
Knesset
The Knesset is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government.
The Knesset passes the controversial Nationality Bill, which defines the State of Israel as the nation-state of the Jewish people.

The Knesset is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government.
Basic Law: Israel as the Nation-State of the Jewish People, informally known as the Nation-State Bill or the Nationality Bill, is an Israeli Basic Law which specifies the nature of the State of Israel as the nation-state of the Jewish people. The law was passed by the Knesset—with 62 in favour, 55 against, and two abstentions—on 19 July 2018, and is largely symbolic and declarative in nature. However, it was met with sharp criticism internationally, including from several prominent Jewish American organizations, and has been branded as racist and undemocratic by some critics.

Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest; it is also bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally.

A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.

Jews or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites and Hebrews of historical Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the ethnic religion of the Jewish people, although its observance varies from strict to none.
Unidentified gunmen perpetrated an armed assault against an Egyptian military checkpoint in the Libyan Desert, killing 22 border guards.
The 2014 Farafra ambush occurred on 19 July 2014 when unidentified gunmen ambushed a desert checkpoint in the Farafra Oasis Road in Egypt's New Valley Governorate. Twenty-two border guards were killed in the attack, which was one of the biggest since the July 2013 ouster of Egyptian president Mohamed Morsi and the second at the same checkpoint in less than three months.

The Libyan Desert is a geographical region filling the north-eastern Sahara Desert, from eastern Libya to the Western Desert of Egypt and far northwestern Sudan. On medieval maps, its use predates today's Sahara, and parts of the Libyan Desert include the Sahara's most arid and least populated regions; this is chiefly what sets the Libyan Desert apart from the greater Sahara. The consequent absence of grazing, and near absence of waterholes or wells needed to sustain camel caravans, prevented Trans-Saharan trade between Kharga close to the Nile, and Murzuk in the Libyan Fezzan. This obscurity saw the region overlooked by early European explorers, and it was not until the early 20th century and the advent of the motor car before the Libyan Desert started to be fully explored.
Gunmen in Egypt's western desert province of New Valley Governorate attack a military checkpoint, killing at least 21 soldiers. Egypt reportedly declares a state of emergency on its border with Sudan.

New Valley Governorate or El Wadi El Gedid Governorate is one of the governorates of Egypt. It is in the southwestern part of the country, in the south of Egypt Western Desert, between the Nile, northern Sudan, and southeastern Libya.
The 2014 Farafra ambush occurred on 19 July 2014 when unidentified gunmen ambushed a desert checkpoint in the Farafra Oasis Road in Egypt's New Valley Governorate. Twenty-two border guards were killed in the attack, which was one of the biggest since the July 2013 ouster of Egyptian president Mohamed Morsi and the second at the same checkpoint in less than three months.

A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state during a natural disaster, civil unrest, armed conflict, medical pandemic or epidemic or other biosecurity risk. Justitium is its equivalent in Roman law—a concept in which the Roman Senate could put forward a final decree that was not subject to dispute yet helped save lives in times of strife.
The NASA spacecraft Cassini took a photograph of Saturn with Earth in the distance (detail pictured), for which people were invited to "wave at Saturn".

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.

Cassini–Huygens, commonly called Cassini, was a space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, including its rings and natural satellites. The Flagship-class robotic spacecraft comprised both NASA's Cassini space probe and ESA's Huygens lander, which landed on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Cassini was the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter its orbit, where it stayed from 2004 to 2017. The two craft took their names from the astronomers Giovanni Cassini and Christiaan Huygens.

The Day the Earth Smiled is a composite photograph taken by the NASA spacecraft Cassini on July 19, 2013. During an eclipse of the Sun, the spacecraft turned to image Saturn and most of its visible ring system, as well as Earth and the Moon as distant pale dots. The spacecraft had twice taken similar photographs in its previous nine years in orbit around the planet. The name also refers to the activities associated with the event, as well as to the photographic mosaic created from it.

Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; however, with its larger volume, Saturn is over 95 times more massive.
Syrian civil war: The People's Protection Units (YPG) capture the city of Kobanî without resistance, starting the Rojava conflict in Northeast Syria.

The Syrian civil war is an ongoing multi-sided civil war in Syria fought between the Syrian Arab Republic led by Syrian president Bashar al-Assad and various domestic and foreign forces that oppose both the Syrian government and each other, in varying combinations.

The People's Defense Units (YPG), also called People's Protection Units, is a mainly-Kurdish militia in Syria and the primary component of the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF).

Kobanî, officially Ayn al-Arab, is a Kurdish-majority city in northern Syria, lying immediately south of the Syria–Turkey border. As a consequence of the Syrian civil war, the city came under the control of the Kurdish-majority People's Protection Units (YPG) militia in 2012 and became the administrative center of the Kobani Canton, later transformed into Euphrates Region of the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria.

The Rojava conflict, also known as the Rojava Revolution, is a political upheaval and military conflict taking place in northern Syria, known among Kurds as Western Kurdistan or Rojava.
Guinean President Alpha Condé survives an attempted assassination and coup d'état at his residence in Conakry.

Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Cote d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sierra Leone and Liberia to the south. It is sometimes referred to as Guinea-Conakry after its capital Conakry, to distinguish it from other territories in the eponymous region such as Guinea-Bissau and Equatorial Guinea. It has a population of 13.5 million and an area of 245,857 square kilometres (94,926 sq mi).

Alpha Condé is a Guinean politician who served as the fourth president of Guinea from 2010 to 2021.
The Sekhoutoureah Presidential Palace in Conakry, Guinea is the official residence of the President of Guinea. The Palais Presidentiel Sekhoutoureah is behind the Cathédrale Sainte-Marie.

Conakry is the capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its population as of the 2014 Guinea census was 1,660,973.
The Troubles: The Provisional Irish Republican Army announced that it would resume its ceasefire, ending its 28-year campaign against British rule in Northern Ireland.

The Troubles were an ethno-nationalist conflict in Northern Ireland that lasted about 30 years from the late 1960s to 1998. Also known internationally as the Northern Ireland conflict, it is sometimes described as an "irregular war" or "low-level war". The conflict began in the late 1960s and is usually deemed to have ended with the Good Friday Agreement of 1998. Although the Troubles mostly took place in Northern Ireland, at times violence spilled over into parts of the Republic of Ireland, England and mainland Europe.

The Irish Republican Army, also known as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, and informally as the Provos, was an Irish republican paramilitary organisation that sought to end British rule in Northern Ireland, facilitate Irish reunification and bring about an independent, socialist republic encompassing all of Ireland. It was the most active republican paramilitary group during the Troubles. It saw itself as the army of the all-island Irish Republic and as the sole legitimate successor to the original IRA from the Irish War of Independence. It was designated a terrorist organisation in the United Kingdom and an unlawful organisation in the Republic of Ireland, both of whose authority it rejected.

From 1969 until 1997, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) conducted an armed paramilitary campaign primarily in Northern Ireland and England, aimed at ending British rule in Northern Ireland in order to create a united Ireland.
The Troubles: The Provisional Irish Republican Army resumes a ceasefire to end their 25-year paramilitary campaign to end British rule in Northern Ireland.

The Troubles were an ethno-nationalist conflict in Northern Ireland that lasted about 30 years from the late 1960s to 1998. Also known internationally as the Northern Ireland conflict, it is sometimes described as an "irregular war" or "low-level war". The conflict began in the late 1960s and is usually deemed to have ended with the Good Friday Agreement of 1998. Although the Troubles mostly took place in Northern Ireland, at times violence spilled over into parts of the Republic of Ireland, England and mainland Europe.

The Irish Republican Army, also known as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, and informally as the Provos, was an Irish republican paramilitary organisation that sought to end British rule in Northern Ireland, facilitate Irish reunification and bring about an independent, socialist republic encompassing all of Ireland. It was the most active republican paramilitary group during the Troubles. It saw itself as the army of the all-island Irish Republic and as the sole legitimate successor to the original IRA from the Irish War of Independence. It was designated a terrorist organisation in the United Kingdom and an unlawful organisation in the Republic of Ireland, both of whose authority it rejected.

From 1969 until 1997, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) conducted an armed paramilitary campaign primarily in Northern Ireland and England, aimed at ending British rule in Northern Ireland in order to create a united Ireland.
A car bomb killed the anti-Mafia judge Paolo Borsellino and five policemen in Palermo, Italy, less than two months after the murder of Borsellino's friend and colleague Giovanni Falcone.

The via D'Amelio bombing was a terrorist attack by the Sicilian Mafia, which took place in Palermo, Sicily, Italy, on 19 July 1992. It killed Paolo Borsellino, the anti-mafia Italian magistrate, and five members of his police escort: Agostino Catalano, Emanuela Loi, Vincenzo Li Muli, Walter Eddie Cosina, and Claudio Traina.
"Mafia" is an informal term that is used to describe criminal organizations that bear a strong similarity to the Italian Mafia. The central activity of such an organization would be the arbitration of disputes between criminals as well as the organization and enforcement of illicit agreements between criminals through the use of or threat of violence. Mafias often engage in secondary activities such as gambling, loan sharking, drug-trafficking, prostitution, and fraud.

Paolo Emanuele Borsellino was an Italian judge and prosecuting magistrate. From his office in the Palace of Justice in Palermo, Sicily, he spent most of his professional life trying to overthrow the power of the Sicilian Mafia. After a long and distinguished career, culminating in the Maxi Trial in 1986–1987, on 19 July 1992, Borsellino was killed by a car bomb in Via D'Amelio, near his mother's house in Palermo.

Palermo is a city in southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is in the northwest of the island of Sicily, by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea.

Giovanni Falcone was an Italian judge and prosecuting magistrate. From his office in the Palace of Justice in Palermo, Sicily, he spent most of his professional life trying to overthrow the power of the Sicilian Mafia. After a long and distinguished career, culminating in the Maxi Trial in 1986–1987, on 23 May 1992, Falcone was assassinated by the Corleonesi Mafia in the Capaci bombing, on the A29 motorway near the town of Capaci.
A car bomb kills Judge Paolo Borsellino and five members of his escort.

The via D'Amelio bombing was a terrorist attack by the Sicilian Mafia, which took place in Palermo, Sicily, Italy, on 19 July 1992. It killed Paolo Borsellino, the anti-mafia Italian magistrate, and five members of his police escort: Agostino Catalano, Emanuela Loi, Vincenzo Li Muli, Walter Eddie Cosina, and Claudio Traina.
United Airlines Flight 232 crashes in Sioux City, Iowa killing 111.

United Airlines Flight 232 was a regularly scheduled United Airlines flight from Stapleton International Airport in Denver to O'Hare International Airport in Chicago, continuing to Philadelphia International Airport. On July 19, 1989, the DC-10 serving the flight crash-landed at Sioux City, Iowa, after suffering a catastrophic failure of its tail-mounted engine due to an unnoticed manufacturing defect in the engine's fan disk, which led to the loss of many flight controls. Of the 296 passengers and crew on board, 112 died during the accident, while 184 people survived. It is also the deadliest single-aircraft accident in the history of United Airlines.
The Val di Stava dam collapses killing 268 people in Val di Stava, Italy.
The Val di Stava Dam collapse occurred on 19 July 1985, when two tailings dams above the village of Stava, near Tesero, Italy, failed. It resulted in one of Italy's worst disasters, killing 268 people, destroying 63 buildings and demolishing eight bridges.
The first three-dimensional reconstruction of a human head in a CT is published.
Michael W. Vannier is a radiologist in Chicago.
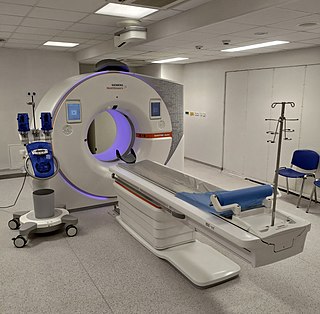
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.
In one of the first militant attacks by Hezbollah, David S. Dodge, president of the American University of Beirut, is kidnapped.

Hezbollah is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's paramilitary wing is the Jihad Council, and its political wing is the Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc party in the Lebanese Parliament.
David Stuart Dodge was an American politician and university president. He was the Vice-President for Administration (1979–83), Acting President (1981–82) and President (1996–97) of the American University of Beirut (AUB).

The American University of Beirut (AUB) is a private, non-sectarian, and independent university chartered in New York with its campus in Beirut, Lebanon. AUB is governed by a private, autonomous board of trustees and offers programs leading to bachelor's, master's, MD, and PhD degrees.
In a private meeting with U.S. President Ronald Reagan, French President François Mitterrand reveals the existence of the Farewell Dossier, a collection of documents showing the Soviet Union had been stealing American technological research and development.

Ronald Wilson Reagan was an American politician who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. A member of the Republican Party from 1962 onward, he also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 to 1975 after having a career as a Hollywood actor and union leader.

François Marie Adrien Maurice Mitterrand was President of France, serving under that position from 1981 to 1995, the longest time in office in the history of France. As First Secretary of the Socialist Party, he was the first left-wing politician to assume the presidency under the Fifth Republic.
The Farewell Dossier was the collection of documents that Colonel Vladimir Vetrov, a KGB defector "en place", gathered and gave to the Direction de la surveillance du territoire (DST) in 1981–82, during the Cold War.
Opening of the Summer Olympics in Moscow.

The 1980 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XXII Olympiad and commonly known as Moscow 1980, were an international multi-sport event held from 19 July to 3 August 1980 in Moscow, Soviet Union, in present-day Russia. The games were the first to be staged in an Eastern Bloc country, as well as the first Olympic Games and only Summer Olympics to be held in a Slavic language-speaking country. They were also the only Summer Olympic Games to be held in a self-proclaimed communist country until the 2008 Summer Olympics held in China. These were the final Olympic Games under the IOC Presidency of Michael Morris, 3rd Baron Killanin before he was succeeded by Juan Antonio Samaranch, a Spaniard, shortly afterwards. Eighty nations were represented at the Moscow Games, the smallest number since 1956. Led by the United States, 66 countries boycotted the games entirely, because of the Soviet–Afghan War. Several alternative events were held outside of the Soviet Union. Some athletes from some of the boycotting countries participated in the games under the Olympic Flag. The Soviet Union later boycotted the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles. The Soviet Union won the most gold and overall medals, and together with East Germany more than half of the available gold and overall medals.

Moscow is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 20 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of 2,511 square kilometers (970 sq mi), while the urban area covers 5,891 square kilometers (2,275 sq mi), and the metropolitan area covers over 26,000 square kilometers (10,000 sq mi). Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent.
The Sandinista rebels overthrow the government of the Somoza family in Nicaragua.

The Sandinista National Liberation Front is a socialist political party in Nicaragua. Its members are called Sandinistas in both English and Spanish. The party is named after Augusto César Sandino, who led the Nicaraguan resistance against the United States occupation of Nicaragua in the 1930s.

A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.

Anastasio "Tachito" Somoza Debayle was the President of Nicaragua from 1 May 1967 to 1 May 1972 and from 1 December 1974 to 17 July 1979. As head of the National Guard, he was de facto ruler of the country between 1972 and 1974, even during the period when he was not the de jure ruler.

Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the largest country in the Central American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the northwest, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. As of 2015, it was estimated to be the second largest city in Central America. The multi-ethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English.
The oil tanker SS Atlantic Empress collides with another oil tanker, causing the largest ever ship-borne oil spill.
SS Atlantic Empress was a Greek oil tanker that in 1979 collided with the oil tanker Aegean Captain in the Caribbean, and eventually sank, having created the fifth largest oil spill on record and the largest ship-based spill having spilled 287,000 metric tonnes of crude oil into the Caribbean Sea. It was built at the Odense Staalskibsværft shipyard in Odense, Denmark, and launched on 16 February 1974.
This is a reverse-chronological list of oil spills that have occurred throughout the world and spill(s) that are currently ongoing. Quantities are measured in tonnes of crude oil with one tonne roughly equal to 308 US gallons, 256 Imperial gallons, 7.33 barrels, or 1165 litres. This calculation uses a median value of 0.858 for the specific gravity of light crude oil; actual values can range from 0.816 to 0.893, so the amounts shown below are inexact. They are also estimates, because the actual volume of an oil spill is difficult to measure exactly.
The world's first Global Positioning System (GPS) signal was transmitted from Navigation Technology Satellite 2 (NTS-2) and received at Rockwell Collins in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, at 12:41 a.m. Eastern time (ET).

The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephonic or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver.

Rockwell Collins was a multinational corporation headquartered in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, providing avionics and information technology systems and services to government agencies and aircraft manufacturers. It was formed when the Collins Radio Company, facing financial difficulties, was purchased by Rockwell International in 1973. In 2001, the avionics division of Rockwell International was spun off to form the current Rockwell Collins, Inc, retaining its name.

Cedar Rapids is the second-largest city in Iowa, United States and is the county seat of Linn County. The city lies on both banks of the Cedar River, 20 miles (32 km) north of Iowa City and 100 miles (160 km) northeast of Des Moines, the state's capital and largest city. It is a part of the Cedar Rapids/Iowa City region of Eastern Iowa, which includes Linn, Benton, Cedar, Iowa, Jones, Johnson, and Washington counties.
Sagarmatha National Park in Nepal is created.

Sagarmāthā National Park is a national park in the Himalayas of eastern Nepal that is dominated by Mount Everest. It encompasses an area of 1,148 km2 (443 sq mi) in the Solukhumbu District and ranges in elevation from 2,845 to 8,848 m at the summit of Mount Everest. In the north, it shares the international border with Qomolangma National Nature Preserve of Tibet. In the east, it is adjacent to Makalu Barun National Park, and in the south it extends to Dudh Kosi river. It is part of the Sacred Himalayan Landscape.
Nepal, formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city.
Dhofar Rebellion: British SAS units help the Omani government against Popular Front for the Liberation of Oman rebels in the Battle of Mirbat.

The Dhofar Rebellion, also known as the Dhofar War or the Omani Civil War, was waged from 1963 to 1976 in the province of Dhofar against the Sultanate of Muscat and Oman. The war began with the formation of the Dhofar Liberation Front, a group which aimed to create an independent state in Dhofar, free from the rule of the Omani Sultan Said bin Taimur. The rebels also held the broader goals of Arab nationalism which included ending British influence in the Persian Gulf region.

The Special Air Service (SAS) is a special forces unit of the British Army. It was founded as a regiment in 1941 by David Stirling and in 1950, it was reconstituted as a corps. The unit specialises in a number of roles including counter-terrorism, hostage rescue, direct action and covert reconnaissance. Much of the information about the SAS is highly classified, and the unit is not commented on by either the British government or the Ministry of Defence due to the secrecy and sensitivity of its operations.

Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of the Persian Gulf. Oman shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen, while sharing maritime borders with Iran and Pakistan. The coast is formed by the Arabian Sea on the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman on the northeast. The Madha and Musandam exclaves are surrounded by the United Arab Emirates on their land borders, with the Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman forming Musandam's coastal boundaries. Muscat is the nation's capital and largest city.

The Popular Front for the Liberation of Oman was a Marxist and Arab nationalist revolutionary organisation in the Sultanate of Oman. It fought against the Sultan (ruler) in the Dhofar Rebellion from the PFLO's foundation until the suppression of the insurgency in 1976.

The Battle of Mirbat was an attack by Communist guerrillas targeting an Omani government position during the Dhofar Rebellion in the town of Mirbat, Oman. During the Dhofar Rebellion, Britain assisted the Omani government by sending elements of its Special Air Service (SAS) both to train soldiers and fight against the Popular Front for the Liberation of the Occupied Arabian Gulf (PFLOAG) guerrillas, also known as the Adoo. The assault was defeated after the arrival of several BAC Strikemaster jetfighters belonging to Oman, firing rockets at PFLOAG's positions which forced the guerrillas to retreat.
Chappaquiddick incident: U.S. Senator Ted Kennedy crashes his car into a tidal pond at Chappaquiddick Island, Massachusetts, killing his passenger Mary Jo Kopechne.

The Chappaquiddick incident occurred on Chappaquiddick Island in Massachusetts some time around midnight between July 18 and 19, 1969, when Senator Edward M. "Ted" Kennedy negligently drove his car off a narrow bridge, causing it to overturn in a tidal pond. This resulted in the drowning death of his 28-year-old passenger Mary Jo Kopechne, who was trapped inside the vehicle.

Edward Moore Kennedy was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States senator from Massachusetts for almost 47 years, from 1962 until his death in 2009. A member of the Democratic Party and the prominent political Kennedy family, he was the second most senior member of the Senate when he died. He is ranked fifth in United States history for length of continuous service as a senator. Kennedy was the younger brother of President John F. Kennedy and U.S. attorney general and U.S. senator Robert F. Kennedy. He was the father of Congressman Patrick J. Kennedy.

Chappaquiddick Island, a part of the town of Edgartown, Massachusetts, is a small peninsula and occasional island on the eastern end of Martha's Vineyard. Norton Point, a narrow barrier beach, connects Martha's Vineyard and Chappaquiddick between Katama and Wasque. Occasional breaches occur due to hurricanes and strong storms separating the islands for periods of time. Most recently, the two were separated for 8 years from 2007 to 2015. While both land forms have mostly been connected to one another in modern history, Chappaquiddick is nevertheless referred to as an island.

Mary Jo Kopechne was an American secretary, and one of the campaign workers for U.S. Senator Robert F. Kennedy's 1968 presidential campaign, a close team known as the "Boiler Room Girls". In 1969, she drowned when a car driven by U.S. Senator Ted Kennedy left a narrow road on Chappaquiddick Island and overturned into Poucha Pond.
Piedmont Airlines Flight 22, a Piedmont Airlines Boeing 727-22 and a twin-engine Cessna 310 collided over Hendersonville, North Carolina, USA. Both aircraft were destroyed and all passengers and crew were killed, including John T. McNaughton, an advisor to Robert McNamara.

Piedmont Airlines Flight 22 was a Piedmont Airlines Boeing 727-22 that collided with a twin-engine Cessna 310 on July 19, 1967, over Hendersonville, North Carolina, United States. Both aircraft were destroyed and all passengers and crew were killed, including John T. McNaughton, an advisor to U.S. Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara. The aircraft were both operating under instrument flight rules and were in radio contact with the Asheville control tower, though on different frequencies. The accident investigation was the first of a major scale conducted by the newly created National Transportation Safety Board. A review of the investigation conducted 39 years after the crash upheld the original findings that had placed primary responsibility on the Cessna pilot.

Piedmont Airlines was a United States airline from 1948 to 1989, when it was acquired by and merged into USAir. Its headquarters were at One Piedmont Plaza in Winston-Salem, North Carolina, a building that is now part of Wake Forest University.

The Boeing 727 is an American narrow-body airliner that was developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. After the heavy 707 quad-jet was introduced in 1958, Boeing addressed the demand for shorter flight lengths from smaller airports. On December 5, 1960, the 727 was launched with 40 orders each from United Airlines and Eastern Air Lines. The first 727-100 rolled out November 27, 1962, first flew on February 9, 1963, and entered service with Eastern on February 1, 1964.

The Cessna 310 is an American four-to-six-seat, low-wing, twin-engine monoplane produced by Cessna between 1954 and 1980. It was the first twin-engine aircraft that Cessna put into production after World War II.

Hendersonville is a city in Henderson County, North Carolina, United States. It is 22 miles (35 km) south of Asheville and is the county seat of Henderson County. Like the county, the city is named for 19th-century North Carolina Supreme Court Chief Justice Leonard Henderson.

The United States of America, commonly known as the United States or informally America, is a country in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. It is the third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. It has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 331 million, it is the third most populous country in the world. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City.

John Theodore McNaughton born in Bicknell, Indiana, was United States Assistant Secretary of Defense for International Security Affairs and Robert S. McNamara's closest advisor. He died in a plane crash at age 45, just before he was to become Secretary of the Navy.

Robert Strange McNamara was an American business executive and the eighth United States Secretary of Defense, serving from 1961 to 1968 under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson. He remains the longest serving Secretary of Defense, having remained in office over seven years. He played a major role in promoting the United States' involvement in the Vietnam War. McNamara was responsible for the institution of systems analysis in public policy, which developed into the discipline known today as policy analysis.
Vietnam War: At a rally in Saigon, South Vietnamese Prime Minister Nguyễn Khánh calls for expanding the war into North Vietnam.

The Vietnam War was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975.

Ho Chi Minh City, formerly known as Saigon, is the largest city in Vietnam, with a population of around 9 million in 2019. Situated in the southeast region of Vietnam, the city surrounds the Saigon River and covers about 2,061 km2 (796 sq mi).

South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam, was a country in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975, the period when the southern portion of Vietnam was a member of the Western Bloc during part of the Cold War after the 1954 division of Vietnam. It first received international recognition in 1949 as the State of Vietnam within the French Union, with its capital at Saigon, before becoming a republic in 1955. South Vietnam was bordered by North Vietnam to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and Thailand across the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. Its sovereignty was recognized by the United States and 87 other nations, though it failed to gain admission into the United Nations as a result of a Soviet veto in 1957. It was succeeded by the Republic of South Vietnam in 1975.

A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not the head of state, but rather the head of government, serving under either a monarch in a democratic constitutional monarchy or under a president in a republican form of government.

Nguyễn Khánh was a South Vietnamese military officer and Army of the Republic of Vietnam general who served in various capacities as head of state and prime minister of South Vietnam while at the head of a military junta from January 1964 until February 1965. He was involved in or against many coup attempts, failed and successful, from 1960 until his defeat and exile from South Vietnam in 1965. Khánh lived out his later years with his family in exile in the United States. He died in 2013 in San Jose, California, at age 85.

North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam was a socialist state supported by the Soviet Union (USSR) and the People's Republic of China (PRC) in Southeast Asia that existed from 1945 to 1976 and was recognized in 1954. Both the North Vietnamese and South Vietnamese states ceased to exist when they unified as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
Joe Walker flies a North American X-15 to a record altitude of 106,010 meters (347,800 feet) on X-15 Flight 90. Exceeding an altitude of 100 km, this flight qualifies as a human spaceflight under international convention.

Joseph Albert Walker was an American World War II pilot, experimental physicist, NASA test pilot, and astronaut who was the first person to fly an airplane to space. He was one of twelve pilots who flew the North American X-15, an experimental spaceplane jointly operated by the Air Force and NASA.

The North American X-15 is a hypersonic rocket-powered aircraft. It was operated by the United States Air Force and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as part of the X-plane series of experimental aircraft. The X-15 set speed and altitude records in the 1960s, reaching the edge of outer space and returning with valuable data used in aircraft and spacecraft design. The X-15's highest speed, 4,520 miles per hour, was achieved on 3 October 1967, when William J. Knight flew at Mach 6.7 at an altitude of 102,100 feet (31,120 m), or 19.34 miles. This set the official world record for the highest speed ever recorded by a crewed, powered aircraft, which remains unbroken.

Flight 90 of the North American X-15 was a research flight conducted by NASA and the US Air Force on July 19, 1963. It was the first of two X-15 missions that passed the 100-km high Kármán line, the FAI definition of space, along with Flight 91 the next month. The X-15 was flown by Joseph A. Walker, who flew both X-15 spaceflights over the Kármán line.

Human spaceflight is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be remotely operated from ground stations on Earth, or autonomously, without any direct human involvement. People trained for spaceflight are called astronauts, cosmonauts (Russian), or taikonauts (Chinese); and non-professionals are referred to as spaceflight participants or spacefarers.
Tunisia imposes a blockade on the French naval base at Bizerte; the French would capture the entire town four days later.

The Bizerte crisis occurred in July 1961 when Tunisia imposed a blockade on the French naval base at Bizerte, Tunisia, hoping to force its evacuation. The crisis culminated in a three-day battle between French and Tunisian forces that left some 630 Tunisians and 24 French dead and eventually led to France ceding the city and naval base to Tunisia in 1963.

Bizerte or Bizerta the classical Hippo, is a city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia. It is the northernmost city in Africa, located 65 km (40mil) north of the capital Tunis. It is also known as the last town to remain under French control after the rest of the country won its independence from France. The city had 142,966 inhabitants in 2014.
The largely autobiographical novel The Ordeal of Gilbert Pinfold by Evelyn Waugh was published.
An autobiographical novel is a form of novel using autofiction techniques, or the merging of autobiographical and fictive elements. The literary technique is distinguished from an autobiography or memoir by the stipulation of being fiction. Because an autobiographical novel is partially fiction, the author does not ask the reader to expect the text to fulfill the "autobiographical pact". Names and locations are often changed and events are recreated to make them more dramatic but the story still bears a close resemblance to that of the author's life. While the events of the author's life are recounted, there is no pretense of exact truth. Events may be exaggerated or altered for artistic or thematic purposes.

The Ordeal of Gilbert Pinfold is a novel by the British writer Evelyn Waugh, first published in July 1957. It is Waugh's penultimate full-length work of fiction, which the author called his "mad book"—a largely autobiographical account of a period of hallucinations caused by bromide intoxication that he experienced in the early months of 1954, recounted through his protagonist Gilbert Pinfold.

Arthur Evelyn St. John Waugh was an English writer of novels, biographies, and travel books; he was also a prolific journalist and book reviewer. His most famous works include the early satires Decline and Fall (1928) and A Handful of Dust (1934), the novel Brideshead Revisited (1945), and the Second World War trilogy Sword of Honour (1952–1961). He is recognised as one of the great prose stylists of the English language in the 20th century.
The largely autobiographical novel The Ordeal of Gilbert Pinfold by Evelyn Waugh was published.
An autobiographical novel is a form of novel using autofiction techniques, or the merging of autobiographical and fictive elements. The literary technique is distinguished from an autobiography or memoir by the stipulation of being fiction. Because an autobiographical novel is partially fiction, the author does not ask the reader to expect the text to fulfill the "autobiographical pact". Names and locations are often changed and events are recreated to make them more dramatic but the story still bears a close resemblance to that of the author's life. While the events of the author's life are recounted, there is no pretense of exact truth. Events may be exaggerated or altered for artistic or thematic purposes.

The Ordeal of Gilbert Pinfold is a novel by the British writer Evelyn Waugh, first published in July 1957. It is Waugh's penultimate full-length work of fiction, which the author called his "mad book"—a largely autobiographical account of a period of hallucinations caused by bromide intoxication that he experienced in the early months of 1954, recounted through his protagonist Gilbert Pinfold.

Arthur Evelyn St. John Waugh was an English writer of novels, biographies, and travel books; he was also a prolific journalist and book reviewer. His most famous works include the early satires Decline and Fall (1928) and A Handful of Dust (1934), the novel Brideshead Revisited (1945), and the Second World War trilogy Sword of Honour (1952–1961). He is recognised as one of the great prose stylists of the English language in the 20th century.
Opening of the Summer Olympics in Helsinki, Finland.

The 1952 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XV Olympiad and commonly known as Helsinki 1952, were an international multi-sport event held from 19 July to 3 August 1952 in Helsinki, Finland.

Helsinki is the capital, primate, and most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of 658,864. The city's urban area has a population of 1,268,296, making it by far the most populous urban area in Finland as well as the country's most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research; while Tampere in the Pirkanmaa region, located 179 kilometres (111 mi) to the north from Helsinki, is the second largest urban area in Finland. Helsinki is located 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of Tallinn, Estonia, 400 km (250 mi) east of Stockholm, Sweden, and 300 km (190 mi) west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has close historical ties with these three cities.
Prime Minister of the shadow Burmese government, Bogyoke Aung San and eight others are assassinated.

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also known as Burma, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia, and has a population of about 54 million as of 2017. Myanmar is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (Rangoon).

Aung San was a Burmese politician, independence activist and revolutionary. He was instrumental in Myanmar's struggle for independence from British rule, but he was assassinated just six months before his goal was realized. Aung San is considered the founder of modern-day Myanmar and the Tatmadaw, and is commonly referred to by the titles "Father of the Nation", "Father of Independence", and "Father of the Tatmadaw".
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have a direct role in matters of the state, may also sometimes be considered an assassination. An assassination may be prompted by political and military motives, or done for financial gain, to avenge a grievance, from a desire to acquire fame or notoriety, or because of a military, security, insurgent or secret police group's command to carry out the assassination. Acts of assassination have been performed since ancient times. A person who carries out an assassination is called an assassin or hitman.
Korean politician Lyuh Woon-hyung is assassinated.

Lyuh Woon-hyung or Yo Un-hyung was a Korean politician who argued that Korean independence was essential to world peace, and a reunification activist who struggled for the independent reunification of Korea following its national division in 1945.
World War II: Rome is heavily bombed by more than 500 Allied aircraft, inflicting thousands of casualties.

The bombing of Rome in World War II took place on several occasions in 1943 and 1944, primarily by Allied and to a smaller degree by Axis aircraft, before the city was liberated by the Allies on June 4, 1944. Pope Pius XII was initially unsuccessful in attempting to have Rome declared an open city, through negotiations with U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt via Archbishop Francis Spellman. Rome was eventually declared an open city on August 14, 1943 by the defending Italian forces.
World War II: The Second Happy Time of Hitler's submarines comes to an end, as the increasingly effective American convoy system compels them to return to the central Atlantic.

The "Second Happy Time" was a phase in the Battle of the Atlantic during which Axis submarines attacked merchant shipping and Allied naval vessels along the east coast of North America. The first "Happy Time" was in 1940–1941 in the North Atlantic and North Sea. Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini declared war on the United States on 11 December 1941, and as a result their navies could begin the "Second Happy Time".
World War II: Battle of Cape Spada: The Royal Navy and the Regia Marina clash; the Italian light cruiser Bartolomeo Colleoni sinks, with 121 casualties.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

The Battle of Cape Spada was a naval battle during the Battle of the Mediterranean in Second World War. It took place on 19 July 1940 in the Mediterranean Sea off Cape Spada, the north-western extremity of Crete.

The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service.

The Regia Marina was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic, the Regia Marina changed its name to Marina Militare.

Bartolomeo Colleoni was an Italian condottiero, who became captain-general of the Republic of Venice. Colleoni "gained reputation as the foremost tactician and disciplinarian of the 15th century". He is also credited with having refurbished the Roman baths at Trescore Balneario.
Field Marshal Ceremony: First occasion in World War II that Adolf Hitler appoints field marshals due to military achievements.

The 1940 Field Marshal Ceremony refers to a promotion ceremony held at the Kroll Opera House in Berlin in which Adolf Hitler promoted twelve generals to the rank of Generalfeldmarschall on 19 July 1940. It was the first occasion in World War II that Hitler appointed field marshals due to military achievements.

Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of Führer und Reichskanzler in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated World War II in Europe by invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of about six million Jews and millions of other victims.
World War II: Army order 112 forms the Intelligence Corps of the British Army.

The Intelligence Corps is a corps of the British Army. It is responsible for gathering, analysing and disseminating military intelligence and also for counter-intelligence and security. The Director of the Intelligence Corps is a brigadier.

The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. As of 2022, the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel.
Spanish Civil War: The CNT and UGT call a general strike in Spain – mobilizing workers' militias against the Nationalist forces.

The Spanish Civil War was a civil war in Spain fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republicans and the Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the left-leaning Popular Front government of the Second Spanish Republic, and consisted of various socialist, communist, separatist, anarchist, and republican parties, some of which had opposed the government in the pre-war period. The opposing Nationalists were an alliance of Falangists, monarchists, conservatives, and traditionalists led by a military junta among whom General Francisco Franco quickly achieved a preponderant role. Due to the international political climate at the time, the war had many facets and was variously viewed as class struggle, a religious struggle, a struggle between dictatorship and republican democracy, between revolution and counterrevolution, and between fascism and communism. According to Claude Bowers, U.S. ambassador to Spain during the war, it was the "dress rehearsal" for World War II. The Nationalists won the war, which ended in early 1939, and ruled Spain until Franco's death in November 1975.

The Confederación Nacional del Trabajo is a Spanish confederation of anarcho-syndicalist labor unions, which was long affiliated with the International Workers' Association (AIT). When working with the latter group it was also known as CNT-AIT. Historically, the CNT has also been affiliated with the Federación Anarquista Ibérica ; thus, it has also been referred to as the CNT-FAI. Throughout its history, it has played a major role in the Spanish labor movement.

The Unión General de Trabajadores is a major Spanish trade union, historically affiliated with the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE).
A general strike refers to a strike action in which participants cease all economic activity, such as working, to strengthen the bargaining position of a trade union or achieve a common social or political goal. They are organised by large coalitions of political, social, and labour organizations and may also include rallies, marches, boycotts, civil disobedience, non-payment of taxes, and other forms of direct or indirect action. Additionally, general strikes might exclude care workers, such as teachers, doctors, and nurses.

The Spanish Republic, commonly known as the Second Spanish Republic, was the form of government in Spain from 1931 to 1939. The Republic was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, after the deposition of King Alfonso XIII, and was dissolved on 1 April 1939 after surrendering in the Spanish Civil War to the Nationalists led by General Francisco Franco.

The Nationalist faction or Rebel faction was a major faction in the Spanish Civil War of 1936 to 1939. It was composed of a variety of right-leaning political groups that supported the Spanish Coup of July 1936 against the Second Spanish Republic and Republican faction and sought to depose Manuel Azaña, including the Falange, the CEDA, and two rival monarchist claimants: the Alfonsist Renovación Española and the Carlist Traditionalist Communion. In 1937, all the groups were merged into the FET y de las JONS. After the death of the faction's early leaders, General Francisco Franco, one of the members of the 1936 coup, would head the Nationalists throughout most of the war and emerge as the dictator of Spain until his death in 1975.
Following Peace Day celebrations marking the end of the First World War, English ex-servicemen unhappy with unemployment and other grievances rioted and burned down Luton Town Hall (pictured).

The Luton Peace Day Riots occurred over three days from 19 to 21 July 1919. Servicemen angry at the lavish spending for London's peace parade, held on the same day, following the end of the First World War, protested that the money should be spent on integrating soldiers returning from the war.

Luton Town Hall is a building at the junction between Manchester Street, Upper George Street and George Street, Luton, England; the current building was completed in 1936 on the site of the older Town Hall, which was burnt down 19 July 1919, following the Peace Day Riots. The current hall, which is the headquarters of Luton Borough Council, is a Grade II listed building.
First World War: The "worst 24 hours in Australia's entire history" occurred when Australian forces unsuccessfully attacked German defences at Fromelles, France.

World War I or the First World War, often abbreviated as WWI or WW1, and referred to by some Anglophone authors as the "Great War" or the "War to End All Wars", was a global conflict which lasted from 1914 to 1918, and is considered one of the deadliest conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war.
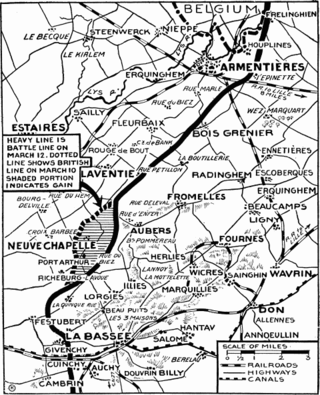
The Attack at Fromelles 19–20 July 1916, was a military operation on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack was carried out by British and Australian troops and was subsidiary to the Battle of the Somme. General Headquarters (GHQ) of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) had ordered the First Army and Second Army to prepare attacks to support the Fourth Army on the Somme, 50 mi (80 km) to the south, to exploit any weakening of the German defences opposite. The attack took place 9.9 mi (16 km) from Lille, between the Fauquissart–Trivelet road and Cordonnerie Farm, an area overlooked from Aubers Ridge to the south. The ground was low-lying and much of the defensive fortification by both sides consisted of building breastworks, rather than trenches.

Fromelles is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. As of 2019 it had a population of 1,041; its inhabitants are called Fromellois. It is located about 16 kilometres (10 mi) to the west of Lille.
World War I: Battle of Fromelles: British and Australian troops attack German trenches as part of the Battle of the Somme.

World War I or the First World War, often abbreviated as WWI or WW1, and referred to by some Anglophone authors as the "Great War" or the "War to End All Wars", was a global conflict which lasted from 1914 to 1918, and is considered one of the deadliest conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war.

The Attack at Fromelles 19–20 July 1916, was a military operation on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack was carried out by British and Australian troops and was subsidiary to the Battle of the Somme. General Headquarters (GHQ) of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) had ordered the First Army and Second Army to prepare attacks to support the Fourth Army on the Somme, 50 mi (80 km) to the south, to exploit any weakening of the German defences opposite. The attack took place 9.9 mi (16 km) from Lille, between the Fauquissart–Trivelet road and Cordonnerie Farm, an area overlooked from Aubers Ridge to the south. The ground was low-lying and much of the defensive fortification by both sides consisted of building breastworks, rather than trenches.

The 61st Division was an infantry division of the British Army raised in 1915 during the Great War as a second-line reserve for the first-line battalions of the 48th Division. The division was sent to the Western Front in May 1916 and served there for the duration of the First World War.

The First Australian Imperial Force was the main expeditionary force of the Australian Army during the First World War. It was formed as the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) following Britain's declaration of war on Germany on 15 August 1914, with an initial strength of one infantry division and one light horse brigade. The infantry division subsequently fought at Gallipoli between April and December 1915, with a newly raised second division, as well as three light horse brigades, reinforcing the committed units.

The German Empire, also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Kaiserreich, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a republic.

The Battle of the Somme, also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 November 1916 on both sides of the upper reaches of the Somme, a river in France. The battle was intended to hasten a victory for the Allies. More than three million men fought in the battle of whom one million were wounded or killed, making it one of the deadliest battles in human history.
French cyclist Maurice Garin won the first edition of the Tour de France.

Maurice-François Garin was an Italian then French road bicycle racer best known for winning the inaugural Tour de France in 1903, and for being stripped of his title in the second Tour in 1904 along with eight others, for cheating. He was of Italian origin but adopted French nationality on 21 December 1901.

The 1903 Tour de France was the first cycling race set up and sponsored by the newspaper L'Auto, ancestor of the current daily, L'Équipe. It ran from 1 to 19 July in six stages over 2,428 km (1,509 mi), and was won by Maurice Garin.

The Tour de France is an annual men's multiple-stage bicycle race primarily held in France, while also occasionally passing through nearby countries. Like the other Grand Tours, it consists of 21 stages, each a day long, over the course of 23 days, coinciding with the Bastille Day holiday. It is the oldest of the Grand Tours and generally considered the most prestigious.
Maurice Garin wins the first Tour de France.

Maurice-François Garin was an Italian then French road bicycle racer best known for winning the inaugural Tour de France in 1903, and for being stripped of his title in the second Tour in 1904 along with eight others, for cheating. He was of Italian origin but adopted French nationality on 21 December 1901.

The 1903 Tour de France was the first cycling race set up and sponsored by the newspaper L'Auto, ancestor of the current daily, L'Équipe. It ran from 1 to 19 July in six stages over 2,428 km (1,509 mi), and was won by Maurice Garin.
The first line of the Paris Métro opens for operation.

Paris Métro Line 1 is one of the sixteen lines of the Paris Métro. It connects La Défense–Grande Arche in the northwest and Château de Vincennes in the southeast. Also, there is a future eastern extension planned to go to Val de Fontenay to make a link with Paris Metro Line 15, RER A, RER E and an extension of Tram 1. With a length of 16.5 km (10.3 mi), it constitutes an important east–west transportation route within the City of Paris. Excluding RER commuter lines, it is the most utilised line on the network with 181.2 million travellers in 2017 or 496,000 people per day on average.

The Paris Métro is a rapid transit system in the Paris metropolitan area, France. A symbol of the city, it is known for its density within the capital's territorial limits, uniform architecture and unique entrances influenced by Art Nouveau. It is mostly underground and 226.9 kilometres (141.0 mi) long. It has 308 stations, of which 64 have transfers between lines. There are 16 lines, numbered 1 to 14, with two lines, 3bis and 7bis, named because they started out as branches of Line 3 and Line 7 respectively. Line 1 and Line 14 are automated. Lines are identified on maps by number and colour, with the direction of travel indicated by the terminus.
Franco-Prussian War: France declares war on Prussia.

The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 January 1871, the conflict was caused primarily by France's determination to reassert its dominant position in continental Europe, which appeared in question following the decisive Prussian victory over Austria in 1866. According to some historians, Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck deliberately provoked the French into declaring war on Prussia in order to induce four independent southern German states—Baden, Württemberg, Bavaria and Hesse-Darmstadt—to join the North German Confederation; other historians contend that Bismarck exploited the circumstances as they unfolded. All agree that Bismarck recognized the potential for new German alliances, given the situation as a whole.

Prussia was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was de facto dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and de jure by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany.
Taiping Rebellion: Third Battle of Nanking: The Qing dynasty finally defeats the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom.

The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive rebellion and civil war that was waged in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Han, Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It lasted from 1850 to 1864, although following the fall of Tianjing the last rebel army was not wiped out until August 1871. After fighting the bloodiest civil war in world history, with over 20 million dead, the established Qing government won decisively, although at a great price to its fiscal and political structure.

The Third Battle of Nanking in 1864 was the last major engagement of the Taiping Rebellion in the Qing Empire. With the fall of Nanking, the capital of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, the rebellion came to an end. The Hunan Army, an unpaid and barely fed militia commissioned by the Qing Empire, lost all their discipline and committed mass-scale random murder, wartime rape, looting and arson against the civilians of Nanjing, seen as "rebels". 100,000 "rebels" were reported dead by Zeng Guofan, the commander-in-chief of the Hunan Army.

The Qing dynasty, officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria. It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing empire lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the fourth-largest empire in world history in terms of territorial size. With 419,264,000 citizens in 1907, it was the world's most populous country at the time.

The Taiping Heavenly Kingdom, later shortened to the Heavenly Kingdom or Heavenly Dynasty, was an unrecognised rebel state in China and a Chinese Christian theocratic absolute monarchy from 1851 to 1864, supporting the overthrow of the Qing dynasty by Hong Xiuquan and his followers. The unsuccessful war it waged against the Qing is known as the Taiping Rebellion. Its capital was at Tianjing.
American Civil War: Morgan's Raid: At Buffington Island in Ohio, Confederate General John Hunt Morgan's raid into the north is mostly thwarted when a large group of his men are captured while trying to escape across the Ohio River.

The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union and the Confederacy, the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.

Morgan's Raid was a diversionary incursion by Confederate cavalry into the Union states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio and West Virginia during the American Civil War. The raid took place from June 11 to July 26, 1863, and is named for the commander of the Confederate troops, Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan. Although it caused temporary alarm in the North, the raid was ultimately classed as a failure.
Buffington Island is an island in the Ohio River in Jackson County, West Virginia near the town of Ravenswood, United States, east of Racine, Ohio. During the American Civil War, the Battle of Buffington Island took place on July 19, 1863, just south of the Ohio community of Portland. Buffington Island is protected as part of the Ohio River Islands National Wildlife Refuge.

Ohio is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The state's capital and largest city is Columbus, with the Columbus metro area, Greater Cincinnati, and Greater Cleveland being the largest metropolitan areas. Ohio is bordered by Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the west, and Michigan to the northwest. Ohio is historically known as the "Buckeye State" after its Ohio buckeye trees, and Ohioans are also known as "Buckeyes". Its state flag is the only non-rectangular flag of all the U.S. states.

The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States, the Confederacy, or "the South", was an unrecognized breakaway republic in North America that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War. Eleven U.S. states, nicknamed Dixie, declared secession and formed the main part of the CSA. They were South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky, and Missouri also had declarations of secession and full representation in the Confederate Congress during their Union army occupation.

John Hunt Morgan was an American soldier who served as a Confederate general in the American Civil War of 1861–1865.
The Battle of Buffington Island, also known as the St. Georges Creek Skirmish, was an American Civil War engagement in Meigs County, Ohio, and Jackson County, West Virginia, on July 19, 1863, during Morgan's Raid. The largest battle in Ohio during the war, Buffington Island contributed to the capture of the famed Confederate cavalry raider, Brig. Gen. John H. Morgan, who was seeking to escape Union army pursuers across the Ohio River at a ford opposite Buffington Island.

The Ohio River is a 981-mile (1,579 km) long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the north-south flowing Mississippi River that divides the eastern from western United States. It is also the 6th oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern U.S. It is the source of drinking water for five million people.
The two-day Seneca Falls Convention, the first women's-rights and feminist convention held in the United States, opened in Seneca Falls, New York.

The Seneca Falls Convention was the first women's rights convention. It advertised itself as "a convention to discuss the social, civil, and religious condition and rights of woman". Held in the Wesleyan Chapel of the town of Seneca Falls, New York, it spanned two days over July 19–20, 1848. Attracting widespread attention, it was soon followed by other women's rights conventions, including the Rochester Women's Rights Convention in Rochester, New York, two weeks later. In 1850 the first in a series of annual National Women's Rights Conventions met in Worcester, Massachusetts.

Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, these rights are institutionalized or supported by law, local custom, and behavior, whereas in others, they are ignored and suppressed. They differ from broader notions of human rights through claims of an inherent historical and traditional bias against the exercise of rights by women and girls, in favor of men and boys.
Feminism is a range of socio-political movements and ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social equality of the sexes. Feminism incorporates the position that society prioritizes the male point of view and that women are treated unjustly in these societies. Efforts to change this include fighting against gender stereotypes and improving educational, professional, and interpersonal opportunities and outcomes for women.

Seneca Falls is a town in Seneca County, New York, United States. The population was 8,942 at the 2020 census.
Women's rights: A two-day Women's Rights Convention opens in Seneca Falls, New York.

Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, these rights are institutionalized or supported by law, local custom, and behavior, whereas in others, they are ignored and suppressed. They differ from broader notions of human rights through claims of an inherent historical and traditional bias against the exercise of rights by women and girls, in favor of men and boys.

The Seneca Falls Convention was the first women's rights convention. It advertised itself as "a convention to discuss the social, civil, and religious condition and rights of woman". Held in the Wesleyan Chapel of the town of Seneca Falls, New York, it spanned two days over July 19–20, 1848. Attracting widespread attention, it was soon followed by other women's rights conventions, including the Rochester Women's Rights Convention in Rochester, New York, two weeks later. In 1850 the first in a series of annual National Women's Rights Conventions met in Worcester, Massachusetts.

Seneca Falls is a hamlet and census-designated place in Seneca County, New York, United States. The population was 6,681 at the 2010 census. The 2020 census population of Seneca Falls CDP was 6,809. The hamlet is in the Town of Seneca Falls, east of Geneva. It was an incorporated village from 1831 to 2011.
The last major fire to affect Manhattan destroyed 345 buildings, killed 30 people, and caused at least $5 million in damage.

The Great New York City Fire of 1845 broke out on July 19, 1845, in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The fire started in a whale oil and candle manufacturing establishment and quickly spread to other wooden structures. It reached a warehouse on Broad Street where combustible saltpeter was stored and caused a massive explosion that spread the fire even farther.

Manhattan, known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state of New York. Located near the southern tip of New York State, Manhattan is based in the Eastern Time Zone and constitutes both the geographical and demographic center of the Northeast megalopolis and the urban core of the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass. Over 58 million people live within 250 miles of Manhattan, which serves as New York City’s economic and administrative center, cultural identifier, and the city’s historical birthplace. Manhattan has been described as the cultural, financial, media, and entertainment capital of the world, is considered a safe haven for global real estate investors, and hosts the United Nations headquarters. New York City is the headquarters of the global art market, centered in Manhattan.
Great New York City Fire of 1845: The last great fire to affect Manhattan begins early in the morning and is subdued that afternoon. The fire kills four firefighters and 26 civilians and destroys 345 buildings.

The Great New York City Fire of 1845 broke out on July 19, 1845, in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The fire started in a whale oil and candle manufacturing establishment and quickly spread to other wooden structures. It reached a warehouse on Broad Street where combustible saltpeter was stored and caused a massive explosion that spread the fire even farther.

Manhattan, known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state of New York. Located near the southern tip of New York State, Manhattan is based in the Eastern Time Zone and constitutes both the geographical and demographic center of the Northeast megalopolis and the urban core of the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass. Over 58 million people live within 250 miles of Manhattan, which serves as New York City’s economic and administrative center, cultural identifier, and the city’s historical birthplace. Manhattan has been described as the cultural, financial, media, and entertainment capital of the world, is considered a safe haven for global real estate investors, and hosts the United Nations headquarters. New York City is the headquarters of the global art market, centered in Manhattan.
SS Great Britain, the first ocean-going ship that had both an iron hull and a screw propeller, was launched in Bristol, England.

SS Great Britain is a museum ship and former passenger steamship that was advanced for her time. She was the largest passenger ship in the world from 1845 to 1854. She was designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel (1806–1859), for the Great Western Steamship Company's transatlantic service between Bristol and New York City. While other ships had been built of iron or equipped with a screw propeller, Great Britain was the first to combine these features in a large ocean-going ship. She was the first iron steamer to cross the Atlantic Ocean, which she did in 1845, in 14 days.

A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top, or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.

A propeller is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are specially shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis.

Bristol is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom.
Brunel's steamship the SS Great Britain is launched, becoming the first ocean-going craft with an iron hull and screw propeller, becoming the largest vessel afloat in the world.

Isambard Kingdom Brunel was an English civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, [who] changed the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions." Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first propeller-driven transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering.

A steamboat is a boat that is propelled primarily by steam power, typically driving propellers or paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S or PS ; however, these designations are most often used for steamships.

SS Great Britain is a museum ship and former passenger steamship that was advanced for her time. She was the largest passenger ship in the world from 1845 to 1854. She was designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel (1806–1859), for the Great Western Steamship Company's transatlantic service between Bristol and New York City. While other ships had been built of iron or equipped with a screw propeller, Great Britain was the first to combine these features in a large ocean-going ship. She was the first iron steamer to cross the Atlantic Ocean, which she did in 1845, in 14 days.

A propeller is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are specially shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis.
The British Medical Association is founded as the Provincial Medical and Surgical Association by Sir Charles Hastings at a meeting in the Board Room of the Worcester Infirmary.
The British Medical Association (BMA) is a registered trade union for doctors in the United Kingdom. The association does not regulate or certify doctors, a responsibility which lies with the General Medical Council. The association's headquarters are in Tavistock Square, London and it has national offices in Cardiff, Belfast, and Edinburgh, a European office in Brussels and a number of offices in English regions. The BMA has a range of representative and scientific committees and is recognised by National Health Service (NHS) employers as the sole contract negotiator for doctors.

Sir Charles Hastings was a medical surgeon and a founder of the British Medical Association, the BMA, on 19 July 1832.

Worcester is a cathedral city in Worcestershire, England, of which it is the county town. It is 30 miles (48 km) south-west of Birmingham, 101 miles (163 km) north-west of London, 27 miles (43 km) north of Gloucester and 23 miles (37 km) north-east of Hereford. The population was 103,872 in the 2021 Census.
Coronation of George IV of the United Kingdom.

George IV was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten years later. At the time of his accession to the throne, he was acting as Prince Regent, having done so since 5 February 1811, during his father's final mental illness.
Georg Anton Schäffer was forced to depart for China after his unsuccessful attempt to seize the Hawaiian Kingdom for the Russian Empire.

Georg Anton Schäffer was a German physician in the employ of the Russian-American Company who attempted to conquer Hawaii for the Company and, ultimately, the Russian Empire. The bloodless Schäffer affair (1815–1817) or the Hawaiian spectacular, as it was called by contemporary Russians, became a significant financial blunder for the Company.
The Schäffer affair was a controversial diplomatic incident caused by Georg Anton Schäffer, a German who attempted to seize the Kingdom of Hawaii for the Russian Empire. While on a trading expedition to the Kingdom, the Russian-American Company (RAC) vessel Bering ran aground during a storm at Waimea on Kauai in January 1815. The chieftain of the island, Kaumualii, seized the company goods on board. Schäffer was sent later that year from Russian America to recover the lost property, where he would spend the following two years courting native allies to overthrow Kamehameha I.

The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi, was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island of Hawaiʻi, conquered the independent islands of Oʻahu, Maui, Molokaʻi and Lānaʻi and unified them under one government. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unified when Kauaʻi and Niʻihau joined the Hawaiian Kingdom voluntarily. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.

The Russian Empire was the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately 22,800,000 square kilometres (8,800,000 sq mi), it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity.
Unsuccessful in his attempt to conquer the Kingdom of Hawaii for the Russian-American Company, Georg Anton Schäffer is forced to admit defeat and leave Kauai.
The Schäffer affair was a controversial diplomatic incident caused by Georg Anton Schäffer, a German who attempted to seize the Kingdom of Hawaii for the Russian Empire. While on a trading expedition to the Kingdom, the Russian-American Company (RAC) vessel Bering ran aground during a storm at Waimea on Kauai in January 1815. The chieftain of the island, Kaumualii, seized the company goods on board. Schäffer was sent later that year from Russian America to recover the lost property, where he would spend the following two years courting native allies to overthrow Kamehameha I.

The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi, was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island of Hawaiʻi, conquered the independent islands of Oʻahu, Maui, Molokaʻi and Lānaʻi and unified them under one government. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unified when Kauaʻi and Niʻihau joined the Hawaiian Kingdom voluntarily. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.

The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the United American Company. Emperor Paul I of Russia chartered the company in the Ukase of 1799. It had the mission of establishing new settlements in Russian America, conducting trade with natives, and carrying out an expanded colonization program.

Georg Anton Schäffer was a German physician in the employ of the Russian-American Company who attempted to conquer Hawaii for the Company and, ultimately, the Russian Empire. The bloodless Schäffer affair (1815–1817) or the Hawaiian spectacular, as it was called by contemporary Russians, became a significant financial blunder for the Company.
Kauaʻi, anglicized as Kauai, is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands. With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island in the United States. Nicknamed the Garden Isle, Kauaʻi lies 73 miles (117 km) across the Kauaʻi Channel, northwest of Oʻahu. This island is the site of Waimea Canyon State Park and the Na Pali Coast State Park.
Great Northern War: Polish–Saxon forces were defeated by a Swedish army half their size at the Battle of Kliszów.

The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony–Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715.

The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 1,000,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi) and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages.

The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony, was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.

The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries. The beginning of the empire is usually taken as the reign of Gustavus Adolphus, who ascended the throne in 1611, and its end as the loss of territories in 1721 following the Great Northern War.

The Battle of Kliszów took place on July 19, 1702, near Kliszów in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. A numerically superior Polish–Saxon army led by king Augustus II the Strong was defeated by a Swedish army half its size under the command of king Charles XII of Sweden.
Great Northern War: A numerically superior Polish-Saxon army of Augustus II the Strong, operating from an advantageous defensive position, is defeated by a Swedish army half its size under the command of King Charles XII in the Battle of Klissow.

The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony–Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715.

Augustus II, most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania in the years 1697–1706 and from 1709 until his death in 1733. He belonged to the Albertine line of the House of Wettin.

Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII or Carolus Rex, was King of Sweden from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of the House of Wittelsbach. Charles was the only surviving son of Charles XI and Ulrika Eleonora the Elder. He assumed power, after a seven-month caretaker government, at the age of fifteen.

The Battle of Kliszów took place on July 19, 1702, near Kliszów in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. A numerically superior Polish–Saxon army led by king Augustus II the Strong was defeated by a Swedish army half its size under the command of king Charles XII of Sweden.
Representatives of the Iroquois Confederacy sign the Nanfan Treaty, ceding a large territory north of the Ohio River to England.
The Iroquois, officially the Haudenosaunee, are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca. After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations.

Deed from the Five Nations to the King, of their Beaver Hunting Ground, more commonly known as the Nanfan Treaty, was an agreement made between the representatives of the Iroquois Confederacy with John Nanfan, the acting colonial governor of New York, on behalf of The Crown. The treaty was conducted in Albany, New York, on July 19, 1701, and amended by both parties on September 14, 1726.

The Ohio River is a 981-mile (1,579 km) long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the north-south flowing Mississippi River that divides the eastern from western United States. It is also the 6th oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern U.S. It is the source of drinking water for five million people.

The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
Anglo-Spanish War: Battle of Gravelines: The Spanish Armada is sighted in the English Channel.

The Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) was an intermittent conflict between the Habsburg Kingdom of Spain and the Kingdom of England. It was never formally declared. The war included much English privateering against Spanish ships, and several widely separated battles. It began with England's military expedition in 1585 to what was then the Spanish Netherlands under the command of the Earl of Leicester, in support of the Dutch rebellion against Spanish Habsburg rule.

The Spanish Armada was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval experience appointed by Philip II of Spain. His orders were to sail up the English Channel, link up with the Duke of Parma in Flanders, and escort an invasion force that would land in England and overthrow Elizabeth I. Its purpose was to reinstate Catholicism in England, end support for the Dutch Republic, and prevent attacks by English and Dutch privateers against Spanish interests in the Americas.

The English Channel is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world.
Mary I was proclaimed Queen of England, deposing Lady Jane Grey after nine days of de facto rule.

Mary I, also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 until her death in 1558. She is best known for her vigorous attempt to reverse the English Reformation, which had begun during the reign of her father, Henry VIII. Her attempt to restore to the Church the property confiscated in the previous two reigns was largely thwarted by Parliament, but during her five-year reign, Mary had over 280 religious dissenters burned at the stake in the Marian persecutions.

This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself King of the Anglo-Saxons from about 886, and while he was not the first king to claim to rule all of the English, his rule represents the start of the first unbroken line of kings to rule the whole of England, the House of Wessex.

Lady Jane Grey, later known as Lady Jane Dudley and as the "Nine Days' Queen", was an English noblewoman who claimed the throne of England and Ireland from 10 July until 19 July 1553.
The attempt to install Lady Jane Grey as Queen of England collapses after only nine days.

Lady Jane Grey, later known as Lady Jane Dudley and as the "Nine Days' Queen", was an English noblewoman who claimed the throne of England and Ireland from 10 July until 19 July 1553.
A queen regnant is a female monarch, equivalent in rank and title to a king, who reigns suo jure over a realm known as a "kingdom"; as opposed to a queen consort, who is the wife of a reigning king; or a queen regent, who is the guardian of a child monarch and rules pro tempore in the child's stead, be it de jure in sharing power or de facto in ruling alone. She is sometimes called a woman king. A princess regnant is a female monarch who reigns suo jure over a "principality"; an empress regnant is a female monarch who reigns suo jure over an "empire".
The English warship Mary Rose (pictured) sank just outside Portsmouth during the Battle of the Solent.

The Mary Rose is a carrack-type warship of the English Tudor navy of King Henry VIII. She served for 33 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her last action on 19 July 1545. She led the attack on the galleys of a French invasion fleet, but sank in the Solent, the strait north of the Isle of Wight.

Portsmouth is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.

The naval Battle of the Solent took place on 18 and 19 July 1545 during the Italian Wars between the fleets of Francis I of France and Henry VIII of England, in the Solent, between Hampshire and the Isle of Wight. The engagement was inconclusive, and is most notable for the sinking of the English carrack, Mary Rose.
The Tudor warship Mary Rose sinks off Portsmouth; in 1982 the wreck is salvaged in one of the most complex and expensive projects in the history of maritime archaeology.

The Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603 in England and Wales and includes the Elizabethan period during the reign of Elizabeth I until 1603. The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England that began with the reign of Henry VII. Historian John Guy (1988) argued that "England was economically healthier, more expansive, and more optimistic under the Tudors" than at any time since the Roman occupation.

The Mary Rose is a carrack-type warship of the English Tudor navy of King Henry VIII. She served for 33 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her last action on 19 July 1545. She led the attack on the galleys of a French invasion fleet, but sank in the Solent, the strait north of the Isle of Wight.

Portsmouth is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Italian War of 1542–46: The first Siege of Boulogne begins.

The Italian War of 1542–1546 was a conflict late in the Italian Wars, pitting Francis I of France and Suleiman I of the Ottoman Empire against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and Henry VIII of England. The course of the war saw extensive fighting in Italy, France, and the Low Countries, as well as attempted invasions of Spain and England. The conflict was inconclusive and ruinously expensive for the major participants.

The First Siege of Boulogne took place from 19 July to 14 September 1544 and the Second Siege of Boulogne took place in October 1544.
Wars of Scottish Independence: Battle of Halidon Hill: The English win a decisive victory over the Scots.

The Wars of Scottish Independence were a series of military campaigns fought between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England in the late 13th and early 14th centuries.
The Battle of Halidon Hill took place on 19 July 1333 when a Scottish army under Sir Archibald Douglas attacked an English army commanded by King Edward III of England and was heavily defeated. The year before, Edward Balliol had seized the Scottish Crown from five-year-old David II, surreptitiously supported by Edward III. This marked the start of the Second War of Scottish Independence. Balliol was shortly expelled from Scotland by a popular uprising, which Edward III used as a casus belli, invading Scotland in 1333. The immediate target was the strategically-important border town of Berwick-upon-Tweed, which the English besieged in March.

The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England. It suffered many invasions by the English, but under Robert the Bruce it fought a successful War of Independence and remained an independent state throughout the late Middle Ages. Following the annexation of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles from the Kingdom of Norway in 1266 and 1472 respectively, and the final capture of the Royal Burgh of Berwick by the Kingdom of England in 1482, the territory of the Kingdom of Scotland corresponded to that of modern-day Scotland, bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the southwest. In 1603, James VI of Scotland became King of England, joining Scotland with England in a personal union. In 1707, during the reign of Queen Anne, the two kingdoms were united to form the Kingdom of Great Britain under the terms of the Acts of Union.
Arab–Byzantine wars: After initial Byzantine gains at the Battle of Apamea, a lone Kurdish rider managed to kill Byzantine commander Damian Dalassenos, allowing Fatimid troops to turn the tide of the battle.

The Arab–Byzantine wars were a series of wars between a number of Muslim Arab dynasties and the Byzantine Empire between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. Conflict started during the initial Muslim conquests, under the expansionist Rashidun and Umayyad caliphs, in the 7th century and continued by their successors until the mid-11th century.

The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians distinguish Byzantium from its earlier incarnation because it was centered on Constantinople, oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by Eastern Orthodox Christianity.

The Battle of Apamea was fought on 19 July 998 between the forces of the Byzantine Empire and the Fatimid Caliphate. The battle was part of a series of military confrontations between the two powers over control of northern Syria and the Hamdanid emirate of Aleppo. The Byzantine regional commander, Damian Dalassenos, had been besieging Apamea, until the arrival of the Fatimid relief army from Damascus, under Jaysh ibn Samsama. In the subsequent battle, the Byzantines were initially victorious, but a lone Kurdish rider managed to kill Dalassenos, throwing the Byzantine army into panic. The fleeing Byzantines were then pursued, with much loss of life, by the Fatimid troops. This defeat forced the Byzantine emperor Basil II to personally campaign in the region the next year, and was followed in 1001 by the conclusion of a ten-year truce between the two states.
Damian Dalassenos was a Byzantine aristocrat and the first known member of the Dalassenos noble family. He is known for his service as the military governor (doux) of Antioch in 996–998. He fought the Fatimids with some success, until he was killed at the Battle of Apamea on 19 July 998.
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dynasty of Arab origin, trace their ancestry to Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband ‘Ali b. Abi Talib, the first Shi‘a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma‘ili communities, but also in many other Muslim lands, including Persia and the adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Tunisia and established the city of "al-Mahdiyya". The Ismaili dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast of Africa and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included – in addition to Egypt – varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hijaz.
Arab–Byzantine wars: Battle of Apamea: Fatimids defeat a Byzantine army near Apamea.

The Arab–Byzantine wars were a series of wars between a number of Muslim Arab dynasties and the Byzantine Empire between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. Conflict started during the initial Muslim conquests, under the expansionist Rashidun and Umayyad caliphs, in the 7th century and continued by their successors until the mid-11th century.

The Battle of Apamea was fought on 19 July 998 between the forces of the Byzantine Empire and the Fatimid Caliphate. The battle was part of a series of military confrontations between the two powers over control of northern Syria and the Hamdanid emirate of Aleppo. The Byzantine regional commander, Damian Dalassenos, had been besieging Apamea, until the arrival of the Fatimid relief army from Damascus, under Jaysh ibn Samsama. In the subsequent battle, the Byzantines were initially victorious, but a lone Kurdish rider managed to kill Dalassenos, throwing the Byzantine army into panic. The fleeing Byzantines were then pursued, with much loss of life, by the Fatimid troops. This defeat forced the Byzantine emperor Basil II to personally campaign in the region the next year, and was followed in 1001 by the conclusion of a ten-year truce between the two states.

The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dynasty of Arab origin, trace their ancestry to Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband ‘Ali b. Abi Talib, the first Shi‘a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma‘ili communities, but also in many other Muslim lands, including Persia and the adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Tunisia and established the city of "al-Mahdiyya". The Ismaili dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast of Africa and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included – in addition to Egypt – varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hijaz.

The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians distinguish Byzantium from its earlier incarnation because it was centered on Constantinople, oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by Eastern Orthodox Christianity.

Apamea, on the right bank of the Orontes River, was an ancient Greek and Roman city. It was the capital of Apamene under the Macedonians, became the capital and Metropolitan Archbishopric of late Roman province Syria Secunda, again in the crusader period.
Battle of Simancas: King Ramiro II of León defeats the Moorish army under Caliph Abd-al-Rahman III near the city of Simancas.
The Battle of Simancas was a military battle that started on 19 July 939 in the Iberian Peninsula between the troops of the King of León Ramiro II and Cordovan caliph Abd al-Rahman III near the walls of the city of Simancas.

Ramiro II, son of Ordoño II and Elvira Menendez, was a King of León from 931 until his death. Initially titular king only of a lesser part of the kingdom, he gained the crown of León after supplanting his brother Alfonso IV and cousin Alfonso Fróilaz in 931. The scant Anales castellanos primeros are a primary source for his reign.

The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.

ʿAbd al-Rahmān ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn al-Ḥakam al-Rabdī ibn Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān al-Dākhil or ʿAbd al-Rahmān III, was the Umayyad Emir of Córdoba from 912 to 929, at which point he founded the Caliphate of Córdoba, serving as its first caliph until his death. Abd al-Rahman won the laqab (sobriquet) al-Nasir li-Dīn Allāh in his early 20s when he supported the Maghrawa Berbers in North Africa against Fatimid expansion and later claimed the title of Caliph for himself. His half-century reign was known for its religious tolerance.

Simancas is a town and municipality of central Spain, located in the province of Valladolid, part of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is situated approximately 10 km southwest of the provincial capital Valladolid, on the road to Zamora and the right bank of the river Pisuerga.
Umayyad conquest of Hispania: Battle of Guadalete: Umayyad forces under Tariq ibn Ziyad defeat the Visigoths led by King Roderic.

Year 711 (DCCXI) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 711 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus.

The Battle of Guadalete was the first major battle of the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, fought in 711 at an unidentified location in what is now southern Spain between the Christian Visigoths under their king, Roderic, and the invading forces of the Muslim Umayyad Caliphate, composed mainly of Berbers and some Arabs under the commander Ṭāriq ibn Ziyad. The battle was significant as the culmination of a series of Berber attacks and the beginning of the Umayyad conquest of Hispania. Roderic was killed in the battle, along with many members of the Visigothic nobility, opening the way for the capture of the Visigothic capital of Toledo.

The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital.
Ṭāriq ibn Ziyād, also known simply as Tarik in English, was a Berber commander who served the Umayyad Caliphate and initiated the Muslim Umayyad conquest of Visigothic Hispania in 711–718 AD. He led a large army and crossed the Strait of Gibraltar from the North African coast, consolidating his troops at what is today known as the Rock of Gibraltar. The name "Gibraltar" is the Spanish derivation of the Arabic name Jabal Ṭāriq, meaning "mountain of Ṭāriq", which is named after him.

The Visigoths were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is known as the Migration Period. The Visigoths emerged from earlier Gothic groups, including a large group of Thervingi, who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and the Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under their first leader, Alaric I, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sacked Rome in August 410. Afterwards, they began settling down, first in southern Gaul and eventually in Hispania, where they founded the Visigothic Kingdom and maintained a presence from the 5th to the 8th centuries AD.

Roderic was the Visigothic king in Hispania between 710 and 711. He is well-known as "the last king of the Goths". He is actually an extremely obscure figure about whom little can be said with certainty. He was the last Goth to rule from Toledo, but not the last Gothic king, a distinction which belongs to Ardo.
Leontius, Roman usurper, is crowned Eastern emperor at Tarsus (modern Turkey). He is recognized in Antioch and makes it his capital.

Leontius was a general of the Eastern Roman Empire and claimant to the throne who led a rebellion against emperor Zeno in 484–488.
A usurper is an illegitimate or controversial claimant to power, often but not always in a monarchy. In other words, one who takes the power of a country, city, or established region for oneself, without any formal or legal right to claim it as one's own. Usurpers can rise to power in a region by often unexpected physical force, as well as through political influence and deceit.

Tarsus is a historic city in south-central Turkey, 20 km inland from the Mediterranean. It is part of the Adana-Mersin metropolitan area, the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Turkey with a population of 3 million people. Tarsus forms an administrative district in the eastern part of the Mersin Province and lies in the core of Çukurova region.

Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its largest city and financial centre.
Antioch on the Orontes was a Hellenistic, and later, a Biblical Christian city, founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. This city served as the capital of the Seleucid Empire and later as regional capital to both the Roman and Byzantine Empire. During the Crusades, Antioch served as the capital of the Principality of Antioch, one of four Crusader states that were founded in the Levant. Its inhabitants were known as Antiochenes; the city's ruin lies on the Orontes River, near Antakya, the modern city in Hatay Province of Turkey (Türkiye), to which the ancient city lends its name.
The Great Fire of Rome began in shops around the Circus Maximus, eventually destroying three of the fourteen regions of the city and severely damaging seven others.
AD 64 (LXIV) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 64th Year of the Anno Domini designation, the 64th year of the 1st millennium, the 64th year of the 1st century, and the 4th year of the 7th decade. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Bassus and Crassus. The denomination AD 64 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Great Fire of Rome occurred in July AD 64. The fire began in the merchant shops around Rome's chariot stadium, Circus Maximus, on the night of 19 July. After six days, the fire was brought under control, but before the damage could be assessed, the fire reignited and burned for another three days. In the aftermath of the fire, two thirds of Rome had been destroyed.

The Circus Maximus is an ancient Roman chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Empire. It measured 621 m (2,037 ft) in length and 118 m (387 ft) in width and could accommodate over 150,000 spectators. In its fully developed form, it became the model for circuses throughout the Roman Empire. The site is now a public park.
In 7 BC, Augustus divided the city of Rome into 14 administrative regions. These replaced the four regiones—or "quarters"—traditionally attributed to Servius Tullius, sixth king of Rome. They were further divided into official neighborhoods.
The Great Fire of Rome causes widespread devastation and rages on for six days, destroying half of the city.
AD 64 (LXIV) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 64th Year of the Anno Domini designation, the 64th year of the 1st millennium, the 64th year of the 1st century, and the 4th year of the 7th decade. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Bassus and Crassus. The denomination AD 64 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Great Fire of Rome occurred in July AD 64. The fire began in the merchant shops around Rome's chariot stadium, Circus Maximus, on the night of 19 July. After six days, the fire was brought under control, but before the damage could be assessed, the fire reignited and burned for another three days. In the aftermath of the fire, two thirds of Rome had been destroyed.
Rutger Hauer, Dutch actor, director, and producer (b. 1944) deaths

Rutger Oelsen Hauer was a Dutch actor. In 1999, he was named by the Dutch public as the Best Dutch Actor of the Century.
Jon Schnepp, American producer, director, voice actor, editor, writer, cartoonist, animator, and cinematographer (b. 1967) deaths

Jonathan David Schnepp was an American producer, director, voice actor, editor, writer, cartoonist, animator, and cinematographer.
Denis Ten, Kazakhstani figure skater (b. 1993) deaths

Denis Yurievich Ten was a Kazakhstani figure skater. He was the 2014 Olympic bronze medalist, a two-time World medalist, the 2015 Four Continents champion, the 2017 Winter Universiade champion, and a five-time national champion of Kazakhstan.
Garry Marshall, American actor, director, and producer (b. 1934) deaths

Garry Kent Marshall was an American filmmaker and actor. He started his career in the 1960s writing for The Lucy Show and The Dick Van Dyke Show before he developed Neil Simon's 1965 play The Odd Couple for television in 1970. He gained fame for creating Happy Days (1974–1984), Laverne and Shirley (1976–1983), and Mork and Mindy (1978–1982). He is also known for directing The Flamingo Kid (1984), Overboard (1987), Beaches (1988), Pretty Woman (1990), Runaway Bride (1999), and the family films The Princess Diaries (2001) and The Princess Diaries 2: Royal Engagement (2004). He also directed the romantic comedy ensemble films Valentine's Day (2010), New Year's Eve (2011), and Mother's Day (2016).
Van Alexander, American composer and conductor (b. 1915) deaths

Van Alexander was an American bandleader, arranger, and composer.
Galina Prozumenshchikova, Ukrainian-Russian swimmer and journalist (b. 1948) deaths

Galina Nikolayevna Prozumenshchikova was a Soviet breaststroke swimmer who also competed in medley relays. She won five Olympic medals in 1964, 1968 and 1972 and five European Championships medals in 1966 and 1970. Her first Olympic medal, the gold in 200 m breaststroke in 1964, was the first Olympic gold in swimming for the Soviet Union. From 1964 to 1966, she set five world records: four in 200 m and one in 100 m breaststroke events. Between 1963 and 1972, she won 15 national titles and set 27 national records.
Carmino Ravosa, American singer-songwriter, pianist, and producer (b. 1930) deaths

Carmino Ravosa was an American composer and lyricist, singer, pianist, as well as a producer, director, and musical historian. Ravosa, who wrote music for children for decades, was one of the most popular songwriters for schools in America. He was an author and editor for Silver Burdett & Ginn's music textbook series "World of Music" and "The Music Connection", and the composer of the theme musicals in the two series. Ravosa also was the songwriter for the CBS children's shows Captain Kangaroo and Romper Room, the PBS program Shining Time Station, and the PBS publication Sesame Street Magazine.
Gennadiy Seleznyov, Russian journalist and politician, 2nd Speaker of the Duma (b. 1947) deaths

Gennadiy Nikolayevich Seleznyov was a Russian politician, the Chairman of the State Duma from 1996 to 2003.

The Chairman of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, also called Speaker (спикер), is the presiding officer of the lower house of the Russian parliament. His responsibilities include overseeing the day-to-day business of the State Duma presiding and maintaining order at the regular sessions of the parliament. The Speaker also chairs the Council of the Duma which includes representatives from all the parliamentary parties and determines the legislative agenda.
Rubem Alves, Brazilian theologian (b. 1933) deaths
Rubem Azevedo Alves was a Brazilian theologian, philosopher, educator, writer and psychoanalyst. Alves was one of the founders of Latin American liberation theology.
David Easton, Canadian-American political scientist and academic (b. 1917) deaths
David Easton was a Canadian-born American political scientist. From 1947 to 1997, he served as a professor of political science at the University of Chicago.
Paul M. Fleiss, American pediatrician and author (b. 1933) deaths
Paul Murray Fleiss was an American pediatrician and author known for his unconventional medical views. Fleiss was a popular and sought-after pediatrician in the Greater Los Angeles area, both among poor and middle-class patients living near his Los Feliz office and among Southern California celebrities. Fleiss was a breastfeeding and anti-circumcision advocate. He recommended but did not insist upon childhood vaccinations, and stated he could be "convinced either way" as to whether HIV causes AIDS. In 1994, he pleaded guilty to conspiracy and bank fraud in relation to his daughter Heidi's prostitution ring.
James Garner, American actor (b. 1928) deaths

James Garner was an American actor. He played leading roles in more than 50 theatrical films, including The Great Escape (1963) with Steve McQueen; Paddy Chayefsky's The Americanization of Emily (1964) with Julie Andrews; Cash McCall (1960) with Natalie Wood; The Wheeler Dealers (1963) with Lee Remick; Darby's Rangers (1958) with Stuart Whitman; Roald Dahl's 36 Hours (1965) with Eva Marie Saint; Raymond Chandler's Marlowe (1969) with Bruce Lee; Support Your Local Sheriff! (1969) with Walter Brennan; Blake Edwards's Victor/Victoria (1982) with Julie Andrews; and Murphy's Romance (1985) with Sally Field, for which he received an Academy Award nomination. He also starred in several television series, including popular roles such as Bret Maverick in the ABC 1950s Western series Maverick and as Jim Rockford in the NBC 1970s private detective show, The Rockford Files
Jerzy Jurka, Polish biologist (b. 1950) deaths

Jerzy Władysław Jurka was a Polish-American computational and molecular biologist. He served as the assistant director of research at the Linus Pauling Institute prior to founding the Genetic Information Research Institute. He collaborated with several notable scientists including Linus Pauling, George Irving Bell, Roy Britten, Temple Smith, and Emile Zuckerkandl. His Erdős number is 3, using the path through Temple Smith and Stanislaw Ulam.
Ray King, English footballer and manager (b. 1924) deaths
Raymond King was an English football goalkeeper. He made 254 league appearances in an 11-year career in the Football League. He was the younger brother of Frank and George King.
Ingemar Odlander, Swedish journalist (b. 1936) deaths

Hertur Roland Ingemar Odlander, was a Swedish journalist who worked for SVT news on its news programmes Aktuellt and Rapport. Between 1975 and 1978 Odlander was the first ever Swedish foreign news reporter stationed in Nairobi. From 1978 and until his death in 2014 Odlander was married to Christina Jutterström.
Harry Pougher, English cricketer (b. 1941) deaths
Harry Pougher was an English cricketer. Pougher was a right-handed batsman who bowled right-arm off break. He was born in Scunthorpe, Lincolnshire.
Leen Vleggeert, Dutch politician (b. 1931) deaths
Leendert "Leen" Vleggeert was a Dutch politician. He served as a member of the Senate of the Netherlands between 1981 and 1983 for the Labour Party. He was also mayor of Puttershoek (1977–1982), interim-mayor of Heinenoord (1980–1982), mayor of Gorinchem (1982–1990), Spijkenisse (1990–1996) and lastly interim-mayor of Vlaardingen (2002).
John Winkin, American baseball player, coach, and journalist (b. 1919) deaths

John W. Winkin Jr. was an American baseball coach, scout, broadcaster, journalist and collegiate athletics administrator. Winkin led the University of Maine Black Bears baseball team to six College World Series berths in an 11-year span. In 2007, at age 87, he was the oldest active head coach in any collegiate sport at any NCAA level. In all, 92 of his former players wound up signing professional baseball contracts. Elected to 11 different halls of fame, including the National College Baseball Hall of Fame in 2013, he finished his college baseball coaching career in 2008 with 1,043 total wins, which ranks 52nd all-time among NCAA head coaches. He died in 2014.
Mikhail Gorsheniov, Russian singer-songwriter (b. 1973) deaths

Mikhail "The Pot" Gorsheniov was a lead singer and composer of Russian horror punk/hard rock band Korol i Shut.
Geeto Mongol, Canadian-American wrestler and trainer (b. 1931) deaths

Newton Tattrie was a Canadian professional wrestler, better known by his ring name, Geeto Mongol.
Mel Smith, English actor, director, and screenwriter (b. 1952) deaths

Melvyn Kenneth Smith was an English comedian, actor and director. Smith worked on the sketch comedy shows Not the Nine O'Clock News and Alas Smith and Jones with his comedy partner, Griff Rhys Jones. Smith and Jones founded Talkback, which grew to be one of the United Kingdom's largest producers of television comedy and light entertainment programming.
Bert Trautmann, German footballer and manager (b. 1923) deaths

Bernhard Carl "Bert" Trautmann EK OBE BVO was a German professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper for Manchester City from 1949 to 1964.
Phil Woosnam, Welsh-American soccer player and manager (b. 1932) deaths

Phillip Abraham Woosnam was a Welsh association football inside-right and manager. A native of Caersws, Powys, Wales, Woosnam played for five clubs in England and one in the United States. He played international football for Wales. He was described as a "gifted inside-forward with a pronounced football intelligence".
Peter Ziegler, Swiss geologist and academic (b. 1928) deaths

Peter Alfred Ziegler was a Swiss geologist, who made contributions to the understanding of the geological evolution of Europe and the North Atlantic borderlands, of intraplate tectonics and of plate tectonic controls on the evolution and hydrocarbon potential of sedimentary basins. Ziegler's career consists of 33 years as exploration geologist with the petroleum industry, 30 of which with Shell, and 20 years of university teaching and research.
Leyla Erbil, Turkish author (b. 1931) deaths
Leyla Erbil (Turkish: Leylâ Erbil – was one of the leading female contemporary writers of Turkey, author of six novels, three collections of short stories and a book of essays. She was the first Turkish female writer to be nominated for a Nobel Prize in Literature by PEN International in 2002. Erbil was a co-founder of the Union of Turkish Artists and the Writers Syndicate of Turkey.
Humayun Ahmed, Bangladeshi director and playwright (b. 1948) deaths

Humayun Ahmed was a Bangladeshi novelist, dramatist, screenwriter, filmmaker, songwriter, scholar, and professor. His breakthrough was his debut novel Nondito Noroke published in 1972. He wrote over 200 fiction and non-fiction books, many of which were bestsellers in Bangladesh. His books were the top sellers at the Ekushey Book Fair during the 1990s and 2000s.
Tom Davis, American comedian, actor, and screenwriter (b. 1952) deaths

Thomas James Davis was an American comedian, writer, and author. He is best known for his comedy partnership with Al Franken, as half of the comedy duo "Franken & Davis" on Saturday Night Live.
Mohammad Hassan Ganji, Iranian meteorologist and academic (b. 1912) deaths

Mohammad Hassan Ganji Ph.D, was an Iranian meteorologist and academic. He was born in Birjand. He is credited as being the father of modern geography in Iran.
Omar Suleiman, Egyptian general and politician, 16th Vice President of Egypt (b. 1935) deaths

Omar Mahmoud Suleiman was an Egyptian army general, politician, diplomat, and intelligence officer. A leading figure in Egypt's intelligence system beginning in 1986, Suleiman was appointed to the long-vacant vice presidency by President Hosni Mubarak on 29 January 2011. On 11 February 2011, Suleiman announced Mubarak's resignation and ceased being vice president; governing power was transferred to the Armed Forces Supreme Council, of which Suleiman was not a member. A new head of intelligence services was appointed by the ruling Supreme Council. Suleiman withdrew from the political scene and did not appear in public after announcing Mubarak's resignation.

The vice-president of the Arab Republic of Egypt is a senior official within the Egyptian government.
Sylvia Woods, American businesswoman, co-founded Sylvia's Restaurant of Harlem (b. 1926) deaths

Sylvia Woods was an American restaurateur who founded the restaurant Sylvia's in Harlem on Lenox Avenue, New York City with her husband, Herbert Woods, in 1962. The soul food eatery is a popular gathering place for Harlem residents and tourists not far from the Apollo Theater.

Sylvia's Restaurant of Harlem, often called Sylvia's Soul Food or just Sylvia's, is a soul food restaurant located at 328 Lenox Avenue, between 126th and 127th Streets, in Harlem, Manhattan, New York City. It was founded in 1962 by Sylvia Woods. It has since expanded to a much larger space at its present location, and an adjacent building. The restaurant also sells a line of prepared foods, beauty and skin care items, cookbooks, and a children's book written by Woods. Woods purchased the original luncheonette by borrowing money from her mother, who had to mortgage her farm to provide it.
Valiulla Yakupov, Islamic cleric (b. 1963) deaths

Valiulla Makhmutovich Yakupov was a prominent Muslim cleric in Tatarstan, Russia and the deputy to the Muslim province's chief mufti. He was also known as a strong critic of radical Islamist organisations which advocate Salafism, a radical form of Islam. According to news agency Interfax, Yakupov founded Russia's first Islamic literary publishing house.
Cécile Aubry, French actress, author, television screenwriter and director (b. 1928) deaths

Cécile Aubry was a French film actress, author, television screenwriter and director.
Jon Cleary, Australian author and playwright (b. 1917) deaths

Jon Stephen Cleary was an Australian writer and novelist. He wrote numerous books, including The Sundowners (1951), a portrait of a rural family in the 1920s as they move from one job to the next, and The High Commissioner (1966), the first of a long series of popular detective fiction works featuring Sydney Police Inspector Scobie Malone. A number of Cleary's works have been the subject of film and television adaptations.
Frank McCourt, American author and educator (b. 1930) deaths

Francis McCourt was an Irish-American teacher and writer. He won a Pulitzer Prize for his book Angela's Ashes, a tragicomic memoir of the misery and squalor of his childhood.
Henry Surtees, English race car driver (b. 1991) deaths

Henry John Surtees was a British racing driver and the son of John Surtees. He died during a Formula Two race at Brands Hatch when he was struck by a wheel which came off another car which had spun into a wall.
Dercy Gonçalves, Brazilian comedian and actress (b. 1907) deaths

Dolores Gonçalves Costa, known by her stage name Dercy Gonçalves, was a Brazilian actress, comedian and singer. In her 86-year-long career, she worked in the theater, revues, film, radio and television, becoming famous by her humorous use of vulgar language. In 1991, at the age of 85, she caused controversy by exposing her breasts while parading with a Samba school in Rio de Janeiro's Carnaval.
A. K. Faezul Huq, Bangladeshi journalist, lawyer, and politician (b. 1945) deaths

Abul Kalam Faezul Huq was a Bangladeshi politician, lawyer, and columnist. Huq served as a member of parliament on three occasions, and held various ministerial portfolios including Public Works, Urban Development, Jute, and Textiles after Bangladesh gained independence. He was first elected as a member of the Pakistan National Assembly from the Banaripara Upazila-Swarupkathi-Nazirpur Upazila constituency as a Awami League nomination in 1970.
Roberto Fontanarrosa, Argentinian cartoonist (b. 1944) deaths

Roberto Alfredo Fontanarrosa, known popularly as El Negro Fontanarrosa, was an Argentine cartoonist, comics artist and writer. During his extended career, Fontanarrosa became one of the most acclaimed historieta artists of his country, as well as a respected fiction and short story writer. He created two hugely popular comic strips, as well as their parodic protagonists: Inodoro Pereyra, a gaucho, and Boogie, el aceitoso, a gun-for-hire. He also created the comic book Los Clásicos según Fontanarrosa, which contained a selection of humorous parodies of universal literature mainstays originally published in the magazine Chaupinela, in the 1970s.
Jack Warden, American actor (b. 1920) deaths

Jack Warden was an American character actor of film and television. He was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for Shampoo (1975) and Heaven Can Wait (1978). He received a BAFTA nomination for the former, and won an Emmy for his performance in Brian's Song (1971).
Edward Bunker, American author and screenwriter (b. 1933) deaths

Edward Heward Bunker was an American author of crime fiction, a screenwriter, convicted felon and an actor. He wrote numerous books, some of which have been adapted into films. He wrote the scripts for—and acted in—Straight Time (1978), Runaway Train (1985) and Animal Factory (2000). He also played a minor role in Reservoir Dogs (1992).
Sylvia Daoust, Canadian sculptor (b. 1902) deaths

Sylvia Daoust, CM, CQ, RCA, born in Montreal, was one of the first female sculptors in Quebec. She studied at the Council of Arts & Manufactures and the École des Beaux-Arts, with Charles Maillard and Maurice Feliz, and later with Edwin Holgate at the Art Association of Montreal.
J. Gordon Edwards, American entomologist, mountaineer, and DDT advocate (b. 1919) deaths

J. Gordon Edwards (1919–2004) was an American entomologist and proponent of the use and safety of the pesticide DDT. He was professor of entomology at San Jose State University for 40 years, and namesake to the university's entomology museum. He was an outspoken critic of Rachel Carson and efforts to ban DDT, famously eating the substance to demonstrate its safety to humans. He was also a noted mountain climber, spending nine seasons as a ranger-naturalist in Glacier National Park during the 1940s and '50s, and returning often to collect insects and map routes. His 1961 book A Climber's Guide to Glacier National Park, republished several times since, made him known as the "patron saint of climbing" in the park, where he died while hiking, aged 84.
Francis A. Marzen, American priest and journalist (b. 1924) deaths
Francis A. Marzen was a priest of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Honolulu, former editor of the Hawaii Catholic Herald and an information specialist for the City & County of Honolulu in the administration of Mayor Frank Fasi.
Zenkō Suzuki, Japanese politician, 70th Prime Minister of Japan (b. 1911) deaths

Zenkō Suzuki was a Japanese politician who was Prime Minister of Japan from 1980 to 1982. He was the last prime minister to have been born in the Meiji era.

The prime minister of Japan is the head of government of Japan. The prime minister chairs the Cabinet of Japan and has the ability to select and dismiss its Ministers of State. The prime minister also serves as the civilian commander-in-chief of the Japan Self Defence Forces and as a sitting member of the House of Representatives. The individual is appointed by the emperor of Japan after being nominated by the National Diet and must retain the nomination of the lower house and answer to parliament to remain in office.
Tyler Downs, American Olympic diver births
Tyler Downs is an American competitive Olympic diver and social media personality.
Bill Bright, American evangelist and author, founded the Campus Crusade for Christ (b. 1921) deaths

William R. Bright was an American evangelist. In 1951 at the University of California, Los Angeles he founded Campus Crusade for Christ as a ministry for university students. In 1952 he wrote The Four Spiritual Laws. In 1979 he produced the film Jesus.

Cru is an interdenominational Christian parachurch organization. It was founded in 1951 at the University of California, Los Angeles by Bill Bright and Vonette Zachary Bright. Since then, Cru has expanded its focus to include adult professionals, athletes, and high school students. In 2020, Cru had 19,000 staff members in 190 countries.
Pierre Graber, Swiss politician, President of the Swiss National Council (b. 1908) deaths

Pierre Graber was a Swiss politician and member of the Swiss Federal Council (1970–1978).
The President of the National Council of Switzerland presides over the National Council and Federal Assembly. The National Council President is often colloquially referred to as the "highest Swiss person", as the highest ranking person subject to the people's vote. However, this is an honorary title and the president is not the head of state. The head of state is the Federal Council). In the official order of precedence, she or he ranks behind the members of the Federal Council, but ahead of the President of the Swiss Council of States.
Dave Carter, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (b. 1952) deaths

Dave Carter was an American folk music singer-songwriter who described his style as "post-modern mythic American folk music". He was one half of the duo Dave Carter and Tracy Grammer, who were heralded as the new "voice of modern folk music" in the months before Carter's unexpected death in July 2002. They were ranked as number one on the year-end list for "Top Artists" on the Folk Music Radio Airplay Chart for 2001 and 2002, and their popularity has endured in the years following Carter's death. Joan Baez, who went on tour with the duo in 2002, spoke of Carter's songs in the same terms that she once used to promote a young Bob Dylan:"There is a special gift for writing songs that are available to other people, and Dave's songs are very available to me. It's a kind of genius, you know, and Dylan has the biggest case of it. But I hear it in Dave's songs, too.
Alan Lomax, American historian, scholar, and activist (b. 1915) deaths

Alan Lomax was an American ethnomusicologist, best known for his numerous field recordings of folk music of the 20th century. He was also a musician himself, as well as a folklorist, archivist, writer, scholar, political activist, oral historian, and film-maker. Lomax produced recordings, concerts, and radio shows in the US and in England, which played an important role in preserving folk music traditions in both countries, and helped start both the American and British folk revivals of the 1940s, 1950s, and early 1960s. He collected material first with his father, folklorist and collector John Lomax, and later alone and with others, Lomax recorded thousands of songs and interviews for the Archive of American Folk Song, of which he was the director, at the Library of Congress on aluminum and acetate discs.
Erin Cuthbert, footballer births

Erin Jacqueline Cuthbert is a Scottish footballer who plays for Chelsea in the FA WSL and is a member of the Scotland national team. She studied at University of the West of Scotland, combining graduation from the Open University with being a professional football player.
Ronaldo Vieira, Bissau-Guinean footballer births
Ronaldo Augusto Vieira Nan ([ʁoˈnawdu viˈɐjɾɐ] is a professional footballer who plays for Italian side Sampdoria, mainly operating as a central midfielder.
Elmer Valo, Polish-American baseball player, coach, and manager (b. 1921) deaths

Elmer William Valo, born Imrich Valo, was a Slovak American professional baseball right fielder, coach, and scout in Major League Baseball (MLB). He batted left-handed and threw right-handed.
Paul Momirovski, Australian rugby league player births

Paul Momirovski is an Australian rugby league footballer who plays as a centre and winger for the Sydney Roosters in the NRL.
Christian Welch, Australian rugby league player births

Christian Welch is an Australian professional rugby league footballer who plays as a prop for the Melbourne Storm in the NRL.
Victor Barbeau, Canadian author and academic (b. 1896) deaths

Victor Barbeau, was a Quebec writer and academic.
Jake Nicholson, English footballer births
Jake Charlie Nicholson is an English former footballer. He is a product of the West Ham United and Tottenham Hotspur youth academies. He has also represented England at under-19 level.
Paolo Borsellino, Italian lawyer and judge (b. 1940) deaths

Paolo Emanuele Borsellino was an Italian judge and prosecuting magistrate. From his office in the Palace of Justice in Palermo, Sicily, he spent most of his professional life trying to overthrow the power of the Sicilian Mafia. After a long and distinguished career, culminating in the Maxi Trial in 1986–1987, on 19 July 1992, Borsellino was killed by a car bomb in Via D'Amelio, near his mother's house in Palermo.
Eray İşcan, Turkish footballer births

Eray İşcan is a Turkish professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper.
Eddie Quillan, American actor (b. 1907) deaths

Edward Quillan was an American film actor and singer whose career began as a child on the vaudeville stages and silent film and continued through the age of television in the 1980s.
Sam McKendry, Australian-New Zealand rugby league player births

Sam McKendry is a former New Zealand Māori and New Zealand international rugby league footballer who played as a prop for the Penrith Panthers in the NRL.
Kazimierz Sabbat, Polish businessman and politician, President of the Republic of Poland (b. 1913) deaths

Kazimierz Aleksander Sabbat, was President of Poland-in-exile from 8 April 1986 until his death, 19 July 1989, after serving as Prime Minister of the Polish government-in-exile.

The president of Poland, officially the president of the Republic of Poland, is the head of state of Poland. Their rights and obligations are determined in the Constitution of Poland. The president heads the executive branch. In addition, the president has a right to dissolve parliament in certain cases, can veto legislation and represents Poland in the international arena.
Shane Dawson, American comedian and actor births

Shane Lee Yaw, known professionally as Shane Dawson, is an American YouTuber. He became one of the first people to rise to fame on the video-sharing platform YouTube.
Kevin Großkreutz, German footballer births

Kevin Großkreutz is a German former professional footballer who plays as a right back and winger for TuS Bövinghausen in the amateur-level Oberliga Westfalen.
Jakub Kovář, Czech ice hockey player births

Jakub Kovář is a Czech professional ice hockey goaltender who is currently playing for HC Sparta Praha in the Czech Extraliga. He was selected by the Philadelphia Flyers in the 4th round of the 2006 NHL Entry Draft. He is the older brother of Jan Kovář.
Jon Jones, American mixed martial artist births

Jonathan Dwight Jones is an American professional mixed martial artist currently signed to the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC), in which he has competed in the light heavyweight division. He is a former two-time UFC Light Heavyweight Champion, holding the title from March 2011 to April 2015 and from December 2018 to August 2020. Jones also held the interim UFC Light Heavyweight Championship in 2016. As of November 14, 2022, he is #13 in the UFC men's pound-for-pound rankings.
Marc Murphy, Australian footballer births

Marc Murphy is a retired Australian rules footballer who played for the Carlton Football Club in the Australian Football League (AFL). He was recruited with the first overall selection in the 2005 AFL draft and served as the captain of Carlton from the 2013 season to 2018. He is the son of John Murphy.
Leandro Greco, Italian footballer births

Leandro Greco is an Italian football coach and a former player who played as a midfielder. He is an assistant coach for Serie B club Südtirol.
LaMarcus Aldridge, American basketball player births

LaMarcus Nurae Aldridge is an American professional basketball player who last played for the Brooklyn Nets of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He played college basketball for two seasons with the Texas Longhorns. Aldridge was selected second overall in the 2006 NBA draft. After spending nine seasons with the Portland Trail Blazers, he signed with the San Antonio Spurs in 2015. In March 2021, he signed with the Brooklyn Nets after the Spurs bought out his contract. He retired after two weeks due to an irregular heartbeat, but returned to the Nets the following season after receiving medical clearance.
Zhou Haibin, Chinese footballer births

Zhou Haibin is a retired Chinese professional footballer who spent the majority of his playing career at Chinese Super League club Shandong Luneng.
Marina Kuzina, Russian basketball player births

Marina Kuzina is a Russian basketball player who competed for the Russian National Team at the 2008 Summer Olympics, winning the bronze medal. She was also part of the 2012 Summer Olympics Russian team who missed out on a bronze medal, losing the bronze medal match 74-83 to Australia.
Hadi Norouzi, Iranian footballer (d. 2015) births

Hadi Norouzi was an Iranian football striker who last played for Persepolis in the Persian Gulf Pro League.
Janusz Zajdel, Polish author (b. 1938) deaths

Janusz Andrzej Zajdel was a Polish science fiction author, second in popularity in Poland to Stanisław Lem. His major genres were social science fiction and dystopia. His main recurring theme involved the gloomy prospects for a space environment into which mankind carried totalitarian ideas and habits: Red Space Republics, or Space Labor Camps, or both. His heroes desperately try to find meaning in the world around them.
Andrea Libman, Canadian voice actress births

Andrea Eva Libman is a Canadian actress whose most popular on-screen appearances are in Little Women, Andre, and a guest role on The X-Files. She is also known for providing voice acting in various animated shows, most notably her worldwide recognition for voicing the characters of Pinkie Pie and Fluttershy in My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic and its spinoffs.
Adam Morrison, American basketball player births

Adam John Morrison is an American former professional basketball player. Morrison played for three years at Gonzaga University and was considered to be one of the top college basketball players in 2005–06. He was a finalist for the Naismith and the Wooden Award. He was named Co-Player of the Year with Duke's JJ Redick by the United States Basketball Writers Association and won the 2006 Chevrolet Player of the Year award. He played for the NBA teams Charlotte Bobcats from 2006 to 2009 and L.A. Lakers in 2009–2010.
Ryan O'Byrne, Canadian ice hockey player births

Ryan David O'Byrne is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player who played in the National Hockey League (NHL) from 2007 - 2013 with the Montreal Canadiens, Colorado Avalanche and the Toronto Maple Leafs. During this time, O'Byrne founded the Ryan O'Byrne Charity Camp, a non-profit hockey camp for youth. At the conclusion of the 2013 season, O'Byrne went on to play in the Kontinental Hockey League (KHL), Swiss National League (NL), and Swedish Hockey League, before retiring from a ten-year professional hockey career in 2016.
Lewis Price, Welsh footballer births

Lewis Peter Price is a retired Welsh international professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper. He is currently the First-Team Goalkeeping Coach for League One club Milton Keynes Dons.
Faina Ranevskaya, Russian actress (b. 1896) deaths

Faina Georgievna Ranevskaya, is recognized as one of the greatest Soviet actresses in both tragedy and comedy. She was also famous for her aphorisms.
Aziz Sami, Iraqi writer and translator (b. 1895) deaths
Aziz Sami Bey Abi-Samim was an Iraqi writer and translator. Born in Kirkuk, then part of the Ottoman Empire he moved to Istanbul to continue his studies and taught in schools in various parts of the Ottoman Empire, before ending up in Iraq upon the empire's disintegration. He held several government positions in the Ministries of Finance and Education. After the 14 July Revolution moved to the Institute of Fine Arts as dean there.
Helen Skelton, English television host and actress births

Helen Elizabeth Skelton is an English television presenter and actress. She co-presented the BBC children's programme Blue Peter from 2008 until 2013, and since 2014 has been a presenter on Countryfile. She also co-presented two series of the BBC One programme Holiday Hit Squad alongside Angela Rippon and Joe Crowley. She also presented the daytime series The Instant Gardener that ran for two seasons.
Fedor Tyutin, Russian ice hockey player births

Fedor Anatolievich Tyutin is a Russian former professional ice hockey defenceman. Tyutin was drafted in the second round, 40th overall by the New York Rangers in the 2001 NHL Entry Draft.
Christopher Bear, American drummer births
Christopher Bear is a drummer and multi-instrumentalist member of the Brooklyn-based indie-rock group Grizzly Bear.
Phil Coke, American baseball player births

Phillip Douglas Coke is an American former professional baseball pitcher. He played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the New York Yankees, Detroit Tigers, Chicago Cubs, Toronto Blue Jays, and Pittsburgh Pirates.
Jared Padalecki, American actor births

Jared Tristan Padalecki is an American actor. He is best known for playing the role of Sam Winchester in the TV series Supernatural. He grew up in Texas and rose to fame in the early 2000s after appearing on the television series Gilmore Girls as well as the films New York Minute (2004) and House of Wax (2005), later starring in Friday the 13th (2009).
Jess Vanstrattan, Australian footballer births

Jess Kedwell Vanstrattan is a retired Australian professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper.
Hugh Everett III, American physicist and mathematician (b. 1930) deaths

Hugh Everett III was an American physicist who first proposed the many-worlds interpretation (MWI) of quantum physics, which he termed his "relative state" formulation. In contrast to the then-dominant Copenhagen interpretation, the MWI posits that the wave function never collapses and that all possibilities of a quantum superposition are objectively real.
Nenê, Brazilian footballer births

Anderson Luiz de Carvalho, known as Nenê, is a Brazilian professional footballer who plays for Vasco da Gama. An attacking midfielder, he is mostly known for his crossing and dribbling ability, also being a free kick specialist.
David Bernard, Jamaican cricketer births
David Eddison Bernard is a West Indian cricketer who has played for the West Indies in Tests and ODIs. He played his second Test for a weakened West Indies team on 9 July 2009. In the second Test he scored 17 and 69.
Mark Gasnier, Australian rugby player and sportscaster births
Mark Gasnier is an Australian former professional rugby league footballer who played in the 2000s and 2010s. A rugby league New South Wales State of Origin and international representative centre, he played eleven seasons in the National Rugby League with the St. George Illawarra Dragons, punctuated by two seasons of rugby union played with the French club Stade Français. Gasnier was a member of the Dragons' NRL premiership-winning team in 2010. He retired at the end of the 2011 season. He is the nephew of the 1960s St. George star Reg Gasnier.
Jimmy Gobble, American baseball player births
Billy James Gobble is a former Major League Baseball pitcher who last played in the Colorado Rockies organization.
Grégory Vignal, French footballer births

Grégory Vignal is a French football coach and former professional player who is a youth coach for the Dundee U18s.
Roger Doucet, Canadian tenor (b. 1919) deaths

Roger Doucet, was a Canadian tenor best known for singing the Canadian national anthem, "O Canada", on televised games of the Montreal Canadiens, Montreal Alouettes, and Montreal Expos during the 1970s. He was particularly known for his bilingual version of the anthem, which began in French and ended in English, in recognition of the two languages of Canada.
Xavier Malisse, Belgian tennis player births

Xavier Malisse is a former Belgian professional tennis player. Born in the north-western Flemish city of Kortrijk and nicknamed X-Man, he is one of only two Belgian men to have been ranked in the top 20 of the ATP Tour, with a career-high singles ranking of world No. 19.
Giorgio Mondini, Italian race car driver births

Giorgio Mondini is an automobile racing driver from Geneva, Switzerland.
Margaret Craven, American journalist and author (b. 1901) deaths

Margaret Craven was an American writer.
Nihat Erim, Turkish jurist and politician, 13th Prime Minister of Turkey (b. 1912) deaths

İsmail Nihat Erim was a Turkish politician and jurist. He served as the 13th Prime Minister of Turkey for almost 14 months after the 1971 Turkish military memorandum. He was assassinated by the Revolutionary People's Liberation Party/Front in Istanbul in 1980.

The prime minister of the Republic of Turkey was the head of government of the Republic of Turkey from 1920 to 2018, who led a political coalition in the Turkish Parliament and presided over the cabinet. Throughout the political history of Turkey, functions and powers of the post have changed occasionally. Prior to its dissolution as a result of the 2017 Constitutional Referendum, the prime minister was generally the dominant figure in Turkish politics, outweighing the president.
Hans Morgenthau, German-American political scientist, philosopher, and academic (b. 1904) deaths

Hans Joachim Morgenthau was a German-American jurist and political scientist who was one of the major 20th-century figures in the study of international relations. Morgenthau's works belong to the tradition of realism in international relations theory; he is usually considered among the most influential realists of the post-World War II period. Morgenthau made landmark contributions to international relations theory and the study of international law. His Politics Among Nations, first published in 1948, went through five editions during his lifetime and was widely adopted as a textbook in U.S. universities. While Morgenthau emphasized the centrality of power and "the national interest", the subtitle of Politics Among Nations—"the struggle for power and peace"—indicates his concern not only with the struggle for power but the ways in which it is limited by ethics, norms and law.
Rick Ankiel, American baseball player births

Richard Alexander Ankiel is an American former professional baseball outfielder and pitcher who played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the St. Louis Cardinals, Kansas City Royals, Atlanta Braves, Washington Nationals, Houston Astros, and New York Mets.
Josué Anunciado de Oliveira, Brazilian footballer births

Josué Anunciado de Oliveira, or simply Josué, is a former Brazilian defensive midfielder.
Dilhara Fernando, Sri Lankan cricketer births

Congenige Randhi Dilhara Fernando is a former professional Sri Lankan international cricketer. He played as a right-handed pace bowler and was a key member of the Sri Lankan teams which finished as runners-up in the 2007 and 2011 ICC Cricket World Cups.
Luke Young, English footballer births

Luke Paul Young is an English former professional footballer who played as a defender.
Jean-Sébastien Aubin, Canadian ice hockey player births

Jean-Sébastien Aubin is a Canadian former professional ice hockey goaltender who played in the National Hockey League (NHL) with the Pittsburgh Penguins, Toronto Maple Leafs and the Los Angeles Kings.
Tony Mamaluke, American wrestler and manager births

Charles John Spencer is a retired American professional wrestler. He is best known for his appearances with World Championship Wrestling under the ring name Tony Marinara and with Extreme Championship Wrestling and World Wrestling Entertainment under the ring name Tony Mamaluke.
Ed Smith, English cricketer and journalist births
Edward Thomas Smith is an English author and journalist, former professional cricketer, and cricket commentator. He played first-class cricket for Kent, Middlesex and England.
Karl Ristikivi, Estonian geographer, author, and poet (b. 1912) deaths
Karl Ristikivi was an Estonian writer. He is among the best Estonian writers for his historical novels.
Benedict Cumberbatch, English actor births

Benedict Timothy Carlton Cumberbatch is an English actor. Known for his work on screen and stage, he has received various accolades, including a British Academy Television Award, a Primetime Emmy Award and a Laurence Olivier Award. He has also been nominated for two Academy Awards, two British Academy Film Awards and four Golden Globe Awards. In 2014, Time magazine named him one of the 100 most influential people in the world, and in 2015, he was appointed a CBE at Buckingham Palace for services to the performing arts and to charity.
Gonzalo de los Santos, Uruguayan footballer and manager births

Gonzalo de los Santos da Rosa is a Uruguayan retired footballer who played as a defensive midfielder, and is a manager.
Luca Castellazzi, Italian footballer births

Luca Castellazzi is an Italian former professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper. He serves as the team manager of Serie A club Torino.
Lefty Frizzell, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (b. 1928) deaths

William Orville "Lefty" Frizzell was an American country music singer-songwriter and honky-tonk singer.
Rey Bucanero, Mexican wrestler births
Arturo García Ortiz is a Mexican luchador or professional wrestler best known under the ring name Rey Bucanero. Ortiz, as Rey Bucanero, has worked for Consejo Mundial de Lucha Libre (CMLL) since 1996. His ring name is Spanish for "Buccaneer King", which was originally reflected in his mask that featured a skull face and an eye patch. Ortiz was unmasked in 1999 and has worked unmasked ever since.
Francisco Copado, German footballer and manager births
Francisco Alberto Copado Álvarez is a German retired footballer of Spanish origin who played as a striker or midfielder.
Josée Piché, Canadian ice dancer births
Josée Piché is a Canadian former ice dancer. She was born in Montreal and competed with partner Pascal Denis for 17 years, winning a bronze medal at the 2000 Canadian Figure Skating Championships and finishing 23rd at the 2004 World Figure Skating Championships, their final competition together.
Vince Spadea, American tennis player births

Vincent Spadea is a former professional tennis player from the United States.
Preston Wilson, American baseball player and sportscaster births

Preston James Richard Wilson is an American former professional baseball center fielder. He played all or parts of ten seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) from 1998 to 2007 for the New York Mets, Florida Marlins, Colorado Rockies, Washington Nationals, Houston Astros and St. Louis Cardinals. He is both the nephew and stepson of former New York Mets outfielder Mookie Wilson.
Ernő Schwarz, Hungarian-American soccer player and coach (b. 1904) deaths
Ernő Schwarz or Schwarcz was a Hungarian American soccer player, coach and promoter who served as head coach of the United States men's national soccer team. He played professionally in Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Austria and the United States, earning two caps, scoring two goals, with the Hungarian national team in 1922. Schwarz founded, owned, managed and played for the New York Americans in the first and second American Soccer Leagues. He was also the ASL and International Soccer League vice president. His daughter was married to United States national team player Ben Zinn.
Martin Powell, English keyboard player and songwriter births

Martin Powell is an English musician. In 1991, Powell auditioned for the position of bass player in the band My Dying Bride, but was turned down as the band had just filled the position. Upon informing the band he was also a violin and keyboard player, he was hired as a session musician, before becoming the band's permanent violinist and keyboardist.
Scott Walker, Canadian ice hockey player and coach births

Scott Walker is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player who currently serves as the co-owner and team president of the Guelph Storm in the OHL. He previously held the position of player development consultant for the Vancouver Canucks.
Ebbe Sand, Danish footballer and manager births

Ebbe Sand is a former professional footballer from Denmark who played as a forward for Brøndby IF in Denmark and FC Schalke 04 in Germany. He was the Bundesliga top scorer in 2001, and won the DFB-Pokal in 2001 and 2002 with Schalke. On the international stage, he represented the Denmark national team at the 1998 and 2002 FIFA World Cup, as well as the 2000 and 2004 European Championships. At the 1998 World Cup, he scored the fastest-ever World Cup goal by a substitute – 16 seconds after entering the match.
Rene Busch, Estonian tennis player and coach births

Rene Busch is a tennis coach and former Estonian tennis player. He achieved his career high ATP ranking in 1995 on No.793.
Vitali Klitschko, Ukrainian boxer and politician, Mayor of Kyiv births

Vitali Volodymyrovych Klitschko is a Ukrainian politician and former professional boxer who serves as mayor of Kyiv and head of the Kyiv City State Administration, having held both offices since June 2014. Klitschko is a former leader of the Petro Poroshenko Bloc and a former Member of the Ukrainian Parliament. He became actively involved in Ukrainian politics in 2005 and combined this with his professional boxing career until his retirement from the sport in 2013. He holds a Doctoral Degree (Ph.D.) from Kyiv University's Physical Science Department.

The Head of Kyiv City, unofficially and more commonly the Mayor of Kyiv, is a city official elected by popular vote who serves as a head of the Kyiv city state administration and a chairperson the Kyiv City Council.
Michael Modest, American wrestler births
Michael K. Cariglio is an American professional wrestler, better known by his stage name, Michael Modest. Modest ran the promotion Pro Wrestling IRON with tag partner Donovan Morgan and Frank Murdoch until its closure in 2005. Modest has also wrestled in Japan for Pro Wrestling Noah, winning the GHC Junior Heavyweight Championship after defeating Yoshinobu Kanemaru. He has also wrestled in Canada, Mexico and Ireland. He is perhaps best known for his appearances in the wrestling documentary Beyond the Mat, the film Ready to Rumble, and the TV special Exposed! Pro Wrestling's Greatest Secrets.
Catriona Rowntree, Australian television host births

Catriona Rowntree is an Australian television presenter.
Lesroy Weekes, Montserratian cricketer births
Lesroy Charlesworth Weekes is a former first-class cricketer.
Bill Chen, American poker player and software designer births

William Chen is an American quantitative analyst, poker player, software designer, and badminton player.
Nicola Sturgeon, Scottish lawyer and politician, First Minister of Scotland births

Nicola Ferguson Sturgeon is a Scottish politician serving as First Minister of Scotland and Leader of the Scottish National Party (SNP) since 2014. She is the first woman to hold either position. She has been a member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) since 1999, first as an additional member for the Glasgow electoral region, and as the member for Glasgow Southside from 2007.

The first minister of Scotland is the leader of the Scottish Government and keeper of the Great Seal of Scotland. The first minister chairs the Scottish Cabinet and is primarily responsible for the formulation, development and presentation of Scottish Government policy. Additional functions of the first minister include promoting and representing Scotland in an official capacity, at home and abroad.
Matthew Libatique, American cinematographer births

Matthew Libatique is an American cinematographer. He is best known for his work with director Darren Aronofsky on the films Pi (1998), Requiem for a Dream (2000), The Fountain (2006), Black Swan (2010), Noah (2014), and Mother! (2017). For his work on Black Swan and Bradley Cooper's directorial debut film, A Star Is Born (2018), Libatique was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Cinematography.
Stratis Myrivilis, Greek soldier and author (b. 1890) deaths

Efstratios Stamatopoulos was a Greek writer. He is known for writing novels, novellas, and short stories under the pseudonym Stratis Myrivilis. He is associated with the "Generation of the '30s". He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature three times.
Robb Flynn, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and producer births

Robert Conrad Flynn is an American musician who is the lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist for heavy metal band Machine Head. Flynn formed the band along with Adam Duce, Logan Mader and Tony Costanza after leaving Bay Area thrash band Vio-lence.
Pavel Kuka, Czech footballer and manager births

Pavel Kuka is a Czech former professional footballer who played as a forward.
Jim Norton, American comedian, actor, and author births

James Joseph Norton is an American comedian, radio personality, actor, author, and television and podcast host. Norton has been the co-host of the podcast UFC Unfiltered with Matt Serra and the morning radio show Jim Norton & Sam Roberts on SiriusXM Radio since 2016, and The Chip Chipperson Podacast since 2017.
Yael Abecassis, Israeli model and actress births

Yael Abecassis is an Israeli actress and model.
Jean-François Mercier, Canadian comedian, screenwriter, and television host births

Jean-François Mercier is a comedian, screenwriter and television host from Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Throughout his comedian career, Mercier has been known for his arguably scruffy appearance and part of his act is to mix social criticism with vulgarity, curse words and expressions of anger.
John T. McNaughton, United States Assistant Secretary of Defense for International Security Affairs and an advisor to Robert McNamara (b. 1921) deaths

John Theodore McNaughton born in Bicknell, Indiana, was United States Assistant Secretary of Defense for International Security Affairs and Robert S. McNamara's closest advisor. He died in a plane crash at age 45, just before he was to become Secretary of the Navy.

The United States under secretary of defense for policy (USDP) is a high level civilian official in the United States Department of Defense. The under secretary of defense for policy is the principal staff assistant and adviser to both the secretary of defense and the deputy secretary of defense for all matters concerning the formation of national security and defense policy.

Robert Strange McNamara was an American business executive and the eighth United States Secretary of Defense, serving from 1961 to 1968 under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson. He remains the longest serving Secretary of Defense, having remained in office over seven years. He played a major role in promoting the United States' involvement in the Vietnam War. McNamara was responsible for the institution of systems analysis in public policy, which developed into the discipline known today as policy analysis.
Odell Shepard, American poet and politician, 66th Lieutenant Governor of Connecticut (b. 1884) deaths
Odell Shepard was an American professor, poet, and politician who was the 86th Lieutenant Governor of Connecticut from 1941 to 1943. He won a Pulitzer Prize in 1938.

The following is a list of lieutenant governors of the State of Connecticut.
Evelyn Glennie, Scottish musician births

Dame Evelyn Elizabeth Ann Glennie, is a Scottish percussionist. She was selected as one of the two laureates for the Polar Music Prize of 2015.
Claus-Dieter Wollitz, German footballer and manager births
Claus-Dieter Wollitz is a German football coach and former player, who manages Energie Cottbus.
Syngman Rhee, South Korean journalist and politician, 1st President of South Korea (b. 1875) deaths

Syngman Rhee was a South Korean politician who served as the first president of South Korea from 1948 to 1960.

The president of the Republic of Korea, also known as the president of South Korea, is the head of state and head of government of the Republic of Korea. The president leads the State Council, and is the chief of the executive branch of the national government as well as the commander-in-chief of the Republic of Korea Armed Forces.
Teresa Edwards, American basketball player births
Teresa Edwards is an American former women's basketball player and four time Olympic gold medalist.
Masahiko Kondō, Japanese singer-songwriter and race car driver births

Masahiko Kondō or Matchy is a Japanese singer, lyricist, actor, racing car manager and former semi-professional racing driver. He was a member of the Tanokin Trio.
Thomas Gabriel Fischer, Swiss musician births

Thomas Gabriel Fischer, also known by his stage names of Tom G. Warrior and Satanic Slaughter, is a Swiss metal musician. He led the groups Hellhammer and Celtic Frost, and today is the frontman of the band Triptykon.
Garth Nix, Australian author births

Garth Richard Nix is an Australian writer who specialises in children's and young adult fantasy novels, notably the Old Kingdom, Seventh Tower and Keys to the Kingdom series. He has frequently been asked if his name is a pseudonym, to which he has responded, "I guess people ask me because it sounds like the perfect name for a writer of fantasy. However, it is my real name."
William Andrew, English priest (b. 1884) deaths
William Shaw Andrew MC was an Anglican priest in the mid 20th Century.
Anthony Edwards, American actor and director births

Anthony Charles Edwards is an American actor and director. He is known for his role as Dr. Mark Greene on the first eight seasons of ER, for which he received a Golden Globe award and six Screen Actors Guild Awards, and was nominated for four consecutive Primetime Emmy Awards. He has appeared in various films and television series, including Top Gun, Zodiac, Gotcha!, Miracle Mile, Revenge of the Nerds, Planes, Northern Exposure and Designated Survivor.
Harsha Bhogle, Indian journalist and author births

Harsha Bhogle is an Indian cricket commentator and journalist. He’s widely known as a "voice of cricket". Bhogle has cemented his reputation as being a personality in the global cricket broadcasting industry.
Maria Filatova, Russian gymnast births
Maria Evgenievna Filatova is a retired Soviet gymnast who competed at the 1976 and 1980 Olympics.
Lisa Lampanelli, American comedian, actress, and author births

Lisa Lampanelli is an American former stand-up comedian, actress and insult comic.
Benoît Mariage, Belgian director and screenwriter births

Benoît Mariage is a Belgian film director.
Hideo Nakata, Japanese director, producer, and screenwriter births

Hideo Nakata is a Japanese filmmaker.
Campbell Scott, American actor, director, and producer births

Campbell Scott is an American actor, producer and director. His roles include Steve Dunne in Singles, Mark Usher in House of Cards, Joseph Tobin in Damages, and Richard Parker in The Amazing Spider-Man and The Amazing Spider-Man 2, as well as narration in The Men Who Built America.
Atom Egoyan, Egyptian-Canadian director, producer, and screenwriter births

Atom Egoyan is a Canadian filmmaker. He was part of a loosely-affiliated group of filmmakers to emerge in the 1980s from Toronto known as the Toronto New Wave. Egoyan made his career breakthrough with Exotica (1994), a film set primarily in and around the fictional Exotica strip club. Egoyan's most critically acclaimed film is the drama The Sweet Hereafter (1997), for which he received two Academy Award nominations, and his biggest commercial success is the erotic thriller Chloe (2009). He is considered by local film critic Geoff Pevere to be one of the greatest filmmakers of his generation.
Kevin Haskins, English drummer and songwriter births
Kevin Michael Dompe, born and best-known as Kevin Michael Haskins, is an English drummer, best known from the British rock group Bauhaus. He was also a member of Tones on Tail and Love and Rockets.
Juan J. Campanella, Argentinian director, producer, and screenwriter births

Juan José Campanella is an Argentine television and film director, writer and producer. He achieved worldwide attention with the release of The Secret in Their Eyes (2009), for which he was awarded the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film.
Brad Drewett, Australian tennis player and sportscaster (d. 2013) births

Brad Drewett was an Australian tennis player and ATP official. He was the 1975 and 1977 Australian Open junior champion and the youngest player at age 17 to win the title since Ken Rosewall and John Newcombe. He was also the third-youngest Australian Open quarterfinalist in his first Grand Slam appearance, at 17 years 5 months in 1975, behind Boris Becker, 17 years 4 days in 1984 and Goran Ivanišević, 17 years 4 months in 1989.
Robert Gibson, American wrestler births

Robert Gibson is an American professional wrestler. He is best known as one half of the tag team known as The Rock 'n' Roll Express, with Ricky Morton. He has competed in singles competition also, and has won various singles championships throughout his career. Gibson was inducted into the WWE Hall of Fame as a member of The Rock 'n' Roll Express, on March 31, 2017.
David Robertson, American conductor births
David Eric Robertson is an American conductor. He was chief conductor of the Sydney Symphony Orchestra, and was formerly music director of the St. Louis Symphony Orchestra from 2005 until 2018. He is Director of Orchestral Studies at Juilliard.
Mark Crispin, American computer scientist, designed the IMAP (d. 2012) births
Mark Reed Crispin is best known as the father of the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), having invented it in 1985 during his time at the Stanford Knowledge Systems Laboratory. He is the author or co-author of numerous RFCs and was the principal author of UW IMAP, one of the reference implementations of the IMAP4rev1 protocol described in RFC 3501. He also designed the MIX mail storage format.
In computing, the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is an Internet standard protocol used by email clients to retrieve email messages from a mail server over a TCP/IP connection. IMAP is defined by RFC 9051.
Roger Binny, Indian cricketer and sportscaster births

Roger Michael Humphrey Binny is an Indian former international cricketer who is the 36th and incumbent president of Board of Control for Cricket in India. He was the president of Karnataka State Cricket Association from 2019 to 2022. Binny won the 1983 Cricket World Cup and the 1985 World Championship of Cricket, being India's highest wicket taker in both tournaments. He was also the head coach of the Indian U-19 team that won the 2000 Under-19 Cricket World Cup and has served as a national selector. He has also worked as a developmental officer in the Asian Cricket Council (ACC).
Dalton McGuinty, Canadian lawyer and politician, 24th Premier of Ontario births

Dalton James Patrick McGuinty Jr. is a former Canadian politician who served as the 24th premier of Ontario from 2003 to 2013. He was the first Liberal leader to win two majority governments since Mitchell Hepburn nearly 70 years earlier. In 2011, he became the first Liberal premier to secure a third consecutive term since Oliver Mowat after his party was re-elected in that year's provincial election.

The premier of Ontario is the head of government of Ontario. Under the Westminster system, the premier governs with the confidence of a majority the elected Legislative Assembly; as such, the premier typically sits as a member of Provincial Parliament (MPP) and leads the largest party or a coalition of parties. As first minister, the premier selects ministers to form the Executive Council, and serves as its chair. Constitutionally, the Crown exercises executive power on the advice of the Executive Council, which is collectively responsible to the legislature.
Mark O'Donnell, American playwright (d. 2012) births
Mark O’Donnell was an American writer and humorist.
Steve O'Donnell, American screenwriter and producer births

Steve O'Donnell is an American television writer. His credits include Late Night with David Letterman, The Simpsons, Seinfeld, and The Chris Rock Show.
Srđa Trifković, Serbian-American journalist and historian births

Srđa Trifković is a Serbian-American publicist, politician and historian.
Allen Collins, American guitarist and songwriter (d. 1990) births

Larkin Allen Collins Jr. was a legendary American guitarist. He was one of the founding members and guitarists of the southern rock band Lynyrd Skynyrd, and co-wrote many of the band's songs with frontman and original lead singer Ronnie Van Zant. He was born in Jacksonville, Florida.
Jayne Anne Phillips American novelist and short story writer births

Jayne Anne Phillips is an American novelist and short story writer who was born in the small town of Buckhannon, West Virginia.
Abel Ferrara, American director, producer, and screenwriter births

Abel Ferrara is an American filmmaker, known for the provocative and often controversial content in his movies and his use of neo-noir imagery and gritty urban settings. A long-time independent filmmaker, some of his best known movies include Ms .45 (1981), King of New York (1990), Bad Lieutenant (1992) and The Funeral (1996).
Per-Kristian Foss, Norwegian politician, Norwegian Minister of Finance births

Per-Kristian Foss is a Norwegian politician for the Conservative Party and from 2014 to 2021 the Auditor General of Norway.
The Minister of Finance is a councilor of state and chief of the Ministry of Finance. The position is since October 2021 held by Trygve Slagsvold Vedum of the Centre Party who is a member of Støre's Cabinet.
Freddy Moore, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births
Frederick George Moore was an American musician best known for his 1980 song "It's Not A Rumour", which he co-wrote with his ex-wife Demi Moore, and recorded with his band The Nu-Kats. The song was not a chart hit, but the video did receive airplay on MTV in the early 1980s. Moore's career spanned decades and included teaching himself to play guitar, writing the lyrics to 1,000 original songs, forming multiple bands, and even starring in a few film roles. Moore's bands performed at legendary Los Angeles clubs, including Whiskey a Go-Go, The Troubadour, and Starwood, and headlined alongside The Police, The Knack, and The Motels. His memoir, It's Not a Rumour, published in 2021, chronicles his unorthodox story of making it big in music and life without ever making a dime.
Adrian Noble, English director and screenwriter births
Adrian Keith Noble is a theatre director, and was also the artistic director and chief executive of the Royal Shakespeare Company from 1990 to 2003.
Kgalema Motlanthe, South African politician, 3rd President of South Africa births

Kgalema Petrus Motlanthe is a South African politician who was South Africa's third president between 25 September 2008 and 9 May 2009, following Thabo Mbeki’s resignation. Thereafter, he was deputy president under Jacob Zuma until 26 May 2014.

The president of South Africa is the head of state and head of government of the Republic of South Africa. The president heads the executive branch of the Government of South Africa and is the commander-in-chief of the South African National Defence Force. Between 1961 and 1994, the office of head of state was the state presidency.
Keith Godchaux, American keyboard player and songwriter (d. 1980) births
Keith Richard Godchaux was a pianist best known for his tenure in the rock group the Grateful Dead from 1971 to 1979.
André Forcier, Canadian director and screenwriter births

André Forcier is a Canadian film director and screenwriter. His work has been linked to Latin American magic realism by its use of fantasy but is firmly rooted in Quebec's reality. His unromanticized, even Rabelaisian, portraits of people on the fringe of society, especially in Bar Salon, Au clair de la lune, Une Historie inventée, Le Vent du Wyoming and The Countess of Baton Rouge, blend observations of minutia of everyday life with elements of fantasy and imaginary.
Hans-Jürgen Kreische, German footballer and manager births

Hans-Jürgen "Hansi" Kreische is a former East German footballer.
Bernie Leadon, American guitarist and songwriter births

Bernie Leadon is an American singer, musician, songwriter and founding member of the Eagles, for which he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1998. Prior to the Eagles, he was a member of three country rock bands: Hearts & Flowers, Dillard & Clark, and the Flying Burrito Brothers. He is a multi-instrumentalist coming from a bluegrass background. He introduced elements of this music to a mainstream audience during his tenure with the Eagles.
Brian May, English singer-songwriter, guitarist, producer, and astrophysicist births

Brian Harold May is an English guitarist, singer, songwriter, and astrophysicist, who achieved worldwide fame as the lead guitarist of the rock band Queen. May was a co-founder of Queen with lead singer Freddie Mercury and drummer Roger Taylor. His songwriting contributions helped Queen become among the most successful acts in music history.
U Razak, Burmese educator and politician (b. 1898) deaths

U Razak was a Burmese politician and an educationalist. He was a Bamar of Tamil ancestry and also was a cabinet minister in Aung San's pre-independence interim government, and was assassinated on 19 July 1947 along with six other cabinet ministers. July 19 is commemorated each year as Martyrs' Day in Myanmar. Razak was Minister of Education and National Planning, and was chairman of the Burma Muslim Congress.
Aung San, Burmese general and politician (b. 1915) deaths

Aung San was a Burmese politician, independence activist and revolutionary. He was instrumental in Myanmar's struggle for independence from British rule, but he was assassinated just six months before his goal was realized. Aung San is considered the founder of modern-day Myanmar and the Tatmadaw, and is commonly referred to by the titles "Father of the Nation", "Father of Independence", and "Father of the Tatmadaw".
Lyuh Woon-hyung, South Korean politician (b. 1886) deaths

Lyuh Woon-hyung or Yo Un-hyung was a Korean politician who argued that Korean independence was essential to world peace, and a reunification activist who struggled for the independent reunification of Korea following its national division in 1945.
Alan Gorrie, Scottish singer-songwriter and musician births

Alan Edward Gorrie is a Scottish bassist, guitarist, keyboardist and singer. He is a founding member of the Average White Band and remains one of two original members in the group's current line-up.
Ilie Năstase, Romanian tennis player and politician births

Ilie Theodoriu Năstase is a former World No. 1 Romanian tennis player. He was ranked world No. 1 in singles from 23 August 1973 to 2 June 1974, and was the first man to hold the top position on the computerized ATP rankings. Năstase is one of the 10 players in history who have won over 100 total ATP titles, with 64 in singles and 45 in doubles.Năstase won seven major titles: two in singles, three in men's doubles and two in mixed doubles. He also won four Masters Grand Prix year-end championship titles and seven Grand Prix Super Series titles (1970–73), the precursors to the current Masters 1000. He was the first professional sports figure to sign an endorsement contract with Nike, doing so in 1972. Năstase wrote several novels in French in the 1980s, and was inducted into the International Tennis Hall of Fame in 1991.
Paule Baillargeon, Canadian actress, director, and screenwriter births
Paule Baillargeon is a Canadian actress and film director. She won the Genie Award for Best Supporting Actress for her role in the film I've Heard the Mermaids Singing, and was a nominee for Best Director for The Sex of the Stars . Her film roles have included August 32nd on Earth , Jesus of Montreal , A Woman in Transit , Réjeanne Padovani and Days of Darkness .
George Frayne, American musician a.k.a. Commander Cody (d. 2021) births

Commander Cody and His Lost Planet Airmen were an American rock band founded in 1967. The group's leader and co-founder was pianist and vocalist George Frayne IV, alias Commander Cody.
Tim McIntire, American actor and singer (d. 1986) births
Timothy John McIntire was an American character actor, probably best known for his starring roles as Alan Freed in the film American Hot Wax (1978), as singer George Jones in the television movie Stand by Your Man (1981), The Gumball Rally (1976) and Brubaker (1980).
Andres Vooremaa, Estonian chess player births
Andres Vooremaa is an Estonian chess player, who twice won the Estonian Chess Championship. He was awarded the Soviet Master title in 1969.
Han Sai Por, Singaporean sculptor and academic births

Han Sai Por is a Singaporean sculptor. A graduate of the Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts (NAFA), East Ham College of Art, Wolverhampton College of Art and Lincoln University, New Zealand, she worked as a teacher and later as a part-time lecturer at NAFA, the LASALLE-SIA College of the Arts, and the National Institute of Education, Nanyang Technological University, before becoming a full-time artist in 1997.
Carla Mazzuca Poggiolini, Italian journalist and politician births

Carla Mazzuca Poggiolini is a professional journalist and Italian politician who served in both chambers of the Italian Parliament. She is the wife of Danilo Poggiolini.
Yekaterina Budanova, Russian captain and pilot (b. 1916) deaths

Yekaterina Vasilyevna Budanova, nicknamed Katya (Катя), was a fighter pilot in the Soviet Air Force during World War II. Usually credited with five or more aerial victories, along with Lydia Litvyak, she is often considered one of the world's two female fighter aces. She was shot down by either Luftwaffe ace Georg Schwientek of JG 52 or ace Emil Bitsch, of JG 3.
Vikki Carr, American singer and actress births

Florencia Vicenta de Casillas-Martínez Cardona, known by her stage name Vikki Carr, is an American vocalist. She has a singing career that spans more than four decades. Born in El Paso, Texas, to Mexican parents, she has performed in a variety of musical genres, including pop, jazz and country, while her greatest success has come from singing in Spanish. She established the Vikki Carr Scholarship Foundation in 1971. Vikki Carr has won three Grammys and was honored with a Lifetime Achievement Award at the Latin Grammys in 2008 at the 9th Annual Latin Grammy Awards.
Neelie Kroes, Dutch politician and diplomat, European Commissioner for Digital Economy and Society births

Neelie Kroes is a retired Dutch politician of the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) and businessperson who served as European Commissioner from 22 November 2004 to 1 November 2014.

The Executive Vice President of the European Commission for A Europe Fit for the Digital Age is an Executive Vice President of the European Commission responsible for media and information issues such as telecoms and IT. The current officeholder is Margrethe Vestager since December 2019.
Rose Hartwick Thorpe, American poet and author (b. 1850) deaths

Rose Hartwick Thorpe was an American poet and writer, remembered largely for the narrative poem, Curfew Must Not Ring Tonight (1867), which gained national popularity. It was translated into nearly every language of the world, and was universally recognized as a veritable classic. Other poems followed, among them being "The Station Agent's Story," "Red Cross," and "In a Mining Town." Although a busy and prolific author, she was ill for some years. In 1888, she and her family removed to San Diego, California, living in Rosemere, Pacific Beach.
Richard Jordan, American actor (d. 1993) births
Robert Anson Jordan Jr. was an American actor. A long-time member of the New York Shakespeare Festival, he performed in many Off Broadway and Broadway plays. His films include Logan's Run, Les Misérables, Old Boyfriends, Raise the Titanic, The Friends of Eddie Coyle, The Yakuza, Interiors, The Bunker, Dune, The Secret of My Success, Timebomb, The Hunt for Red October, Posse and Gettysburg.
Jayant Narlikar, Indian astrophysicist and astronomer births

Jayant Vishnu Narlikar is an Indian astrophysicist and emeritus professor at the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA). He developed with Sir Fred Hoyle the conformal gravity theory, known as Hoyle–Narlikar theory. It synthesises Albert Einstein's theory of relativity and Mach's principle. It proposes that the inertial mass of a particle is a function of the masses of all other particles, multiplied by a coupling constant, which is a function of cosmic epoch.
Tom Raworth, English poet and academic (d. 2017) births

Thomas Moore Raworth was an English-Irish poet, publisher, editor, and teacher who published over 40 books of poetry and prose during his life. His work has been translated and published in many countries. Raworth was a key figure in the British Poetry Revival.
George Hamilton IV, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 2014) births

George Hege Hamilton IV was an American country musician. He began performing in the late 1950s as a teen idol, switching to country music in the early 1960s.
David Colquhoun, English pharmacologist and academic births

David Colquhoun is a British pharmacologist at University College London (UCL). He has contributed to the general theory of receptor and synaptic mechanisms, and in particular the theory and practice of single ion channel function. He held the A.J. Clark chair of Pharmacology at UCL from 1985 to 2004, and was the Hon. Director of the Wellcome Laboratory for Molecular Pharmacology. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) in 1985 and an honorary fellow of UCL in 2004. Colquhoun runs the website DC's Improbable Science, which is critical of pseudoscience, particularly alternative medicine, and managerialism.
Nick Koback, American baseball player and golfer (d. 2015) births

Nicholas Nicholie Koback was a Russian American professional baseball player whose career spanned eight seasons, three of which were spent with the Major League Baseball (MLB) Pittsburgh Pirates (1953–55). At the age of 17, Koback signed with the Pirates as a bonus baby out of Hartford Public High School. He made his MLB debut without ever playing in the minor leagues. At the time, he was the youngest Pittsburgh Pirates player ever. During his first career start, Koback caught a complete game shutout by Pirates pitcher Murry Dickson. Most of Koback's time with Pittsburgh was spent as a bullpen catcher. Over his three-year MLB career, Koback compiled a .121 batting average with one run scored, four hits, one triple and one base on balls in 16 games played. The majority of his playing career was spent in the minor leagues with the Lincoln Chiefs, Williamsport Grays (1956), Hollywood Stars (1956–57), New Orleans Pelicans (1956–57), Columbus/Gastonia Pirates (1958) and Charleston Senators (1960). He batted and threw right-handed. During his career, he weighed 187 pounds (85 kg) and stood at 6 feet (180 cm). After retiring from baseball, Koback played pro–am golf in Connecticut.
Francisco de Sá Carneiro, Portuguese lawyer and politician, 111th Prime Minister of Portugal (d. 1980) births

Francisco Manuel Lumbrales de Sá Carneiro, GCTE, GCC, GCL was a Portuguese politician, Prime Minister of Portugal for most of 1980, and founder of the Social Democratic Party. He only held office of Prime Minister for eleven months, dying in a plane crash with his partner, "Snu" Abecassis, on 4 December 1980. A parliamentary inquiry said in 2004 that there was evidence of a bomb in the aircraft, after a 1995 inquiry had concluded there was evidence of sabotage.

The prime minister of Portugal is the head of government of Portugal. As head of government, the prime minister coordinates the actions of ministers, represents the Government of Portugal to the other bodies of state, is accountable to parliament and keeps the president informed. The prime minister can hold the role of head of government with the portfolio of one or more ministries.
Kaarle Krohn, Finnish historian and academic (b. 1863) deaths

Kaarle Krohn was a Finnish folklorist, professor and developer of the geographic-historic method of folklore research. He was born into the influential Krohn family of Helsinki. Krohn is best known outside of Finland for his contributions to international folktale research. He devoted most of his life to the study of the epic poetry that forms the basis for the Finnish national epic, the Kalevala.
Buster Benton, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 1996) births

Arley "Buster" Benton was an American blues guitarist and singer. He played guitar in Willie Dixon's Blues All-Stars and is best known for his solo rendition of Dixon's song "Spider in My Stew." Benton was tenacious, and despite the amputation of parts of both legs in the latter part of his lengthy career, he never stopped playing his own version of Chicago blues.
Jan Lindblad, Swedish biologist and photographer (d. 1987) births
Jan Victor Armas Lindblad was a Swedish naturalist, writer, photographer, film maker, and whistling artist who imitated animals.
Robert Stout, Scottish-New Zealand politician, 13th Prime Minister of New Zealand (b. 1844) deaths

Sir Robert Stout was a New Zealand politician who was the 13th premier of New Zealand on two occasions in the late 19th century, and later Chief Justice of New Zealand. He was the only person to hold both these offices. He was noted for his support of liberal causes such as women's suffrage, and for his strong belief that philosophy and theory should always triumph over political expediency.

The prime minister of New Zealand is the head of government of New Zealand. The incumbent prime minister, Jacinda Ardern, leader of the New Zealand Labour Party, took office on 26 October 2017.
Gaston Glock, Austrian engineer and businessman, co-founded Glock Ges.m.b.H. births
Gaston Glock is an Austrian engineer and businessman who is the founder of the company Glock, who are best known for developing the Glock pistol in 1981.

Glock Ges.m.b.H. is a weapons manufacturer headquartered in Deutsch-Wagram, Austria, named after its founder, Gaston Glock. While the company is best known for its line of polymer-framed pistols, it also produces field knives, entrenching tools, and apparel.
Orville Turnquest, Bahamian politician births
Sir Orville Alton Turnquest is a politician who was the Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister of the Bahamas from 1992 to 1994, and the sixth governor-general of the Bahamas from 3 January 1995 until his retirement on 13 November 2001.
Samuel John Hazo, American author births
Samuel John Hazo is a poet, playwright, fiction novelist, and the founder and director of the International Poetry Forum in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. He is also McAnulty Distinguished Professor of English Emeritus at Duquesne University, where he taught for forty-three years.
Choi Yun-chil, South Korean long-distance runner and a two-time national champion in the marathon (d. 2020) births
Choi Yun-chil was a South Korean long-distance runner who was a two-time Olympian and a two-time national champion in the marathon.

The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of 42.195 km, usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair divisions. More than 800 marathons are held throughout the world each year, with the vast majority of competitors being recreational athletes, as larger marathons can have tens of thousands of participants.
Helen Gallagher, American actress, singer, and dancer births

Helen Gallagher is an American actress, dancer, and singer. She is the recipient of three Emmy Awards, two Tony Awards, and a Drama Desk Award.
Sue Thompson, American singer (d. 2021) births
Sue Thompson was an American pop and country music singer. She was best known for the million selling hits "Sad Movies " and "Norman", both pop hits in the early 1960s, and her 1965 hit "Paper Tiger".
John Indermaur, British lawyer (b. 1851) deaths
John Indermaur was a British lawyer and legal writer, with his writing focus was on common law. He is known for having written An Epitome of Leading Common Law Cases in 1875, Principles of Common Law in 1876, and The Student's Guide to Trusts and Partnerships in 1885. Indermaur qualified as a solicitor in 1874. He and his law partner, Charles Thwaites, had a law firm on Chancery Lane in the City of London and began teaching and writing about law together in 1884. Other legal works written by Indermaur include A Manual of the Principals of Equity, The Student's Guide to Procedure and Evidence, and Principals and Practice in Matters Appertaining to Conveyancing.
Stanley K. Hathaway, American soldier, lawyer, and politician, 40th United States Secretary of the Interior (d. 2005) births

Stanley Knapp Hathaway served as the 27th Governor of Wyoming from January 2, 1967 to January 6, 1975, and as United States Secretary of the Interior under President Gerald Ford from June to October, 1975.

The United States secretary of the interior is the head of the United States Department of the Interior. The secretary and the Department of the Interior are responsible for the management and conservation of most federal land along with natural resources, leading such agencies as the Bureau of Land Management, the United States Geological Survey, Bureau of Indian Affairs and the National Park Service. The secretary also serves on and appoints the private citizens on the National Park Foundation Board. The secretary is a member of the United States Cabinet and reports to the president of the United States. The function of the U.S. Department of the Interior is different from that of the interior minister designated in many other countries.
Pat Hingle, American actor and producer (d. 2009) births

Martin Patterson Hingle was an American character actor who appeared in stage productions and in hundreds of television shows and feature films. His first film was On the Waterfront in 1954. He often played tough authority figures. Hingle was a close friend of Clint Eastwood and appeared in the Eastwood films Hang 'em High, The Gauntlet, and Sudden Impact. He also portrayed Jim Gordon in the Batman film franchise from 1989 to 1997.
Arthur Rankin Jr., American director, producer, and screenwriter (d. 2014) births
Arthur Gardner Rankin Jr. was an American director, producer and writer, who mostly worked in animation. Co-creator of Rankin/Bass Productions with his friend Jules Bass, he created stop-motion animation features such as Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer, Frosty the Snowman, Santa Claus Is Comin' to Town and the 1977 cartoon special of The Hobbit. He is credited on over 1,000 television programs.
Theo Barker, English historian (d. 2001) births
Theodore Cardwell Barker, usually known as Theo Barker, was a British social and economic historian.
Alex Hannum, American basketball player and coach (d. 2002) births

Alexander Murray Hannum was a professional basketball player and coach. Hannum coached two National Basketball Association (NBA) teams and one American Basketball Association (ABA) team to league championships. He had a combined NBA-ABA record of 649–564 (.535) in the regular season and 61–46 (.570) in the playoffs over 16 seasons. In 1998, he was inducted into the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame as a coach.
Joseph Hansen, American author and poet (d. 2004) births

Joseph Hansen was an American crime writer and poet, best known for a series of novels featuring private eye Dave Brandstetter.
William A. Rusher, American lawyer and journalist (d. 2011) births

William Allen Rusher was an American lawyer, author, activist, and conservative columnist. He was one of the founders of the conservative movement and was one of its most prominent spokesmen for thirty years as publisher of National Review magazine, which was edited by William F. Buckley Jr. Historian Geoffrey Kabaservice argues that, "in many ways it was Rusher, not Buckley, who was the founding father of the conservative movement as it currently exists. We have Rusher, not Buckley, to thank for the populist, operationally sophisticated, and occasionally extremist elements that characterize the contemporary movement."
Lon Simmons, American baseball player and sportscaster (d. 2015) births

Lonnie Alexander "Lon" Simmons was an American sports announcer, best known for his play-by-play broadcasts of San Francisco Giants baseball and San Francisco 49ers football.
George McGovern, American lieutenant, historian, and politician (d. 2012) births

George Stanley McGovern was an American historian and South Dakota politician who was a U.S. representative and three-term U.S. senator, and the Democratic Party presidential nominee in the 1972 presidential election.
Rachel Robinson, American professor, registered nurse, and the widow of baseball player Jackie Robinson births

Rachel Annetta Robinson is the widow of professional baseball player Jackie Robinson, as well as an American former professor and registered nurse.
Harold Camping, American evangelist, author, radio host (d. 2013) births

Harold Egbert Camping was an American Christian radio broadcaster and evangelist. Beginning in 1958, he served as president of Family Radio, a California-based radio station group that, at its peak, broadcast to more than 150 markets in the United States. In October 2011, he retired from active broadcasting following a stroke, but still maintained a role at Family Radio until his death. Camping is notorious for issuing a succession of failed predictions of dates for the End Times, which temporarily gained him a global following and millions of dollars of donations.
André Moynet, French soldier, race car driver, and politician (d. 1993) births

André Moynet was a much decorated French wartime fighter pilot who moved on to become a test pilot and an entrepreneur-businessman. He was also a politician.
Elizabeth Spencer, American novelist, short story writer, and playwright (d. 2019) births

Elizabeth Spencer was an American writer. Spencer's first novel, Fire in the Morning, was published in 1948. She wrote a total of nine novels, seven collections of short stories, a memoir, and a play. Her novella The Light in the Piazza (1960) was adapted for the screen in 1962 and transformed into a Broadway musical of the same name in 2005. She was a five-time recipient of the O. Henry Award for short fiction.
Rosalyn Sussman Yalow, American physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 2011) births

Rosalyn Sussman Yalow was an American medical physicist, and a co-winner of the 1977 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for development of the radioimmunoassay technique. She was the second woman, and the first American-born woman, to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
Robert Mann, American violinist, composer, and conductor (d. 2018) births

Robert Nathaniel Mann was a violinist, composer, conductor, and founding member of the Juilliard String Quartet, as well as a faculty member at the Manhattan School of Music. Mann, the first violinist at Juilliard, served on the school's string quartet for over fifty years until his retirement in 1997.
Richard Oriani, Salvadoran-American metallurgist and engineer (d. 2015) births

Richard A. Oriani was an El Salvador-born American chemical engineer and metallurgist who was instrumental in the study of the effects of hydrogen in metal. He also made significant contributions to the field of cold fusion.
Patricia Medina, English-American actress (d. 2012) births

Patricia Paz Maria Medina was a British actress. She is perhaps best known for her roles in the films Phantom of the Rue Morgue (1954) and Mr. Arkadin (1955).
Miltos Sachtouris, Greek poet and author (d. 2005) births
Miltos Sachtouris or Miltos Sahtouris was a Greek poet. He was a descendant of Georgios Sachtouris, whose origins were the Island of Ydra. When he was young he abandoned his law studies to follow his real passion, poetry, adopting the pen name Miltos Chrysanthis. Sachtouris wrote his first poem, The Music Of My Islands, under his pen name in 1941.
Ron Searle, English-Canadian soldier, publisher, and politician, 4th Mayor of Mississauga (d. 2015) births
Ronald Alfred Searle was an English-born Canadian soldier, publisher, and politician who served as the fourth mayor of Mississauga, Ontario from 1976 to 1978.

The mayor of Mississauga is the head of Mississauga City Council and chief executive officer of the municipal government. The mayor is elected alongside city council every four years on the fourth Monday of October; there are no term limits. While in office, mayors are styled His/Her Worship.
William Scranton, American captain and politician, 13th United States Ambassador to the United Nations (d. 2013) births

William Warren Scranton was an American Republican Party politician and diplomat. Scranton served as the 38th Governor of Pennsylvania from 1963 to 1967, and as United States Ambassador to the United Nations from 1976 to 1977. "Many who serve as governor today are still measured against Bill Scranton's leadership - some 50 years later," said former state Republican National Committeewoman Elsie Hillman when she learned of Scranton's death in 2013.

The United States ambassador to the United Nations is the leader of the U.S. delegation, the U.S. Mission to the United Nations. The position is formally known as the permanent representative of the United States of America to the United Nations, with the rank and status of ambassador extraordinary and plenipotentiary, and representative of the United States of America in the United Nations Security Council.
Phil Cavarretta, American baseball player and manager (d. 2010) births

Philip Joseph Cavarretta was an American Major League Baseball first baseman, outfielder, and manager. He was known to friends and family as "Phil" and was also called "Philibuck", a nickname bestowed by Cubs manager Charlie Grimm.
Åke Hellman, Finnish painter (d. 2017) births

Åke Fredrik Hellman was a Swedish-speaking Finnish still life and portrait artist and art professor. He worked as art teacher at the University of Helsinki. In 1963, he received the order of the Lion of Finland.
Marius Russo, American baseball player (d. 2005) births

Marius Ugo Russo was a starting pitcher in Major League Baseball who played for the New York Yankees. Russo batted right-handed and threw left-handed.
Kay Linaker, American actress and screenwriter (d. 2008) births

Mary Katherine Linaker was an American actress and screenwriter who appeared in many B movies during the 1930s and 1940s, most notably Kitty Foyle (1940) starring Ginger Rogers. Linaker used her married name, Kate Phillips, as a screenwriter, notably for the cult movie hit The Blob (1958). She is credited with coining the name "The Blob" for the movie, which was originally titled "The Molten Meteor".
Clímaco Calderón, Colombian lawyer and politician, 15th President of Colombia (b. 1852) deaths

Clímaco Calderón Reyes was a Colombian lawyer and politician, who became 15th President of Colombia for one day, following the death of President Francisco Javier Zaldúa.

The president of Colombia, officially known as the president of the Republic of Colombia or president of the nation is the head of state and head of government of Colombia. The office of president was established upon the ratification of the Constitution of 1819, by the Congress of Angostura, convened in December 1819, when Colombia was the "Gran Colombia". The first president, General Simón Bolívar, took office in 1819. His position, initially self-proclaimed, was subsequently ratified by Congress.
Peter Leo Gerety, American prelate (d. 2016) births

Peter Leo Gerety was an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as the Archbishop of Newark in New Jersey from 1974 to 1986, having previously served as Bishop of Portland in Maine from 1969 to 1974. Gerety was the oldest living Catholic bishop in the world at the time of his death at age 104.
Balamani Amma, Indian poet and author (d. 2004) births

Nalapat Balamani Amma was an Indian poet who wrote in Malayalam. Amma (Mother), Muthassi (Grandmother), and Mazhuvinte Katha are some of her well-known works. She was a recipient of many awards and honours, including the Padma Bhushan, Saraswati Samman, Sahitya Akademi Award, and Ezhuthachan Award. She was the mother of writer Kamala Surayya.
Daniel Fry, American contactee (d. 1992) births
Daniel William Fry was an American contactee who claimed he had multiple contacts with an alien and took a ride in a remotely piloted alien spacecraft on July 4, 1949. He was born in Verdon Township, Minnesota.
Isabel Jewell, American actress (d. 1972) births

Isabel Jewell was an American actress who rose to prominence in the 1930s and early 1940s. Some of her more famous films were Ceiling Zero, Marked Woman, A Tale of Two Cities, and Gone with the Wind.
Robert Todd Lincoln Beckwith, American lawyer and farmer (d. 1985) births

Robert Todd Lincoln Beckwith was an American gentleman farmer known as a great-grandson of Abraham Lincoln. In 1975, he became the last undisputed descendant of Lincoln when his sister, Mary Lincoln Beckwith, died without children.
Samudrala Sr., Indian singer, director, producer, and screenwriter (d. 1968) births
Samudrala Raghavacharya, also known as Samudrala Sr., was an Indian screenwriter, lyricist, playback singer, director, and producer known for his works in Telugu cinema. Samudrala Senior made his screen debut in 1937, and known for his collaborations with Ghantasala. grand son samudrala srinivaas
Balai Chand Mukhopadhyay, Indian physician, author, poet, and playwright (d. 1979) births

Balai Chand Mukhopadhyay was an Indian Bengali-language novelist, short story writer, playwright, poet, and physician who wrote under the pen name of Banaphul. He was a recipient of the civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan.
Herbert Marcuse, German-American sociologist and philosopher (d. 1979) births

Herbert Marcuse was a German-American philosopher, social critic, and political theorist, associated with the Frankfurt School of critical theory. Born in Berlin, Marcuse studied at the Humboldt University of Berlin and then at Freiburg, where he received his PhD. He was a prominent figure in the Frankfurt-based Institute for Social Research – what later became known as the Frankfurt School. He was married to Sophie Wertheim (1924–1951), Inge Neumann (1955–1973), and Erica Sherover (1976–1979). In his written works, he criticized capitalism, modern technology, Soviet Communism and popular culture, arguing that they represent new forms of social control.
Reginald Baker, English film producer (d. 1985) births
Reginald Poynton Baker, MC FCA FRSA was a British film producer and a major contributor to the development of the British film industry. Along with his younger brother Leslie Forsyth, he played a decisive role in establishing Ealing Studios. He was the father of Conservative MP Peter Baker. Baker died in Australia aged 89.
A. J. Cronin, Scottish physician and novelist (d. 1981) births

Archibald Joseph Cronin, known as A. J. Cronin, was a Scottish physician and novelist. His best-known novel is The Citadel (1937), about a Scottish doctor who serves in a Welsh mining village before achieving success in London, where he becomes disillusioned about the venality and incompetence of some doctors. Cronin knew both areas, as a medical inspector of mines and as a doctor in Harley Street. The book exposed unfairness and malpractice in British medicine and helped to inspire the National Health Service. The Stars Look Down, set in the North East of England, is another of his best-selling novels inspired by his work among miners. Both novels have been filmed, as have Hatter's Castle, The Keys of the Kingdom and The Green Years. His 1935 novella Country Doctor inspired a long-running BBC radio and TV series, Dr. Finlay's Casebook (1962–1971), set in the 1920s. There was a follow-up series in 1993–1996.
Bob Meusel, American baseball player and sailor (d. 1977) births

Robert William Meusel was an American baseball left and right fielder who played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for eleven seasons from 1920 through 1930, all but the last for the New York Yankees. He was best known as a member of the Yankees' championship teams of the 1920s, nicknamed the "Murderers' Row", during which time the team won its first six American League (AL) pennants and first three World Series titles.
Abraham H. Cannon, American publisher and religious leader (b. 1859) deaths

Abraham Hoagland Cannon was a member of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Xu Beihong, Chinese painter and academic (d. 1953) births

Xu Beihong, also known as Ju Péon, was a Chinese painter.
Aleksandr Khinchin, Russian mathematician and academic (d. 1959) births

Aleksandr Yakovlevich Khinchin was a Soviet mathematician and one of the most significant contributors to the Soviet school of probability theory.
Khawaja Nazimuddin, Bangladeshi-Pakistani politician, 2nd Prime Minister of Pakistan (d. 1965) births

Sir Khawaja Nazimuddin, KCIE was a Pakistani barrister, politician and statesman and among the founding fathers of Pakistan. He served as the 2nd Governor-General of Pakistan from 1948 to 1951 and as 2nd Prime Minister of Pakistan from 1951 to 1953.

The prime minister of Pakistan is the head of government of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Executive authority is vested in the prime minister and his chosen cabinet, despite the president of Pakistan serving as the nominal head of executive. The prime minister is often the leader of the party or the coalition with a majority in the lower house of the Parliament of Pakistan, the National Assembly where he serves as Leader of the House. Prime minister holds office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the National Assembly. The prime minister is designated as the "Chief Executive of the Islamic Republic".
Percy Spencer, American physicist and inventor of the microwave oven (d. 1969) births
Percy Lebaron Spencer was an American physicist and inventor. He became known as the inventor of the microwave oven.

A microwave oven is an electric oven that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range. This induces polar molecules in the food to rotate and produce thermal energy in a process known as dielectric heating. Microwave ovens heat foods quickly and efficiently because excitation is fairly uniform in the outer 25–38 mm (1–1.5 inches) of a homogeneous, high-water -content food item.
Vladimir Mayakovsky, Russian actor, playwright, and poet (d. 1930) births

Vladimir Vladimirovich Mayakovsky was a Russian and Soviet poet, playwright, artist, and actor.
Dick Irvin, Canadian ice hockey player and coach (d. 1957) births

James Dickinson "Dick" Irvin Jr. was a Canadian professional ice hockey player and coach. He played for professional teams in the Pacific Coast Hockey Association, the Western Canada Hockey League, and the National Hockey League (NHL) from 1916 to 1928, when he had to retire from repeated injuries. Irvin was one of the greatest players of his day, balancing a torrid slap shot and tough style with gentlemanly play. For his playing career, Irvin was named to the Hockey Hall of Fame in 1958. After playing, Irvin built a successful career as a coach in the NHL with the Chicago Black Hawks, Toronto Maple Leafs, and Montreal Canadiens. He won one Stanley Cup as a coach with Toronto, three more with Montreal, finishing with over 600 wins as a coach. He also served in the Canadian Expeditionary Force during the First World War.
George II of Greece (d. 1947) births

George II was King of Greece from September 1922 to March 1924 and from November 1935 to his death in April 1947.
Enno Lolling, German physician (d. 1945) births

Enno Lolling was a Nazi doctor. As a member of the SS, he served as a Lagerarzt at Dachau concentration camp. He later headed up the medical division for all the SS concentration camps. Lolling committed suicide in Flensburg as the war was ending.
Michael Fekete, Hungarian-Israeli mathematician and academic (d. 1957) births

Michael (Mihály) Fekete was a Hungarian-Israeli mathematician.
Max Fleischer, Austrian-American animator and producer (d. 1972) births

Max Fleischer was an American animator, inventor, film director and producer, and studio founder and owner. Born in Kraków, Fleischer immigrated to the United States where he became a pioneer in the development of the animated cartoon and served as the head of Fleischer Studios, which he co-founded with his younger brother Dave. He brought such comic characters as Koko the Clown, Betty Boop, Popeye, and Superman to the movie screen, and was responsible for several technological innovations, including the rotoscope, the "follow the bouncing ball" technique pioneered in the Ko-Ko Song Car-Tunes films, and the "stereoptical process". Film director Richard Fleischer was his son.
John William Bean, English criminal and failed regicide (b. 1824) deaths
John William Bean was a British criminal and mental patient. He was most known for attempting to assassinate Queen Victoria with a gun loaded with paper and tobacco. Born a dwarf with a hunchback, Bean shot at the Queen because he wanted to be transported to a penal colony as he was unhappy with his life in England. Instead he was sentenced to 18 months' imprisonment for misdemeanour assault. Bean died in 1882 after committing suicide.
Friedrich Dessauer, German physicist and philosopher (d. 1963) births
Friedrich Dessauer was a physicist, a philosopher, a socially engaged entrepreneur and a journalist.
Yegor Ivanovich Zolotarev, Russian mathematician and academic (b. 1847) deaths

Yegor (Egor) Ivanovich Zolotarev was a Russian mathematician.
Arthur Fielder, English cricketer (d. 1949) births

Arthur Fielder was an English professional cricketer who played as a fast bowler for Kent County Cricket Club and the England cricket team from 1900 to 1914. He played a major role in Kent's four County Championship wins in the years before World War I and toured Australia twice with the England team making six Test match appearances. He was chosen as one of Wisden's Cricketers of the Year in 1907.
Joseph Fielding Smith, American religious leader, 10th President of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (d. 1972) births

Joseph Fielding Smith Jr. was an American religious leader and writer who served as the tenth president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints from 1970 until his death in 1972. He was the son of former church president Joseph F. Smith and the great-nephew of Church founder Joseph Smith.

The President of the Church is the highest office of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. It was the office held by Joseph Smith, the church's founder. The church's president is its leader and the head of the First Presidency, its highest governing body. Latter-day Saints consider the president of the church to be a "prophet, seer, and revelator" and refer to him as "the Prophet", a title that was originally given to Smith. When the name of the president is used by adherents, it is usually prefaced by the title "President". Russell M. Nelson has been the president since January 14, 2018.
Alice Dunbar Nelson, American poet and activist (d. 1935) births

Alice Dunbar Nelson was an American poet, journalist, and political activist. Among the first generation born free in the South after the Civil War, she was one of the prominent African Americans involved in the artistic flourishing of the Harlem Renaissance. Her first husband was the poet Paul Laurence Dunbar. After his death, she married physician Henry A. Callis; and, lastly, was married to Robert J. Nelson, a poet and civil rights activist. She achieved prominence as a poet, author of short stories and dramas, newspaper columnist, activist for women's rights, and editor of two anthologies.
Xenophon Stratigos, Greek general and politician, Greek Minister of Transport (d. 1927) births

Xenophon Stratigos was a senior staff officer of the Hellenic Army who played a major role in the Balkan Wars of 1912–13 and the Asia Minor Campaign in 1921–22, serving also as de facto Chief of the Hellenic Army General Staff in 1916–17 and in 1921. He retired from the army in September 1921 and served as Minister for Transport in 1922. Condemned to life imprisonment at the Trial of the Six, he was later pardoned and left for Switzerland, where he lived until his death.
The Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport is a government department of Greece headquartered in Cholargos, Athens.
Florence Foster Jenkins, American soprano and educator (d. 1944) births

Florence Foster Jenkins was an American socialite and amateur soprano who became known, and mocked, for her flamboyant performance costumes and notably poor singing ability. Stephen Pile ranked her "the world's worst opera singer ... No one, before or since, has succeeded in liberating themselves quite so completely from the shackles of musical notation."
Georges Friedel, French mineralogist and crystallographer (d. 1933) births

Georges Friedel was a French mineralogist and crystallographer.
Charles Horace Mayo, American surgeon, co-founder of the Mayo Clinic (d. 1939) births

Charles Horace Mayo was an American medical practitioner and was one of the founders of the Mayo Clinic along with his brother William James Mayo, Augustus Stinchfield, Christopher Graham, E. Star Judd, Henry Stanley Plummer, Melvin Millet, and Donald Balfour.

The Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staff, across three major campuses: Rochester, Minnesota; Jacksonville, Florida; and Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona. The practice specializes in treating difficult cases through tertiary care and destination medicine. It is home to the top-15 ranked Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine in addition to many of the highest regarded residency education programs in the United States. It spends over $660 million a year on research and has more than 3,000 full-time research personnel.
Fiammetta Wilson, English astronomer (d. 1920) births

Fiammetta Wilson was a British astronomer elected a fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society in 1916.
Lizzie Borden, American woman, tried and acquitted for the murders of her father and step-mother in 1892 (d. 1927) births

Lizzie Andrew Borden was an American woman tried and acquitted of the August 4, 1892 axe murders of her father and stepmother in Fall River, Massachusetts. No one else was charged in the murders, and despite ostracism from other residents, Borden spent the remainder of her life in Fall River. She died of pneumonia at age 66, just days before the death of her older sister, Emma.
Stefano Franscini, Swiss statistician and politician (b. 1796) deaths

Stefano Franscini was a Swiss politician and statistician. He was one of the initial members of the Swiss Federal Council elected in 1848 and Switzerland's first native Italian speaking federal councillor. Franscini was affiliated to the Liberal Radical Party of Switzerland. During his office tenure he held the Department of Home Affairs. Important elements of his political legacy include political reforms in the Ticino during the 1830s and 1840s, Switzerland's first federal population census in 1850, and the creation of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in 1854/1855.
Konstantin Batyushkov, Russian poet and translator (b. 1787) deaths

Konstantin Nikolayevich Batyushkov was a Russian poet, essayist and translator of the Romantic era. He also served in the diplomatic corps, spending an extended period in 1818 and 1819 as a secretary to the Russian diplomatic mission at Naples.
Margaret Fuller, American journalist and critic (b. 1810) deaths

Sarah Margaret Fuller, sometimes referred to as Margaret Fuller Ossoli, was an American journalist, editor, critic, translator, and women's rights advocate associated with the American transcendentalism movement. She was the first American female war correspondent and full-time book reviewer in journalism. Her book Woman in the Nineteenth Century is considered the first major feminist work in the United States.
Ferdinand Brunetière, French scholar and critic (d. 1906) births

Ferdinand Brunetière was a French writer and critic.
Edward Charles Pickering, American astronomer and physicist (d. 1919) births

Edward Charles Pickering was an American astronomer and physicist and the older brother of William Henry Pickering. Along with Carl Vogel, Pickering discovered the first spectroscopic binary stars. He wrote Elements of Physical Manipulations.
Frederic T. Greenhalge, English-American lawyer and politician, 38th Governor of Massachusetts (d. 1896) births

Frederic Thomas Greenhalge was a British-born lawyer and politician in the United States state of Massachusetts. He served in the United States House of Representatives and was the state's 38th governor. He was elected three consecutive times, but died early in his third term. He was the state's first foreign-born governor.

The governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the chief executive officer of the government of Massachusetts. The governor is the head of the state cabinet and the commander-in-chief of the commonwealth's military forces.
Pierre Louis Dulong, French physicist and chemist (b. 1785) deaths

Pierre Louis Dulong FRS FRSE was a French physicist and chemist. He is remembered today largely for the law of Dulong and Petit, although he was much-lauded by his contemporaries for his studies into the elasticity of steam, conduction of heat, and specific heats of gases. He worked most extensively on the specific heat capacity and the expansion and refractive indices of gases. He collaborated several times with fellow scientist Alexis Petit, the co-creator of the Dulong–Petit law.
Justo Rufino Barrios, Guatemalan president (d. 1885) births

Justo Rufino Barrios Auyón was a Guatemalan politician and military general who served as President of Guatemala from 1873 to his death in 1885. He was known for his liberal reforms and his attempts to reunite Central America.

Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. Guatemala is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Honduras; to the southeast by El Salvador and to the south by the Pacific Ocean, respectively. With an estimated population of around 17.6 million, it is the most populous country in Central America and is the 11th most populous country in the Americas. Guatemala is a representative democracy; its capital and largest city is Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the largest city in Central America.

The president of Guatemala, officially known as the President of the Republic of Guatemala, is the head of state and head of government of Guatemala, elected to a single four-year term. The position of President was created in 1839.
Edgar Degas, French painter, sculptor, and illustrator (d. 1917) births

Edgar Degas was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
Mangal Pandey, Indian soldier (d. 1857) births

Mangal Pandey was an Indian soldier who played a key part in the events immediately preceding the outbreak of the Indian rebellion of 1857. He was a sepoy (infantryman) in the 34th Bengal Native Infantry (BNI) regiment of the British East India Company. In 1984, the Indian government issued a postage stamp to remember him. His life and actions have also been portrayed in several cinematic productions.
Agustín de Iturbide, Mexican general and emperor (b. 1783) deaths

Agustín de Iturbide, full name Agustín Cosme Damián de Iturbide y Arámburu and also known as Agustín of Mexico, was a Mexican army general and politician. During the Mexican War of Independence, he built a successful political and military coalition that took control in Mexico City on 27 September 1821, decisively gaining independence for Mexico. After securing the secession of Mexico from Spain, Iturbide was proclaimed president of the Regency in 1821; a year later, he was proclaimed Emperor of Mexico, reigning briefly from 19 May 1822 to 19 March 1823. In May 1823 he went into exile in Europe. When he returned to Mexico in July 1824, he was arrested and executed. He designed the Mexican flag.
Princess Augusta of Cambridge (d. 1916) births

Princess Augusta of Cambridge was a member of the British royal family, a granddaughter of George III. She married into the Grand Ducal House of Mecklenburg-Strelitz and became the Grand Duchess of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
Gottfried Keller, Swiss author, poet, and playwright (d. 1890) births

Gottfried Keller was a Swiss poet and writer of German literature. Best known for his novel Green Henry and his cycle of novellas called The People from Seldwyla, he became one of the most popular narrators of literary realism in the late 19th century.
Samuel Colt, American businessman, founded the Colt's Manufacturing Company (d. 1862) births

Samuel Colt was an American inventor, industrialist, and businessman who established Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Manufacturing Company and made the mass production of revolvers commercially viable.

Colt's Manufacturing Company, LLC is an American firearms manufacturer, founded in 1855 by Samuel Colt and is now a subsidiary of Czech holding company Colt CZ Group. It is the successor corporation to Colt's earlier firearms-making efforts, which started in 1836. Colt is known for the engineering, production, and marketing of firearms, most especially between the 1850s and World War I, when it was a dominating force in its industry and a seminal influence on manufacturing technology. Colt's earliest designs played a major role in the popularization of the revolver and the shift away from earlier single-shot pistols. Although Samuel Colt did not invent the revolver concept, his designs resulted in the first very successful ones.
Matthew Flinders, English navigator and cartographer (b. 1774) deaths

Captain Matthew Flinders was a British navigator and cartographer who led the first inshore circumnavigation of mainland Australia, then called New Holland. He is also credited as being the first person to utilise the name Australia to describe the entirety of that continent including Van Diemen's Land, a title he regarded as being "more agreeable to the ear" than previous names such as Terra Australis.
Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Prussian queen (b. 1776) deaths

Duchess Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz was Queen of Prussia as the wife of King Frederick William III. The couple's happy, though short-lived, marriage produced nine children, including the future monarchs Frederick William IV of Prussia and Wilhelm I, German Emperor.
Juan José Flores, Venezuelan general and politician, 1st President of Ecuador (d. 1864) births

Juan José Flores y Aramburu was a Venezuelan-born military general who became the first, third and fourth President of the new Republic of Ecuador. He is often referred to as "The Founder of the Republic".

The president of Ecuador, officially called the Constitutional President of the Republic of Ecuador, serves as both the head of state and head of government of Ecuador. It is the highest political office in the country as the head of the executive branch of government. Per the current constitution, the President can serve two four-year terms. Prior to that, the president could only serve one four-year term.
José Justo Corro, Mexican politician and president (d. 1864) births

José Justo Corro Silva was a Mexican lawyer and statesman who was made president of Mexico on March 2, 1836, after the sudden death of President Miguel Barragán. During his administration, he oversaw the transition from the First Mexican Republic to the Centralist Republic of Mexico and the publication of the new constitution: the Siete Leyes. The nation also faced the ongoing Texas Revolution, and Mexican independence was recognized by Spain and by the Holy See.
John Martin, English painter, engraver, and illustrator (d. 1854) births

John Martin was an English Romantic painter, engraver and illustrator. He was celebrated for his typically vast and dramatic paintings of religious subjects and fantastic compositions, populated with minute figures placed in imposing landscapes. Martin's paintings, and the prints made from them, enjoyed great success with the general public—in 1821 Thomas Lawrence referred to him as "the most popular painter of his day"—but were lambasted by John Ruskin and other critics.
Thomas Talbot, Irish-Canadian colonel and politician (d. 1853) births

Thomas Talbot was an Irish-born Canadian soldier and colonial administrator. He founded the community of Port Talbot, Ontario, which was at one time the most prosperous town in the region due to his insistence on building quality roads, and was responsible for enticing 50,000 people to settle in the Thames River area.
Marianna Auenbrugger, Austrian pianist and composer (d. 1782) births
Marianna Auenbrugger was an Austrian pianist and composer.
Seraphim of Sarov, Russian monk and saint (d. 1833) births

Seraphim of Sarov, born Prókhor Isídorovich Moshnín (Mashnín) [Про́хор Иси́дорович Мошни́н (Машни́н)], is one of the most renowned Russian saints and is venerated in the Eastern Orthodox Church. He is generally considered the greatest of the 18th-century startsy (elders). Seraphim extended the monastic teachings of contemplation, theoria and self-denial to the layperson. He taught that the purpose of the Christian life was to receive the Holy Spirit. Perhaps his most popular quotation amongst his devotees is "acquire a peaceful spirit, and thousands around you will be saved."
Heinrich Christian Boie, German author and poet (d. 1806) births

Heinrich Christian Boie was a German author.
William Somervile, English poet and author (b. 1675) deaths

William Somervile or Somerville was an English poet who wrote in many genres and is especially remembered for "The Chace", in which he pioneered an early English georgic.
Giuseppe Castiglione, Italian missionary and painter (d. 1766) births
Giuseppe Castiglione, S.J., was an Italian Jesuit brother and missionary in China, where he served as an artist at the imperial court of three Qing emperors – the Kangxi, Yongzheng and Qianlong emperors. He painted in a style that is a fusion of European and Chinese traditions.
Richard Leveridge, English singer-songwriter (d. 1758) births

Richard Leveridge was an English bass singer of the London stage and a composer of baroque music, including many popular songs.
Cesare Cremonini, Italian philosopher and academic (b. 1550) deaths

Cesare Cremonini, sometimes Cesare Cremonino, was an Italian professor of natural philosophy, working rationalism and Aristotelian materialism inside scholasticism. His Latinized name was Cæsar Cremoninus. or Cæsar Cremonius.
Conrad Vorstius, Dutch theologian (d. 1622) births

Conrad Vorstius was a German-Dutch heterodox Remonstrant theologian, and successor to Jacobus Arminius in the theology chair at Leiden University. His appointment, and the controversy surrounding it, became an international matter in the political and religious affairs of the United Provinces during the Twelve Years' Truce, supplying a pretext for the irregular intervention of King James I of England in those affairs. Vorstius published theological views which were taken to show sympathy with the Socinians, and was declared a heretic at the Synod of Dort in 1619.
Mary Boleyn, English daughter of Elizabeth Boleyn, Countess of Wiltshire (b. 1499) deaths

Mary Boleyn, also known as Lady Mary, was the sister of English queen consort Anne Boleyn, whose family enjoyed considerable influence during the reign of King Henry VIII.
Elizabeth Boleyn, Countess of Wiltshire was an English noblewoman, noted for being the mother of Anne Boleyn and as such the maternal grandmother of Elizabeth I of England. The eldest daughter of Thomas Howard, 2nd Duke of Norfolk and his first wife Elizabeth Tilney, she married Thomas Boleyn sometime in the later 15th century. Elizabeth became Viscountess Rochford in 1525 when her husband was elevated to the peerage, subsequently becoming Countess of Ormond in 1527 and Countess of Wiltshire in 1529.
William VIII, Marquess of Montferrat (d. 1483) births
William VIII Palaiologos was the Marquis of Montferrat from 1464 until his death.
Philippa of Lancaster, Portuguese queen (b. 1360) deaths

Philippa of Lancaster was Queen of Portugal from 1387 until 1415 by marriage to King John I. Born into the royal family of England, her marriage secured the Treaty of Windsor and produced several children who became known as the "Illustrious Generation" in Portugal.
Petrarch, Italian poet and scholar (b. 1304) deaths

Francesco Petrarca, commonly anglicized as Petrarch, was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
John Campbell, Scottish nobleman deaths
John Campbell, Earl of Atholl was a Scottish nobleman.
Alexander Bruce, Scottish nobleman deaths
Alexander Bruce, Earl of Carrick was an illegitimate son of Edward Bruce, Earl of Carrick, younger brother of King Robert the Bruce, and Isabella, daughter of John de Strathbogie, 9th Earl of Atholl. According to The Brus they were married, but The Scots Peerage points out that this is unlikely because he did not immediately inherit his father's lands and titles, Freedom's Sword also says he was illegitimate.
Sir Archibald Douglas, Scottish nobleman deaths
Sir Archibald Douglas was a Scottish nobleman, Guardian of Scotland, and military leader. He is sometimes given the epithet "Tyneman", but this may be a reference to his great-nephew Archibald Douglas, 4th Earl of Douglas. He fought and died at the Battle of Halidon Hill.
Maol Choluim II, Scottish nobleman deaths

Mormaer Maol Choluim II of Lennox was mormaer of Lennox from 1303 to his death.
Kenneth de Moravia, 4th Earl of Sutherland deaths

Kenneth de Moravia was the 4th Earl of Sutherland and chief of the Clan Sutherland, a Scottish clan of the Scottish Highlands.
Jacopo Tiepolo, doge of Venice deaths

Jacopo Tiepolo, also known as Giacomo Tiepolo, was Doge of Venice from 1229 to 1249. He had previously served as the first Venetian Duke of Crete, and two terms as Podestà of Constantinople. During his first term, following the capture and mysterious end of Peter of Courtenay, Tiepolo acted as de facto ruler of the Latin Empire, negotiating treaties on behalf of the Empire with Egypt and the Seljuk Turks.
Floris IV, Dutch nobleman (b. 1210) deaths
Floris IV was the count of Holland from 1222 to 1234. He was born in The Hague, a son of William I of Holland and his first wife, Adelaide of Guelders.
Baibars, sultan of Egypt (d. 1277) births

Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari, of Turkic Kipchak origin, commonly known as Baibars or Baybars – nicknamed Abu al-Futuh – was the fourth Mamluk sultan of Egypt and Syria in the Bahri dynasty, succeeding Qutuz. He was one of the commanders of the Egyptian forces that inflicted a defeat on the Seventh Crusade of King Louis IX of France. He also led the vanguard of the Egyptian army at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, which marked the first substantial defeat of the Mongol army and is considered a turning point in history.
Adalberon, French bishop deaths
Adalberon, or Ascelin, was a French bishop and poet. He was a son of Reginar of Bastogne, and a nephew of Adalberon, Archbishop of Reims.
Damian Dalassenos, Byzantine general (b. 940) deaths
Damian Dalassenos was a Byzantine aristocrat and the first known member of the Dalassenos noble family. He is known for his service as the military governor (doux) of Antioch in 996–998. He fought the Fatimids with some success, until he was killed at the Battle of Apamea on 19 July 998.
Kyunyeo, Korean monk and poet (b. 917) deaths
Gyunyeo or Kyun Yeo was a Korean Buddhist monk and poet. He came from the Hwangju Byeon clan. Among his works are "Songs of the Ten Vows Samantabhara." These songs are set out in 1075 in the biography The Life of Kuehne. This is the first extant collection of poetry in Korean. He played an important role in the spread of the Hwaeom school of Buddhism.
Muhammad al-Bukhari, Persian scholar (d. 870) births

Muhammad ibn Isma'il al-Bukhari, commonly referred to as Imām al-Bukhāri or Imām Bukhāri, was a 9th-century Muslim muhaddith. Widely regarded as one of the most important hadith scholars in the history of Islam, Al-Bukhari's extant works include the hadith collection Sahih al-Bukhari, Al-Tarikh al-Kabir, and Al-Adab al-Mufrad.
Li Shigu, Chinese general (b. 778) deaths
Li Shigu was a Chinese military general and politician of the Tang dynasty, who, as the military governor (Jiedushi) of Pinglu Circuit, ruled the circuit in a de facto independent manner from the imperial regime.
Symmachus, pope of the Catholic Church deaths
Pope Symmachus was the bishop of Rome from 22 November 498 to his death. His tenure was marked by a serious schism over who was elected pope by a majority of the Roman clergy.
Palace Day
Christian feast day: Arsenius (Catholic Church)
Saint Arsenius (Arsenios) of Corfu, also known as Arsenius of Kerkyra, is one of the principal patron saints of Corfu along with Saint Spyridon. He was born in Constantinople to the Jewish faith. He became a Christian and the first bishop of Corfu.

The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2019. As the world's oldest and largest continuously functioning international institution, it has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. The church consists of 24 sui iuris churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state.
Christian feast day: Bernold, Bishop of Utrecht

Saint Bernulf or Bernold of Utrecht was Bishop of Utrecht (1026/27–1054).
Christian feast day: Justa and Rufina

Saints Justa and Rufina (Ruffina) are venerated as martyrs. They are said to have been martyred at Hispalis (Seville) during the 3rd century.
Christian feast day: Kirdjun (or Abakerazum)
Saint Kirdjun was a robber converted to Christianity. He was a reformed robber and bandit. He died as a martyr in Alexandria and was buried at Banuar. His feast day is July 19. He is referenced in Les Martyrs d'Égypte by Hippolyte Delehaye.
Christian feast day: Macrina the Younger, Sister of St. Basil the Great

Macrina the Younger was an early Christian consecrated virgin. She is regarded as a saint in the Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, and Anglican churches. Macrina was elder sister of Basil the Great, Gregory of Nyssa and Peter of Sebaste. Gregory of Nyssa wrote a work entitled Life of Macrina in which he describes her sanctity and asceticism throughout her life. Macrina lived a chaste and humble life, devoting her time to prayer and the spiritual education of her younger brother Peter.

Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great, was a bishop of Caesarea Mazaca in Cappadocia, Asia Minor. He was an influential theologian who supported the Nicene Creed and opposed the heresies of the early Christian church, fighting against both Arianism and the followers of Apollinaris of Laodicea. His ability to balance his theological convictions with his political connections made Basil a powerful advocate for the Nicene position.
Christian feast day: Symmachus
Pope Symmachus was the bishop of Rome from 22 November 498 to his death. His tenure was marked by a serious schism over who was elected pope by a majority of the Roman clergy.
Christian feast day: July 19 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)

July 18 - Eastern Orthodox Church calendar - July 20
Martyrs' Day (Myanmar)
Martyrs' Day is a Burmese national holiday observed on 19 July to commemorate Gen. Aung San and seven other leaders of the pre-independence interim government, and one bodyguard —Thakin Mya, Ba Cho, Abdul Razak, Ba Win, Mahn Ba Khaing, Sao San Tun, Ohn Maung and Ko Htwe—all of whom were assassinated on that day in 1947. It is customary for high-ranking government officials to visit the Martyrs' Mausoleum in Yangon in the morning of that day to pay respects.

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, also known as Burma, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia, and has a population of about 54 million as of 2017. Myanmar is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (Rangoon).
Sandinista Day or Liberation Day (Nicaragua)
Liberation Day is a day, often a public holiday, that marks the liberation of a place, similar to an independence day. Liberation marks the date of either a revolution, as in Cuba, the fall of a dictatorship, as in Portugal, or the end of an occupation by another state, as in the Netherlands, thereby differing from original independence day or creation of statehood.

Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the largest country in the Central American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the northwest, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. As of 2015, it was estimated to be the second largest city in Central America. The multi-ethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English.