Pareidolia is the tendency for perception to impose a meaningful interpretation on a nebulous stimulus, usually visual, so that one sees an object, pattern, or meaning where there is none.
Viking program: Viking 1 takes the famous Face on Mars photo.

The Viking program consisted of a pair of identical American space probes, Viking 1 and Viking 2, which landed on Mars in 1976. Each spacecraft was composed of two main parts: an orbiter designed to photograph the surface of Mars from orbit, and a lander designed to study the planet from the surface. The orbiters also served as communication relays for the landers once they touched down.

Viking 1 was the first of two spacecraft, along with Viking 2, each consisting of an orbiter and a lander, sent to Mars as part of NASA's Viking program. The lander touched down on Mars on July 20, 1976, the first successful Mars lander in history. Viking 1 operated on Mars for 2307 days or 2245 Martian solar days, the longest Mars surface mission until the record was broken by the Opportunity rover on May 19, 2010.

Cydonia is a region on the planet Mars that has attracted both scientific and popular interest. The name originally referred to the albedo feature that was visible from earthbound telescopes. The area borders the plains of Acidalia Planitia and the highlands of Arabia Terra. The region includes the named features Cydonia Mensae, an area of flat-topped mesa-like features; Cydonia Colles, a region of small hills or knobs; and Cydonia Labyrinthus, a complex of intersecting valleys. As with other albedo features on Mars, the name Cydonia was drawn from classical antiquity, in this case from Kydonia, a historic polis on the island of Crete. Cydonia contains the "Face on Mars", located about halfway between the craters Arandas and Bamberg.
Soviet Mars 5 space probe is launched.

The Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad, Kiev, Minsk, Tashkent, Alma-Ata, and Novosibirsk. It was the largest country in the world, covering over 22,402,200 square kilometres (8,649,500 sq mi) and spanning eleven time zones.
The Mars program was a series of uncrewed spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1973. The spacecraft were intended to explore Mars, and included flyby probes, landers and orbiters.
The Sohagpur massacre is perpetrated by the Pakistan Army.
The Sohagpur massacre was a mass killing of 187 civilians on 25 July 1971 in the Mymensingh District of East Pakistan during the Liberation War. The massacre was perpetrated by the Pakistan Army and Al-Badr, a paramilitary force opposing Bangladeshi independence. Following the massacre, Sohagpur became known as the "village of widows."
Vietnam War: U.S. President Richard Nixon declares the Nixon Doctrine, stating that the United States now expects its Asian allies to take care of their own military defense. This is the start of the "Vietnamization" of the war.

The Vietnam War was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975.

The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces.

Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was the 36th vice president from 1953 to 1961 under President Dwight D. Eisenhower. His five years in the White House saw reduction of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War, détente with the Soviet Union and China, the first manned Moon landings, and the establishment of the Environmental Protection Agency and Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Nixon's second term ended early, when he became the only president to resign from office, as a result of the Watergate scandal.
The Nixon Doctrine was put forth during a press conference in Guam on July 25, 1969 by President of the United States Richard Nixon and later formalized in his speech on Vietnamization of the Vietnam War on November 3, 1969. According to Gregg Brazinsky, author of "Nation Building in South Korea: Koreans, Americans, and the Making of a Democracy", Nixon stated that "the United States would assist in the defense and developments of allies and friends", but would not "undertake all the defense of the free nations of the world." This doctrine meant that each ally nation was in charge of its own security in general, but the United States would act as a nuclear umbrella when requested. The Doctrine argued for the pursuit of peace through a partnership with American allies.

Vietnamization was a policy of the Richard Nixon administration to end U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War through a program to "expand, equip, and train South Vietnamese forces and assign to them an ever-increasing combat role, at the same time steadily reducing the number of U.S. combat troops". Brought on by the Viet Cong's Tet Offensive, the policy referred to U.S. combat troops specifically in the ground combat role, but did not reject combat by the U.S. Air Force, as well as the support to South Vietnam, consistent with the policies of U.S. foreign military assistance organizations. U.S. citizens' mistrust of their government that had begun after the offensive worsened with the release of news about U.S. soldiers massacring civilians at My Lai (1968), the invasion of Cambodia (1970), and the leaking of the Pentagon Papers (1971).
Bob Dylan, who had previously been known for folk music, gave a controversial performance at the Newport Folk Festival playing songs with an electric guitar.

Bob Dylan is an American singer-songwriter. Often regarded as one of the greatest songwriters of all time, Dylan has been a major figure in popular culture during a career spanning more than 60 years. Much of his most celebrated work dates from the 1960s, when songs such as "Blowin' in the Wind" (1963) and "The Times They Are a-Changin'" (1964) became anthems for the civil rights and antiwar movements. His lyrics during this period incorporated a range of political, social, philosophical, and literary influences, defying pop music conventions and appealing to the burgeoning counterculture.

Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has been defined in several ways: as music transmitted orally, music with unknown composers, music that is played on traditional instruments, music about cultural or national identity, music that changes between generations, music associated with a people's folklore, or music performed by custom over a long period of time. It has been contrasted with commercial and classical styles. The term originated in the 19th century, but folk music extends beyond that.

Newport Folk Festival is an annual American folk-oriented music festival in Newport, Rhode Island, which began in 1959 as a counterpart to the Newport Jazz Festival. It was one of the first modern music festivals in America, and remains a focal point in the expanding genre of folk music. The festival was held annually from 1959 to 1969, except in 1961 and 1962. In 1985, its founder revived it in Newport, where it has been held at Fort Adams State Park ever since.

By 1965, Bob Dylan was the leading songwriter of the American folk music revival. The response to his albums The Freewheelin' Bob Dylan and The Times They Are a-Changin' led the media to label him the "spokesman of a generation".
Bob Dylan goes electric at the Newport Folk Festival, signaling a major change in folk and rock music.

Bob Dylan is an American singer-songwriter. Often regarded as one of the greatest songwriters of all time, Dylan has been a major figure in popular culture during a career spanning more than 60 years. Much of his most celebrated work dates from the 1960s, when songs such as "Blowin' in the Wind" (1963) and "The Times They Are a-Changin'" (1964) became anthems for the civil rights and antiwar movements. His lyrics during this period incorporated a range of political, social, philosophical, and literary influences, defying pop music conventions and appealing to the burgeoning counterculture.

By 1965, Bob Dylan was the leading songwriter of the American folk music revival. The response to his albums The Freewheelin' Bob Dylan and The Times They Are a-Changin' led the media to label him the "spokesman of a generation".

Newport Folk Festival is an annual American folk-oriented music festival in Newport, Rhode Island, which began in 1959 as a counterpart to the Newport Jazz Festival. It was one of the first modern music festivals in America, and remains a focal point in the expanding genre of folk music. The festival was held annually from 1959 to 1969, except in 1961 and 1962. In 1985, its founder revived it in Newport, where it has been held at Fort Adams State Park ever since.
Cold War: In a speech John F. Kennedy emphasizes that any attack on Berlin is an attack on NATO.

The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. Historians do not fully agree on its starting and ending points, but the period is generally considered to span from the announcement of the Truman Doctrine on 12 March 1947 to the dissolution of the Soviet Union on 26 December 1991. The term cold war is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race.

John Fitzgerald Kennedy, often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination near the end of his third year in office. Kennedy was the youngest person to assume the presidency by election. He was also the youngest president at the end of his tenure. Kennedy served at the height of the Cold War, and the majority of his work as president concerned relations with the Soviet Union and Cuba. A Democrat, he represented Massachusetts in both houses of the U.S. Congress prior to his presidency.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implemented the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the perceived threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa. The organization's motto is animus in consulendo liber.
The African Regroupment Party holds its first congress in Cotonou.
The African Regroupment Party was a political party in the French African colonies.

Cotonou is a city in Benin. Its official population count was 761,137 inhabitants in 2006; however, some estimates indicate its population to be as high as 2.4 million.
The Tunisian King Muhammad VIII al-Amin is replaced by President Habib Bourguiba.

Muhammad VIII al-Amin commonly known as Lamine Bey, was the last Bey of Tunis, and also the only King of Tunisia.

Habib Bourguiba was a Tunisian lawyer, nationalist leader and statesman who led the country from 1956 to 1957 as the prime minister of the Kingdom of Tunisia (1956–57) then as the first president of Tunisia (1957–87). Prior to his presidency, he led the nation to independence from France, ending the 75-year-old protectorate and earning the title of "Supreme Combatant".
Forty-five miles south of Nantucket Island, the Italian ocean liner SS Andrea Doria collides with the MS Stockholm in heavy fog and sinks the next day, killing 51.

Nantucket is an island about 30 miles (50 km) south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachusetts. It is the only such consolidated town-county in Massachusetts. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,255, making it the least populated county in Massachusetts. Part of the town is designated the Nantucket CDP, or census-designated place. The region of Surfside on Nantucket is the southernmost settlement in Massachusetts.

An ocean liner is a passenger ship primarily used as a form of transportation across seas or oceans. Ocean liners may also carry cargo or mail, and may sometimes be used for other purposes.

SS Andrea Doria pronounced [anˈdrɛːa ˈdɔːrja], was an ocean liner for the Italian Line home-ported in Genoa, Italy, known for its sinking in 1956, where of the 1,706 passengers and crew, 1,660 were rescued, while 46 passengers and crew died.

MV Astoria is a ship that was constructed as the transatlantic ocean liner MS Stockholm for Swedish American Line, and rebuilt as a cruise ship in 1993. Ordered in 1944, and commenced service in 1948, at 73 years old, she is the oldest passenger liner still sailing in deep water routes. As Stockholm, she was best known for an accidental collision with Andrea Doria in July 1956, resulting in the sinking of the latter ship and 46 fatalities off the coast of Nantucket, Massachusetts, United States.
Australia (captain pictured) set a world record for the highest successful run-chase in Test cricket history during the Fourth Test of the Ashes series against England.

The Australia men's national cricket team represents Australia in men's international cricket. As the joint oldest team in Test cricket history, playing in the first ever Test match in 1877, the team also plays One-Day International (ODI) and Twenty20 International (T20I) cricket, participating in both the first ODI, against England in the 1970–71 season and the first T20I, against New Zealand in the 2004–05 season, winning both games. The team draws its players from teams playing in the Australian domestic competitions – the Sheffield Shield, the Australian domestic limited-overs cricket tournament and the Big Bash League.

Test cricket is a form of first-class cricket played at international level between teams representing full member countries of the International Cricket Council (ICC). A match consists of four innings and is scheduled to last for up to five days. In the past, some Test matches had no time limit and were called Timeless Tests. The term "test match" was originally coined in 1861–62 but in a different context.

The Fourth Test of the 1948 Ashes series was one of five Tests in a cricket series between Australia and England. The match was played at Headingley Cricket Ground at Leeds from 22 to 27 July with a rest day on 25 July. Australia won the match by seven wickets to take an unassailable 3–0 series lead. In successfully chasing a target of 404, they set a new world record for the highest victorious runchase in Test history, a record lasting until 1976.

The 1948 Ashes series was that year's edition of the long-standing cricket rivalry between England and Australia. Starting on 10 June 1948, England and Australia played five Tests. Australia had not lost a Test since the Second World War and were strong favourites. Their captain Don Bradman had publicly expressed his ambition of going through the tour without defeat, and Australia won 10 of their 12 lead-up matches, eight by an innings. The England team, however, had several notable players themselves, including Len Hutton, Denis Compton and Alec Bedser. Nevertheless, the final result was a 4–0 series win for Australia, with the Third Test being drawn. They thus retained The Ashes. The Australians remained undefeated for their entire tour of England, earning them the sobriquet of The Invincibles.
The England cricket team represents England and Wales in international cricket. Since 1997, it has been governed by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), having been previously governed by Marylebone Cricket Club since 1903. England, as a founding nation, is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) with Test, One Day International (ODI) and Twenty20 International (T20I) status. Until the 1990s, Scottish and Irish players also played for England as those countries were not yet ICC members in their own right.
The Crossroads Baker device is the first underwater nuclear weapon test.

Operation Crossroads was a pair of nuclear weapon tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll in mid-1946. They were the first nuclear weapon tests since Trinity in July 1945, and the first detonations of nuclear devices since the atomic bombing of Nagasaki on August 9, 1945. The purpose of the tests was to investigate the effect of nuclear weapons on warships.
World War II: Operation Spring is one of the bloodiest days for the First Canadian Army during the war.

Operation Spring was an offensive operation of the Second World War conducted by II Canadian Corps during the Normandy campaign in 1944. The plan was intended to create pressure on the German forces operating on the British and Canadian front simultaneous with Operation Cobra, an American offensive. Operation Spring was intended to capture Verrières Ridge and the villages on the south slope of the ridge. The German defence of the ridge contained the offensive on the first day and inflicted many casualties on the Canadians.

The First Canadian Army was a field army and a formation of the Canadian Army in World War II in which most Canadian elements serving in North-West Europe were assigned. It served on the Western Front from July 1944 until May 1945.
World War II: Benito Mussolini is forced out of office by the King (encouraged by the Grand Council of Fascism) and is replaced by Pietro Badoglio.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 1943, and "Duce" of Italian Fascism from the establishment of the Italian Fasces of Combat in 1919 until his execution in 1945 by Italian partisans. As dictator of Italy and principal founder of fascism, Mussolini inspired and supported the international spread of fascist movements during the inter-war period.
The fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, also known in Italy as 25 Luglio, came as a result of parallel plots led respectively by Count Dino Grandi and King Victor Emmanuel III during the spring and summer of 1943, culminating with a successful vote of no confidence against the Prime Minister Benito Mussolini at the meeting of the Grand Council of Fascism on 24–25 July 1943. As a result, a new government was established, putting an end to the 21 years of Fascist rule in the Kingdom of Italy, and Mussolini was placed under arrest.

The Grand Council of Fascism was the main body of Mussolini's Fascist government in Italy, that held and applied great power to control the institutions of government. It was created as a body of the National Fascist Party in 1922, and became a state body on 9 December 1928. The council usually met at the Palazzo Venezia, Rome, which was also the seat of the head of the Italian government. The Council became extinct following a series of events in 1943, in which Benito Mussolini was voted out of the Prime Ministry of Italy.

Pietro Badoglio, 1st Duke of Addis Abeba, 1st Marquess of Sabotino, was an Italian general during both World Wars and the first viceroy of Italian East Africa. With the fall of the Fascist regime in Italy, he became Prime Minister of Italy.
The Norwegian Manifesto calls for nonviolent resistance to the German occupation.

The Norwegian resistance to the occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany began after Operation Weserübung in 1940 and ended in 1945. It took several forms:Asserting the legitimacy of the exiled government, and by implication the lack of legitimacy of Vidkun Quisling's pro-Nazi regime and Josef Terboven's military administration The initial defence in Southern Norway, which was largely disorganised, but succeeded in allowing the government to escape capture The more organised military defence and counter-attacks in parts of Western and Northern Norway, aimed at securing strategic positions and the evacuation of the government Armed resistance, in the form of sabotage, commando raids, assassinations and other special operations during the occupation Civil disobedience and unarmed resistance
General Henri Guisan orders the Swiss Army to resist German invasion and makes surrender illegal.

Henri Guisan was a Swiss army officer who held the office of the General of the Swiss Armed Forces during the Second World War. He was the fourth and the most recent man to be appointed to the rarely used Swiss rank of general, and was possibly Switzerland's most famous soldier. He is best remembered for effectively mobilizing the Swiss Armed Forces and Swiss people in order to prepare resistance against a possible invasion by Nazi Germany in 1940. Guisan was voted the fourth-greatest Swiss figure of all time in 2010.
The Swiss Armed Forces operates on land and in the air, serving as the primary armed forces of Switzerland. Under the country's militia system, regular soldiers constitute a small part of the military and the rest are conscripts or volunteers aged 19 to 34. Because of Switzerland's long history of neutrality, the Swiss Armed Forces do not take part in conflicts in other countries, but do participate in international peacekeeping missions. Switzerland is part of the NATO Partnership for Peace programme.
The Nazis assassinate Austrian Chancellor Engelbert Dollfuss in a failed coup attempt.

Nazi Germany was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe.

Engelbert Dollfuss was an Austrian clerical fascist politician who served as Chancellor of Austria between 1932 and 1934. Having served as Minister for Forests and Agriculture, he ascended to Federal Chancellor in 1932 in the midst of a crisis for the conservative government. In early 1933, he dissolved parliament and assumed dictatorial powers. Suppressing the Socialist movement in February 1934 during the Austrian Civil War and later banning the Austrian Nazi Party, he cemented the rule of "Austrofascism" through the authoritarian First of May Constitution. Dollfuss was assassinated as part of a failed coup attempt by Nazi agents in 1934. His successor Kurt Schuschnigg maintained the regime until Adolf Hitler's annexation of Austria in 1938.
Telegraph Agency of the Soviet Union (TASS) is established.

The Russian News Agency TASS, abbreviated TASS (ТАСС), is a major Russian state-owned news agency founded in 1904. TASS is the largest Russian news agency and one of the largest news agencies worldwide.
Sir Robert Borden introduces the first income tax in Canada as a "temporary" measure (lowest bracket is 4% and highest is 25%).

Sir Robert Laird Borden was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Canada from 1911 to 1920. He is best known for his leadership of Canada during World War I.
Income taxes in Canada constitute the majority of the annual revenues of the Government of Canada, and of the governments of the Provinces of Canada. In the fiscal year ending 31 March 2018, the federal government collected just over three times more revenue from personal income taxes than it did from corporate income taxes.
RFC Captain Lanoe Hawker becomes the first British pursuit aviator to earn the Victoria Cross.

The Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was the air arm of the British Army before and during the First World War until it merged with the Royal Naval Air Service on 1 April 1918 to form the Royal Air Force. During the early part of the war, the RFC supported the British Army by artillery co-operation and photographic reconnaissance. This work gradually led RFC pilots into aerial battles with German pilots and later in the war included the strafing of enemy infantry and emplacements, the bombing of German military airfields and later the strategic bombing of German industrial and transport facilities.

Lanoe George Hawker, was a British flying ace of the First World War. Having seven credited victories, he was the third pilot to receive the Victoria Cross, the highest decoration for gallantry awarded to British and Commonwealth servicemen.

Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield permits bombers and attack aircraft to engage in tactical and strategic bombing of enemy targets.

The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously awarded by countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, most of which have established their own honours systems and no longer recommend British honours. It may be awarded to a person of any military rank in any service and to civilians under military command. No civilian has received the award since 1879. Since the first awards were presented by Queen Victoria in 1857, two-thirds of all awards have been personally presented by the British monarch. The investitures are usually held at Buckingham Palace.
Louis Blériot makes the first flight across the English Channel in a heavier-than-air machine from Calais to Dover, England, United Kingdom in 37 minutes.

Louis Charles Joseph Blériot was a French aviator, inventor, and engineer. He developed the first practical headlamp for cars and established a profitable business manufacturing them, using much of the money he made to finance his attempts to build a successful aircraft. Blériot was the first to use the combination of hand-operated joystick and foot-operated rudder control as used to the present day to operate the aircraft control surfaces. Blériot was also the first to make a working, powered, piloted monoplane. In 1909 he became world-famous for making the first airplane flight across the English Channel, winning the prize of £1,000 offered by the Daily Mail newspaper. He was the founder of Blériot Aéronautique, a successful aircraft manufacturing company.

The English Channel is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world.

The Blériot XI is a French aircraft of the pioneer era of aviation. The first example was used by Louis Blériot to make the first flight across the English Channel in a heavier-than-air aircraft, on 25 July 1909. This is one of the most famous accomplishments of the pioneer era of aviation, and not only won Blériot a lasting place in history but also assured the future of his aircraft manufacturing business. The event caused a major reappraisal of the importance of aviation; the English newspaper The Daily Express led its story of the flight with the headline "Britain is no longer an Island".

Calais is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. The population of the city proper is 72,929; that of the urban area is 149,673 (2018). Calais overlooks the Strait of Dover, the narrowest point in the English Channel, which is only 34 km (21 mi) wide here, and is the closest French town to England. The White Cliffs of Dover can easily be seen on a clear day from Calais. Calais is a major port for ferries between France and England, and since 1994, the Channel Tunnel has linked nearby Coquelles to Folkestone by rail.

Dover is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at 33 kilometres (21 mi) from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover.
Ajinomoto is founded. Kikunae Ikeda of the Tokyo Imperial University discovers that a key ingredient in kombu soup stock is monosodium glutamate (MSG), and patents a process for manufacturing it.

Ajinomoto Co., Inc. is a Japanese multinational food and biotechnology corporation which produces seasonings, interlayer insulating materials for semiconductor packages for use in personal computers, cooking oils, frozen foods, beverages, sweeteners, amino acids, and pharmaceuticals. Aji-No-Moto is the trade name for the company's original monosodium glutamate (MSG) product, the first of its kind, since 1909. The corporation's head office is located in Chūō, Tokyo. As of 2021, Ajinomoto operates in 36 countries and employs an estimated 33,651 people. Its yearly revenue in 2021 is around ¥1.1 trillion JPY or $8 billion USD.

Kikunae Ikeda was a Japanese chemist and Tokyo Imperial University professor of chemistry who, in 1908, uncovered the chemical basis of a taste he named umami. It is one of the five basic tastes along with sweet, bitter, sour and salty.

The University of Tokyo , abbreviated as Todai or UTokyo, is a public research university located in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Established in 1877, the university was the first Imperial University and is currently a Top Type university of the Top Global University Project by the Japanese government.

Konbu is edible kelp mostly from the family Laminariaceae and is widely eaten in East Asia. It may also be referred to as dasima or haidai.

Monosodium glutamate (MSG), also known as sodium glutamate, is the sodium salt of glutamic acid. MSG is found naturally in some foods including tomatoes and cheese in this glutamic acid form. MSG is used in cooking as a flavor enhancer with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavor of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups.
Spanish–American War: After more than two months of sea-based bombardment, the United States invaded Puerto Rico.

The Spanish–American War was a period of armed conflict between Spain and the United States. Hostilities began in the aftermath of the internal explosion of USS Maine in Havana Harbor in Cuba, leading to United States intervention in the Cuban War of Independence. The war led to the United States emerging predominant in the Caribbean region, and resulted in U.S. acquisition of Spain's Pacific possessions. It led to United States involvement in the Philippine Revolution and later to the Philippine–American War.

The Puerto Rico campaign was the American military sea and land operation on the island of Puerto Rico during the Spanish–American War. The offensive began on May 12, 1898, when the United States Navy attacked the capital, San Juan. Though the damage inflicted on the city was minimal, the Americans were able to establish a blockade in the city's harbor, San Juan Bay. On June 22, the cruiser Isabel II and the destroyer Terror delivered a Spanish counterattack, but were unable to break the blockade and Terror was damaged.
Spanish–American War: The American invasion of Spanish-held Puerto Rico begins, as United States Army troops under General Nelson A. Miles land and secure the port at Guánica.

The Spanish–American War was a period of armed conflict between Spain and the United States. Hostilities began in the aftermath of the internal explosion of USS Maine in Havana Harbor in Cuba, leading to United States intervention in the Cuban War of Independence. The war led to the United States emerging predominant in the Caribbean region, and resulted in U.S. acquisition of Spain's Pacific possessions. It led to United States involvement in the Philippine Revolution and later to the Philippine–American War.

Puerto Rico, officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Caribbean island and unincorporated territory of the United States. It is located in the northeast Caribbean Sea, approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Miami, Florida, between the Dominican Republic and the U.S. Virgin Islands, and includes the eponymous main island and several smaller islands, such as Mona, Culebra, and Vieques. It has roughly 3.2 million residents, and its capital and most populous city is San Juan. Spanish and English are the official languages of the executive branch of government, though Spanish predominates.

The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution. The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the Continental Army, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army. The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be the origin of that armed force in 1775.

Nelson Appleton Miles was an American military general who served in the American Civil War, the American Indian Wars, and the Spanish–American War.

Guánica is a town and municipality in southern Puerto Rico, bordering the Caribbean Sea, south of Sabana Grande, east of Lajas, and west of Yauco. It is part of the Yauco metropolitan statistical area.
American author Jack London embarks on a sailing trip to take part in the Klondike's gold rush, from which he wrote his first successful stories.

John Griffith Chaney, better known as Jack London, was an American novelist, journalist and activist. A pioneer of commercial fiction and American magazines, he was one of the first American authors to become an international celebrity and earn a large fortune from writing. He was also an innovator in the genre that would later become known as science fiction.

The klondike is a region of the territory of Yukon, in northwestern Canada. It lies around the Klondike River, a small river that enters the Yukon River from the east at Dawson City.

A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Zealand, Brazil, Chile, South Africa, the United States, and Canada while smaller gold rushes took place elsewhere.
The First Sino-Japanese War begins when the Japanese fire upon a Chinese warship.

The First Sino-Japanese War was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895.
The Corinth Canal (pictured), which bisects Greece's narrow Isthmus of Corinth, was formally opened, connecting the Ionian Sea's Gulf of Corinth with the Aegean Sea's Saronic Gulf.

The Corinth Canal is an artificial canal in Greece, that connects the Gulf of Corinth in the Ionian Sea with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea. It cuts through the narrow Isthmus of Corinth and separates the Peloponnese from the Greek mainland, arguably making the peninsula an island. The canal was dug through the Isthmus at sea level and has no locks. It is 6.4 kilometres in length and only 24.6 metres wide at sea level, making it impassable for many modern ships. It is currently of little economic importance and is mainly a tourist attraction.

The Isthmus of Corinth is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The word "isthmus" comes from the Ancient Greek word for "neck" and refers to the narrowness of the land. The Isthmus was known in the ancient world as the landmark separating the Peloponnese from mainland Greece. In the first century AD the geographer Strabo noted a stele on the Isthmus of Corinth, which bore two inscriptions. One towards the East, i.e. towards Megara, reading: "Here is not Peloponnesus, but Ionia" and the one towards the West, i.e. towards the Peloponnese: "Here is Peloponnesus, not Ionia" ; Plutarch ascribed the erection of the stele to the Attic hero Theseus, on his way to Athens.

The Ionian Sea is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania to the north, and the west coast of Greece, including the Peloponnese.

The Gulf of Corinth or the Corinthian Gulf is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea, separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece. It is bounded in the east by the Isthmus of Corinth which includes the shipping-designed Corinth Canal and in the west by the Strait of Rion which widens into the shorter Gulf of Patras and of which the narrowest point is crossed since 2004 by the Rio–Antirrio bridge. The gulf is bordered by the large administrative divisions : Aetolia-Acarnania and Phocis in the north, Boeotia in the northeast, Attica in the east, Corinthia in the southeast and south and Achaea in the southwest. The gulf is in tectonic movement comparable to movement in parts of Iceland and Turkey, growing by 10 mm (0.39 in) per year.
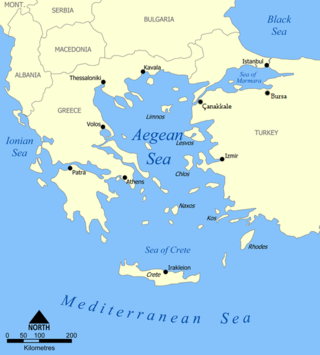
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639m to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea.

The Saronic Gulf or Gulf of Aegina in Greece is formed between the peninsulas of Attica and Argolis and forms part of the Aegean Sea. It defines the eastern side of the isthmus of Corinth, being the eastern terminus of the Corinth Canal, which cuts across the isthmus. The Saronic Islands in the gulf have played a pivotal role in the history of Greece, with the largest, Salamis, naming a significant naval battle in the Greco-Persian wars. The Megara Gulf makes up the northern end of the Saronic Gulf.
The Japanese daimyōs begin returning their land holdings to the emperor as part of the Meiji Restoration reforms. (Traditional Japanese Date: June 17, 1869).
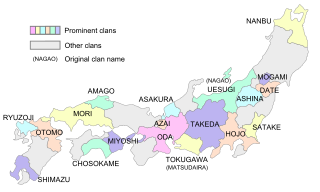
Daimyo were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the emperor and the kuge. In the term, dai (大) means 'large', and myō stands for myōden (名田), meaning 'private land'.

The emperor of Japan is the monarch and the head of the Imperial Family of Japan. Under the Constitution of Japan, he is defined as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, and his position is derived from "the will of the people with whom resides sovereign power". Imperial Household Law governs the line of imperial succession. The emperor is immune from prosecution by the Supreme Court of Japan. He is also the head of the Shinto religion. In Japanese, the emperor is called Tennō , literally "Emperor of heaven or "Heavenly Sovereign". The Japanese Shinto religion holds him to be the direct descendant of the sun goddess Amaterasu. The emperor is also the head of all national Japanese orders, decorations, medals, and awards. In English, the use of the term Mikado (帝/御門) for the emperor was once common but is now considered obsolete.

The Meiji Restoration , referred to at the time as the Honorable Restoration , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ruling emperors before the Meiji Restoration, the events restored practical abilities and consolidated the political system under the Emperor of Japan. The goals of the restored government were expressed by the new emperor in the Charter Oath.

Japanese calendar types have included a range of official and unofficial systems. At present, Japan uses the Gregorian calendar together with year designations stating the year of the reign of the current Emperor. The written form starts with the year, then the month and finally the day, coinciding with the ISO 8601 standard. For example, February 16, 2003 can be written as either 2003年2月16日 or 平成15年2月16日. 年 reads nen and means "year", 月 reads gatsu or 「がつ」and means "month" and finally 日 (usually) reads nichi and means "day".
The Wyoming Territory is established.

The Territory of Wyoming was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 25, 1868, until July 10, 1890, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Wyoming. Cheyenne was the territorial capital. The boundaries of the Wyoming Territory were identical to those of the modern State of Wyoming.
The United States Congress passes legislation authorizing the rank of General of the Army. Lieutenant General Ulysses S. Grant becomes the first to be promoted to this rank.

Military ranks are a system of hierarchical relationships, within armed forces, police, intelligence agencies or other institutions organized along military lines. The military rank system defines dominance, authority, and responsibility in a military hierarchy. It incorporates the principles of exercising power and authority into the military chain of command—the succession of commanders superior to subordinates through which command is exercised. The military chain of command constructs an important component for organized collective action.

General of the Army is a five-star general officer and the second-highest possible rank in the United States Army. It is generally equivalent to the rank of Field Marshal in other countries. In the United States, a General of the Army ranks above generals and is equivalent to a fleet admiral and a general of the Air Force. The General of the Army insignia consisted of five 3⁄8-inch (9.5 mm) stars in a pentagonal pattern, with touching points. The insignia was paired with the gold and enameled United States Coat of Arms on service coat shoulder loops. The silver colored five-star metal insignia alone would be worn for use as a collar insignia of grade and on the garrison cap. Soft shoulder epaulettes with five 7⁄16-inch (11 mm) stars in silver thread and gold-threaded United States Coat of Arms on green cloth were worn with shirts and sweaters.
In the United States Armed Forces, a lieutenant general is a three-star general officer in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force.

Ulysses S. Grant was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Army to victory in the American Civil War in 1865 and thereafter briefly served as Secretary of War. Later, as president, Grant was an effective civil rights executive who signed the bill that created the Justice Department and worked with Radical Republicans to protect African Americans during Reconstruction.
American Civil War: The United States Congress passes the Crittenden–Johnson Resolution, stating that the war is being fought to preserve the Union and not to end slavery, in the wake of the defeat at the First Battle of Bull Run.

The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union and the Confederacy, the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.

The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The vice president of the United States has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members.
The Crittenden–Johnson Resolution was proposed in the United States Congress early in the American Civil War, as a conciliatory message to the slave states assuring them that the Northern war effort was not aimed at interfering with their rights, but solely at restoring the Union. It was passed almost unanimously, with the North in a state of alarm after the shocking defeat at the First Battle of Bull Run, but it was repealed in December 1861 when the emergency subsided.

During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states.

The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during early colonial days, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing.

The First Battle of Bull Run, also known as the Battle of First Manassas, was the first major battle of the American Civil War. The battle was fought on July 21, 1861, in Prince William County, Virginia, just north of the city of Manassas and about thirty miles west-southwest of Washington, D.C. The Union's forces were slow in positioning themselves, allowing Confederate reinforcements time to arrive by rail. Each side had about 18,000 poorly trained and poorly led troops. It was a Confederate victory, followed by a disorganized retreat of the Union forces.
Joaquin Murrieta, the famous Californio bandit known as the "Robin Hood of El Dorado", is killed.

Joaquin Murrieta Carrillo, also called the Robin Hood of the West or the Robin Hood of El Dorado, was a Mexican-American figure of disputed historicity. The novel The Life and Adventures of Joaquín Murieta: The Celebrated California Bandit (1854) by John Rollin Ridge ostensibly recounts his story.

Californio is a term used to designate a Hispanic Californian, especially those descended from Spanish and Mexican settlers of the 17th through 19th centuries. California's Spanish-speaking community has resided there since 1683 and is made up of varying Spanish and Mexican origins, including criollos, Mestizos, Indigenous Californian peoples, and small amounts of Mulatos. Alongside the Tejanos of Texas and Neomexicanos of New Mexico and Colorado, Californios are part of the larger Spanish-American/Mexican-American/Hispano community of the United States, which has inhabited the American Southwest and the West Coast since the 16th century. Some may also identify as Chicanos, a term that came about in the 1960’s.
The first commercial use of an electrical telegraph is successfully demonstrated in London by William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone.

An electrical telegraph was a point-to-point text messaging system, primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging systems called telegraphs, that were devised to communicate text messages more rapidly than by physical transportation. Electrical telegraphy can be considered to be the first example of electrical engineering.

Sir William Fothergill Cooke was an English inventor. He was, with Charles Wheatstone, the co-inventor of the Cooke-Wheatstone electrical telegraph, which was patented in May 1837. Together with John Ricardo he founded the Electric Telegraph Company, the world's first public telegraph company, in 1846. He was knighted in 1869.

Sir Charles Wheatstone FRS FRSE DCL LLD, was an English scientist and inventor of many scientific breakthroughs of the Victorian era, including the English concertina, the stereoscope, and the Playfair cipher. However, Wheatstone is best known for his contributions in the development of the Wheatstone bridge, originally invented by Samuel Hunter Christie, which is used to measure an unknown electrical resistance, and as a major figure in the development of telegraphy.
Costa Rica annexes Guanacaste from Nicaragua.

Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of 51,060 km2 (19,710 sq mi). An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area.

Guanacaste is a province of Costa Rica located in the northwestern region of the country, along the coast of the Pacific Ocean. It is bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Alajuela Province to the east, and Puntarenas Province to the southeast. It is the most sparsely populated of all the provinces of Costa Rica. The province covers an area of 10,141 square kilometres (3,915 sq mi) and as of 2010, had a population of 354,154, with annual revenue of $2 million.

Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the largest country in the Central American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the northwest, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. As of 2015, it was estimated to be the second largest city in Central America. The multi-ethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English.
War of 1812: An American attack on Canada is repulsed.

The War of 1812 was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It began when the United States declared war on 18 June 1812 and, although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by Congress on 17 February 1815.

The Battle of Lundy's Lane, also known as the Battle of Niagara, was a battle fought on 25 July 1814, during the War of 1812, between an invading American army and a British and Canadian army near present-day Niagara Falls, Ontario. It was one of the bloodiest battles of the war, and one of the deadliest battles ever fought in Canada, with over 1,731 casualties including 258 killed.
Napoleon Bonaparte defeats a numerically superior Ottoman army under Mustafa Pasha at the Battle of Abukir.

Napoleon Bonaparte, later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the de facto leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history, but between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars.

Mustafa Pasha was an Ottoman commander, born in Edirne and a paternal Uncle of Muhammad Ali of Egypt, who had fought against Russia and Napoleon's army in Egypt. He lost the Battle of Abukir in 1799.

The Battle of Abukir was a battle in which Napoleon Bonaparte defeated Seid Mustafa Pasha's Ottoman army on 25 July 1799, during the French campaign in Egypt. It is considered the first pitched battle with this name, as there already had been a naval battle on 1 August 1798, the Battle of the Nile. No sooner had the French forces returned from a campaign to Syria, than the Ottoman forces were transported to Egypt by Sidney Smith's British fleet to put an end to French rule in Egypt.
Horatio Nelson loses more than 300 men and his right arm during the failed conquest attempt of Tenerife (Spain).

Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy, and unconventional tactics brought about a number of decisive British naval victories during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest naval commanders in history.

Tenerife is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the archipelago. With a land area of 2,034 square kilometres (785 sq mi) and a population of 978,100 inhabitants as of January 2022, it is also the most populous island of Spain and of Macaronesia.
The Brunswick Manifesto is issued to the population of Paris promising vengeance if the French royal family is harmed.

The Brunswick Manifesto was a proclamation issued by Charles William Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick, commander of the Allied Army, on 25 July 1792 to the population of Paris, France during the War of the First Coalition. The manifesto threatened that if the French royal family were harmed, then French civilians would be harmed. It was said to have been a measure intended to intimidate Paris, but rather helped further spur the increasingly radical French Revolution and finally led to the war between revolutionary France and counter-revolutionary monarchies.
Mozart completed his Symphony No. 40, one of his two extant minor-key symphonies.

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition resulted in more than 800 works of virtually every genre of his time. Many of these compositions are acknowledged as pinnacles of the symphonic, concertante, chamber, operatic, and choral repertoire. Mozart is widely regarded as among the greatest composers in the history of Western music, with his music admired for its "melodic beauty, its formal elegance and its richness of harmony and texture".

Symphony No. 40 in G minor, K. 550 was written by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart in 1788. It is sometimes referred to as the "Great G minor symphony", to distinguish it from the "Little G minor symphony", No. 25. The two are the only extant minor key symphonies Mozart wrote.
In music theory, the key of a piece is the group of pitches, or scale, that forms the basis of a musical composition in classical, Western art, and Western pop music.Tonality or key: Music which uses the notes of a particular scale is said to be "in the key of" that scale or in the tonality of that scale.
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart completes his Symphony No. 40 in G minor (K550).

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition resulted in more than 800 works of virtually every genre of his time. Many of these compositions are acknowledged as pinnacles of the symphonic, concertante, chamber, operatic, and choral repertoire. Mozart is widely regarded as among the greatest composers in the history of Western music, with his music admired for its "melodic beauty, its formal elegance and its richness of harmony and texture".

Symphony No. 40 in G minor, K. 550 was written by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart in 1788. It is sometimes referred to as the "Great G minor symphony", to distinguish it from the "Little G minor symphony", No. 25. The two are the only extant minor key symphonies Mozart wrote.
American Revolutionary War: The war's last action, the Siege of Cuddalore, is ended by a preliminary peace agreement.

The American Revolutionary War, also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, secured American independence from Great Britain. Fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean.

The siege of Cuddalore was a siege attempt by British troops against a combined French and Mysorean garrison at the fortress of Cuddalore in the Second Anglo-Mysore War. The siege ended when news arrived of a preliminary peace treaty between France and Britain.
French and Indian War: In Western New York, British forces capture Fort Niagara from the French, who subsequently abandon Fort Rouillé.

The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the start of the war, the French colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on their native allies.

Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all sources agree WNY includes the cities of Buffalo, Niagara Falls, Jamestown, and the surrounding suburbs, as well as the outlying rural areas of the Great Lakes lowlands and Niagara Frontier, and Chautauqua-Alleghany. Many would also place Rochester and the Genesee Valley in the region while some would also include the western Finger Lakes within the region. Others would describe the latter three areas as being in a separate Finger Lakes region.

Fort Niagara is a fortification originally built by New France to protect its interests in North America, specifically control of access between the Niagara River and Lake Ontario, the easternmost of the Great Lakes. The fort is on the river's eastern bank at its mouth on Lake Ontario. Youngstown, New York, later developed near here.

Fort Rouillé was a French trading post located in what is now Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Fort Rouillé was constructed by the French in 1751, building upon the success of a trading post they established in the area a year earlier, known as Fort Toronto. Fort Rouillé was named for Antoine Louis Rouillé, who at the time of its establishment was Secretary of State for the Navy in the administration of King Louis XV of France. It served as a trading post with the local indigenous peoples from the region.
British governor Charles Lawrence and the Nova Scotia Council order the deportation of the Acadians.

The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, 23 per cent of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered 35.5 million km2 (13.7 million sq mi), 24 per cent of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories.

Brigadier-General Charles Lawrence was a British military officer who, as lieutenant governor and subsequently governor of Nova Scotia, is perhaps best known for overseeing the Expulsion of the Acadians and settling the New England Planters in Nova Scotia. He was born in Plymouth, England, and died in Halifax, Nova Scotia. According to historian Elizabeth Griffiths, Lawrence was seen as a "competent", "efficient" officer with a "service record that had earned him fairly rapid promotion, a person of considerable administrative talent who was trusted by both Cornwallis and Hopson." He is buried in the crypt of St. Paul's Church (Halifax).

Nova Scotia is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".

The Expulsion of the Acadians, also known as the Great Upheaval, the Great Expulsion, the Great Deportation, and the Deportation of the Acadians, was the forced removal, by the British, of the Acadian people from parts of a Canadian-American region historically known as Acadia, between 1755–1764. The area included the present-day Canadian Maritime provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island, and the present-day U.S. state of Maine. The Expulsion, which caused the deaths of thousands of people, occurred during the French and Indian War and was part of the British military campaign against New France.

The Acadians are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the descendants of a few Acadians who escaped the Expulsion of the Acadians re-settled. Most Acadians in Canada continue to live in majority French-speaking communities, notably those in New Brunswick where Acadians and Francophones are granted autonomy in areas such as education and health.
Dummer's War begins along the Maine-Massachusetts border.

Dummer's War (1722–1725) is also known as Father Rale's War, Lovewell's War, Greylock's War, the Three Years War, the Wabanaki-New England War, or the Fourth Anglo-Abenaki War. It was a series of battles between the New England Colonies and the Wabanaki Confederacy, who were allied with New France. The eastern theater of the war was located primarily along the border between New England and Acadia in Maine, as well as in Nova Scotia; the western theater was located in northern Massachusetts and Vermont at the border between Canada and New England. During this time, Maine and Vermont were part of Massachusetts.

Maine is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and northwest, respectively. The largest state by total area in New England, Maine is the 12th-smallest by area, the 9th-least populous, the 13th-least densely populated, and the most rural of the 50 U.S. states. It is also the northeasternmost among the contiguous United States, the northernmost state east of the Great Lakes, the only state whose name consists of a single syllable, and the only state to border exactly one other U.S. state. Approximately half the area of Maine lies on each side of the 45th parallel north in latitude. The most populous city in Maine is Portland, while its capital is Augusta.

Massachusetts, officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders on the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Maine to the east, Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, and New York to the west. The state's capital and most populous city, as well as its cultural and financial center, is Boston. Massachusetts is also home to the urban core of Greater Boston, the largest metropolitan area in New England and a region profoundly influential upon American history, academia, and the research economy, Originally dependent on agriculture, fishing, and trade. Massachusetts was transformed into a manufacturing center during the Industrial Revolution. During the 20th century, Massachusetts's economy shifted from manufacturing to services. Modern Massachusetts is a global leader in biotechnology, engineering, higher education, finance, and maritime trade.
At the behest of Tsar Peter the Great, the construction of the Kadriorg Palace, dedicated to his wife Catherine, begins in Tallinn.

Peter I, most commonly known as Peter the Great, was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from 7 May [O.S. 27 April] 1682 to 1721 and subsequently the Russian Empire until his death in 1725, jointly ruling with his elder half-brother, Ivan V until 1696. He is primarily credited with the modernisation of the country, transforming it into a European power.

Kadriorg Palace is an 18th-century Petrine Baroque palace in Kadriorg, Tallinn, the capital of Estonia. Both the Estonian and the German name for the palace means "Catherine's valley". It was built in 1718–1725 to Nicola Michetti's designs by Gaetano Chiaveri and Mikhail Zemtsov. The palace currently houses the Kadriorg Art Museum, a branch of the Art Museum of Estonia, displaying foreign art from the 16th to 20th centuries. The building of the Kumu branch of the museum, showing Estonian art from the 18th century onwards is located nearby in the Kadriorg Park.

Catherine I was the second wife and empress consort of Peter the Great, and Empress Regnant of Russia from 1725 until her death in 1727.

Tallinn is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 and administratively lies in the Harju maakond (county). Tallinn is the main financial, industrial, and cultural centre of Estonia. It is located 187 km (116 mi) northwest of the country's second largest city Tartu, however only 80 km (50 mi) south of Helsinki, Finland, also 320 km (200 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia, 300 km (190 mi) north of Riga, Latvia, and 380 km (240 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden. From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known in most of the world by variants of its other historical name Reval.
Ignacio de Maya founds the Real Santiago de las Sabinas, now known as Sabinas Hidalgo, Nuevo León, Mexico.

Sabinas Hidalgo is a city and municipality located in the Mexican state of Nuevo León.
A magnitude 8.5 earthquake strikes eastern China, killing over 42,000 people.
The Great Tancheng earthquake, also known as the Shandong earthquake, was a major seismic event that occurred during the rule of the Qing dynasty. The earthquake occurred in Shandong Province on July 25, 1668. The earthquake had an estimated magnitude of Ms 8.5, making it the largest historical earthquake in East China, and one of the largest to occur on land. The earthquake had cataclysmic implications to the region. An estimated 43,000 to 50,000 lives were lost in the earthquake, and its effects were widely felt. The epicenter may have been located between Ju County and Tancheng counties, northeast of the prefecture-level city of Linyi in southern Shandong.
The English ship Sea Venture, en route to Virginia, is deliberately driven ashore during a storm at Bermuda to prevent its sinking; the survivors go on to found a new colony there.

Sea Venture was a seventeenth-century English sailing ship, part of the Third Supply mission to the Jamestown Colony, that was wrecked in Bermuda in 1609. She was the 300 ton purpose-built flagship of the London Company and a highly unusual vessel for her day, given that she was the first single timbered merchantman built in England, and also the first dedicated emigration ship. Sea Venture's wreck is widely thought to have been the inspiration for William Shakespeare's play The Tempest.

The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey Gilbert in 1583 and the colony of Roanoke by Sir Walter Raleigh in the late 1580s.

Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The Bermuda archipelago consists of 181 islands with a total land area of 54 km2 (21 sq mi). The closest land outside the territory is in the US state of North Carolina, approximately 1,035 km (643 mi) to the west-northwest.
James VI and I and Anne of Denmark are crowned in Westminster Abbey.

James VI and I was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until his death in 1625. The kingdoms of Scotland and England were individual sovereign states, with their own parliaments, judiciaries, and laws, though both were ruled by James in personal union.

Anne of Denmark was the wife of King James VI and I; as such, she was Queen of Scotland from their marriage on 20 August 1589 and Queen of England and Ireland from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until her death in 1619.

The coronation of James I and his wife Anne as King and Queen of England was held on 25 July 1603 at Westminster Abbey. James had reigned as King James VI of Scotland since 1567. Anne was anointed and consecrated with prayers alluding to Esther, the Wise Virgins, and other Biblical heroines. It was the first coronation to be conducted in English instead of Latin. A planned ceremonial Royal Entry to London was deferred until 15 March 1604.

Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is a large, mainly Gothic abbey church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United Kingdom's most notable religious buildings and a burial site for English and, later, British monarchs. Since the coronation of William the Conqueror in 1066, all coronations of English and British monarchs have occurred in Westminster Abbey. Sixteen royal weddings have occurred at the abbey since 1100.
Henry IV of France publicly converts from Protestantism to Roman Catholicism.

Henry IV, also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarch of France from the House of Bourbon, a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. He was assassinated in 1610 by François Ravaillac, a Catholic zealot, and was succeeded by his son Louis XIII.

Protestantism is a form of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation: a movement within Western Christianity that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to be errors, abuses, innovations, discrepancies, and theological novums developing within the Catholic Church.

The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2019. As the world's oldest and largest continuously functioning international institution, it has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. The church consists of 24 sui iuris churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state.
The Duke of Parma is defeated near the Dutch city of Nijmegen by an Anglo-Dutch force led by Maurice of Orange.

Alexander Farnese was an Italian noble and condottiero and later a general of the Spanish army, who was Duke of Parma, Piacenza and Castro from 1586 to 1592, as well as Governor of the Spanish Netherlands from 1578 to 1592. Thanks to a steady influx of troops from Spain, during 1581–1587 Farnese captured more than thirty towns in the south and returned them to the control of Catholic Spain. During the French Wars of Religion he relieved Paris for the Catholics. His talents as a field commander, strategist and organizer earned him the regard of his contemporaries and military historians as the first captain of his age.

The siege of Knodsenburg, Relief of Knodzenburg or also known as Battle of the Betuwe was a military action that took place during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War at a sconce known as Knodsenburg in the district of Nijmegen. A siege by a Spanish army under the command of the Duke of Parma took place from 15th to the 25th July 1591. The fort was defended by the Dutch Republic's commander Gerrit de Jong and his company which was then subsequently relieved through the intervention of a Dutch and English army led by Maurice of Orange and Francis Vere respectively on July 25. As a result, the Spanish army was defeated and Parma managed to retreat by getting his army across the River Waal.

Nijmegen is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. It is about 60 km south east of Utrecht and 50 km north east of Eindhoven. Nijmegen is the oldest city in the Netherlands, the second to be recognized as such in Roman times, and in 2005 celebrated 2,000 years of existence.

Maurice of Orange was stadtholder of all the provinces of the Dutch Republic except for Friesland from 1585 at the earliest until his death in 1625. Before he became Prince of Orange upon the death of his eldest half-brother Philip William in 1618, he was known as Maurice of Nassau.
Don Diego de Losada founds the city of Santiago de Leon de Caracas, modern-day Caracas, the capital city of Venezuela.

Caracas, officially Santiago de León de Caracas, abbreviated as CCS, is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas. Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern part of the country, within the Caracas Valley of the Venezuelan coastal mountain range. The valley is close to the Caribbean Sea, separated from the coast by a steep 2,200-meter-high (7,200 ft) mountain range, Cerro El Ávila; to the south there are more hills and mountains. The Metropolitan Region of Caracas has an estimated population of almost 5 million inhabitants.

Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of 916,445 km2 (353,841 sq mi), and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas.
The royal wedding of Mary I and Philip II of Spain celebrated at Winchester Cathedral.

Mary I of England (1516-1558) and Philip II of Spain (1527-1598) married at Winchester Cathedral on Wednesday 25 July 1554.

Mary I, also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 until her death in 1558. She is best known for her vigorous attempt to reverse the English Reformation, which had begun during the reign of her father, Henry VIII. Her attempt to restore to the Church the property confiscated in the previous two reigns was largely thwarted by Parliament, but during her five-year reign, Mary had over 280 religious dissenters burned at the stake in the Marian persecutions.

Philip II, also known as Philip the Prudent, was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He was also jure uxoris King of England and Ireland from his marriage to Queen Mary I in 1554 until her death in 1558. He was also Duke of Milan from 1540. From 1555, he was Lord of the Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands.

The Cathedral Church of the Holy Trinity, Saint Peter, Saint Paul and Saint Swithun, commonly known as Winchester Cathedral, is the cathedral of the city of Winchester, England, and is among the largest of its kind in Northern Europe. The cathedral is the seat of the Bishop of Winchester and is the mother church for the ancient Diocese of Winchester. It is run by a dean and chapter, under the Dean of Winchester.
Henry II of France is crowned.

Henry II was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559. The second son of Francis I and Duchess Claude of Brittany, he became Dauphin of France upon the death of his elder brother Francis in 1536.

A coronation is the act of placement or bestowal of a crown upon a monarch's head. The term also generally refers not only to the physical crowning but to the whole ceremony wherein the act of crowning occurs, along with the presentation of other items of regalia, marking the formal investiture of a monarch with regal power. Aside from the crowning, a coronation ceremony may comprise many other rituals such as the taking of special vows by the monarch, the investing and presentation of regalia to the monarch, and acts of homage by the new ruler's subjects and the performance of other ritual deeds of special significance to the particular nation. Western-style coronations have often included anointing the monarch with holy oil, or chrism as it is often called; the anointing ritual's religious significance follows examples found in the Bible. The monarch's consort may also be crowned, either simultaneously with the monarch or as a separate event.
The city of Guayaquil is founded by the Spanish Conquistador Francisco de Orellana and given the name Muy Noble y Muy Leal Ciudad de Santiago de Guayaquil.

Guayaquil, officially Santiago de Guayaquil, is the second largest city in Ecuador and also the nation's main port. The city is the capital of Guayas Province and the seat of Guayaquil Canton.

Conquistadors or conquistadores were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, Oceania, Africa, and Asia, colonizing and opening trade routes. They brought much of the Americas under the dominion of Spain and Portugal.

Francisco de Orellana Bejarano Pizarro y Torres de Altamirano was a Spanish explorer and conquistador. In one of the most improbably successful voyages in known history, Orellana managed to sail the length of the Amazon, arriving at the river's mouth on 24 August 1542. He and his party sailed along the Atlantic coast until reaching Cubagua Island, near the coast of Venezuela.
Sebastián de Belalcázar on his search of El Dorado founds the city of Santiago de Cali.

Sebastián de Belalcázar was a Spanish conquistador. De Belalcázar, also written as de Benalcázar, is known as the founder of important early colonial cities in the northwestern part of South America; Quito in 1534 and Cali, Pasto and Popayán in 1537. De Belalcázar led expeditions in present-day Ecuador and Colombia and died of natural causes after being sentenced to death in Cartagena, at the Caribbean coast in 1551.

El Dorado, originally El Hombre Dorado or El Rey Dorado, was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (zipa) or king of the Muisca people, an indigenous people of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense of Colombia, who as an initiation rite, covered himself with gold dust and submerged in Lake Guatavita. The legends surrounding El Dorado changed over time, as it went from being a man, to a city, to a kingdom, and then finally to an empire.

Santiago de Cali, or Cali, is the capital of the Valle del Cauca department, and the most populous city in southwest Colombia, with 2,227,642 residents according to the 2018 census. The city spans 560.3 km2 (216.3 sq mi) with 120.9 km2 (46.7 sq mi) of urban area, making Cali the second-largest city in the country by area and the third most populous after Bogotá and Medellín. As the only major Colombian city with access to the Pacific Coast, Cali is the main urban and economic center in the south of the country, and has one of Colombia's fastest-growing economies. The city was founded on 25 July 1536 by the Spanish explorer Sebastián de Belalcázar.
The Battle of Molinella: The first battle in Italy in which firearms are used extensively.

The Battle of Riccardina or Battle of Molinella, fought on July 25, 1467, in Molinella, was one of the most important battles of the 15th century in Italy.
The naval Battle of Algeciras takes place in the context of the Spanish Reconquista resulting in a victory for the Emirate of Granada and the Maranid Dynasty over the Kingdom of Castile.

The Battle of Algeciras was a naval battle which occurred on July 25, 1278. The battle pitted the fleets of the Kingdom of Castile, commanded by the Admiral of Castile, Pedro Martínez de Fe, and the combined fleets of the Marinid dynasty and that of the Emirate of Granada, commanded by Abu Yaqub Yusuf an-Nasr. The battle was fought in the context of the Moorish naval expeditions to the Iberian Peninsula. The battle, which took place in the Strait of Gibraltar, resulted in a Muslim victory.

The Reconquista is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada in 1492, in which the Christian kingdoms expanded through war and conquered al-Andalus; the territories of Iberia ruled by Muslims. The concept of a Reconquista emerged in Western and especially in Spanish historiography in the 19th century, and was a fundamental component of Spanish nationalism.

The Emirate of Granada, also known as the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada, was an Islamic realm in southern Iberia during the Late Middle Ages. It was the last independent Muslim state in Western Europe.

The Kingdom of Castile was a large and powerful state on the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region. It began in the 9th century as the County of Castile, an eastern frontier lordship of the Kingdom of León. During the 10th century, its counts increased their autonomy, but it was not until 1065 that it was separated from León and became a kingdom in its own right. Between 1072 and 1157, it was again united with León, and after 1230, this union became permanent. Throughout this period, the Castilian kings made extensive conquests in southern Iberia at the expense of the Islamic principalities. The Kingdoms of Castile and of León, with their southern acquisitions, came to be known collectively as the Crown of Castile, a term that also came to encompass overseas expansion.
Nicaean–Latin wars: Alexios Strategopoulos led Nicaean forces to recapture Constantinople, leading to the reestablishment of the Byzantine Empire and the end of the Latin Empire.

The Nicaean–Latin wars were a series of wars between the Latin Empire and the Empire of Nicaea, starting with the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. The Latin Empire was aided by other Crusader states established on Byzantine territory after the Fourth Crusade, as well as the Republic of Venice, while the Empire of Nicaea was assisted occasionally by the Second Bulgarian Empire, and sought the aid of Venice's rival, the Republic of Genoa. The conflict also involved the Greek state of Epirus, which also claimed the Byzantine inheritance and opposed Nicaean hegemony. The Nicaean reconquest of Constantinople in 1261 AD and the restoration of the Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty did not end the conflict, as the Byzantines launched on and off efforts to reconquer southern Greece and the Aegean islands until the 15th century, while the Latin powers, led by the Angevin Kingdom of Naples, tried to restore the Latin Empire and launched attacks on the Byzantine Empire.
Alexios Komnenos Strategopoulos was a Byzantine aristocrat and general who rose to the rank of megas domestikos and Caesar. Distantly related to the Komnenian dynasty, he appears in the sources already at an advanced age in the early 1250s, leading armies for the Empire of Nicaea against Epirus. After falling out of favour and being imprisoned by Theodore II Laskaris, Strategopoulos sided with the aristocrats around Michael VIII Palaiologos, and supported him in his rise to the throne after Theodore II's death in 1258. He participated in the Pelagonia campaign in 1259, going on to capture Epirus, but his successes were undone in the next year and he was captured by the Epirotes. Released after a few months, he led the unexpected reconquest of Constantinople from the Latin Empire in July 1261, restoring the Byzantine Empire. He was captured again by the Epirotes in the next year and spent several years in captivity in Italy, before being released. He retired from public affairs and died in the early 1270s.
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek rump states founded by the aristocracy of the Byzantine/Roman Empire that fled after Constantinople was occupied by Western European and Venetian armed forces during the Fourth Crusade, a military event known as the Sack of Constantinople. Like other Byzantine rump states that formed after the 1204 fracturing of the empire, such as the Empire of Trebizond and the Empire of Thessalonica, it was a continuation of the eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived well into the medieval period. A fourth state, known in historiography as the Latin Empire, was established by an army of Crusaders and the Republic of Venice after the capture of Constantinople and the surrounding environs.

Constantinople was the capital of the Roman Empire, and later, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Officially renamed Istanbul in 1930, the city is today the largest city and financial centre of the Republic of Turkey (1923–present). It is also the largest city in Europe.

The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Palaiologos dynasty in the period between 1261 and 1453, from the restoration of Byzantine rule to Constantinople by the usurper Michael VIII Palaiologos following its recapture from the Latin Empire, founded after the Fourth Crusade (1204), up to the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire. Together with the preceding Nicaean Empire and the contemporary Frankokratia, this period is known as the late Byzantine Empire.

The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors.
The city of Constantinople is recaptured by Nicaean forces under the command of Alexios Strategopoulos, re-establishing the Byzantine Empire.

Constantinople was the capital of the Roman Empire, and later, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Officially renamed Istanbul in 1930, the city is today the largest city and financial centre of the Republic of Turkey (1923–present). It is also the largest city in Europe.

The Reconquest of Constantinople (1261) was the recapture of the city of Constantinople by the forces of the Empire of Nicaea, leading to the re-establishment of the Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty, after an interval of 57 years where the city had been the capital of the Latin Empire installed by the Fourth Crusade in 1204.

The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek rump states founded by the aristocracy of the Byzantine/Roman Empire that fled after Constantinople was occupied by Western European and Venetian armed forces during the Fourth Crusade, a military event known as the Sack of Constantinople. Like other Byzantine rump states that formed after the 1204 fracturing of the empire, such as the Empire of Trebizond and the Empire of Thessalonica, it was a continuation of the eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived well into the medieval period. A fourth state, known in historiography as the Latin Empire, was established by an army of Crusaders and the Republic of Venice after the capture of Constantinople and the surrounding environs.
Alexios Komnenos Strategopoulos was a Byzantine aristocrat and general who rose to the rank of megas domestikos and Caesar. Distantly related to the Komnenian dynasty, he appears in the sources already at an advanced age in the early 1250s, leading armies for the Empire of Nicaea against Epirus. After falling out of favour and being imprisoned by Theodore II Laskaris, Strategopoulos sided with the aristocrats around Michael VIII Palaiologos, and supported him in his rise to the throne after Theodore II's death in 1258. He participated in the Pelagonia campaign in 1259, going on to capture Epirus, but his successes were undone in the next year and he was captured by the Epirotes. Released after a few months, he led the unexpected reconquest of Constantinople from the Latin Empire in July 1261, restoring the Byzantine Empire. He was captured again by the Epirotes in the next year and spent several years in captivity in Italy, before being released. He retired from public affairs and died in the early 1270s.

The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians distinguish Byzantium from its earlier incarnation because it was centered on Constantinople, oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by Eastern Orthodox Christianity.
Prince Afonso Henriques led Portuguese troops to victory over the Almoravid Moors at the Battle of Ourique, which soon resulted in Portuguese independence from the Kingdom of León.

Afonso I of Portugal, also called Afonso Henriques, nicknamed the Conqueror by the Portuguese, and El-Bortukali and Ibn-Arrink or Ibn Arrinq by the Moors whom he fought, was the first king of Portugal. He achieved the independence of the County of Portugal, establishing a new kingdom and doubling its area with the Reconquistacode: spa promoted to code: es , an objective that he pursued until his death.

The Almoravid dynasty was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almohads in 1147. The Almoravid capital was Marrakesh, a city founded by the Almoravid leader Abu Bakr ibn Umar circa 1070. The dynasty emerged from a coalition of the Lamtuna, Gudala, and Massufa, nomadic Berber tribes living in what is now Mauritania and the Western Sahara, traversing the territory between the Draa, the Niger, and the Senegal rivers.

The Battle of Ourique was a battle that took place on 25 July 1139, in which the forces of Portuguese count Afonso Henriques defeated those led by the Almoravid governor of Córdoba, Muhammad Az-Zubayr Ibn Umar, identified as "King Ismar" in Christian chronicles.

The Kingdom of León was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in 910 when the Christian princes of Asturias along the northern coast of the peninsula shifted their capital from Oviedo to the city of León. The kings of León fought civil wars, wars against neighbouring kingdoms, and campaigns to repel invasions by both the Moors and the Vikings, all in order to protect their kingdom's changing fortunes.
Battle of Ourique: The Almoravids, led by Ali ibn Yusuf, are defeated by Prince Afonso Henriques who is proclaimed King of Portugal.

The Battle of Ourique was a battle that took place on 25 July 1139, in which the forces of Portuguese count Afonso Henriques defeated those led by the Almoravid governor of Córdoba, Muhammad Az-Zubayr Ibn Umar, identified as "King Ismar" in Christian chronicles.

The Almoravid dynasty was an imperial Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire in the 11th century that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almohads in 1147. The Almoravid capital was Marrakesh, a city founded by the Almoravid leader Abu Bakr ibn Umar circa 1070. The dynasty emerged from a coalition of the Lamtuna, Gudala, and Massufa, nomadic Berber tribes living in what is now Mauritania and the Western Sahara, traversing the territory between the Draa, the Niger, and the Senegal rivers.

Ali ibn Yusuf was the 5th Almoravid emir. He reigned from 1106–1143.

Afonso I of Portugal, also called Afonso Henriques, nicknamed the Conqueror by the Portuguese, and El-Bortukali and Ibn-Arrink or Ibn Arrinq by the Moors whom he fought, was the first king of Portugal. He achieved the independence of the County of Portugal, establishing a new kingdom and doubling its area with the Reconquistacode: spa promoted to code: es , an objective that he pursued until his death.
Eleanor of Aquitaine marries Prince Louis, later King Louis VII of France, at the Cathedral of Saint-André in Bordeaux.

Eleanor was Queen of France from 1137 to 1152 as the wife of King Louis VII, Queen of England from 1154 to 1189 as the wife of King Henry II, and Duchess of Aquitaine in her own right from 1137 until her death in 1204. As the heiress of the House of Poitiers, which controlled much of southwestern France, she was one of the wealthiest and most powerful women in western Europe during the High Middle Ages. She was a patron of poets such as Wace, Benoît de Sainte-Maure, and Bernart de Ventadorn. She was a key leading figure in the unsuccessful Second Crusade.

Louis VII, called the Younger, or the Young, was King of the Franks from 1137 to 1180. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI and married Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine, one of the wealthiest and most powerful women in western Europe. The marriage temporarily extended the Capetian lands to the Pyrenees.

Bordeaux Cathedral, officially known as the Primatial Cathedral of St Andrew of Bordeaux, is a Roman Catholic church dedicated to Saint Andrew and located in Bordeaux, France. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Bordeaux.
The Edict of Pistres of Charles the Bald orders defensive measures against the Vikings.

The Edict of Pîtres was a capitulary promulgated at Pîtres on 25 June 864. It is often cited by historians as an example of successful government action on the part of Charles the Bald, King of West Francia.

Charles the Bald, also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during the reign of his father, Louis the Pious, Charles succeeded, by the Treaty of Verdun (843), in acquiring the western third of the empire. He was a grandson of Charlemagne and the youngest son of Louis the Pious by his second wife, Judith.

Vikings is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia, who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and settled throughout parts of Europe. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean, North Africa, Volga Bulgaria, the Middle East, and North America. In some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a collective whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the early medieval history of Scandinavia, the British Isles, France, Estonia, and Kievan Rus'.
Climax of the Siege of Thessalonica by the Slavs in a three-day assault on the city walls.
The siege of Thessalonica in 676–678 was an attempt by the local Slavic tribes to capture the Byzantine city of Thessalonica, taking advantage of the preoccupation of the Byzantine Empire with the repulsion of the First Arab Siege of Constantinople. The events of the siege are described in the second book of the Miracles of Saint Demetrius.
The Arch of Constantine is completed near the Colosseum in Rome to commemorate Constantine I's victory over Maxentius at the Milvian Bridge.

The Arch of Constantine is a triumphal arch in Rome dedicated to the emperor Constantine the Great. The arch was commissioned by the Roman Senate to commemorate Constantine's victory over Maxentius at the Battle of Milvian Bridge in AD 312. Situated between the Colosseum and the Palatine Hill, the arch spans the Via Triumphalis, the route taken by victorious military leaders when they entered the city in a triumphal procession. Dedicated in 315, it is the largest Roman triumphal arch, with overall dimensions of 21 m (69 ft) high, 25.9 m (85 ft) wide and 7.4 m (24 ft) deep. It has three bays, the central one being 11.5 m (38 ft) high and 6.5 m (21 ft) wide and the laterals 7.4 m (24 ft) by 3.4 m (11 ft) each. The arch is constructed of brick-faced concrete covered in marble.

The Colosseum is an oval amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphitheatre ever built, and is still the largest standing amphitheatre in the world today, despite its age. Construction began under the emperor Vespasian in 72 and was completed in 80 AD under his successor and heir, Titus. Further modifications were made during the reign of Domitian. The three emperors that were patrons of the work are known as the Flavian dynasty, and the amphitheatre was named the Flavian Amphitheatre by later classicists and archaeologists for its association with their family name (Flavius).

Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maxentius was a Roman emperor, who reigned from 306 until his death in 312. Despite ruling in Italy and North Africa, and having the recognition of the Senate in Rome, he was not recognized as a legitimate emperor by his fellow emperors.

The Milvian Bridge is a bridge over the Tiber in northern Rome, Italy. It was an economically and strategically important bridge in the era of the Roman Empire and was the site of the famous Battle of the Milvian Bridge in 312, which led to the imperial rule of Constantine.
Constantine the Great was proclaimed Roman emperor by his troops after the death of Constantius Chlorus.

Constantine I, also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, and the first to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea, he was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, was a Greek Christian of low birth. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces before being recalled in the west to fight alongside his father in Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine became emperor. He was acclaimed by his army at Eboracum, and eventually emerged victorious in the civil wars against emperors Maxentius and Licinius to become the sole ruler of the Roman Empire by 324.

The Roman emperor was the ruler of the Roman Empire during the imperial period. The emperors used a variety of different titles throughout history. Often when a given Roman is described as becoming "emperor" in English it reflects his taking of the title augustus. Another title often used was caesar, used for heirs-apparent, and imperator, originally a military honorific. Early emperors also used the title princeps civitatis. Emperors frequently amassed republican titles, notably princeps senatus, consul, and pontifex maximus.

Flavius Valerius Constantius "Chlorus", also called Constantius I, was Roman emperor from 305 to 306. He was one of the four original members of the Tetrarchy established by Diocletian, first serving as caesar from 293 to 305 and then ruling as augustus until his death. Constantius was also father of Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor of Rome. The nickname Chlorus was first popularized by Byzantine-era historians and not used during the emperor's lifetime. After his re-conquering of Roman Britain, he was given the title 'Redditor Lucis Aeternae', meaning 'The Restorer of Eternal Light'.
Constantine I is proclaimed Roman emperor by his troops.

Constantine I, also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, and the first to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea, he was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, was a Greek Christian of low birth. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces before being recalled in the west to fight alongside his father in Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine became emperor. He was acclaimed by his army at Eboracum, and eventually emerged victorious in the civil wars against emperors Maxentius and Licinius to become the sole ruler of the Roman Empire by 324.

The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western Roman Empire to Germanic kings conventionally marks the end of classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. Because of these events, along with the gradual Hellenization of the Eastern Roman Empire, historians distinguish the medieval Roman Empire that remained in the Eastern provinces as the Byzantine Empire.
Paul Sorvino, American actor (b. 1939) deaths

Paul Anthony Sorvino was an American actor. He often portrayed authority figures on both the criminal and the law enforcement sides of the law.
Peter Green, English blues rock guitarist, singer-songwriter and founder of Fleetwood Mac (b. 1946) deaths

Peter Allen Greenbaum, known professionally as Peter Green, was an English blues rock singer-songwriter and guitarist. As the founder of Fleetwood Mac, he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1998. Green founded Fleetwood Mac in 1967 after a stint in John Mayall's Bluesbreakers and quickly established the new band as a popular live act in addition to a successful recording act, before departing in 1970. Green's songs, such as "Albatross", "Black Magic Woman", "Oh Well", "The Green Manalishi " and "Man of the World", appeared on singles charts, and several have been adapted by a variety of musicians.

Fleetwood Mac are a British-American rock band, formed in London in 1967. Fleetwood Mac were founded by guitarist Peter Green, drummer Mick Fleetwood and guitarist Jeremy Spencer, before bassist John McVie joined the line-up for their eponymous debut album. Danny Kirwan joined as a third guitarist in 1968. Keyboardist and vocalist Christine Perfect, who contributed as a session musician from the second album, married McVie and joined in 1970.
Lou Henson, American college basketball coach (b. 1932) deaths
Louis Ray Henson was an American college basketball coach. He retired as the all-time leader in victories at the University of Illinois with 423 victories and New Mexico State with 289 victories. Overall, Henson won 779 games putting him in sixteenth place on the all-time list. Henson was also one of only four NCAA coaches to have amassed at least 200 total wins at two institutions. On February 17, 2015, Henson was selected as a member of the National Collegiate Basketball Hall of Fame. In August 2015, prior to the reopening of the newly renovated State Farm Center at the University of Illinois, the hardwood floor was dedicated and renamed Lou Henson Court in his honor. The court at the Pan American Center at New Mexico State University is also named in his honor.

In United States colleges, top-tier basketball is governed by collegiate athletic bodies including National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), the National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics (NAIA), the United States Collegiate Athletic Association (USCAA), the National Junior College Athletic Association (NJCAA), and the National Christian College Athletic Association (NCCAA). Each of these various organizations is subdivided into one to three divisions, based on the number and level of scholarships that may be provided to the athletes.
Beji Caid Essebsi, 4th President and 9th Prime Minister of Tunisia (b. 1926) deaths

Beji Caid Essebsi was a Tunisian politician who served as the 6th president of Tunisia from 31 December 2014 until his death on 25 July 2019. Previously, he served as the minister of foreign affairs from 1981 to 1986 and as the prime minister from February 2011 to December 2011.

The president of Tunisia, officially the president of the Tunisian Republic, is the head of state of Tunisia. Tunisia is a presidential republic, whereby the president is the head of state and head of government. Under Article 77 of the Constitution of Tunisia, the president is also the commander-in-chief of the Tunisian Armed Forces. The incumbent president is Kais Saied who has held this position since 23 October 2019 following the death of Beji Caid Essebsi on 25 July 2019. 2022 Tunisian constitutional referendum turned Tunisia into a presidential republic, giving the president sweeping powers while largely limiting the role of the parliament.

The prime minister of Tunisia is the head of the executive branch of the government of Tunisia. The prime minister directs the executive branch along with the president and, together with the prime minister's cabinet, is accountable to the Assembly of the Representatives of the People, to the prime minister's political party and, ultimately, to the electorate for the policies and actions of the executive and the legislature.

Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a part of the Maghreb region of North Africa, bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. It features the archaeological sites of Carthage dating back to the 9th century, as well as the Great Mosque of Kairouan. Known for its ancient architecture, souks and blue coasts, it covers 163,610 km2 (63,170 sq mi), and has a population of 12.1 million. It contains the eastern end of the Atlas Mountains and the northern reaches of the Sahara desert; much of its remaining territory is arable land. Its 1,300 km (810 mi) of coastline include the African conjunction of the western and eastern parts of the Mediterranean Basin. Tunisia is home to Africa's northernmost point, Cape Angela; and its capital and largest city is Tunis, which is located on its northeastern coast, and lends the country its name.
Sergio Marchionne, Italian-Canadian businessman (b. 1952) deaths

Sergio Marchionne was an Italian-Canadian businessman, widely known for his turnarounds of the automakers Fiat and Chrysler, his business acumen and his outspoken and often frank approach, especially when dealing with unpalatable issues related to his companies and the automotive industry.
Michael Johnson, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (b. 1944) deaths

Michael Jay Johnson was an American pop, country, and folk singer-songwriter and guitarist. He is best remembered for his 1978 hit song "Bluer Than Blue". He charted four hits on the Billboard Hot 100 chart and nine more on Hot Country Songs, including two number one country hits in 1986's "Give Me Wings" and "The Moon Is Still Over Her Shoulder". He also co-wrote "Cain's Blood", the debut single of 1990s country group 4 Runner.
Tim LaHaye, American Christian minister and author (b. 1926) deaths

Timothy Francis LaHaye was an American Baptist evangelical Christian minister who wrote more than 85 books, both fiction and non-fiction, including the Left Behind series of apocalyptic fiction, which he co-authored with Jerry B. Jenkins. He was a founder of the Council for National Policy, a right-wing conservative Christian advocacy group. LaHaye was vociferously anti-homosexual, a harsh critic of Roman Catholicism, and a strong believer of the Illuminati global conspiracy theory.
Tom Peterson, American television personality (b. 1930) deaths
Thomas Howard Peterson was an American retailer, pitchman, and television personality from Portland, Oregon. Peterson opened his first store in 1964, which grew to a regional consumer electronics, home appliance, and furniture chain in the 1970s. His memorable television commercials and unusual promotions made him a widely recognized personality in the Portland area by the 1980s, leading to several cameo appearances in the films of Gus Van Sant.
Jacques Andreani, French diplomat, French ambassador to the United States (b. 1929) deaths
Jacques Andreani was French ambassador to Egypt, Italy and the United States.
The French ambassador to the United States is the diplomatic representation of the French Republic to the United States. They reside in Washington, D.C. The current ambassador is Philippe Étienne.
R. S. Gavai, Indian lawyer and politician, 18th Governor of Kerala (b. 1929) deaths

Ramkrishna Suryabhan Gavai, popularly known as Dadasaheb Gavai, was an Indian politician, social activist, senior leader of the Ambedkarite movement, and founder of the Republican Party of India (Gavai). He was the President of Ambedkar's ideological party Republican Party of India, through this party, he did many works in political and social fields. Gavai also worked with Babasaheb Ambedkar, a polymath and the father of the republic of India. He was the Governor of the three states of Bihar, Sikkim and Kerala, as well as he has served in both houses of the Indian Parliament, the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha. Gavai was a 30-year member (MLC) of the Maharashtra Legislative Council during which he served on the posts of the chairman, the deputy chairman, and the Opposition leader of the council.

The governor of Kerala is the constitutional head of state of the southern Indian state of Kerala. The governor is appointed by the president of India for a term of five years and holds office at the president's pleasure. The governor is de jure head of the government of Kerala; all its executive actions are taken in the governor's name. However, the governor must act on the advice of the popularly elected council of ministers, headed by the chief minister of Kerala, who thus holds de facto executive authority in the state. The Constitution of India also empowers the governor to act upon his or her own discretion, such as the ability to appoint or dismiss a ministry, recommend President's rule, or reserve bills for the president's assent. Over the years, the exercise of these discretionary powers have given rise to conflict between the elected chief minister and the central government–appointed governor.
Bob Kauffman, American basketball player and coach (b. 1946) deaths

Robert Kauffman was an American professional basketball player and coach. Kaufmann was a three time NBA All-Star.
Bel Kaufman, German-American author and academic (b. 1911) deaths

Bella Kaufman was an American teacher and author, well known for writing the bestselling 1964 novel Up the Down Staircase.
Richard Larter, Australian painter and illustrator (b. 1929) deaths
Richard Larter was an Australian painter, often identified as one of Australia's few highly recognisable pop artists. Larter also frequently painted in a Pointillist style. He took advantage of unusual techniques with painting: using a syringe filled with paint to create his early works, and juxtaposing multiple images on to a canvas. Many of his works are brightly coloured and draw on popular culture for source materials, reproducing news photographs, film stills, and images from pornography. He was married to Pat Larter, an artist who was involved in the Mail art movement, then performance art and finally painting in a brightly coloured style similar to Richard's. The Larters emigrated to Australia in 1962. Richard Larter's pop art was less ironic than his American and English counterparts. In this Larter is similar to other noted Australian pop artists, such as, Mike Brown and Martin Sharp.
Walter De Maria, American sculptor, illustrator, and composer (b. 1935) deaths

Walter Joseph De Maria was an American artist, sculptor, illustrator and composer, who lived and worked in New York City. Walter de Maria's artistic practice is connected with minimal art, conceptual art, and land art of the 1960s.
William J. Guste, American lawyer and politician (b. 1922) deaths
William Joseph Guste Jr. was an American attorney and politician from the state of Louisiana. He was Attorney General of Louisiana from 1972 to 1992.
Hugh Huxley, English-American biologist and academic (b. 1924) deaths

Hugh Esmor Huxley MBE FRS was a British molecular biologist who made important discoveries in the physiology of muscle. He was a graduate in physics from Christ's College, Cambridge. However, his education was interrupted for five years by the Second World War, during which he served in the Royal Air Force. His contribution to development of radar earned him an MBE.
B. R. Ishara, Indian director and screenwriter (b. 1934) deaths
Babu Ram Ishara was an Indian film director and screenwriter best known for his films of the 1970s. He filmed 35 Bollywood films between 1964 and 1996. He was much popular for his film Chetana, Log Kya Kahengey, Milap, Man Jaiye, Ghar Ki Laaj, Woh Phir Ayegi, Sautela Bhai.doosra roop 1982
Barry Langford, English director and producer (b. 1926) deaths

Barry Langford was a television and music director, producer, and businessman. He directed many television programmes for the BBC in the 1960s and 1970s, and also worked as manager for musical artists including David Bowie and Tom Jones. He was one of the pioneers of cut editing and rapid perspective changes in BBC television programming, and was a major force behind the creation of Israeli television in the 1970s.
Greg Mohns, American-Canadian football player and coach (b. 1950) deaths
Gregory R. Mohns was a football executive and coach who served as the Assistant General Manager and Director of Player Personnel of the Toronto Argonauts until February 19, 2010.
Franz West, Austrian painter and sculptor (b. 1947) deaths

Franz West was an Austrian artist.
Michael Cacoyannis, Cypriot-Greek director, producer, and screenwriter (b. 1922) deaths

Michael Cacoyannis, sometimes credited as Michael Yannis, was a Greek Cypriot theatre and film director, writer, producer, and actor.
Vernon Forrest, American boxer (b. 1971) deaths
Vernon Forrest was an American professional boxer who competed from 1992 to 2008. He held multiple world championships in two weight classes, including the WBC, IBF, Ring magazine and lineal welterweight between 2002 and 2003, and the WBC super welterweight title twice between 2007 and 2009. In 2002, Forrest was named Fighter of the Year by The Ring and the Boxing Writers Association of America.
Stanley Middleton, English author (b. 1919) deaths

Stanley Middleton FRSL was a British novelist.
Harry Patch, English soldier (b. 1898) deaths

Henry John Patch, dubbed in his later years "the Last Fighting Tommy", was an English supercentenarian, briefly the oldest man in Europe, and the last surviving trench combat soldier of the First World War from any country. Patch was not the longest-surviving soldier of the First World War, but he was the fifth-longest-surviving veteran of any sort from the First World War, behind British veterans Claude Choules and Florence Green, Frank Buckles of the United States and John Babcock of Canada. At the time of his death, aged 111 years, 1 month, 1 week and 1 day, Patch was the third-oldest man in the world, behind Walter Breuning and Jiroemon Kimura, the latter of whom would become the oldest verified man ever.
Yasmin Ahmad, Malaysian film director (b. 1958) deaths

Yasmin binti Ahmad was a Malaysian film director, writer and scriptwriter. She was the executive creative director at Leo Burnett Kuala Lumpur. Her television commercials and films are well known in Malaysia for being humorous and touching. Her work crossed cross-cultural barriers, particularly her ads for Petronas, the national oil and gas company. Her works have won multiple awards both within Malaysia and internationally. In Malaysia, her films were highly controversial due to their depiction of events and relationships, which have been considered 'forbidden' by social conservatives, especially hard-line interpretations of Islam. She was a central figure of the "first" New Wave of Malaysian cinema.
Jeff Fehring, Australian footballer (b. 1955) deaths
Jeff Fehring was an Australian rules footballer who played for Geelong and St Kilda in the Victorian Football League from 1977 to 1981.
Tracy Hall, American chemist and academic (b. 1919) deaths
Howard Tracy Hall was an American physical chemist and one of the early pioneers in the research of synthetic diamonds, using a press of his own design.
Randy Pausch, American computer scientist and educator (b. 1960) deaths

Randolph Frederick Pausch was an American educator, a professor of computer science, human–computer interaction, and design at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
Bernd Jakubowski, German footballer and manager (b. 1952) deaths

Bernd Jakubowski was an East German footballer who played as a goalkeeper.
Ezra Fleischer, Romanian-Israeli poet and philologist (b. 1928) deaths

Ezra Fleischer was a Romanian-Israeli Hebrew-language poet and philologist.
Albert Mangelsdorff, German trombonist (b. 1928) deaths

Albert Mangelsdorff was a German jazz trombonist. Working mainly in free jazz, he was an innovator in multiphonics.
John Passmore, Australian philosopher and academic (b. 1914) deaths

John Passmore AC was an Australian philosopher.
Ludwig Bölkow, German engineer (b. 1912) deaths

Ludwig Bölkow was one of the aeronautical pioneers of Germany.
John Schlesinger, English actor, director, producer, and screenwriter (b. 1926) deaths

John Richard Schlesinger was an English film and stage director, and actor. He won the Academy Award for Best Director for Midnight Cowboy, and was nominated for the same award for two other films.
Abdel Rahman Badawi, Egyptian philosopher and poet (b. 1917) deaths
Abdel Rahman Badawi was an Egyptian existentialist philosopher, professor of philosophy and poet. He has been called the "foremost master of Arab existentialism." He authored more than 150 works, amongst them 75 which were encyclopaedic. He wrote easily in his native Arabic, English, Spanish, French, German and Italian, and read Greek, Latin and Persian.
Rudi Faßnacht, German footballer, coach, and manager (b. 1934) deaths
Rudolf "Rudi" Faßnacht was a German football manager.
Evangelos Papastratos, Greek businessman, co-founded Papastratos (b. 1910) deaths
Evangelos Papastratos was a Greek businessman born in the city of Agrinio in Aetolia-Acarnania, Greece.

Papastratos is a Greek tobacco company and is the largest manufacturer and distributor of cigarettes in Greece. The company was formed in 1930 by Evangelos Papastratos with its first factory located in Piraeus. Its second factory opened in 1933 in Berlin but was forced to close in 1936 under pressure from the Nazi regime. In 1937, the company opened its third factory in Cairo, which closed in 1955.
Nat Butcher, Australian rugby league player births

Nathaniel Butcher is an Australian professional rugby league footballer who plays as a lock and second-row forward for the Sydney Roosters in the NRL. He won an NRL premiership with the Roosters in 2019.
Ben Hogan, American golfer (b. 1912) deaths

William Ben Hogan was an American professional golfer who is generally considered to be one of the greatest players in the history of the game. He is notable for his profound influence on golf swing theory and his ball-striking ability.
Maria Sakkari, Greek tennis player births
Maria Sakkari is a Greek professional tennis player. She has been ranked as high as world No. 3 by the Women's Tennis Association (WTA), which she first achieved on 21 March 2022, making her the highest-ranked Greek player in history alongside Stefanos Tsitsipas. Her career-best doubles ranking is world No. 169, achieved on 9 September 2019.
Charlie Rich, American singer-songwriter (b. 1932) deaths

Charles Allan Rich was an American country music singer, songwriter, and musician. His eclectic style of music was often difficult to classify, encompassing the rockabilly, jazz, blues, country, soul, and gospel genres.
Natalija Stevanović, Serbian tennis player births

Natalija Stevanović is a Serbian tennis player.
Sergei Simonov, Russian ice hockey player (d. 2016) births
Sergei Sergeevich Simonov was a Russian professional ice hockey player. He played with HC Lipetsk of the Russian Hockey League.
Alfred Drake, American actor and singer (b. 1914) deaths

Alfred Drake was an American actor and singer.
Hasan Piker, Twitch streamer births

Hasan Doğan Piker, also known as HasanAbi, is a Turkish-American Twitch streamer and left-wing political commentator. He has previously worked as a broadcast journalist and producer at The Young Turks and as a columnist at HuffPost. He is currently one of the most-viewed and most-subscribed-to streamers on Twitch, where he covers news, plays a variety of video games, and discusses politics from a socialist perspective.
Toni Duggan, English footballer births

Toni Duggan is an English footballer who plays as a winger or forward for Everton and the England national team, but is currently on a hiatus/maternity leave, after announcing her pregnancy on 27 September 2022. She has previously played in England for Everton and Manchester City, and in Spain for Barcelona and Atlético Madrid.
Lazar Kaganovich, Soviet politician (b. 1893) deaths

Lazar Moiseyevich Kaganovich, also Kahanovich, was a Soviet politician and administrator, and one of the main associates of Joseph Stalin. He was one of several associates who helped Stalin to seize power, demonstrating exceptional brutality towards those deemed threats to Stalin's regime and facilitating the executions of thousands of people.
Thodoris Karapetsas, Greek footballer births
Thodoris "Theodoros" Karapetsas is a Greek footballer.
Natalia Vieru, Russian basketball player births

Natalia Stanislavovna Vieru is a Russian basketball player. She is a member of the Russia women's national basketball team and competed in the 2012 Summer Olympics. Vieru played last for the Russian club UMMC Ekaterinburg as a center from 2015-2020.
Steve Rubell, American businessman, co-owner of Studio 54 (b. 1943) deaths
Steve Rubell was an American entrepreneur and co-owner of the New York City disco Studio 54.

Studio 54 is a Broadway theater and a former disco nightclub at 254 West 54th Street in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City. Operated by the Roundabout Theatre Company, Studio 54 has 1,006 seats on two levels. The theater was designed by Eugene De Rosa for producer Fortune Gallo and opened in 1927 as the Gallo Opera House. The current Broadway theater is named after a nightclub on the same site, founded by Steve Rubell and Ian Schrager, which operated within the theater's space in the late 1970s and the 1980s.
John Goossens, Dutch footballer births

John Goossens is a Dutch former professional footballer who mainly played as a defensive midfielder, although he was capable of playing in several positions in midfield, and even as a left winger. Since his retirement from football in 2022, he has worked as a financial counsellor for professional footballers.
Tom Hiariej, Dutch footballer births

Tom Jan Hiariej is a Dutch professional footballer who is currently without a club. He is of Moluccan descent.
Stacey Kemp, English skater births

Stacey King is an English former competitive pair skater who represented Great Britain. With her husband David King, she is an eight-time British national champion.
Paulinho, Brazilian footballer births

José Paulo Bezerra Maciel Júnior, known as Paulinho, is a Brazilian professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for Sport Club Corinthians Paulista. He is also a former Brazil international, making 56 caps between 2011 and 2018.
Anthony Stokes, Irish footballer births

Anthony Christopher Stokes is an Irish professional footballer, who plays as a striker. He was also an Irish international, having played at the under-21, team B and Republic of Ireland national football team.
Judith Barsi, American child actress (b. 1978) deaths

Judith Eva Barsi was an American child actress. She began her career in television, making appearances in commercials and television series, as well as the 1987 film Jaws: The Revenge. She also provided the voices of Ducky in The Land Before Time and Anne-Marie in All Dogs Go to Heaven. She and her mother, Maria, were killed in July 1988 in a double murder–suicide committed in their home by her father, József Barsi.
Richard Bachman, American ice hockey player births

Richard Harrison Bachman is an American former professional ice hockey goaltender who is currently the goaltending coach for the Iowa Wild of the American Hockey League (AHL). He played two seasons of college ice hockey at Colorado College before enjoying a career in the National Hockey League with the Dallas Stars, Edmonton Oilers and the Vancouver Canucks. Bachman was born in Salt Lake City, Utah, but grew up in Highlands Ranch, Colorado.
Mitchell Burgzorg, Dutch footballer and rapper births
Mitchell Burgzorg is a Dutch former professional footballer and a rapper under the name Priester.
Fernando, Brazilian footballer births

Fernando Francisco Reges, known simply as Fernando, is a Brazilian professional footballer who plays for Spanish club Sevilla as a defensive midfielder.
Jax Jones, English DJ, singer and songwriter births

Timucin Lam, known professionally as Jax Jones, is an English DJ, songwriter, record producer and remixer. He rose to fame in 2014 by featuring on Duke Dumont's number-one single "I Got U". He followed this up with his own singles "You Don't Know Me" featuring Raye and "Instruction" featuring Demi Lovato and Stefflon Don in 2016 and 2017, respectively. Jax's debut studio album, Snacks (Supersize), was released on 6 September 2019. It was preceded by the single "One Touch" featuring Jess Glynne.
Eran Zahavi, Israeli footballer births

Eran Zahavi is an Israeli professional footballer who plays as a forward for Israeli Premier League club Maccabi Tel Aviv.
Abraham Gneki Guié, Ivorian footballer births

Abraham Guié Guié is an Ivorian former professional footballer who played as a winger or striker.
Hulk, Brazilian footballer births

Givanildo Vieira de Sousa, known as Hulk, is a Brazilian professional footballer who plays as a forward for Atlético Mineiro.
Vincente Minnelli, American director and screenwriter (b. 1903) deaths

Vincente Minnelli was an American stage director and film director. He directed the classic movie musicals Meet Me in St. Louis (1944), An American in Paris (1951), The Band Wagon (1953), and Gigi (1958). An American in Paris and Gigi both won the Academy Award for Best Picture, with Minnelli winning Best Director for Gigi. In addition to having directed some of the best known musicals of his day, Minnelli made many comedies and melodramas. He was married to Judy Garland from 1945 until 1951; the couple were the parents of Liza Minnelli.
James Lafferty, American actor and athlete births

James Martin Lafferty is an American actor, director, and producer. He is best known for his portrayal of Nathan Scott on The WB/CW teen drama television series One Tree Hill (2003–2012).
Nelson Piquet Jr., Brazilian race car driver births

Nelson Angelo Tamsma Piquet Souto Maior, also known as Nelson Piquet Junior or Nelsinho Piquet, is a Brazilian stock car racing driver and former Formula One and Formula E driver where he was champion in the 2014–15 season. He currently competes full-time in the Brazilian Stock Car Pro Series, driving the No. 33 Toyota Corolla E210 for Motul TMG Racing.
Hugo Rodallega, Colombian footballer births

Hugo Rodallega Martínez is a Colombian professional footballer who plays as a forward for Bahia.
Loukas Mavrokefalidis, Greek basketball player births

Loukas Mavrokefalidis is a Greek professional basketball player and the team captain for Ionikos Nikaias of the Greek Basket League. He has also represented the senior Hellenic national team. Born in Jeseník, Czechoslovakia, he is a 2.10 m, 120 kg (265 lbs.) power forward and center. He was selected by the Minnesota Timberwolves in the 2nd round of the 2006 NBA draft.
Bryan Hextall, Canadian ice hockey player (b. 1913) deaths

Bryan Aldwyn Hextall was a Canadian professional ice hockey forward who played for the New York Rangers in the National Hockey League (NHL). Considered one of the top wingers of the 1940s, he led the NHL in goal scoring twice and in points once. Additionally, he was named a first-team All-Star three times, and a second-team All-Star once.
Big Mama Thornton, American singer-songwriter (b. 1926) deaths

Willie Mae Thornton, better known as Big Mama Thornton, was an American singer and songwriter of the blues and R&B genres. She was the first to record Leiber and Stoller's "Hound Dog", in 1952, which became her biggest hit, staying seven weeks at number one on the Billboard R&B chart in 1953 and selling almost two million copies. Thornton's other recordings included the original version of "Ball and Chain", which she wrote.
Nenad Krstić, Serbian basketball player births

Nenad Krstić is a Serbian basketball executive and former professional player. He currently serves as the vice president of the Basketball Federation of Serbia, in charge of the men's basketball.
Brad Renfro, American actor and musician (d. 2008) births

Brad Barron Renfro was an American actor. He made his film debut at the age of 11 with a starring role in The Client (1994). He went on to appear in 21 feature films and won several awards.
Jason Dundas, Australian TV host births

Jason Dundas is an Australian-born television presenter, actor, producer and director, known for his roles as special correspondent for CBS's Entertainment Tonight, the host of The X Factor Australia in 2016, host of America's Best Dance Crew on MTV, VH1's Big Morning Buzz Live, travel series Getaway in Australia, and the founder and director of Dundas Media.
Hal Foster, Canadian-American author and illustrator (b. 1892) deaths

Harold Rudolf Foster, FRSA was a Canadian-American comic strip artist and writer best known as the creator of the comic strip Prince Valiant. His drawing style is noted for its high level of draftsmanship and attention to detail.
Conor Casey, American soccer player births

Conor Patrick Casey is an American former soccer player. He played for 16 seasons, finishing his career with Columbus Crew SC, before turning to coaching with his former club Colorado Rapids.
Constantinos Charalambidis, Cypriot footballer births

Constantinos Charalambidis was a professional Cypriot footballer.
Yūichi Komano, Japanese footballer births
Yuichi Komano is a Japanese professional footballer who plays as a defender for FC Imabari. He played for Japan national team.
Mac Lethal, American rapper and producer births
David McCleary Sheldon, known professionally as Mac Lethal, is an American rapper, songwriter and author from Kansas City, Missouri. He is the founder of Black Clover Records and formerly a radio host on KRBZ 96.5 the Buzz show, Black Clover Radio.
Jani Rita, Finnish ice hockey player births

Jani Markus Rita is a Finnish former professional ice hockey winger who last played with Jokerit of the Russian KHL, for whom he played most of his career.
Rosa A. González, Puerto Rican nurse, author, feminist, and activist (b. 1889) deaths

Rosa A. González, RN, was a nurse, author, feminist and activist. She established various health clinics throughout Puerto Rico and was the founder of The Association of Registered Nurses of Puerto Rico. In 1929, Gonzalez wrote a book titled Los Hechos Desconocidos, in which she denounced the discrimination against women and nurses in Puerto Rico. González’s book convinced James R. Beverley, the Interim Governor of Puerto Rico, to sign Ley 77 in May 1930, which established a Nurses Examining Board. In 1978, she was the first recipient of the Public Health Department of Puerto Rico Garrido Morales Award.
Shawn Riggans, American baseball player births

Shawn Willis Riggans is a former professional baseball catcher for the Tampa Bay Rays, spending parts of four seasons with the club from 2006 through 2009.
Toni Vilander, Finnish race car driver births

Toni Markus Vilander is a Finnish professional racing driver who currently drives for the Risi Competizione Ferrari team in various categories of sports car racing.
David Wachs, American actor and producer births
David Wachs is an American actor and musician. He was born and raised in Palm Desert, California to parents who were both musicians. He has appeared in several TV shows, including ER, Living with Fran, Still Standing, as well as in films such as Hotel California (2008), The Last Hurrah (2009), among others.
Scott Waldrom, New Zealand rugby player births
Scott Waldrom is a New Zealand former rugby union player. When Waldroms playing career finished in 2012 due to injury he was playing for the Waikato Chiefs in Super Rugby and Taranaki in the ITM Cup. He played in the openside flanker position.
Vladimir Vysotsky, Russian singer-songwriter, guitarist, and actor (b. 1938) deaths

Vladimir Semyonovich Vysotsky, was a Soviet singer-songwriter, poet, and actor who had an immense and enduring effect on Soviet culture. He became widely known for his unique singing style and for his lyrics, which featured social and political commentary in often humorous street-jargon. He was also a prominent stage- and screen-actor. Though the official Soviet cultural establishment largely ignored his work, he achieved remarkable fame during his lifetime, and to this day exerts significant influence on many of Russia's popular musicians and actors years after his death.
Ali Carter, English snooker player births

Allister Carter is an English professional snooker player. He has twice been the World Championship runner-up, in 2008 and 2012, losing both finals to Ronnie O'Sullivan. He has won four ranking titles and briefly reached number two in the world rankings in 2010. His nickname, "The Captain", comes from his hobby of piloting aeroplanes.
Tom Lungley, English cricketer and umpire births
Tom Lungley is an English first-class cricketer and umpire. He is a left-handed batsman and a right-arm medium-pace bowler.
Gerard Warren, American football player births

Gerard Thurston Warren is an American former college and professional football player who was a defensive tackle in the National Football League (NFL) for eleven seasons. He played college football for the University of Florida. He was drafted by the Cleveland Browns third overall in the 2001 NFL Draft, and has also played professionally for the Denver Broncos, Oakland Raiders and New England Patriots of the NFL.
Louise Joy Brown, first human to be born via IVF births
Louise Joy Brown is an English woman who was the first human to have been born after conception by in vitro fertilisation experiment (IVF). Her birth, following a procedure pioneered in Britain, has been lauded among "the most remarkable medical breakthroughs of the 20th Century".

In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro. The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova from their ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
Kenny Thomas, American basketball player births

Kenneth Cornelius Thomas is an American retired professional basketball player who played eleven seasons in the National Basketball Association (NBA).
Shivrampant Damle, Indian educationist (b. 1900) deaths
Captain Shivrampant Damle was an Indian educationist. He is best remembered for founding the Maharashtriya Mandal in 1924.
Marcos Assunção, Brazilian footballer births

Marcos dos Santos Assunção is a Brazilian former professional footballer. A central midfielder, he was renowned as a world-class free kick specialist.
Jovica Tasevski-Eternijan, Macedonian poet and critic births
Jovica Tasevski-Eternijan is a Macedonian poet, essayist and literary critic.
Javier Vázquez, Puerto Rican-American baseball player births

Javier Carlos Vázquez is a Puerto Rican former Major League Baseball starting pitcher. He played for the Florida Marlins (2011), Atlanta Braves (2009), Chicago White Sox (2006–2008), Arizona Diamondbacks (2005), New York Yankees, and Montreal Expos (1998–2003).
Jody Craddock, English footballer and coach births

Jody Darryl Craddock is an English former professional footballer and artist who played as a centre back in the Premier League for Sunderland and Wolverhampton Wanderers.
Jean-Claude Darcheville, Guianan-French footballer births
Jean-Claude Jacques Ducan Darcheville is a French Guianese former professional footballer who played as a striker. He played for various clubs in France, England, Scotland, and Greece. He represented French Guiana at the 2012 Caribbean Cup.
El Zorro, Mexican wrestler births

Jesús Cristóbal Martínez Rodriguez is a Mexican luchador who is best known as El Zorro. His gimmick started out very similar to the fictional character Zorro complete with mask, but in recent years it has evolved and the mask has been eliminated. He is best known for his work in the Lucha Libre AAA Worldwide (AAA) promotion in Mexico, where he is a former AAA Mega Champion. He has in the past worked both in Europe, Japan and made a few brief appearances for the World Wrestling Federation show WWF Super Astros. He was the "Deputy leader" of the La Legión Extranjera faction headed by Konnan. In December 2012, Martínez was repackaged as La Parka Negra, the storyline nemesis of La Parka. He returned as El Zorro in October 2013, before departing the company in February 2017.
Brian Gibson, American bass player births

Brian Gibson is a musician, artist, and video game developer based out of Providence, Rhode Island. Gibson is best known as the bassist for the band Lightning Bolt. In the summer of 2015 he co-founded the game development company Drool. At Drool, he created the art and music for the video game Thumper and co-designed the game alongside Marc Flury. Thumper was released with critical acclaim in October 2016. He was previously a lead artist working at video game company Harmonix since 2001, but quit in the summer of 2015.
Evgeni Nabokov, Russian ice hockey player births

Yevgeni Viktorovich Nabokov is a Kazakhstani-Russian former professional ice hockey goaltender who played for the San Jose Sharks, New York Islanders, and Tampa Bay Lightning of National Hockey League (NHL) and for Torpedo Ust-Kamenogorsk, Dynamo Moscow, Metallurg Magnitogorsk and SKA Saint Petersburg of the Russian Super League (RSL) and Kontinental Hockey League (KHL) from 1991 to 2015.
Lauren Faust, American animator, producer, and screenwriter births

Lauren J. Faust is an American animator, writer, voice director, and storyboard artist, best known as the creator of the animated series My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic. Faust has collaborated with her husband Craig McCracken on his four animated series The Powerpuff Girls, Foster's Home for Imaginary Friends, Wander Over Yonder, and Kid Cosmic. Faust developed the 2019 television series DC Super Hero Girls.
Julia Laffranque, Estonian lawyer and judge births

Julia Laffranque, is an Estonian jurist, judge, legal scientist, visiting professor of European law Justice at the Supreme Court of Estonia, Judge at the European Court of Human Rights 2011 - 2020. Since 4 June 2018 also a member of the Scientific Committee of the European Union Fundamental Rights Agency, earlier professor of European law at the University of Tartu. Since 2020 member of the Board of Trustees, the Foundation Academy of European Law Trier. In 2019 she was a candidate for the post of European Ombudsman. In 2020 she was appointed as Director of Programme of the European Law Academy (ERA) and in 2021 the Council of the European Union on the proposal of European Parliament by 586 votes in favor, appointed her as a member of Article 255 TFEU panel, which is to give opinion on candidates suitability to perform the duties of judge and advocate general of the Court of Justice and the General Court of the European Union.
Kenzo Suzuki, Japanese rugby player and wrestler births

Kenzo Suzuki is a Japanese professional wrestler. He is perhaps best known for his appearances with New Japan Pro-Wrestling (NJPW) and in the United States with World Wrestling Entertainment (WWE), where he was a one-time WWE Tag Team Champion in the latter company. He currently performs for All Japan Pro Wrestling (AJPW) under the ring name Kenso, where he is a one-time World Tag Team Champion and a one-time Gaora TV Champion.
Dani Filth, English singer-songwriter births

Daniel Lloyd Davey, known professionally as Dani Filth, is a British singer who is the vocalist, lyricist and founding member of the extreme metal band Cradle of Filth. He has a five-octave vocal range.
Kevin Phillips, English footballer births

Kevin Mark Phillips is an English former professional footballer who is currently manager of NPL Premier Division club South Shields.
Igli Tare, Albanian footballer births

Igli Tare is an Albanian retired professional footballer who played as a forward. He is the sporting director at Serie A club Lazio.
Amy Jacques Garvey, Jamaican-American journalist and activist (b. 1895) deaths

Amy Euphemia Jacques Garvey was a Jamaican-born journalist and activist. She was the second wife of Marcus Garvey. She was one of the pioneering female Black journalists and publishers of the 20th century.
Louis St. Laurent, Canadian lawyer and politician, 12th Prime Minister of Canada (b. 1882) deaths

Louis Stephen St. Laurent was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 12th prime minister of Canada from 1948 to 1957.

The prime minister of Canada is the head of government of Canada. Under the Westminster system, the prime minister governs with the confidence of a majority the elected House of Commons; as such, the prime minister typically sits as a member of Parliament (MP) and leads the largest party or a coalition of parties. As first minister, the prime minister selects ministers to form the Cabinet, and serves as its chair. Constitutionally, the Crown exercises executive power on the advice of the Cabinet, which is collectively responsible to the House of Commons.
David Penna, Australian rugby league player and coach births
David Penna is an Australian rugby league coach and former footballer who played for the Parramatta Eels and the South Sydney Rabbitohs during his long professional career.
Roger Creager, American singer-songwriter births

Roger Creager is an American Texas country music singer and songwriter from Corpus Christi, Texas.
Tracy Murray, American basketball player births
Tracy Lamont Murray is a retired American professional basketball player who currently works as an analyst with the UCLA Sports Network for all of the games during the UCLA Bruins' basketball season. Tracy is also a part-time analyst on the Slam Dunk Show on ABC7 Los Angeles. He worked as an assistant coach for the Los Angeles Lakers of the National Basketball Association (NBA) for the 2015–16 NBA season.
Billy Wagner, American baseball player and coach births

William Edward Wagner, nicknamed "Billy the Kid", is an American former professional baseball pitcher who played 16 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB). He pitched for the Houston Astros (1995–2003), Philadelphia Phillies (2004–2005), New York Mets (2006–2009), Boston Red Sox (2009), and Atlanta Braves (2010). Wagner is one of only six major league relief pitchers to accumulate at least 400 career saves. A left-handed batter and thrower, Wagner stands 5 feet 10 inches (1.78 m) tall and weighs 180 pounds (82 kg).
John Meyers, American swimmer and water polo player (b. 1880) deaths
John Meyers was an American freestyle swimmer and water polo player who competed in the 1904 Summer Olympics in St. Louis, Missouri. In the 1904 Olympics he won a bronze medal as a member of the Missouri Athletic Club water polo team. He also competed in one-mile freestyle, but did not finish the competition.
Leroy Robertson, American composer and educator (b. 1896) deaths
Leroy Robertson was an American composer and music educator.
Jon Barry, American basketball player and sportscaster births

Jon Alan Barry is an American former basketball player and current television analyst for ABC and ESPN.
Annastacia Palaszczuk, Australian politician, 39th Premier of Queensland births

Annastacia Palaszczuk is an Australian politician who has been the 39th premier of Queensland since 2015 and the leader of the Queensland branch of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) since 2012. She was first elected to the Legislative Assembly of Queensland for the district of Inala at the 2006 election.

The premier of Queensland is the head of government in the Australian state of Queensland.
Rudi Bryson, South African cricketer births
Rudi Edwin Bryson is a former South African cricketer who played seven One Day Internationals in 1997. He also played in 96 first-class and 155 List A matches during his career.
Shi Tao, Chinese journalist and poet births
Shi Tao is a Chinese journalist, writer and poet, who in 2005 was sentenced to 10 years in prison for releasing a document of the Communist Party to an overseas Chinese democracy site. Yahoo! China was later discovered to have facilitated his arrest by providing his personal details to the Chinese government. Yahoo! was subsequently rebuked by a panel of the U.S. Congress, settled a lawsuit by Shi's family out of court, and pledged to reform its practices.
Matt LeBlanc, American actor and producer births

Matthew Steven LeBlanc is an American actor. He garnered global recognition with his portrayal of Joey Tribbiani in the NBC sitcom Friends and in its spin-off series, Joey. For his work on Friends, LeBlanc received three nominations at the Primetime Emmy Awards. He has also starred as a fictionalized version of himself in Episodes (2011–2017), for which he won a Golden Globe Award and received four additional Emmy Award nominations. He co-hosted Top Gear from 2016 to 2019. From 2016 to 2020, he played patriarch Adam Burns in the CBS sitcom Man with a Plan.
Ruth Peetoom, Dutch minister and politician births

Gerhardine Ruth Peetoom is a Dutch politician of the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA). She is the Party Chair of the Christian Democratic Appeal since 2 April 2011.
Tommy Skjerven, Norwegian footballer and referee births

Tommy Skjerven is a Norwegian football referee from Kaupanger. He debuted as a referee in 1984, and served as a FIFA referee from 2001 until 2012. He is no longer included on the FIFA list as of 2013, because he reached the international retirement age of 45 in 2012. Skjerven represents Kaupanger IL. Skjerven was the main referee in the cup final between Odd Grenland and Vålerenga in 2002. His day job is working for noreg.no in Hermansverk in Leikanger municipality.
Konstantinos Parthenis, Egyptian-Greek painter (b. 1878) deaths

Konstantinos Parthenis was a distinguished Greek painter, born in Alexandria. Parthenis broke with the Greek academic tradition of the 19th century and introduced modern elements together with traditional themes, like the figure of Christ, in his art.
Daryl Halligan, New Zealand rugby player and sportscaster births

Daryl John Halligan is a rugby league commentator and former professional player. A New Zealand international winger, he was the pre-eminent goal-kicker of his era, retiring as the highest point scorer in Australian premiership history. Halligan played club football in Australia for the North Sydney Bears and Canterbury-Bankstown Bulldogs, winning the 1995 ARL Premiership with the latter.
Maureen Herman, American bass player births

Maureen Herman is an American writer and a musician known as the bassist for the Minneapolis-based band Babes in Toyland from 1992 until 1996 and from 2014 until August 2015.
Diana Johnson, English politician births

Dame Diana Ruth Johnson is a British politician who has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Kingston upon Hull North since the 2005 general election. A member of the Labour Party, she was elected as Chair of the Home Affairs Select Committee on 15 December 2021, replacing Yvette Cooper.
Frank O'Hara, American poet and critic (b. 1926) deaths

Francis Russell "Frank" O'Hara was an American writer, poet, and art critic. A curator at the Museum of Modern Art, O'Hara became prominent in New York City's art world. O'Hara is regarded as a leading figure in the New York School, an informal group of artists, writers, and musicians who drew inspiration from jazz, surrealism, abstract expressionism, action painting, and contemporary avant-garde art movements.
Marty Brown, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births
Dennis Marty Brown is an American country music artist. Active between 1991 and 1996, he has released six studio albums and has charted one single on the Billboard Hot Country Songs charts. Marty Brown and his wife, Shellie, currently reside in Simpson County, Franklin, Kentucky, since July 2004.
Illeana Douglas, American actress, director, producer, and screenwriter births

Illeana Hesselberg, known professionally as Illeana Douglas, is an American actress and filmmaker. She appeared in three episodes of Six Feet Under, for which she received a Primetime Emmy Award nomination as Outstanding Guest Actress in a Drama Series and won the Best Guest Actress in a Drama Series award from OFTA, the Online Film & Television Association, and in the TV series Action opposite Jay Mohr, for which she won a Satellite Award for Best Actress – Television Series Musical or Comedy. As of 2015, she can be seen on Turner Classic Movies where she hosts specials focused on unheralded women directors from film history.
Dale Shearer, Australian rugby league player births
Dale Shearer, also known by the nickname of "Rowdy", is an Australian former professional rugby league footballer who played in the 1980s and 1990s. A Queensland State of Origin and Australian international representative of Aboriginal heritage, he played club football in Queensland, New South Wales and England. His playing career included a NSWRL Premiership win with Manly-Warringah in 1987 and a Rugby League World Cup Final win in 1988. Ten years after his retirement, Shearer was still the all-time top try-scorer in State of Origin and he was named on the wing of the Indigenous Australian team of the century.
Anne Applebaum, American journalist and author births

Anne Elizabeth Applebaum is an American journalist and historian. She has written extensively about the history of Communism and the development of civil society in Central and Eastern Europe.
Tony Granato, American ice hockey player and coach births

Anthony Lewis Granato is an American former professional ice hockey left winger and current head coach of the Wisconsin Badgers men's ice hockey team. He served as head coach of the United States men's national ice hockey team at the 2018 Winter Olympics. Previously, he also served as head coach of the National Hockey League (NHL)'s Colorado Avalanche, as well as with the Detroit Red Wings and Pittsburgh Penguins as an assistant coach.
Breuk Iversen, American designer and journalist births
Breuk Iversen is a designer and writer. Iversen was nicknamed the Mayor of Williamsburg, Brooklyn, one of the liveliest and largest art communities in the world. He is famous for his production, with Jan McLaughlin, at the Dam Stuhltrager Gallery of the "Salon des Refuses": the Offal Project, a site-specific exhibit that explored issues of economy, aesthetics, politics and popular culture through society's by-products.
Denis Coderre, Canadian politician, 44th Mayor of Montreal births

Denis Coderre is a Canadian politician from Quebec. Coderre was the member of Parliament for the riding of Bourassa from 1997 until 2013, and was the Immigration minister from 2002 to 2003 and became the mayor of Montreal in 2013, but lost in 2017 to Valérie Plante. In 2021, he was defeated once again by Valérie Plante after a second mayoral race. He has been an administrator of Eurostar since 2018 and special advisor for the FIA since 2019.

The mayor of Montreal is head of the executive branch of the Montreal City Council. The current mayor is Valérie Plante, who was elected into office on November 5, 2017, and sworn in on November 16. The office of the mayor administers all city services, public property, police and fire protection, most public agencies, and enforces all city and provincial laws within Montreal, Quebec. The mayor is directly elected by citizens, by a plurality of votes, for a four-year term. The mayor's office is located in Montreal City Hall.
Julian Hodgson, Welsh chess player births

Julian Michael "Jules" Hodgson is a British chess player, grandmaster, and former British chess champion.
Ugo Cerletti, Italian neurologist and academic (b. 1877) deaths

Ugo Cerletti was an Italian neurologist who discovered the method of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) used in psychiatry. Electroconvulsive therapy is a therapy in which electric current is used to provoke a seizure for a short duration. This therapy is used in an attempt to treat certain mental disorders, and may be useful when other possible treatments have not, or cannot, cure the person of their mental disorder.
Carin Bakkum, Dutch tennis player births
Carin Bakkum is a Dutch former tennis player. During her career, Bakkum won two ITF singles titles as well as one WTA and 11 ITF doubles titles. She reached a singles ranking high of world number 141 on 27 March 1989 and on 22 June 1987 reached a doubles ranking high of world number 69.
Doug Drabek, American baseball player and coach births

Douglas Dean Drabek is an American former Major League Baseball pitcher and current Pitching Coach for the Reno Aces, the Triple-A affiliate of the Arizona Diamondbacks. He played for the New York Yankees, Pittsburgh Pirates, Houston Astros, Chicago White Sox and Baltimore Orioles between 1986 and 1998. Drabek batted and threw right-handed. Known for his fluid pitching motion and sound mechanics, he won the National League Cy Young Award in 1990.
Thibaudeau Rinfret, Canadian lawyer and jurist, 9th Chief Justice of Canada (b. 1879) deaths

Thibaudeau Rinfret was a Canadian jurist and the ninth Chief Justice of Canada and Administrator of Canada in 1952.

The chief justice of Canada is the presiding judge of the nine-member Supreme Court of Canada, the highest judicial body in Canada. As such, the chief justice is the highest-ranking judge of the Canadian court system. The Supreme Court Act makes the chief justice, a Crown in Council appointment, meaning the Crown acting on the advice of the prime minister and minister of justice. The chief justice serves until they resign, turn 75 years old, die, or are removed from office for cause. By tradition, a new chief justice is chosen from among the court's incumbent puisne justices.
Alain Robidoux, Canadian snooker player births
Alain Robidoux is a Canadian retired professional snooker player. Robidoux played on the sport's main tour from 1987 to 2004 and continues to play in events in Canada.
Justice Howard, American photographer births

Justice Howard is an American photographer whose work includes shooting erotica, pin-up and celebrities. Her work has appeared in over 50 hardcover books and in thousands of magazines including Vogue Paris, Esquire, Easyriders, Playboy, Cosmopolitan, People, In Touch Weekly, Skin Two, and a 25-page spread in Bound by Ink, as well as being displayed in over 60 art gallery exhibits and numerous museum shows. She has also been featured in DankLook's "On Women in Black and White Fine Art Photography." Her photography features themes of female empowerment, freedom, and inner strength. She was previously a model before "graduating to photography" and training under a master German photographer. Her work has been compared to that of Annie Leibovitz and Herb Ritts.
Māris Martinsons, Latvian film director, producer, screenwriter, and editor births
Māris Martinsons is a Latvian film director, producer, screenwriter and film editor. From 1991 he has lived and worked in Lithuania, but moved back to his homeland Latvia in 2010.
Fyodor Cherenkov, Russian footballer and manager (d. 2014) births
Fyodor Fyodorovich Cherenkov was a Soviet and Russian football midfielder who played for Spartak Moscow and Red Star Football Club (1990–91).
Geoffrey Zakarian, American chef and author births

Geoffrey Zakarian is an American chef, restaurateur, television personality and author. He is the executive chef of several restaurants in New York City, Atlantic City and Miami. He is featured on several television programs on the Food Network, including Chopped and The Next Iron Chef on which, in 2011, he won the right to join Iron Chef America.
Yitzhak HaLevi Herzog, Polish-born Irish rabbi and author (b. 1888) deaths

Yitzhak HaLevi Herzog, also known as Isaac Herzog or Hertzog, was the first Chief Rabbi of Ireland, his term lasting from 1921 to 1936. From 1936 until his death in 1959, he was Ashkenazi Chief Rabbi of the British Mandate of Palestine and of Israel after its independence in 1948. He was the father of Chaim Herzog and grandfather of Isaac Herzog, both presidents of Israel.
Alexei Filippenko, American astrophysicist and academic births

Alexei Vladimir "Alex" Filippenko is an American astrophysicist and professor of astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley. Filippenko graduated from Dos Pueblos High School in Goleta, California. He received a Bachelor of Arts in physics from the University of California, Santa Barbara in 1979 and a Ph.D. in astronomy from the California Institute of Technology in 1984, where he was a Hertz Foundation Fellow. He was a postdoctoral Miller Fellow at UC Berkeley and was subsequently appointed to a faculty position at the same institution. He was later named a Miller Research Professor for Spring 1996 and Spring 2005, and he is now a Senior Miller Fellow. His research focuses on supernovae and active galaxies at optical, ultraviolet, and near-infrared wavelengths, as well as on black holes, gamma-ray bursts, and the expansion of the Universe.
Thurston Moore, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and producer births

Thurston Joseph Moore is an American musician best known as a member of Sonic Youth. He has also participated in many solo and group collaborations outside Sonic Youth, as well as running the Ecstatic Peace! record label. Moore was ranked 34th in Rolling Stone's 2004 edition of the "100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time."
Otto Lasanen, Finnish wrestler (b. 1891) deaths

Otto Abraham Lasanen was a featherweight Greco-Roman wrestler from Finland. He won a bronze medal at the 1912 Summer Olympics and placed fourth at the 1914 unofficial European Championships. In 1917 he won a Russian title, as Finland was part of Russia then. Lasanen was a car driver by profession.
Mark Hunter, English politician births

Mark James Hunter is a British Liberal Democrat politician and leader of Stockport Metropolitan Borough Council who became Member of Parliament (MP) for Cheadle at a 2005 by-election. At the 2015 general election, Hunter lost his seat to Mary Robinson of the Conservative Party. Since 19 May 2022, Hunter has served as the leader of Stockport Metropolitan Borough Council.
Steve Podborski, Canadian skier births

Stephen Gregory "Steve" Podborski, is a Canadian former World Cup and Olympic downhill ski racer.
Frances Arnold, American scientist and engineer births

Frances Hamilton Arnold is an American chemical engineer and Nobel Laureate. She is the Linus Pauling Professor of Chemical Engineering, Bioengineering and Biochemistry at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). In 2018, she was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for pioneering the use of directed evolution to engineer enzymes.
Iman, Somalian-English model and actress births

Iman Abdulmajid is a Somali fashion model, supermodel, actress and entrepreneur. A muse of the designers Gianni Versace, Thierry Mugler, Calvin Klein, Donna Karan and Yves Saint Laurent, she is also noted for her philanthropic work. She was married to the rock musician David Bowie from 1992 until his death in 2016.
Randall Bewley, American guitarist and songwriter (d. 2009) births
Randall Eugene Bewley was the guitarist for the Athens, Georgia band Pylon. Born in Bradenton, Florida, United States. He lived in Sarasota, Florida, Washington, DC and near Atlanta, Georgia while growing up. Bewley attended the University of Georgia art school where he met Michael Lachowski, a fellow art student. They became roommates and decided to form a band. He and Lachowski, along with fellow art students Vanessa Briscoe Hay and Curtis Crowe, formed Pylon, having their first performance in 1979. On their first trip to New York City, they were reviewed in Interview Magazine.
Ken Greer, Canadian guitarist, keyboard player, and producer births

Kenneth William Greer is a Canadian guitarist and keyboardist. He is one of the founding members of the Canadian rock band Red Rider.
Sheena McDonald, Scottish journalist births

Sheena Elizabeth McDonald is a Scottish journalist and broadcaster.
Walter Payton, American football player and race car driver (d. 1999) births

Walter Jerry Payton was an American football running back who played in the National Football League (NFL) for 13 seasons with the Chicago Bears. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest football players of all time. A nine-time Pro Bowl selectee, Payton is remembered as a prolific rusher, once holding records for career rushing yards, touchdowns, carries, yards from scrimmage, all-purpose yards, and many other categories. Payton also retired with the most receptions by a non-receiver, and he had eight career touchdown passes.
Jochem Ziegert, German footballer and manager births
Jochem Ziegert is a former German footballer.
Joseph A. Tunzi, Chicago based author, foremost expert on Elvis Presley births
Joseph Anthony Tunzi is a Chicago, Illinois-based author, publisher, and producer. He has been described as "a renowned author from Chicago" and "one of the foremost authorities on Elvis Presley," authoring, self-publishing, and producing over 60 titles about Presley, amongst others, for the past 34 years. Tunzi has also compiled a massive photo archive, from which he licenses photographs of Presley.

Chicago is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and the third-most populous in the United States, after New York City and Los Angeles. With a population of 2,746,388 in the 2020 census, it is also the most populous city in the Midwestern United States. As the seat of Cook County, the city is the center of the Chicago metropolitan area, one of the largest in the world.

Elvis Aaron Presley, or simply Elvis, was an American singer and actor. Dubbed the "King of Rock and Roll", he is regarded as one of the most significant cultural figures of the 20th century. His energized interpretations of songs and sexually provocative performance style, combined with a singularly potent mix of influences across color lines during a transformative era in race relations, led him to both great success and initial controversy.
Robert Zoellick, American banker and politician, 14th United States Deputy Secretary of State births

Robert Bruce Zoellick is an American public official and lawyer who was the eleventh president of the World Bank, a position he held from July 1, 2007 to June 30, 2012. He was previously a managing director of Goldman Sachs, United States Deputy Secretary of State and U.S. Trade Representative, from February 7, 2001 until February 22, 2005. Zoellick has been a senior fellow at Harvard's Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs since ending his term with the World Bank. He is currently a Senior Counselor at Brunswick Group.

The deputy secretary of state of the United States is the principal deputy to the secretary of state. The current deputy secretary of state is Wendy Ruth Sherman, serving since April 2021 under secretary of state Antony Blinken. If the secretary of state resigns or dies, the deputy secretary of state becomes acting secretary of state until the president nominates and the Senate confirms a replacement. The position was created in 1972. Prior to July 13, 1972, the under secretary of state had been the second ranking officer of the Department of State. The position is currently held by Wendy Sherman.
Eduardo Souto de Moura, Portuguese architect, designed the Estádio Municipal de Braga births

Eduardo Elísio Machado Souto de Moura, better known as Eduardo Souto de Moura, is a Portuguese architect who was the recipient of the Pritzker Architecture Prize in 2011 and the Wolf Prize in Arts in 2013. Along with Fernando Távora and Álvaro Siza, he is one of the alumni of the Porto School of Architecture, where he was appointed a Professor.

The Municipal Stadium of Braga is an all-seater football stadium located in Braga, Portugal, and the current home of Sporting Clube de Braga. It has a capacity of 30,286 spectators, making it the seventh largest football stadium in Portugal. The stadium was designed by Portuguese architect Eduardo Souto de Moura who was awarded the Pritzker Architecture Prize in part for this design.
Herbert Murrill, English organist and composer (b. 1909) deaths
Herbert Henry John Murrill was an English musician, composer, and organist.
Jack Thompson, American lawyer and activist births

John Bruce Thompson is an American activist and disbarred attorney. As an attorney, Thompson focused his legal efforts against what he perceives as obscenity in modern culture. Thompson gained recognition as an anti-video game activist, criticizing the content of video games and their alleged effects on children. He also targeted rap music and radio personality Howard Stern.
Verdine White, American bass player and producer births

Verdine Adams White is an American musician, best known as a founding member and bassist for the band Earth, Wind & Fire. White was placed at No. 19 on Rolling Stone's list of The 50 Greatest Bassists of All Time.
Mark Clarke, English singer-songwriter and bass player births

Mark Clarke is an English musician, bass player and singer, best known for his work with Colosseum and Mountain, as well as brief stints with Uriah Heep and Rainbow.
Steve Goodman, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 1984) births

Steven Benjamin Goodman was an American folk and country singer-songwriter from Chicago. He wrote the song "City of New Orleans," which was recorded by Arlo Guthrie and many others including John Denver, The Highwaymen, and Judy Collins; in 1985, it received a Grammy award for best country song, as performed by Willie Nelson. Goodman had a small but dedicated group of fans for his albums and concerts during his lifetime. His most frequently sung song is the Chicago Cubs anthem, "Go Cubs Go". Goodman died of leukemia in September 1984.
José Areas, Nicaraguan drummer births

José Octavio "Chepito" Areas Dávila is a Nicaraguan percussionist best known for having played timbales and Conga drums in the Latin rock group Santana in 1969–1977 and 1987–1989. In 1998, he was inducted into the Rock & Roll Hall of Fame for his work in Santana. In 1997, he performed on Abraxas Pool with other members of the early 1970s iteration of Santana, including Gregg Rolie, Neal Schon, Michael Carabello and Michael Shrieve. Previously, he released an eponymous solo album on Columbia/CBS Records in 1974. La Gigantona, a 1976 collaboration with Nicaraguan singer-songwriter and childhood friend Alfonso Noel Lovo, was reissued by Numero Group in 2012. He was featured along with Richard Bean and Rich Aldana in 2003 CD The Sounds of Santana by "The Tellstars", and he played alongside Michael Shrieve and Rich Aldana in the 2007 CD "Cha Cha Time" by "The Tellstars". Jose Chepito Areas, was the featured artist on, Ray Cepeda’ “The Neo Maya Experience”, 2000, “Solo”, 2012, “Angels over Avalon & Aztlan 2008, Areas of Santaana, 2018, “Areas 51: Return of the Alien” 2019, Ray Cepeda, released on World Rock Records.
Nicole Farhi, French fashion designer and sculptor births
Nicole Farhi, Lady Hare, CBE is a former French fashion designer, now sculptor born in Nice, France.
John Gibson, American radio host births
John David Gibson is an American radio talk show host. As of September 2008, he hosts the syndicated radio program The John Gibson Show. Gibson was formerly the co-host of the weekday edition of The Big Story on the Fox News TV channel.
Rita Marley, Cuban-Jamaican singer births

Alferita Constantia Marley is a Cuban-born Jamaican singer and the widow of Bob Marley. She was a member of the vocal group the I Threes, along with Marcia Griffiths and Judy Mowatt, who gained recognition as the backing vocalists for Bob Marley and the Wailers.
P. Selvarasa, Sri Lankan politician births
Ponnambalam Selvarasa is a Sri Lankan Tamil politician and former Member of Parliament.
Ljupka Dimitrovska, Macedonian-Croatian pop singer (d. 2016) births
Ljupka Dimitrovska was a Macedonian-born Croatian singer. Internationally, she was best known for "Adio", written by Nikica Kalogjera and Ivica Krajač, which won the first prize at the 1970 Athens pop song festival. She died in Zagreb, aged 70.
Sally Beauman, English journalist and author (d. 2016) births
Sally Vanessa Beauman was an English journalist and writer, author of eight widely translated and best-selling novels.
Jim McCarty, English singer and drummer births

James Stanley McCarty is an English musician, best known as the drummer for the Yardbirds and Renaissance. Following Chris Dreja's departure from the Yardbirds in 2013, McCarty became the only member of the band to feature in every line up. He was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1992 as a member of the Yardbirds.
Erika Steinbach, Polish-German politician births

Erika Steinbach is a German right-wing politician. She previously served as a member of the Bundestag from 1990 until 2017.
Bruce Woodley, Australian singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Bruce William Woodley is an Australian singer-songwriter and musician. He was a founding member of the successful folk-pop group The Seekers, and co-composer of the songs "I Am Australian," "Red Rubber Ball," and Simon & Garfunkel's "Cloudy."
Fred Englehardt, American triple jumper (b. 1879) deaths

Frederick William Englehardt was an American athlete who competed mainly in the long jump and triple jump. He competed for the United States in the 1904 Summer Olympics held in St Louis, United States in the triple jump where he won the silver medal. He was also 4th in the long jump.
Manny Charlton, Spanish-born Scottish rock musician and songwriter (d. 2022) births

Manuel Charlton was a Scottish musician, who was known as a founding member of the influential Scottish hard rock band Nazareth and was their lead guitarist from 1968 to 1990. He also produced a string of successful Nazareth albums in the 1970's, including the seminal album "Hair of the Dog" (1975).
Nate Thurmond, American basketball player (d. 2016) births

Nathaniel Thurmond was an American basketball player who spent the majority of his 14-year career in the National Basketball Association (NBA) with the Golden State Warriors franchise. He played the center and power forward positions. Thurmond was a seven-time All-Star and the first player in NBA history to record an official quadruple-double. In 1965, he grabbed 42 rebounds in a game; only Wilt Chamberlain and Bill Russell recorded more rebounds in an NBA game. Thurmond was named a member of the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame in 1985, one of the 50 Greatest Players in NBA History, and part of the NBA 75th Anniversary Team in 2021.
Emmett Till, American lynching victim (d. 1955) births

Emmett Louis Till was a 14-year-old African American boy who was abducted, tortured, and lynched in Mississippi in 1955, after being accused of offending a white woman, Carolyn Bryant, in her family's grocery store. The brutality of his murder and the fact that his killers were acquitted drew attention to the long history of violent persecution of African Americans in the United States. Till posthumously became an icon of the civil rights movement.
Richard Ballantine, American-English journalist and author (d. 2013) births
Richard Ballantine was a cycling writer, journalist and cycling advocate. Born in America, the son of Ian and Betty Ballantine of Ballantine Books, and educated at the Browning School in New York and Columbia University, he principally resided in London, England. He is most famous for his 1972 Richard's Bicycle Book and its subsequent editions. He was also an editor at Rufus Publications and founded several magazines including Bicycle magazine.
S. Ramadoss, Indian politician births
S. Ramadoss is an Indian politician. He is the founder of the Pattali Makkal Katchi, an Indian political party.
Colin Renfrew, Baron Renfrew of Kaimsthorn, English archaeologist and academic births

Andrew Colin Renfrew, Baron Renfrew of Kaimsthorn, is a British archaeologist, paleolinguist and Conservative peer noted for his work on radiocarbon dating, the prehistory of languages, archaeogenetics, neuroarchaeology, and the prevention of looting at archaeological sites.
Gerry Ashmore, English race car driver (d. 2021) births
Gerald Ashmore was a British motor racing driver from England. He participated in four Formula One World Championship Grands Prix, scoring no championship points.
Glenn Murcutt, English-Australian architect and academic births

Glenn Marcus Murcutt AO is an Australian architect and winner of the 1992 Alvar Aalto Medal, the 2002 Pritzker Architecture Prize, the 2009 American Institute of Architects Gold Medal and the 2021 Praemium Imperiale. Glenn Murcutt works as a sole practitioner without staff, builds only within Australia and is known to be very selective with his projects. Being the only Australian winner of the prestigious Pritzker Prize, he is often referred to as Australia's most famous architect.
Barbara Harris, American actress and singer (d. 2018) births

Barbara Densmoor Harris was an American actress. She appeared in such movies as A Thousand Clowns, Plaza Suite, Nashville, Family Plot, Freaky Friday, Peggy Sue Got Married, and Grosse Pointe Blank. Harris won a Tony Award and was nominated for an Academy Award. She also received four Golden Globe Award nominations.
Adnan Khashoggi, Saudi Arabian businessman (d. 2017) births

Adnan Khashoggi was a Saudi businessman and arms dealer known for his lavish business deals and lifestyle. He was estimated to have had a peak net worth of around US$4 billion in the early 1980s.
Gilbert Parent, Canadian educator and politician, 33rd Speaker of the House of Commons of Canada (d. 2009) births

Gilbert "Gib" Parent was a Canadian member of Parliament. He is best known in his role as speaker of the House of Commons of Canada between 1994 and 2001.

The speaker of the House of Commons is the presiding officer of the lower house of the Parliament of Canada. A member of Parliament (MP), they are elected at the beginning of each new parliament by fellow MPs. The speaker's role in presiding over Canada's House of Commons is similar to that of speakers elsewhere in other countries that use the Westminster system.
John Robinson, American football player and coach births
John Alexander Robinson is a former American football player and coach best known for his two stints as head coach of the University of Southern California (USC) football team and for his tenure as head coach of the NFL's Los Angeles Rams (1983–1991). Robinson's USC teams won four Rose Bowls and captured a share of the national championship in the 1978 season. Robinson is one of the few college football head coaches to have non-consecutive tenure at the same school. In 2009, he was elected to the College Football Hall of Fame.
Larry Sherry, American baseball player and coach (d. 2006) births

Lawrence Sherry was an American professional baseball player and coach. He played in Major League Baseball as a right-handed relief pitcher from 1958 to 1968, most prominently as a member of the Los Angeles Dodgers and Detroit Tigers. He was named the Most Valuable Player of the 1959 World Series as the Dodgers won their first championship since relocating from Brooklyn just two years earlier. After his playing career, Sherry managed in the minor leagues before serving as a major league coach for the Pittsburgh Pirates and the California Angels.
Lars Werner, Swedish lawyer and politician (d. 2013) births

Lars Helge Werner was a Swedish socialist politician.
Don Ellis, American trumpet player and composer (d. 1978) births

Donald Johnson Ellis was an American jazz trumpeter, drummer, composer, and bandleader. He is best known for his extensive musical experimentation, particularly in the area of time signatures. Later in his life he worked as a film composer, contributing a score to 1971's The French Connection and 1973's The Seven-Ups.
Claude Zidi, French director and screenwriter births
Claude Zidi is a French film director and screenwriter noted for his mainstream burlesque comedies. Born in Paris, he started as a cameraman and then a cinematographer, and he made his directorial and screenwriting debut in 1971. He won the César Award for Best Director for My New Partner, for which he was also nominated for Best Writing.
François Coty, French businessman, founded Coty, Inc. (b. 1874) deaths

François Coty was a French perfumer, businessman, newspaper publisher, politician and patron of the arts. He was the founder of the Coty perfume company, today a multinational. He is considered the founding father of the modern perfume industry.

Coty Inc. is an American-French multinational beauty company founded in 1904 by François Coty. With its subsidiaries, it develops, manufactures, markets, and distributes fragrances, cosmetics, skin care, nail care, and both professional and retail hair care products. Coty owns around 77 brands as of 2018.
Engelbert Dollfuss, Austrian politician, 14th Chancellor of Austria (b. 1892) deaths

Engelbert Dollfuss was an Austrian clerical fascist politician who served as Chancellor of Austria between 1932 and 1934. Having served as Minister for Forests and Agriculture, he ascended to Federal Chancellor in 1932 in the midst of a crisis for the conservative government. In early 1933, he dissolved parliament and assumed dictatorial powers. Suppressing the Socialist movement in February 1934 during the Austrian Civil War and later banning the Austrian Nazi Party, he cemented the rule of "Austrofascism" through the authoritarian First of May Constitution. Dollfuss was assassinated as part of a failed coup attempt by Nazi agents in 1934. His successor Kurt Schuschnigg maintained the regime until Adolf Hitler's annexation of Austria in 1938.

The chancellor of the Republic of Austria is the head of government of the Republic of Austria. The position corresponds to that of Prime Minister in several other parliamentary democracies.
Nestor Makhno, Ukrainian anarchist revolutionary (b. 1888) deaths

Nestor Ivanovych Makhno, also known as Bat'ko Makhno, was a Ukrainian anarchist revolutionary and the commander of the Revolutionary Insurgent Army of Ukraine during the Ukrainian Civil War.
Paul J. Weitz, American astronaut (d. 2017) births

Paul Joseph Weitz was an American naval officer and aviator, aeronautical engineer, test pilot, and NASA astronaut, who flew into space twice. He was a member of the three-man crew who flew on Skylab 2, the first crewed Skylab mission. He was also Commander of the STS-6 mission, the maiden flight of the Space Shuttle Challenger.
James Butler, English sculptor and educator (d. 2022) births
James Walter Butler MBE RA was a British sculptor most famous for his 1980 statue of Richard III in Leicester.
Murray Chapple, New Zealand cricketer and manager (d. 1985) births

Murray Ernest Chapple was a New Zealand cricketer who played 14 Test matches over 13 years. However, he was largely unsuccessful, with only three fifties and a highest score of 76.
Maureen Forrester, Canadian actress and singer (d. 2010) births

Maureen Kathleen Stewart Forrester, was a Canadian operatic contralto.
Alice Parizeau, Polish-Canadian journalist and criminologist (d. 1990) births

Alice Parizeau, OC was a Polish-Canadian writer, essayist, journalist and criminologist.
Herbert Scarf, American economist and academic (d. 2015) births

Herbert Eli "Herb" Scarf was an American mathematical economist and Sterling Professor of Economics at Yale University.
Annie Ross, Scottish-American singer and actress (d. 2020) births
Annabelle McCauley Allan Short, known professionally as Annie Ross, was a British-American singer and actress, best known as a member of the jazz vocal trio Lambert, Hendricks & Ross.
Judd Buchanan, Canadian businessman and politician, 36th Canadian Minister of Public Works births
Judd Buchanan, is a Canadian former politician and businessman.
The Minister of Public Works was a position in the Cabinet of Canada who oversaw the public works portfolio of the federal government.
Somnath Chatterjee, Indian lawyer and politician, 14th Speaker of the Lok Sabha (d. 2018) births

Somnath Chatterjee was an Indian politician who was associated with the Communist Party of India (Marxist) for most of his life, though he had been a non affiliated independent during his last decade. He was the Speaker of the Lok Sabha from 2004 to 2009.

The speaker of the Lok Sabha is the presiding officer and the highest authority of the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India. The speaker is elected generally in the first meeting of the Lok Sabha following general elections. Serving for a term of five years, the speaker chosen from sitting members of the Lok Sabha.
Eddie Mazur, Canadian ice hockey player (d. 1995) births
Edward Joseph "Spider" Mazur was a Canadian ice hockey forward. He played in the National Hockey League with the Montreal Canadiens and Chicago Black Hawks between 1951 and 1956. The rest of his career, which lasted from 1948 to 1966, was spent in the minor leagues.
Dolphy, Filipino actor, singer, and producer (d. 2012) births

Rodolfo Vera Quizon Sr., better known by his stage names Dolphy, Pidol, and Golay, was a Filipino comedian and actor. He is widely regarded as the country's "King of Comedy" for his comedic talent embodied by his long roster of works on stage, radio, television and movies.
Mario Montenegro, Filipino actor (d. 1988) births
Mario Montenegro was a Filipino film actor best known for his heroic leading roles.
Nils Taube, Estonian-English businessman (d. 2008) births
Baron Nils Taube was Britain's longest serving fund manager. A colleague of George Soros and advisor to Lord Rothschild, he also anticipated the 1987 stockmarket crash, while delivering an annual return of 15 percent for over 35 years while he ran his own fund.
Daniel Ceccaldi, French actor, director, and screenwriter (d. 2003) births
Daniel Ceccaldi was a French actor.
Midge Decter, American journalist and author births
Midge Decter was an American journalist and author. Originally a liberal, she was one of the pioneers of the neoconservative movement in the 1970s and 1980s.
Sadiq Hussain Qureshi, Pakistani politician, 10th Governor of Punjab (d. 2000) births
Nawab Sadiq Hussain Qureshi was a Pakistani politician who served as both Governor and Chief Minister of Punjab under Zulfikar Ali Bhutto in the 1970s. A close aid of Mr. Bhutto during his time in power, he retired from all active politics after the military coup of 1977 that ousted Bhutto's government.

The Governor of Punjab is the appointed head of state of the provincial government in Punjab, Pakistan. Although the Governor is the head of the province on paper, it is largely a ceremonial position; and the main powers lie with the Chief Minister Punjab and Chief Secretary Punjab.
Jean-Marie Seroney, Kenyan activist and politician (d. 1982) births

Jean-Marie Seroney was a Kenyan human rights advocate, a legislator, and an Amnesty International prisoner of conscience. He was detained as a prisoner of conscience for 1,155 days.
Whitey Lockman, American baseball player, coach, and manager (d. 2009) births

Carroll Walter "Whitey" Lockman was a left-handed hitting first baseman and outfielder, coach, manager and front office executive in Major League Baseball.
Bernard Thompson, British television producer and director (d. 1998) births
Bernard Thompson was a British television producer and director most famous for his work on Last of the Summer Wine and Are You Being Served?. Thompson served as producer and director during Last of the Summer Wine's second series. Thompson also served as a director on Are You Being Served?.
Beatriz Segall, Brazilian actress (d. 2018) births

Beatriz de Toledo Segall was a Brazilian actress. One of her most notable works is the role of Odete Roitman on the telenovela Vale Tudo (1988).
Benny Benjamin, American R&B drummer (d. 1969) births

William "Benny" Benjamin, nicknamed Papa Zita, was an American musician, most notable as the primary drummer for the Motown Records studio band The Funk Brothers. He was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 2003 and was named the eleventh best drummer of all time by the Rolling Stone magazine in 2016.
Jerry Paris, American actor and director (d. 1986) births

William Gerald Paris was an American actor and director best known for playing Jerry Helper, the dentist and next-door neighbor of Rob and Laura Petrie, on The Dick Van Dyke Show, and for directing the majority of the episodes of the sitcom Happy Days.
Dick Passwater, American race car driver (d. 2020) births
Richard Passwater was an American racecar driver who raced in NASCAR and USAC Stock Cars. He won the fifth race of the 1953 NASCAR Grand National Series at Charlotte Speedway.
Jutta Zilliacus, Finnish journalist and politician births

Jutta Armelle Zilliacus is a Finnish-born ethnic Estonian journalist and author in the Swedish language. She was also a politician, and served as a Member of Parliament for the Swedish People's Party for Helsinki from 1975 to 1986 and a member of the Helsinki City Council from 1968 to 1984.
Frank Church, American lawyer and politician (d. 1984) births

Frank Forrester Church III was an American politician and lawyer. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as a United States senator from Idaho from 1957 until his defeat in 1981. As of 2022, he is the longest serving Democratic senator from the state as he is the only Democrat from the state who has served more than two terms in the Senate. He was a prominent figure in American foreign policy, and established a reputation as a member of the party's liberal wing.
Scotch Taylor, South African cricketer and hockey player (d. 2004) births
Alistair Innes "Scotch" Taylor was a South African sportsman who played first-class cricket and hockey for Transvaal, and captained the Transvaal cricket team for four seasons. Taylor represented South Africa in one cricket Test in 1956. He was an alumnus of the King Edward VII School, set up a squash section in the Old Edwardians club, and was elected president of the South African Hockey Union.
Estelle Getty, American actress (d. 2008) births

Estelle Gettleman, known professionally as Estelle Getty, was an American actress and comedian best known for her portrayal of Sophia Petrillo on The Golden Girls (1985–92), for which she won a Golden Globe Award for Best Actress – Television Series Musical or Comedy and a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Comedy Series. She reprised the role for appearances on Empty Nest (1993–95), The Golden Palace (1992–93), Blossom (1990–95), and Nurses (1991–94). Notable films in which she appeared include Mask (1985), a semibiographical film in which she played the grandmother of Roy L. Dennis, Mannequin , and Stuart Little (1999). She retired from acting in 2001 due to failing health, and died in 2008 from dementia with Lewy bodies.
Edgar Gilbert, American mathematician and theorist (d. 2013) births
Edgar Nelson Gilbert was an American mathematician and coding theorist, a longtime researcher at Bell Laboratories whose accomplishments include the Gilbert–Varshamov bound in coding theory, the Gilbert–Elliott model of bursty errors in signal transmission, and the Erdős–Rényi model for random graphs.
Maria Gripe, Swedish journalist and author (d. 2007) births
Maria Gripe, born Maja Stina Walter, was a Swedish author of books for children and young adults, which were often written in magical and mystical tone. She has written almost forty books, with many of her characters presented in short series of three or four books. For her lasting contribution to children's literature, she received the Hans Christian Andersen Medal for Writing in 1974.
Adolph Herseth, American soldier and trumpet player (d. 2013) births

Adolph Sylvester "Bud" Herseth was principal trumpet in the Chicago Symphony Orchestra from 1948 until 2001, and served as principal trumpet emeritus from 2001 until his retirement in 2004.
Lionel Terray, French mountaineer (d. 1965) births

Lionel Terray was a French climber who made many first ascents, including on the 1955 French Makalu expedition in the Himalaya and Cerro Fitz Roy in the Patagonian Andes.
Rosalind Franklin, English biophysicist, chemist, and academic (d. 1958) births

Rosalind Elsie Franklin was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA, RNA, viruses, coal, and graphite. Although her works on coal and viruses were appreciated in her lifetime, her contributions to the discovery of the structure of DNA were largely unrecognized during her life, for which she has been variously referred to as the "wronged heroine", the "dark lady of DNA", the "forgotten heroine", a "feminist icon", and the "Sylvia Plath of molecular biology".
Jane Frank, American painter and sculptor (d. 1986) births

Jane Schenthal Frank was an American multidisciplinary artist, known as a painter, sculptor, mixed media artist, illustrator, and textile artist. Her landscape-like, mixed-media abstract paintings are included in public collections, including those of the Corcoran Gallery of Art, the Baltimore Museum of Art, and the Smithsonian American Art Museum. She studied with artists, Hans Hofmann and Norman Carlberg.
Fritz Honegger, Swiss lawyer and politician (d. 1999) births

Fritz Honegger was a Swiss politician.
Lucien Saulnier, Canadian lawyer and politician (d. 1989) births
Lucien Saulnier, was a Canadian politician. He was chair of the Montreal Urban Community during the October Crisis. He was also Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the Société de développement industriel du Québec.
S. U. Ethirmanasingham, Sri Lankan businessman and politician births
Somasunderam Udayar Ethirmanasingham MBE is a former Ceylon Tamil businessman, politician and Member of Parliament.
Joseph P. Kennedy Jr., American lieutenant and pilot (d. 1944) births

Joseph Patrick Kennedy Jr. was the eldest of the nine children born to Joseph P. Kennedy Sr. and Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy. A US Navy lieutenant, he was killed in action during World War II while serving as a land-based patrol bomber pilot, and posthumously awarded the Navy Cross.
Woody Strode, American football player and actor (d. 1994) births

Woodrow Wilson Woolwine Strode was an American athlete and actor. He was a decathlete and football star who was one of the first Black American players in the National Football League in the postwar era. After football, he went on to become a film actor, where he was nominated for a Golden Globe Award for Best Supporting Actor for his role in Spartacus in 1960. Strode also served in the United States Army Air Corps during World War II.
Bill Bowes, English cricketer (d. 1987) births

William Eric Bowes was an English professional cricketer active from 1929 to 1947 who played in 372 first-class matches as a right arm fast bowler and a right-handed tail end batsman. He took 1,639 wickets with a best performance of nine for 121 and completed ten wickets in a match 27 times. He scored 1,531 runs with a highest score of 43* and is one of very few major players whose career total of wickets taken exceeded his career total of runs scored. He did not rate himself as a fielder but he nevertheless held 138 catches.
Ambroise-Marie Carré, French priest and author (d. 2004) births
Ambroise-Marie Carré OP was a Catholic priest, author and member of the Académie française. Born in Fleury-les-Aubrais in Loiret, France, Carré studied at l'école Saint-Joseph and the collège Sainte-Croix de Neuilly before entering the Dominican order in 1926 and being ordained a priest in 1933. Not long thereafter, he was to edit, from 1936 until 1939, the Revue des Jeunes. Under the German Occupation, following the capitulation of the French government to the Nazis during the Second World War, Carré aided those persecuted by the Vichy government, regardless of their religion or ethnicity; for this, he was awarded the Légion d'honneur and the Croix de Guerre.
Jack Gilford, American actor (d. 1990) births

Jack Gilford was an American Broadway, film, and television actor. He was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for Save the Tiger (1973).
Johnny Hodges, American saxophonist and clarinet player (d. 1970) births

Cornelius "Johnny" Hodges was an American alto saxophonist, best known for solo work with Duke Ellington's big band. He played lead alto in the saxophone section for many years. Hodges was also featured on soprano saxophone, but refused to play soprano after 1946. Along with Benny Carter, Hodges is considered to be one of the definitive alto saxophone players of the big band era.
Elias Canetti, Bulgarian-Swiss novelist, playwright, and memoirist, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1994) births

Elias Canetti was a German-language writer, born in Ruse, Bulgaria to a Sephardic family. They moved to Manchester, England, but his father died in 1912, and his mother took her three sons back to continental Europe. They settled in Vienna.

The Nobel Prize in Literature is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in the field of literature, produced the most outstanding work in an idealistic direction". Though individual works are sometimes cited as being particularly noteworthy, the award is based on an author's body of work as a whole. The Swedish Academy decides who, if anyone, will receive the prize. The academy announces the name of the laureate in early October. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895. Literature is traditionally the final award presented at the Nobel Prize ceremony. On some occasions the award has been postponed to the following year, most recently in 2018 as of May 2022.
Georges Grignard, French race car driver (d. 1977) births
Auguste Georges Paul Grignard was a racing driver from France. He raced in Formula One from 1947 to 1953, participating in one World Championship Grand Prix on 28 October 1951. He also participated in numerous non-Championship races, including winning the 1950 Paris Grand Prix.
Denys Watkins-Pitchford, English author and illustrator (d. 1990) births
Denys James Watkins-Pitchford MBE was a British naturalist, an illustrator, art teacher and a children's author under the pseudonym "BB". He won the 1942 Carnegie Medal for British children's books.
Eric Hoffer, American philosopher and author (d. 1983) births

Eric Hoffer was an American moral and social philosopher. He was the author of ten books and was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in February 1983. His first book, The True Believer (1951), was widely recognized as a classic, receiving critical acclaim from both scholars and laymen, although Hoffer believed that The Ordeal of Change (1963) was his finest work. The Eric Hoffer Book Award is an international literary prize established in his honor. The University of California, Berkeley awards an annual literary prize named jointly for Hoffer.
Ruth Krauss, American author and poet (d. 1993) births
Ruth Ida Krauss was an American writer of children's books, including The Carrot Seed, and of theatrical poems for adult readers. Many of her books are still in print.
Mohammed Helmy, Egyptian physician and Righteous Among the Nations (d. 1982) births

Dr Mohammed Helmy was an Egyptian medical doctor who saved several Jews from Nazi persecution in Berlin during the Holocaust. He has been recognized as Righteous Among the Nations by Yad Vashem, the first Arab to be recognized as such.

Righteous Among the Nations is an honorific used by the State of Israel to describe non-Jews who risked their lives during the Holocaust to save Jews from extermination by the Nazis for altruistic reasons. The term originates with the concept of "righteous gentiles", a term used in rabbinic Judaism to refer to non-Jews, called ger toshav, who abide by the Seven Laws of Noah.
Lila Lee, American actress and singer (d. 1973) births

Lila Lee was a prominent screen actress, primarily a leading lady, of the silent film and early sound film eras.
Jack Perrin, American actor and stuntman (d. 1967) births

Jack Perrin was an American actor specializing in Westerns.
Josephine Tey, Scottish author and playwright (d. 1952) births

Josephine Tey was a pseudonym used by Elizabeth MacKintosh, a Scottish author. Her novel The Daughter of Time was a detective work investigating the role of Richard III of England in the death of the Princes in the Tower, and named as the greatest crime novel of all time by the Crime Writers' Association. Her first play Richard of Bordeaux, written under another pseudonym, Gordon Daviot, starred John Gielgud in its successful West End run.
Ingeborg Spangsfeldt, Danish actress (d. 1968) births
Ingeborg Spangsfeldt was a Danish film actress whose career began in the early 1910s until her retirement upon getting married in 1924.
Walter Brennan, American actor (d. 1974) births

Walter Andrew Brennan was an American actor and singer. He won the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for his performances in Come and Get It (1936), Kentucky (1938), and The Westerner (1940), making him one of only three male actors to win three Academy Awards, and the only male or female actor to win three awards in the supporting actor category. Brennan was also nominated for his performance in Sergeant York (1941). Other noteworthy performances were in To Have and Have Not (1944), My Darling Clementine (1946), Red River (1948), and Rio Bravo (1959).
Gavrilo Princip, Bosnian Serb revolutionary (d. 1918) births

Gavrilo Princip was a Bosnian Serb student who assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria and his wife Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg, in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914.
John Taylor, American religious leader, 3rd President of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (b. 1808) deaths

John Taylor was an English-born religious leader who served as the third president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints from 1880 to 1887. He is the first and so far only president of the LDS Church to have been born outside the United States.

The President of the Church is the highest office of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. It was the office held by Joseph Smith, the church's founder. The church's president is its leader and the head of the First Presidency, its highest governing body. Latter-day Saints consider the president of the church to be a "prophet, seer, and revelator" and refer to him as "the Prophet", a title that was originally given to Smith. When the name of the president is used by adherents, it is usually prefaced by the title "President". Russell M. Nelson has been the president since January 14, 2018.
Edward Cummins, American golfer (d. 1926) births

Edward McClellan Cummins was an American golfer who competed in the 1904 Summer Olympics. In 1904 he was part of the American team which won the gold medal. He finished 25th in this competition. In the individual competition he finished 25th in the qualification and was eliminated in the first round of the match play.
Alfredo Casella, Italian pianist, composer, and conductor (d. 1947) births

Alfredo Casella was an Italian composer, pianist and conductor.
George S. Rentz, American commander (d. 1942) births

George Snavely Rentz was a United States Navy chaplain who served during World War I and World War II. For selfless heroism following the loss of USS Houston (CA-30) in the Battle of Sunda Strait, he was posthumously awarded the Navy Cross— the only Navy Chaplain to be so honored during World War II.
Masaharu Anesaki, Japanese philosopher and scholar (d. 1949) births

Masaharu Anesaki , also known under his pen name "Chōfū Anesaki" , was a leading Japanese intellectual and scholar of the Meiji period. Anesaki is credited as being the father of religious studies in Japan, but also wrote on a variety of subjects including culture, literature, and politics. He was also a member of the International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation of the League of Nations.
Jim Corbett, Indian hunter, environmentalist, and author (d. 1955) births

Edward James Corbett was a British hunter, tracker, naturalist, and author who hunted a number of man-eating tigers and leopards in the Indian subcontinent. He held the rank of colonel in the British Indian Army and was frequently called upon by the Government of the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh, now the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand, to kill man-eating tigers and leopards that were preying on people in the nearby villages of the Kumaon-Garhwal Regions.
Maxfield Parrish, American painter and illustrator (d. 1966) births

Maxfield Parrish was an American painter and illustrator active in the first half of the 20th century. He is known for his distinctive saturated hues and idealized neo-classical imagery. His career spanned fifty years and was wildly successful: the National Museum of American Illustration deemed his painting Daybreak (1922) to be the most successful art print of the 20th century.
Platon, Estonian bishop and saint (d. 1919) births

Platon, born Paul Kulbusch was an Estonian bishop and the first Orthodox saint of Estonian ethnicity.
Max Dauthendey, German author and painter (d. 1918) births

Max Dauthendey was a German author and painter of the impressionist period. He was born in Würzburg and died in Malang. Together with Richard Dehmel and Eduard von Keyserling he is regarded as one of the most influential authors of that period. Dauthendey was stranded in Java at the outbreak of World War One. Attempts to provide him with a safe passage back to Germany failed.
Alexander Rummler, American painter (d. 1959) births

Alexander Joseph Rummler was an American painter best known for his work on murals and billboards.
Frederick Blackman, English physiologist and academic (d. 1947) births
Frederick Frost Blackman FRS was a British plant physiologist.
Jac. P. Thijsse, Dutch botanist and conservationist (d. 1945) births

Jacobus Pieter Thijsse was a Dutch conservationist and botanist. He founded the Society for Preservation of Nature Monuments in the Netherlands.
James Barry, English soldier and surgeon (b. 1799) deaths

James Barry was a military surgeon in the British Army. Originally from the city of Cork in Ireland, Barry obtained a medical degree from the University of Edinburgh Medical School, then served first in Cape Town, South Africa, and subsequently in many parts of the British Empire. Before retirement, Barry had risen to the rank of Inspector General in charge of military hospitals, the second-highest medical office in the British Army. Barry not only improved conditions for wounded soldiers, but also the conditions of the native inhabitants, and performed the first recorded caesarean section by a European in Africa in which both the mother and child survived the operation.
Jonas Furrer, Swiss lawyer and politician, President of the Swiss Confederation (b. 1805) deaths

Jonas Furrer was a Swiss lawyer and politician who served as member of the Federal Council, from 1848 to 1861, and as the first president of the Swiss Confederation from 1848 to 1849, and again in 1852, 1855 and 1858. He was one of the leading figures in the foundation of Switzerland as a federal state. He was a member of the Radical Party.

The president of the Swiss Confederation, also known as the president of the Confederation or colloquially as the president of Switzerland, is the head of Switzerland's seven-member Federal Council, the country's executive branch. Elected by the Federal Assembly for one year, the officeholder chairs the meetings of the Federal Council and undertakes special representational duties.
Frank J. Sprague, American naval officer and inventor (d. 1934) births

Frank Julian Sprague was an American inventor who contributed to the development of the electric motor, electric railways, and electric elevators. His contributions were especially important in promoting urban development by increasing the size cities could reasonably attain and by allowing greater concentration of business in commercial sections. He became known as the "Father of Electric Traction". Demonstrating an aptitude for science and mathematics, Sprague secured an appointment to the U.S. Naval Academy in 1874 and, after graduation in 1878 and 2 years at sea, resigned to pursue his career in electrical engineering.
Arthur Balfour, Scottish-English lieutenant and politician, 33rd Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (d. 1930) births

Arthur James Balfour, 1st Earl of Balfour,, also known as Lord Balfour, was a British Conservative statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1905. As foreign secretary in the Lloyd George ministry, he issued the Balfour Declaration of 1917 on behalf of the cabinet, which supported a "home for the Jewish people" in Palestine.

The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern prime ministers hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons, they sit as members of Parliament.
Paul Langerhans, German pathologist, physiologist and biologist (d. 1888) births

Paul Langerhans was a German pathologist, physiologist and biologist, credited with the discovery of the cells that secrete insulin, named after him as the islets of Langerhans.
Thomas Eakins, American painter, sculptor, and photographer (d. 1916) births

Thomas Cowperthwait Eakins was an American realist painter, photographer, sculptor, and fine arts educator. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the most important American artists.
Charles Macintosh, Scottish chemist and inventor of waterproof fabric (b. 1766) deaths

Charles Macintosh FRS was a Scottish chemist and the inventor of the modern waterproof raincoat. The Mackintosh raincoat is named after him.
Dominique Jean Larrey, French physician and surgeon (b. 1766) deaths

Baron Dominique Jean Larrey was a French surgeon and military doctor, who distinguished himself in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. An important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, he is often considered the first modern military surgeon.
Francis Garnier, French captain and explorer (d. 1873) births

Marie Joseph François Garnier was a French officer, inspector of Indigenous Affairs of Cochinchina and explorer. He eventually became mission leader of the Mekong Exploration Commission in 19th century Southeast Asia.
Samuel Taylor Coleridge, English philosopher, poet, and critic (b. 1772) deaths

Samuel Taylor Coleridge was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who, with his friend William Wordsworth, was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets. He also shared volumes and collaborated with Charles Lamb, Robert Southey, and Charles Lloyd. He wrote the poems The Rime of the Ancient Mariner and Kubla Khan, as well as the major prose work Biographia Literaria. His critical work, especially on William Shakespeare, was highly influential, and he helped introduce German idealist philosophy to English-speaking cultures. Coleridge coined many familiar words and phrases, including "suspension of disbelief". He had a major influence on Ralph Waldo Emerson and American transcendentalism.
Maria Szymanowska, Polish composer and pianist (b. 1789) deaths

Maria Szymanowska was a Polish composer and one of the first professional virtuoso pianists of the 19th century. She toured extensively throughout Europe, especially in the 1820s, before settling permanently in St. Petersburg. In the Russian imperial capital, she composed for the court, gave concerts, taught music, and ran an influential salon.
Kondraty Ryleyev, Russian poet and publisher (b. 1795) deaths

Kondraty Fyodorovich Ryleyev, also spelled Kondraty Feodorovich Ryleev was a Russian poet, publisher, and a leader of the Decembrist Revolt, which attempted to overthrow the Russian monarchy in 1825.
Maria Weston Chapman, American abolitionist (d. 1885) births

Maria Weston Chapman was an American abolitionist. She was elected to the executive committee of the American Anti-Slavery Society in 1839 and from 1839 until 1842, she served as editor of the anti-slavery journal The Non-Resistant.
Princess Augusta of Hesse-Kassel (d. 1889) births

Princess Augusta of Hesse-Kassel was the wife of Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge, the tenth-born child, and seventh son, of George III of the United Kingdom and Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz. The longest-lived daughter-in-law of George III, she was the maternal grandmother of Mary of Teck, wife of George V.
André Chénier, Greek-French poet and author (b. 1762) deaths

André Marie Chénier was a French poet of Greek and Franco-Levantine origin, associated with the events of the French Revolution of which he was a victim. His sensual, emotive poetry marks him as one of the precursors of the Romantic movement. His career was brought to an abrupt end when he was guillotined for supposed "crimes against the state", just three days before the end of the Reign of Terror. Chénier's life has been the subject of Umberto Giordano's opera Andrea Chénier and other works of art.
Jean-Antoine Roucher, French poet and author (b. 1745) deaths

Jean-Antoine Roucher, was a French poet.
Friedrich von der Trenck, Prussian adventurer and author (b. 1726) deaths

Friedrich Freiherr von der Trenck was a Prussian officer, adventurer, and author.
Isaac Low, American merchant and politician (b. 1735) deaths

Isaac Low was an American merchant in New York City who served as a member of the Continental Congress, where he signed the Continental Association. He later served as a delegate to the New York Provincial Congress. Though originally a Patriot, he later joined the Loyalist cause in the American Revolution.
Johann Bernhard Basedow, German educator and reformer (b. 1723) deaths

Johann Bernhard Basedow was a German educational reformer, teacher and writer. He founded the Philanthropinum, a short-lived but influential progressive school in Dessau, and was the author of "Elementarwerk", a popular illustrated textbook for children.
William Livingston, American soldier and politician, 1st Governor of New Jersey (b. 1723) deaths

William Livingston was an American politician who served as the first governor of New Jersey (1776–1790) during the American Revolutionary War. As a New Jersey representative in the Continental Congress, he signed the Continental Association and the United States Constitution. He is considered one of the Founding Fathers of the United States and a Founding Father of New Jersey.

The governor of New Jersey is the head of government of New Jersey. The office of governor is an elected position with a four-year term. There is a two consecutive term term limit, with no limitation on non-consecutive terms. The official residence of the governor is Drumthwacket, a mansion located in Princeton, New Jersey. The governor’s office is located inside of the New Jersey State House in Trenton, making New Jersey notable as the executive’s office is located in the same building as the legislature. New Jersey is also notable for being one of the few states in which the governor’s official residence is not located in the state capital.
Santiago de Liniers, 1st Count of Buenos Aires, French-Spanish captain and politician, 10th Viceroy of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata (d. 1810) births

Santiago Antonio María de Liniers y Bremond, 1st Count of Buenos Aires, KOM, OM was a French officer in the Spanish military service, and a viceroy of the Spanish colonies of the Viceroyalty of the River Plate. Although born Jacques de Liniers in France, he is more widely known by the Spanish form of his name, Santiago de Liniers.

The Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata meaning "River of the Silver", also called "Viceroyalty of the River Plate" in some scholarly writings, in southern South America, was the last to be organized and also the shortest-lived of the Viceroyalties of the Spanish Empire in the Americas. The name "Provincias del Río de la Plata" was formally adopted in 1810 during the Cortes of Cádiz to designate the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
Henry Knox, American general and politician, 1st United States Secretary of War (d. 1806) births

Henry Knox, a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the revolution, he oversaw the War Department under the Articles of Confederation, 1785—1789. Washington, at the start of his first administration, appointed Knox the nation's first Secretary of War, a position he held from 1789—1794. He is perhaps best remembered today as the namesake of Fort Knox in Kentucky, the repository of a large portion of the nation's gold reserves.

The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation between 1781 and 1789. Benjamin Lincoln and later Henry Knox held the position. When Washington was inaugurated as the first President under the Constitution, he appointed Knox to continue serving as Secretary of War.
Pieter Langendijk, Dutch playwright and poet (d. 1756) births

Pieter Langendijk was a damask weaver, city artist, dramatist, and poet.
Urian Oakes, English-American minister and educator (b. 1631) deaths
Urian Oakes was an English-born American Congregational minister and educator.
Archibald Campbell, 1st Duke of Argyll, Scottish general (d. 1703) births

Archibald Campbell, 1st Duke of Argyll, 10th Earl of Argyll was a Scottish peer.
Philipp Heinrich Erlebach, German composer (d. 1714) births
Philipp Heinrich Erlebach was a German Baroque composer, a prolific writer of church music and secular music. Much of his work is lost due to a fire.
Agostino Steffani, Italian composer and diplomat (d. 1728) births

Agostino Steffani was an Italian ecclesiastic, diplomat and composer.
Robert Pierrepont, 1st Earl of Kingston-upon-Hull, English general and politician (b. 1584) deaths

Robert Pierrepont, 1st Earl of Kingston-upon-Hull was an English nobleman who joined the Royalist side in the English Civil War after some delay and became lieutenant-general of the counties of Lincoln, Rutland, Huntingdon, Cambridge and Norfolk. He was killed in a friendly fire incident after being captured by Parliamentary forces.
Joseph Williamson, English politician (d. 1701) births

Sir Joseph Williamson, PRS was an English civil servant, diplomat and politician who sat in the House of Commons of England variously between 1665 and 1701 and in the Irish House of Commons between 1692 and 1699. He was Secretary of State for the Northern Department from 1674 to 1679.
Andreas Libavius, German physician and chemist (b. 1550) deaths

Andreas Libavius or Andrew Libavius was born in Halle, Germany c. 1550 and died in July 1616. Libavius was a renaissance man who spent time as a professor at the University of Jena teaching history and poetry. After which he became a physician at the Gymnasium in Rothenburg and later founded the Gymnasium at Coburg. Libavius was most known for practicing alchemy and writing a book called Alchemia, one of the first chemistry textbooks ever written.
Pomponio Nenna, Italian composer (b. 1556) deaths
Pomponio Nenna was a Neapolitan Italian composer of the Renaissance. He is mainly remembered for his madrigals, which were influenced by Gesualdo, and for his polychoral sacred motets, posthumously published as Sacrae Hebdomadae Responsoria in 1622.
Theodore Haak, German scholar (d. 1690) births

Theodore Haak was a German Calvinist scholar, resident in England in later life. Haak's communications abilities and interests in the new science provided the backdrop for convening the "1645 Group", a precursor of the Royal Society.
Brian Twyne, English archivist (d. 1644) births

Brian Twyne was an antiquary and an academic at the University of Oxford. After being educated at Corpus Christi College, Oxford, and becoming a Fellow of the college in 1606, he published his one main work, a history of the university, in 1608. This was designed to prove that Oxford was older than Cambridge University, and has been described by a modern writer as a "remarkable achievement for a young scholar of twenty-eight." His main accomplishment was to play a leading role in the revision of the university statutes under William Laud. He was rewarded by appointment in 1634 to the new position of Keeper of the Archives, in which role he obtained a new royal charter for Oxford to confirm its rights and privileges, and helped the university in its disputes with the city authorities.
Christoph Scheiner, German astronomer and Jesuit (d. 1650) births

Christoph Scheiner SJ was a Jesuit priest, physicist and astronomer in Ingolstadt.
Isaac Luria, Ottoman rabbi and mystic (b. 1534) deaths

Isaac ben Solomon Luria Ashkenazi, commonly known in Jewish religious circles as "Ha'ARI", "Ha'ARI Hakadosh" or "ARIZaL", was a leading rabbi and Jewish mystic in the community of Safed in the Galilee region of Ottoman Syria, now Israel. He is considered the father of contemporary Kabbalah, his teachings being referred to as Lurianic Kabbalah. While his direct literary contribution to the Kabbalistic school of Safed was extremely minute, his spiritual fame led to their veneration and the acceptance of his authority. The works of his disciples compiled his oral teachings into writing. Every custom of Luria was scrutinized, and many were accepted, even against previous practice.
Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor (b. 1503) deaths

Ferdinand I was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564. Before his accession as Emperor, he ruled the Austrian hereditary lands of the Habsburgs in the name of his elder brother, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. Also, he often served as Charles' representative in the Holy Roman Empire and developed encouraging relationships with German princes. In addition, Ferdinand also developed valuable relationships with the German banking house of Jakob Fugger and the Catalan bank, Banca Palenzuela Levi Kahana.
Katō Kiyomasa, Japanese warlord (d. 1611) births

Katō Kiyomasa was a Japanese daimyō of the Azuchi–Momoyama and Edo periods. His court title was Higo-no-kami. His name as a child was Yashamaru, and first name was Toranosuke. He was one of Hideyoshi's Seven Spears of Shizugatake.
George Peele, English translator, poet, and dramatist (d. 1596) births
George Peele was an English translator, poet, and dramatist, who is most noted for his supposed but not universally accepted collaboration with William Shakespeare on the play Titus Andronicus. Many anonymous Elizabethan plays have been attributed to him, but his reputation rests mainly on Edward I, The Old Wives' Tale, The Battle of Alcazar, The Arraignment of Paris, and David and Bethsabe. The Troublesome Reign of John, King of England, the immediate source for Shakespeare's King John, has been published under his name.
Alphonsus Rodriguez, Jesuit lay brother and saint (d. 1617) births

Alphonsus Rodríguez, SJ was a Spanish Jesuit who served as a religious brother and is now venerated as a saint. He was a native of Segovia.
Hernando de Aragón, Archbishop of Zaragoza (d. 1575) births

Hernando de Aragón y de Gurrea, OCist, Archbishop of Zaragoza and Lieutenant General of Aragon, was an Aragonese humanist and historian.

The Archdiocese of Saragossa is a Roman Catholic ecclesiastical territory located in north-eastern Spain, in the province of Zaragoza, part of the autonomous community of Aragón. The archdiocese heads the ecclesiastical province of Saragossa, having metropolitan authority over the suffragan dioceses of Barbastro-Monzón, Huesca, Tarazona, and Teruel and Albarracín.
Innocent VIII, pope of the Catholic Church (b. 1432) deaths

Pope Innocent VIII, born Giovanni Battista Cybo, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 29 August 1484 to his death in July 1492. Son of the viceroy of Naples, Battista spent his early years at the Neapolitan court. He became a priest in the retinue of Cardinal Calandrini, half-brother to Pope Nicholas V (1447–55), Bishop of Savona under Pope Paul II, and with the support of Cardinal Giuliano Della Rovere. After intense politicking by Della Rovere, Cibo was elected pope in 1484. King Ferdinand I of Naples had supported Cybo's competitor, Rodrigo Borgia. The following year, Pope Innocent supported the barons in their failed revolt.
Albrecht VII, Duke of Mecklenburg (d. 1547) births

Albrecht VII, the Handsome, Duke of Mecklenburg in Güstrow, was a minor ruler in North Germany of the 16th century. He also asserted claims to Scandinavian thrones based on the royal lineage of the House of Mecklenburg.
Charles of Artois, French nobleman (b. 1394) deaths
Charles of Artois, son of Philip of Artois, Count of Eu, and Marie of Berry, was Count of Eu from 16 June 1397 until his death 75 years later. He was taken prisoner by the English at the Battle of Agincourt on 25 October 1415, and was not released until 1438. In 1448, he married Jeanne of Saveuse and on 23 September 1454, Helene of Melun, but he had no children. He was appointed Lieutenant of the King in Normandy and Guyenne, as well as Governor of Paris, during the War of the Public Weal in 1465. He was succeeded by his nephew John II, Count of Nevers.
Thomas à Kempis, German priest and mystic deaths

Thomas à Kempis was a German-Dutch canon regular of the late medieval period and the author of The Imitation of Christ, published anonymously in Latin in the Netherlands c. 1418–1427, one of the most popular and best known Christian devotional books. His name means "Thomas of Kempen", Kempen being his home town.
Jakob Wimpfeling, Renaissance humanist (d. 1528) births
Jakob Wimpfeling was a Renaissance humanist and theologian.
Henry Percy, 3rd Earl of Northumberland, English politician (d. 1461) births

Henry Percy, 3rd Earl of Northumberland, was an English magnate.
Martin I, king of Sicily (b. 1376) deaths

Martin I of Sicily, called "The Younger", was King of Sicily from his marriage to Queen Maria in 1390 until his death.
Philip I, Duke of Brabant (d. 1430) births

Philip I, also known as Philip of Saint Pol, was the younger son of Antoine, Duke of Brabant and Jeanne of Saint-Pol. He succeeded his brother John IV as Duke of Brabant in 1427, while he had inherited Saint-Pol and Ligny as an appanage on the death of his maternal grandfather, Waleran III of Luxembourg, Count of Ligny, in 1415.
James I, king of Scotland (d. 1437) births

James I was King of Scots from 1406 until his assassination in 1437. The youngest of three sons, he was born in Dunfermline Abbey to King Robert III and Annabella Drummond. His older brother David, Duke of Rothesay, died under suspicious circumstances during detention by their uncle, Robert, Duke of Albany. James' other brother, Robert, died young. Fears surrounding James's safety grew through the winter of 1405/6 and plans were made to send him to France. In February 1406, James was forced to take refuge in the castle of the Bass Rock in the Firth of Forth after his escort was attacked by supporters of Archibald, 4th Earl of Douglas. He remained at the castle until mid-March, when he boarded a vessel bound for France. On 22nd March, English pirates captured the ship and delivered the prince to Henry IV of England. The ailing Robert III died on 4 April and the 11-year-old James, now the uncrowned King of Scots, would not regain his freedom for another eighteen years.
Albert I, Duke of Bavaria (d. 1404) births
Albert I, Duke of Lower Bavaria, was a feudal ruler of the counties of Holland, Hainaut, and Zeeland in the Low Countries. Additionally, he held a portion of the Bavarian province of Straubing, his Bavarian ducal line's appanage and seat, Lower Bavaria.
Hawys Gadarn, Welsh noblewoman (d. 1353) births
Hawys Gadarn , also known as the Hardy, the Powerful, the Intrepid, and Hawise de la Pole, was the daughter of Owen de la Pole and the heir to Powys Wenwynwyn in Wales. She was married to John Charleton after seeking the intervention of Edward II of England to support her inheritance against the schemes of four of her uncles to take her lands.
Arthur II, Duke of Brittany (d. 1312) births

Arthur II, of the House of Dreux, was Duke of Brittany from 1305 to his death. He was the first son of John II and Beatrice, daughter of Henry III of England and Eleanor of Provence.
Herrad of Landsberg, abbess, author, and illustrator (b. c. 1130) deaths

Herrad of Landsberg was a 12th-century Alsatian nun and abbess of Hohenburg Abbey in the Vosges mountains. She was known as the author of the pictorial encyclopedia Hortus deliciarum.
Sibylla, queen of Jerusalem deaths

Sibylla was Queen of Jerusalem from 1186 to 1190. She reigned alongside her husband Guy of Lusignan, to whom she was unwaveringly attached despite his unpopularity among the barons of the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
Ibn Arabi, Andalusian Sufi mystic, poet, and philosopher (d. 1240) births

Ibn ʿArabī, nicknamed al-Qushayrī and Sulṭān al-ʿĀrifīn, was an Arab Andalusian Muslim scholar, mystic, poet, and philosopher, extremely influential within Islamic thought. Out of the 850 works attributed to him, some 700 are authentic while over 400 are still extant. His cosmological teachings became the dominant worldview in many parts of the Muslim world.
Afonso I, king of Portugal (d. 1185) births

Afonso I of Portugal, also called Afonso Henriques, nicknamed the Conqueror by the Portuguese, and El-Bortukali and Ibn-Arrink or Ibn Arrinq by the Moors whom he fought, was the first king of Portugal. He achieved the independence of the County of Portugal, establishing a new kingdom and doubling its area with the Reconquistacode: spa promoted to code: es , an objective that he pursued until his death.
Casimir I the Restorer, duke of Poland (d. 1058) births

Casimir I the Restorer, a member of the Piast dynasty, was the duke of Poland from 1040 until his death. Casimir was the son of Mieszko II Lambert and Richeza of Lotharingia. He is known as the Restorer because he managed to reunite parts of the Kingdom of Poland after a period of turmoil. He reincorporated Masovia, and conquered Silesia and Pomerania. However, he failed to crown himself King of Poland, mainly because of internal and external threats to his rule.
Ichijō, emperor of Japan (b. 980) deaths

Emperor Ichijō was the 66th emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession.
Thietmar, bishop of Merseburg (d. 1018) births

Thietmar, Prince-Bishop of Merseburg from 1009 until his death, was an important chronicler recording the reigns of German kings and Holy Roman Emperors of the Ottonian (Saxon) dynasty. Two of Thietmar's great-grandfathers, both referred to as Liuthar, were the Saxon nobles Lothar II, Count of Stade, and Lothar I, Count of Walbeck. They were both killed fighting the Slavs at the Battle of Lenzen.
Ragenold, margrave of Neustria deaths
Ragenold was the Count of Herbauges from 852 and Count of Maine and Margrave of Neustria from 878. His family is unidentified, but he may have been a son of Reginald of Herbauges.
Constantius Chlorus, Roman emperor (b. 250) deaths

Flavius Valerius Constantius "Chlorus", also called Constantius I, was Roman emperor from 305 to 306. He was one of the four original members of the Tetrarchy established by Diocletian, first serving as caesar from 293 to 305 and then ruling as augustus until his death. Constantius was also father of Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor of Rome. The nickname Chlorus was first popularized by Byzantine-era historians and not used during the emperor's lifetime. After his re-conquering of Roman Britain, he was given the title 'Redditor Lucis Aeternae', meaning 'The Restorer of Eternal Light'.
Christian feast day: Anne (Eastern Christianity)

According to Christian apocryphal and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the canonical gospels. In writing, Anne's name and that of her husband Joachim come only from New Testament apocrypha, of which the Gospel of James seems to be the earliest that mentions them. The mother of Mary is mentioned but not named in the Quran.

Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and the Malabar coast of South Asia, and ephemerally parts of Persia, Central Asia, the Near East and the Far East. The term does not describe a single communion or religious denomination.
Christian feast day: Christopher (Western Christianity)

Saint Christopher is venerated by several Christian denominations as a martyr killed in the reign of the 3rd-century Roman emperor Decius or alternatively under the emperor Maximinus Daia. There appears to be confusion due to the similarity in names "Decius" and "Daia". Churches and monasteries were named after him by the 7th century.

Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity. Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic Church, Independent Catholicism and Restorationism.
Christian feast day: Cucuphas

Saint Cucuphas is a martyr of Spain. His feast day is 25 July but in some areas it is celebrated on 27 July to avoid conflict with the important feast day of Santiago, the patron saint of Spain. His name is said to be of Phoenician origin with the meaning of "he who jokes, he who likes to joke."
Christian feast day: Glodesind
Glodesind (572−608) was a saint, nun, abbess, and founder of a convent in Metz, France, during the time of King Childebert II (575−596) of Austrasia. She was a member of the Carolingian nobility. When she was 11 or 12 years old, she married a young nobleman, who was arrested by the French government shortly after their wedding and executed a year later. Instead of remarrying as her family wanted, she fled to Metz and took refuge at the Church of St. Stephen. Her family gave up forcing her to marry, and she became a nun and later, the abbess of a convent that was built by her parents. She was abbess for six years until her death in 608 at the age of 30. Her feast day is 8 July.
Christian feast day: James the Great (Western Christianity)

James the Great, also known as James, son of Zebedee, Saint James the Great, Saint James the Greater, Saint James the Elder, or Saint Jacob, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus, the first apostle to be martyred according to the New Testament. Saint James is the patron saint of Spain and, according to tradition, his remains are held in Santiago de Compostela in Galicia.

Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity. Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic Church, Independent Catholicism and Restorationism.
Christian feast day: John I Agnus

Saint John I Agnus was the 25th bishop of Tongres. He lived in the 7th century and is considered as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church.
Christian feast day: Julian of Le Mans (translation)
Saint Julian of Le Mans is a saint venerated in both the Roman Catholic and Orthodox Church, honored as the first bishop of Le Mans. His feast day is 27 January. The translation of his relics is celebrated on 25 July.

In Christianity, the translation of relics is the removal of holy objects from one locality to another ; usually only the movement of the remains of the saint's body would be treated so formally, with secondary relics such as items of clothing treated with less ceremony. Translations could be accompanied by many acts, including all-night vigils and processions, often involving entire communities.
Christian feast day: Magnerich of Trier
Magneric of Tier was a Frankish bishop of Trier. He is a Catholic and Orthodox saint, with a feast day on July 25. Magneric was one of the first bishops with a Germanic name. He was a friend and admirer of Gregory of Tours, mentioned in his History of the Franks, and ordained St Géry, one of his disciples, who became bishop of Cambrai-Arras on the ascent of King Childebert II. Venantius Fortunatus described the Bishop as virtuous and charitable, and an "ornament of bishops".
Christian feast day: July 25 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)

July 24 - Eastern Orthodox calendar - July 26
Earliest day on which Father's Day can fall, while July 31 is the latest; celebrated on last Sunday in July. (Dominican Republic)

Father's Day is a holiday of honoring fatherhood and paternal bonds, as well as the influence of fathers in society. In Catholic countries of Europe, it has been celebrated on 19 March as Saint Joseph's Day since the Middle Ages. In the United States, Father's Day was founded by Sonora Smart Dodd, and celebrated on the third Sunday of June for the first time in 1910. The day is held on various dates across the world, and different regions maintain their own traditions of honoring fatherhood.

The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with Haiti, making Hispaniola one of only two Caribbean islands, along with Saint Martin, that is shared by two sovereign states. The Dominican Republic is the second-largest nation in the Antilles by area at 48,671 square kilometers (18,792 sq mi), and third-largest by population, with approximately 10.7 million people, down from 10.8 million in 2020, of whom approximately 3.3 million live in the metropolitan area of Santo Domingo, the capital city. The official language of the country is Spanish.
Earliest day on which National Tree Planting Day can fall, while July 31 is the latest; celebrated on last Sunday in July. (Australia)

Arbor Day is a secular day of observance in which individuals and groups are encouraged to plant trees. Today, many countries observe such a holiday. Though usually observed in the spring, the date varies, depending on climate and suitable planting season.

Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of 7,617,930 square kilometres (2,941,300 sq mi), Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east, and mountain ranges in the south-east.
Earliest day on which Navy Day can fall, while July 31 is the latest; celebrated on last Sunday in July. (Russia)

Several nations observe or have observed a Navy Day to recognize their navy.

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,098,246 square kilometres (6,601,670 sq mi), and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan.
Guanacaste Day (Costa Rica)
Guanacaste Day is a Costa Rican holiday celebrating Costa Rica's annexation of the Guanacaste province in 1824. It is celebrated on July 25th.

Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of 51,060 km2 (19,710 sq mi). An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area.
National Baha'i Day (Jamaica)
The Baháʼí Faith in Jamaica begins with a mention by ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, then head of the religion, in 1916 as Latin America being among the places Baháʼís should take the religion to. The community of the Baháʼís begins in 1942 with the arrival of Dr. Malcolm King. The first Baháʼí Local Spiritual Assembly of Jamaica, in Kingston, was elected in 1943. By 1957 the Baháʼís of Jamaica were organized under the regional National Spiritual Assembly of the Greater Antilles, and on the eve of national independence in 1962, the Jamaica Baháʼís elected their own National Spiritual Assembly in 1961. By 1981 hundreds of Baháʼís and hundreds more non-Baháʼís turned out for weekend meetings when Rúhíyyih Khánum spent six days in Jamaica. Public recognition of the religion came in the form of the Governor General of Jamaica, Sir Howard Cooke, proclaiming a National Baháʼí Day first on July 25 in 2003 and it has been an annual event since. While there is evidence of several active communities by 2008 in Jamaica, estimates of the Baháʼís population range from the hundreds to the thousands.

Jamaica is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning 10,990 square kilometres (4,240 sq mi) in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about 145 kilometres (90 mi) south of Cuba, and 191 kilometres (119 mi) west of Hispaniola ; the British Overseas Territory of the Cayman Islands lies some 215 kilometres (134 mi) to the north-west.
National Day of Galicia (Galicia, Spain)

Dia Nacional de Galicia is when the autonomous community of Galicia in Spain celebrates its national holiday. It falls on 25 July.

Galicia is an autonomous community of Spain and historic nationality under Spanish law. Located in the northwest Iberian Peninsula, it includes the provinces of A Coruña, Lugo, Ourense, and Pontevedra.
Puerto Rico Constitution Day (Puerto Rico)
Law #1 of August 4, 1952 of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico established a full state holiday on July 25 of every year, to be known as Puerto Rico Constitution Day. The holiday commemorates the day the Constitution of Puerto Rico, approved on July 3, 1952, was signed into law by Governor Luis Muñoz Marín the same year.

Puerto Rico, officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Caribbean island and unincorporated territory of the United States. It is located in the northeast Caribbean Sea, approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Miami, Florida, between the Dominican Republic and the U.S. Virgin Islands, and includes the eponymous main island and several smaller islands, such as Mona, Culebra, and Vieques. It has roughly 3.2 million residents, and its capital and most populous city is San Juan. Spanish and English are the official languages of the executive branch of government, though Spanish predominates.
Republic Day (Tunisia)
This is a list of holidays in Tunisia.January 1: New Year's Day March 20: Independence Day April 9: Martyrs' Day May 1: Labour Day July 25: Republic Day August 13: Women's Day October 15: Evacuation Day December 17: Revolution Day Eid al-Fitr Eid al-Adha Islamic New Year Mawlid