
Mohsen Fakhrizadeh
Mohsen Fakhrizadeh Mahabadi was an Iranian nuclear physicist and scientist. He was regarded as the chief of Iran's nuclear program.
Nuclear physicist Mohsen Fakhrizadeh, regarded as the chief of Iran's nuclear program, was assassinated, allegedly by Mossad.

Mohsen Fakhrizadeh Mahabadi was an Iranian nuclear physicist and scientist. He was regarded as the chief of Iran's nuclear program.
The nuclear program of Iran is an ongoing scientific effort by Iran to research nuclear technology that can be used to make nuclear weapons. Iran has several research sites, two uranium mines, a research reactor, and uranium processing facilities that include three known uranium enrichment plants.

Mossad is the national intelligence agency of Israel. It is one of the main entities in the Israeli Intelligence Community, along with Aman and Shin Bet.
Iran's top nuclear scientist, Mohsen Fakhrizadeh, is assassinated near Tehran.

Mohsen Fakhrizadeh Mahabadi was an Iranian nuclear physicist and scientist. He was regarded as the chief of Iran's nuclear program.

Tehran is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and 15 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most populous city in Iran and Western Asia, and has the second-largest metropolitan area in the Middle East, after Cairo. It is ranked 24th in the world by metropolitan area population.
Days after the announcement of its discovery, the Utah monolith is removed by recreationists.

The Utah monolith is a metal pillar that stood in a red sandstone slot canyon in northern San Juan County, Utah, United States. The pillar is 3 m (9.8 ft) tall and made of metal sheets riveted into a triangular prism. It was unlawfully placed on public land between July and October 2016; it stood unnoticed for over four years until its discovery and removal in late 2020. The identity of its makers is unknown, as are their objectives.
An active shooter inside a Planned Parenthood facility in Colorado Springs, Colorado, shoots at least four police officers. One officer later dies. Two civilians are also killed, and six injured. The shooter later surrendered.
The Planned Parenthood Federation of America, Inc. (PPFA), or simply Planned Parenthood, is a nonprofit organization that provides reproductive health care in the United States and globally. It is a tax-exempt corporation under Internal Revenue Code section 501(c)(3) and a member association of the International Planned Parenthood Federation (IPPF).

Colorado Springs is a home rule municipality in, and the county seat of, El Paso County, Colorado, United States. It is the largest city in El Paso County, with a population of 478,961 at the 2020 United States Census, a 15.02% increase since 2010. Colorado Springs is the second-most populous city and the most extensive city in the state of Colorado, and the 40th-most populous city in the United States. It is the principal city of the Colorado Springs metropolitan area and the second-most prominent city of the Front Range Urban Corridor. It is located in east-central Colorado, on Fountain Creek, 70 miles (113 km) south of Denver.
On November 27, 2015, a mass shooting occurred in a Planned Parenthood clinic in Colorado Springs, Colorado, resulting in the deaths of three people and injuries to nine. A police officer and two civilians were killed; five police officers and four civilians were injured. After a standoff that lasted five hours, police SWAT teams crashed armored vehicles into the lobby and the attacker surrendered.

The Colorado Springs Police Department (CSPD) is the police department for the City of Colorado Springs, Colorado. CSPD was involved in the capture and surrender of several members of the Texas Seven.
A bomb exploded under, and derailed, a Russian high-speed train travelling between Moscow and Saint Petersburg, killing 28 passengers.

The 2009 Nevsky Express bombing occurred on 27 November 2009 when a bomb exploded under a high speed train travelling between the Russian cities of Moscow and Saint Petersburg causing derailment near the town of Bologoye, Tver Oblast, on the Moscow–Saint Petersburg Railway. The derailment occurred at 21:34 local time. Russian officials had stated that 39 people were killed and 95 injured but later retracted that estimate. 27 deaths had been reported by 2 December. A second bomb exploded at the scene of the investigation the following day, injuring one. It was reported to have been triggered by a remote mobile phone.
Nevsky Express bombing: A bomb explodes on the Nevsky Express train between Moscow and Saint Petersburg, derailing it and causing 28 deaths and 96 injuries.

The 2009 Nevsky Express bombing occurred on 27 November 2009 when a bomb exploded under a high speed train travelling between the Russian cities of Moscow and Saint Petersburg causing derailment near the town of Bologoye, Tver Oblast, on the Moscow–Saint Petersburg Railway. The derailment occurred at 21:34 local time. Russian officials had stated that 39 people were killed and 95 injured but later retracted that estimate. 27 deaths had been reported by 2 December. A second bomb exploded at the scene of the investigation the following day, injuring one. It was reported to have been triggered by a remote mobile phone.

The Nevsky Express is a Russian Railways express train, formerly the fastest on the prominent route between the Leningradsky Rail Terminal in Moscow and the Moskovsky Rail Terminal in Saint Petersburg. The train has a maximum speed of 200 km/h (125 mph) and does not make any intermediate station stops. It consists of a Škoda Chs200 locomotive, 13 passenger cars and a restaurant car. It features 6-person compartments in some cars and airline style seating in other cars.

Moscow is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 20 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of 2,511 square kilometers (970 sq mi), while the urban area covers 5,891 square kilometers (2,275 sq mi), and the metropolitan area covers over 26,000 square kilometers (10,000 sq mi). Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent.

Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), is the second-largest city in Russia. It is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a historically strategic port, it is governed as a federal city.
XL Airways Germany Flight 888T: An Airbus A320 performing a flight test crashes near the French commune of Canet-en-Roussillon, killing all seven people on board.

XL Airways Germany Flight 888T (GXL888T) was an acceptance flight for an Airbus A320 on 27 November 2008. The aircraft crashed into the Mediterranean Sea, 7 km off Canet-en-Roussillon on the French coast, close to the Spanish border, killing all seven people on board.

The Airbus A320 family is a series of narrow-body airliners developed and produced by Airbus. The A320 was launched in March 1984, first flew on 22 February 1987, and was introduced in April 1988 by Air France. The first member of the family was followed by the longer A321, the shorter A319, and the even shorter A318 . Final assembly takes place in Toulouse in France; Hamburg in Germany; Tianjin in China since 2009; and in Mobile, Alabama in the United States since April 2016.
Flight testing is a branch of aeronautical engineering that develops specialist equipment required for testing aircraft behaviour and systems. Instrumentation systems are developed using proprietary transducers and data acquisition systems. Data is sampled during the flight of an aircraft, or atmospheric testing of launch vehicles and reusable spacecraft. This data is validated for accuracy and analyzed before being passed to specialist engineering groups for further analysis to validate the design of the vehicle.

The communecode: fra promoted to code: fr is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French communescode: fra promoted to code: fr are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, Gemeindencode: deu promoted to code: de in Germany, comunicode: ita promoted to code: it in Italy, or municipioscode: spa promoted to code: es in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. Communescode: fra promoted to code: fr are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The communescode: fra promoted to code: fr are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France.

Canet-en-Roussillon is a commune and town in the French department of the Pyrénées-Orientales, administrative region of Occitania.
The House of Commons of Canada approves a motion introduced by Prime Minister Stephen Harper recognizing the Québécois as a nation within Canada.

The House of Commons of Canada is the lower house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the Senate of Canada, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada.

The prime minister of Canada is the head of government of Canada. Under the Westminster system, the prime minister governs with the confidence of a majority the elected House of Commons; as such, the prime minister typically sits as a member of Parliament (MP) and leads the largest party or a coalition of parties. As first minister, the prime minister selects ministers to form the Cabinet, and serves as its chair. Constitutionally, the Crown exercises executive power on the advice of the Cabinet, which is collectively responsible to the House of Commons.

Stephen Joseph Harper is a Canadian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Canada from 2006 to 2015. Harper is the first and only prime minister to come from the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada, serving as the party's first leader from 2004 to 2015.
The Québécois nation motion was a parliamentary motion tabled by Prime Minister of Canada Stephen Harper on Wednesday, November 22, 2006 and approved by the House of Commons of Canada on Monday, November 27, 2006. It was approved 265–16 with supporters in every party in the Commons. The English motion read:That this House recognize that the Québécois form a nation within a united Canada."
Pope John Paul II returns the relics of Saint John Chrysostom to the Eastern Orthodox Church.

Pope John Paul II was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his death in April 2005, and was later canonised as Pope Saint John Paul II.

John Chrysostom was an important Early Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and political leaders, his Divine Liturgy of Saint John Chrysostom, and his ascetic sensibilities. The epithet Χρυσόστομος means "golden-mouthed" in Greek and denotes his celebrated eloquence. Chrysostom was among the most prolific authors in the early Christian Church, although both Origen of Alexandria and Augustine of Hippo exceeded Chrysostom.

The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via local synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the head of the Roman Catholic Church—the Pope—but the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognized by them as primus inter pares, which may be explained as a representative of the church. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played a prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern and Southeastern Europe. The Eastern Orthodox Church officially calls itself the Orthodox Catholic Church.
Astronomers announced the detection of sodium in the atmosphere of the extrasolar planet HD 209458 b (artist's impression pictured), the first exoplanet atmosphere to be measured.

Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans.

An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, initially detected in 1988, was confirmed in 2003. As of 1 December 2022, there are 5,284 confirmed exoplanets in 3,899 planetary systems, with 847 systems having more than one planet.

HD 209458 b, which is also nicknamed Osiris after the Egyptian god, is an exoplanet that orbits the solar analog HD 209458 in the constellation Pegasus, some 159 light-years from the Solar System. The radius of the planet's orbit is 0.047 AU, or one-eighth the radius of Mercury's orbit. This small radius results in a year that is 3.5 Earth-days long and an estimated surface temperature of about 1,000 °C. Its mass is 220 times that of Earth and its volume is some 2.5 times greater than that of Jupiter. The high mass and volume of HD 209458 b indicate that it is a gas giant.
The study of extraterrestrial atmospheres is an active field of research, both as an aspect of astronomy and to gain insight into Earth's atmosphere. In addition to Earth, many of the other astronomical objects in the Solar System have atmospheres. These include all the gas giants, as well as Mars, Venus and Titan. Several moons and other bodies also have atmospheres, as do comets and the Sun. There is evidence that extrasolar planets can have an atmosphere. Comparisons of these atmospheres to one another and to Earth's atmosphere broaden our basic understanding of atmospheric processes such as the greenhouse effect, aerosol and cloud physics, and atmospheric chemistry and dynamics.
A hydrogen atmosphere is discovered on the extrasolar planet Osiris by the Hubble Space Telescope, the first atmosphere detected on an extrasolar planet.

Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula H2. It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons.

An atmosphere is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules.

An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, initially detected in 1988, was confirmed in 2003. As of 1 December 2022, there are 5,284 confirmed exoplanets in 3,899 planetary systems, with 847 systems having more than one planet.

HD 209458 b, which is also nicknamed Osiris after the Egyptian god, is an exoplanet that orbits the solar analog HD 209458 in the constellation Pegasus, some 159 light-years from the Solar System. The radius of the planet's orbit is 0.047 AU, or one-eighth the radius of Mercury's orbit. This small radius results in a year that is 3.5 Earth-days long and an estimated surface temperature of about 1,000 °C. Its mass is 220 times that of Earth and its volume is some 2.5 times greater than that of Jupiter. The high mass and volume of HD 209458 b indicate that it is a gas giant.

The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft.
The Labour Party defeated the governing National Party in the New Zealand general election, with Labour's Helen Clark becoming the country's first female prime minister to have won office at an election.
The New Zealand Labour Party, or simply Labour, is a centre-left political party in New Zealand. The party's platform programme describes its founding principle as democratic socialism, while observers describe Labour as social-democratic and pragmatic in practice. The party participates in the international Progressive Alliance. It is one of two major political parties in New Zealand, alongside its traditional rival, the National Party.
The New Zealand National Party, shortened to National or the Nats, is a centre-right political party in New Zealand. It is one of two major parties that dominate contemporary New Zealand politics, alongside its traditional rival, the Labour Party.

The 1999 New Zealand general election was held on 27 November 1999 to determine the composition of the 46th New Zealand Parliament. The governing National Party, led by Prime Minister Jenny Shipley, was defeated, being replaced by a coalition of Helen Clark's Labour Party and the smaller Alliance. This marked an end to nine years of the Fourth National Government, and the beginning of the Fifth Labour Government which would govern for nine years in turn, until its loss to the National Party in the 2008 general election. It was the first New Zealand election where both major parties had female leaders.

Helen Elizabeth Clark is a New Zealand politician who served as the 37th prime minister of New Zealand from 1999 to 2008, and was the administrator of the United Nations Development Programme from 2009 to 2017. She was New Zealand's fifth-longest-serving prime minister, and the second woman to hold that office.
The centre-left Labour Party takes control of the New Zealand government with leader Helen Clark becoming the first elected female Prime Minister in New Zealand's history.
The New Zealand Labour Party, or simply Labour, is a centre-left political party in New Zealand. The party's platform programme describes its founding principle as democratic socialism, while observers describe Labour as social-democratic and pragmatic in practice. The party participates in the international Progressive Alliance. It is one of two major political parties in New Zealand, alongside its traditional rival, the National Party.

New Zealand is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island and the South Island —and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering 268,021 square kilometres (103,500 sq mi). New Zealand is about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland.

Helen Elizabeth Clark is a New Zealand politician who served as the 37th prime minister of New Zealand from 1999 to 2008, and was the administrator of the United Nations Development Programme from 2009 to 2017. She was New Zealand's fifth-longest-serving prime minister, and the second woman to hold that office.
Twenty-five people are killed in the second Souhane massacre in Algeria.
The largest of the Souhane massacres took place in the small mountain town of Souhane on 20–21 August 1997. 64 people were killed, and 15 women kidnapped; the resulting terror provoked a mass exodus, bringing the town's population down from 4000 before the massacre to just 103 in 2002. Smaller-scale massacres later took place on November 27, 1997 and 2 March 2000, when some 10 people from a single household were killed by guerrillas. The massacres were blamed on Islamist groups such as the GIA.

Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in North Africa. Algeria is bordered to the northeast by Tunisia; to the east by Libya; to the southeast by Niger; to the southwest by Mali, Mauritania, and Western Sahara; to the west by Morocco; and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea. It is considered part of the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has a semi-arid geography, with most of the population living in the fertile north and the Sahara dominating the geography of the south. Algeria covers an area of 2,381,741 square kilometres (919,595 sq mi), making it the world's tenth largest nation by area, and the largest nation in Africa, being more than 200 times as large as the smallest country in the continent, The Gambia. With a population of 44 million, Algeria is the ninth-most populous country in Africa, and the 32nd-most populous country in the world. The capital and largest city is Algiers, located in the far north on the Mediterranean coast.
For the second time in a year, military forces try to overthrow president Carlos Andrés Pérez in Venezuela.

A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats.

Carlos Andrés Pérez Rodríguez also known as CAP and often referred to as El Gocho, was a Venezuelan politician and the president of Venezuela from 12 March 1974 to 12 March 1979 and again from 2 February 1989 to 21 May 1993. He was one of the founders of Acción Democrática, the dominant political party in Venezuela during the second half of the twentieth century. His first presidency was known as the Saudi Venezuela due to its economic and social prosperity thanks to enormous income from petroleum exportation. However, his second presidency saw a continuation of the economic crisis of the 1980s, a series of social crises, widespread riots known as Caracazo and two coup attempts in 1992. In May 1993 he became the first Venezuelan president to be forced out of office by the Supreme Court on charges for the embezzlement of 250 million bolívars belonging to a presidential discretionary fund, whose money was used to support the electoral process in Nicaragua and hire bodyguards for President Violeta Chamorro.

Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of 916,445 km2 (353,841 sq mi), and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas.
A bomb placed by the Medellín Cartel in an attempt to kill Colombian presidential candidate César Gaviria destroyed Avianca Flight 203, killing 110 people, but Gaviria was not on the flight.

The Medellín Cartel was a powerful and highly organized Colombian drug cartel and terrorist organization originating in the city of Medellín, Colombia that was founded and led by Pablo Escobar. It is often considered the first major “drug cartel” and was referred to as such due to the organization's upper echelons being built on a partnership between multiple Colombian traffickers operating alongside Escobar. Included were Jorge Luis Ochoa Vásquez, Juan David Ochoa Vásquez, José Gonzalo Rodríguez Gacha and Carlos Lehder. The cartel operated from 1967 to 1993 in Bolivia, Colombia, Panama, Central America, Peru, the Bahamas, the United States, as well as in Canada. Although the organization started out as a smuggling network in the late 1960s, it wasn't until 1976 that the organization turned to trafficking cocaine. This was a result of Escobar getting introduced to the lucrative idea of cocaine smuggling by fellow Colombian trafficker Griselda Blanco. At the height of its operations, the Medellín Cartel smuggled multiple tons of cocaine each week into countries around the world and brought in up to US$60 million daily in drug profits.

César Augusto Gaviria Trujillo is a Colombian economist and politician who served as the President of Colombia from 1990 to 1994, Secretary General of the Organization of American States from 1994 to 2004 and National Director of the Colombian Liberal Party from 2005 to 2009. During his tenure as president, he summoned the Constituent Assembly of Colombia that enacted the Constitution of 1991.

Avianca Flight 203 was a Colombian domestic passenger flight from El Dorado International Airport in Bogotá to Alfonso Bonilla Aragón International Airport in Cali, Colombia. It was destroyed by a bomb over the municipality of Soacha on November 27, 1989. All 107 people on board as well as 3 people on the ground were killed. The bombing had been ordered by the Medellín drug cartel.
Avianca Flight 203: A Boeing 727 explodes in mid-air over Colombia, killing all 107 people on board and three people on the ground. The Medellín Cartel will claim responsibility for the attack.

Avianca Flight 203 was a Colombian domestic passenger flight from El Dorado International Airport in Bogotá to Alfonso Bonilla Aragón International Airport in Cali, Colombia. It was destroyed by a bomb over the municipality of Soacha on November 27, 1989. All 107 people on board as well as 3 people on the ground were killed. The bombing had been ordered by the Medellín drug cartel.

The Boeing 727 is an American narrow-body airliner that was developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. After the heavy 707 quad-jet was introduced in 1958, Boeing addressed the demand for shorter flight lengths from smaller airports. On December 5, 1960, the 727 was launched with 40 orders each from United Airlines and Eastern Air Lines. The first 727-100 rolled out November 27, 1962, first flew on February 9, 1963, and entered service with Eastern on February 1, 1964.

Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with an insular region in North America. It is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south, the Pacific Ocean to the west and Panama to the northwest. Colombia comprises 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi), with a population of 50 million. Colombia's cultural heritage reflects influences by various Amerindian civilizations, European settlement, enslaved Africans, as well as immigration from Europe and the Middle East. Spanish is the nation's official language, besides which over 70 languages are spoken.

The Medellín Cartel was a powerful and highly organized Colombian drug cartel and terrorist organization originating in the city of Medellín, Colombia that was founded and led by Pablo Escobar. It is often considered the first major “drug cartel” and was referred to as such due to the organization's upper echelons being built on a partnership between multiple Colombian traffickers operating alongside Escobar. Included were Jorge Luis Ochoa Vásquez, Juan David Ochoa Vásquez, José Gonzalo Rodríguez Gacha and Carlos Lehder. The cartel operated from 1967 to 1993 in Bolivia, Colombia, Panama, Central America, Peru, the Bahamas, the United States, as well as in Canada. Although the organization started out as a smuggling network in the late 1960s, it wasn't until 1976 that the organization turned to trafficking cocaine. This was a result of Escobar getting introduced to the lucrative idea of cocaine smuggling by fellow Colombian trafficker Griselda Blanco. At the height of its operations, the Medellín Cartel smuggled multiple tons of cocaine each week into countries around the world and brought in up to US$60 million daily in drug profits.
Under the Brussels Agreement signed between the governments of the United Kingdom and Spain, the former agrees to enter into discussions with Spain over Gibraltar, including sovereignty.
The Brussels Agreement, 1984, was an agreement between the governments of the United Kingdom and of Spain concerning the territorial dispute over Gibraltar. The agreement was criticised by Gibraltar politicians for limiting the participation of Gibraltarians in their self-determination.

Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory and city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula. It has an area of 6.7 km2 (2.6 sq mi) and is bordered to the north by Spain. The landscape is dominated by the Rock of Gibraltar, at the foot of which is a densely populated town area, home to over 32,000 people, primarily Gibraltarians.
Avianca Flight 011: A Boeing 747 crashes near Madrid's Barajas Airport, killing 181.

Avianca Flight 011, registration HK-2910X, was a Boeing 747-200B on an international scheduled passenger flight from Frankfurt via Paris, Madrid, and Caracas to Bogotá, Colombia that crashed near Madrid on 27 November 1983. It took off from Charles de Gaulle Airport in Paris at 22:25 on 26 November 1983 for Madrid Barajas Airport; take-off was delayed waiting for additional passengers from a Lufthansa flight due to a cancellation of the Paris-Frankfurt-Paris segment by Avianca for operational reasons.

The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022. After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet 2+1⁄2 times its size, to reduce its seat cost by 30% to democratize air travel. In 1965, Joe Sutter left the 737 development program to design the 747, the first twin-aisle airliner. In April 1966, Pan Am ordered 25 Boeing 747-100 aircraft and in late 1966, Pratt & Whitney agreed to develop its JT9D engine, a high-bypass turbofan. On September 30, 1968, the first 747 was rolled out of the custom-built Everett Plant, the world's largest building by volume. The first flight took place on February 9, 1969, and the 747 was certified in December of that year. It entered service with Pan Am on January 22, 1970. The 747 was the first airplane dubbed "Jumbo Jet", the first wide-body airliner.

Madrid is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and its monocentric metropolitan area is the third-largest in the EU. The municipality covers 604.3 km2 (233.3 sq mi) geographical area.

Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport, commonly known as Madrid–Barajas Airport, is the main international airport serving Madrid in Spain. At 3,050 ha in area, it is the second-largest airport in Europe by physical size behind Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport. In 2019, 61.8 million passengers travelled through Madrid–Barajas, making it the country's busiest airport as well as Europe's sixth-busiest.
San Francisco mayor George Moscone and openly gay supervisor Harvey Milk were assassinated by supervisor Dan White.

George Richard Moscone was an American attorney and Democratic politician. He was the 37th mayor of San Francisco, California from January 1976 until his assassination in November 1978. He was known as "The People's Mayor", who opened up City Hall and its commissions to reflect the diversity of San Francisco, appointing African Americans, Asian Americans, and homosexuals. Moscone served in the California State Senate from 1967 until becoming Mayor. In the Senate, he served as Majority Leader. Moscone is remembered for being an advocate of civil progressivism.

Harvey Bernard Milk was an American politician and the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, as a member of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors. Milk was born and raised in New York where he acknowledged his homosexuality as an adolescent, but chose to pursue sexual relationships with secrecy and discretion well into his adult years. His experience in the counterculture of the 1960s caused him to shed many of his conservative views about individual freedom and the expression of sexuality.

On November 27, 1978, San Francisco Mayor George Moscone and San Francisco Supervisor Harvey Milk were shot and killed in San Francisco City Hall by former Supervisor Dan White. On the morning of that day, Moscone intended to announce that the Supervisor position White resigned from would be given to someone else. White, angered, entered City Hall before the scheduled announcement time and first shot Moscone in the Mayor's office, then Harvey Milk in White's former office space, before escaping the building. Board of Supervisors President Dianne Feinstein first announced Moscone and Milk's deaths to the media, and because of Moscone's death, succeeded him as Acting Mayor of San Francisco.

Daniel James White was an American politician who assassinated San Francisco Mayor George Moscone and Supervisor Harvey Milk, on Monday, November 27, 1978, at City Hall. White was convicted of manslaughter for the deaths of Milk and Moscone. White served five years of a seven-year prison sentence. Less than two years after his release, he returned to San Francisco, and later died by suicide.
In San Francisco, city mayor George Moscone and openly gay city supervisor Harvey Milk are assassinated by former supervisor Dan White.

San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th most populous in the United States, with 815,201 residents as of 2021. It covers a land area of 46.9 square miles, at the end of the San Francisco Peninsula, making it the second most densely populated large U.S. city after New York City, and the fifth most densely populated U.S. county, behind only four of the five New York City boroughs. Among the 331 U.S. cities proper with more than 100,000 residents, San Francisco was ranked first by per capita income and fifth by aggregate income as of 2019. Colloquial nicknames for San Francisco include SF, San Fran, The City, Frisco, and Baghdad by the Bay.

George Richard Moscone was an American attorney and Democratic politician. He was the 37th mayor of San Francisco, California from January 1976 until his assassination in November 1978. He was known as "The People's Mayor", who opened up City Hall and its commissions to reflect the diversity of San Francisco, appointing African Americans, Asian Americans, and homosexuals. Moscone served in the California State Senate from 1967 until becoming Mayor. In the Senate, he served as Majority Leader. Moscone is remembered for being an advocate of civil progressivism.
Gay is a term that primarily refers to a homosexual person or the trait of being homosexual. The term originally meant 'carefree', 'cheerful', or 'bright and showy'.
A board of supervisors is a governmental body that oversees the operation of county government in the U.S. states of Arizona, California, Iowa, Mississippi, Virginia, and Wisconsin, as well as 16 counties in New York. There are equivalent agencies in other states.

Harvey Bernard Milk was an American politician and the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, as a member of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors. Milk was born and raised in New York where he acknowledged his homosexuality as an adolescent, but chose to pursue sexual relationships with secrecy and discretion well into his adult years. His experience in the counterculture of the 1960s caused him to shed many of his conservative views about individual freedom and the expression of sexuality.

On November 27, 1978, San Francisco Mayor George Moscone and San Francisco Supervisor Harvey Milk were shot and killed in San Francisco City Hall by former Supervisor Dan White. On the morning of that day, Moscone intended to announce that the Supervisor position White resigned from would be given to someone else. White, angered, entered City Hall before the scheduled announcement time and first shot Moscone in the Mayor's office, then Harvey Milk in White's former office space, before escaping the building. Board of Supervisors President Dianne Feinstein first announced Moscone and Milk's deaths to the media, and because of Moscone's death, succeeded him as Acting Mayor of San Francisco.

Daniel James White was an American politician who assassinated San Francisco Mayor George Moscone and Supervisor Harvey Milk, on Monday, November 27, 1978, at City Hall. White was convicted of manslaughter for the deaths of Milk and Moscone. White served five years of a seven-year prison sentence. Less than two years after his release, he returned to San Francisco, and later died by suicide.
The Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) is founded in the Turkish village of Fis.

The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of southeastern Turkey and northern Iraq. Since 1984, the PKK has utilized asymmetric warfare in the Kurdish–Turkish conflict. Although the PKK once sought an independent Kurdish state, in the 1990s its aims shifted toward autonomy and increased rights for Kurds within Turkey.
The Provisional IRA assassinates Ross McWhirter, after a press conference in which McWhirter had announced a reward for the capture of those responsible for multiple bombings and shootings across England.

The Irish Republican Army, also known as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, and informally as the Provos, was an Irish republican paramilitary organisation that sought to end British rule in Northern Ireland, facilitate Irish reunification and bring about an independent, socialist republic encompassing all of Ireland. It was the most active republican paramilitary group during the Troubles. It saw itself as the army of the all-island Irish Republic and as the sole legitimate successor to the original IRA from the Irish War of Independence. It was designated a terrorist organisation in the United Kingdom and an unlawful organisation in the Republic of Ireland, both of whose authority it rejected.

Alan Ross McWhirter was, with his twin brother, Norris, the cofounder of the 1955 Guinness Book of Records and a contributor to the television programme Record Breakers. He was killed by the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) in 1975.
A press conference or news conference is a media event in which notable individuals or organizations invite journalists to hear them speak and ask questions. Press conferences are often held by politicians, corporations, non-governmental organizations, as well as organizers for newsworthy events.

England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight.
Twenty-fifth Amendment: The United States Senate votes 92–3 to confirm Gerald Ford as Vice President of the United States. (On December 6, the House will confirm him 387–35).

The Twenty-fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution deals with presidential succession and disability.

The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.

Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected to the office of president or vice president. He previously served as the leader of the Republican Party in the House of Representatives, and was appointed to be the 40th vice president in 1973. When President Richard Nixon resigned in 1974, Ford succeeded to the presidency, but was defeated for election to a full term in 1976.

The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice president is also an officer in the legislative branch, as the president of the Senate. In this capacity, the vice president is empowered to preside over Senate deliberations at any time, but may not vote except to cast a tie-breaking vote. The vice president is indirectly elected together with the president to a four-year term of office by the people of the United States through the Electoral College.

The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they comprise the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The Soviet space program's Mars 2 orbiter releases a descent module. It malfunctions and crashes, but it is the first man-made object to reach the surface of Mars.

The Soviet space program was the national space program of the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), active from 1955 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.
The Mars program was a series of uncrewed spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1973. The spacecraft were intended to explore Mars, and included flyby probes, landers and orbiters.

Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos.
Penny Ann Early becomes the first woman to play major professional basketball for the Kentucky Colonels in an ABA game against the Los Angeles Stars.
Penny Ann Early is an American athlete who achieved two notable firsts in her lifetime as she was the first female jockey to be licensed to ride parimutuel horse races, and the first woman ever to play in a professional men's basketball league during the 1960s.

The Kentucky Colonels were a member of the American Basketball Association for all of the league's nine years. The name is derived from the historic Kentucky colonels. The Colonels won the most games and had the highest winning percentage of any franchise in the league's history, but the team did not join the NBA in the 1976 ABA–NBA merger. The downtown Louisville Convention Center was the Colonels' original venue for the first three seasons before moving to Freedom Hall for the remaining seasons, beginning with the 1970–71 schedule.

The American Basketball Association (ABA) was a major men's professional basketball league from 1967 to 1976. The ABA ceased to exist with the American Basketball Association–National Basketball Association merger in 1976, leading to four ABA teams joining the National Basketball Association (NBA) and to the introduction of the 3-point shot in the NBA in 1979.

The Anaheim Amigos/Los Angeles Stars/Utah Stars were a charter member American Basketball Association (ABA) team based in Southern California. They were the Amigos during their first season in Anaheim and later moved to Los Angeles to become the Stars. The team existed from 1967 to 1976. In 1970, it moved from southern California to Utah.
Vietnam War: The Pentagon tells U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson that if planned operations are to succeed, the number of American troops in Vietnam has to be increased from 120,000 to 400,000.

The Vietnam War was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975.

The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense. It was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As a symbol of the U.S. military, the phrase The Pentagon is often used as a metonym for the Department of Defense and its leadership.

Lyndon Baines Johnson, often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice president from 1961 to 1963 under President John F. Kennedy, and was sworn in shortly after Kennedy's assassination. A Democrat from Texas, Johnson also served as a U.S. representative, U.S. senator and the Senate's majority leader. He holds the distinction of being one of the few presidents who served in all elected offices at the federal level.

Vietnam or Viet Nam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of 311,699 square kilometres (120,348 sq mi) and population of 96 million, making it the world's fifteenth-most populous country. Vietnam borders China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City.
Alger Hiss is released from prison after serving 44 months for perjury.

Alger Hiss was an American government official accused in 1948 of having spied for the Soviet Union in the 1930s. Statutes of limitations had expired for espionage, but he was convicted of perjury in connection with this charge in 1950. Before the trial Hiss was involved in the establishment of the United Nations, both as a U.S. State Department official and as a U.N. official. In later life he worked as a lecturer and author.
Perjury is the intentional act of swearing a false oath or falsifying an affirmation to tell the truth, whether spoken or in writing, concerning matters material to an official proceeding.
A consortium of twenty-two U.S. charities founded CARE with the mission of delivering food aid to Europe in the aftermath of World War II.
CARE is a major international humanitarian agency delivering emergency relief and long-term international development projects. Founded in 1945, CARE is nonsectarian, impartial, and non-governmental. It is one of the largest and oldest humanitarian aid organizations focused on fighting global poverty. In 2019, CARE reported working in 104 countries, supporting 1,349 poverty-fighting projects and humanitarian aid projects, and reaching over 92.3 million people directly and 433.3 million people indirectly.
The aftermath of World War II was the beginning of a new era started in late 1945 for all countries involved, defined by the decline of all colonial empires and simultaneous rise of two superpowers; the Soviet Union (USSR) and the United States (US). Once Allies during World War II, the US and the USSR became competitors on the world stage and engaged in the Cold War, so called because it never resulted in overt, declared total war between the two powers but was instead characterized by espionage, political subversion and proxy wars. Western Europe and Asia were rebuilt through the American Marshall Plan, whereas Central and Eastern Europe fell under the Soviet sphere of influence and eventually behind an "Iron Curtain". Europe was divided into a US-led Western Bloc and a USSR-led Eastern Bloc. Internationally, alliances with the two blocs gradually shifted, with some nations trying to stay out of the Cold War through the Non-Aligned Movement. The war also saw a nuclear arms race between the two superpowers; part of the reason that the Cold War never became a "hot" war was that the Soviet Union and the United States had nuclear deterrents against each other, leading to a mutually assured destruction standoff.
CARE (then the Cooperative for American Remittances to Europe) is founded to send CARE Packages of food relief to Europe after World War II.
CARE is a major international humanitarian agency delivering emergency relief and long-term international development projects. Founded in 1945, CARE is nonsectarian, impartial, and non-governmental. It is one of the largest and oldest humanitarian aid organizations focused on fighting global poverty. In 2019, CARE reported working in 104 countries, supporting 1,349 poverty-fighting projects and humanitarian aid projects, and reaching over 92.3 million people directly and 433.3 million people indirectly.
The CARE Package was the original unit of aid distributed by the humanitarian organization CARE. Originally CARE was dubbed the Cooperative for American Remittances to Europe, and in 1946 CARE sent the world's first CARE Package. Although "CARE Package" is a registered trademark, the term has since been widely adopted as a generic term for a parcel of food or supplies sent for relief or comfort purposes.
Between 3,500 and 4,000 tonnes of ordnance exploded at the RAF Fauld underground munitions storage depot in the largest non-nuclear explosion in the United Kingdom.

The RAF Fauld explosion was a military accident which occurred at 11:11 am on Monday, 27 November 1944 at the RAF Fauld underground munitions storage depot in Staffordshire, England. It was one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in history and the largest on UK soil.

Royal Air Force Fauld is a former Royal Air Force underground munitions storage depot located 2 miles (3.2 km) south west of Tutbury, Staffordshire and 10.4 miles (16.7 km) north east of Rugeley, Staffordshire, England.

There have been many extremely large explosions, accidental and intentional, caused by modern high explosives, boiling liquid expanding vapour explosions (BLEVEs), older explosives such as gunpowder, volatile petroleum-based fuels such as gasoline, and other chemical reactions. This list contains the largest known examples, sorted by date. An unambiguous ranking in order of severity is not possible; a 1994 study by historian Jay White of 130 large explosions suggested that they need to be ranked by an overall effect of power, quantity, radius, loss of life and property destruction, but concluded that such rankings are difficult to assess.
World War II: RAF Fauld explosion: An explosion at a Royal Air Force ammunition dump in Staffordshire kills seventy people.

The RAF Fauld explosion was a military accident which occurred at 11:11 am on Monday, 27 November 1944 at the RAF Fauld underground munitions storage depot in Staffordshire, England. It was one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in history and the largest on UK soil.

The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain.

Staffordshire is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands County and Worcestershire to the south and Shropshire to the west.
World War II: At Toulon, the French navy scuttles its ships and submarines to keep them out of Nazi hands.

Toulon is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the prefecture of the Var department.

The scuttling of the French fleet at Toulon was orchestrated by Vichy France on 27 November 1942 to prevent Nazi German forces from taking it over. After the Allied invasion of North Africa the Germans invaded the territory administered by Vichy under the Armistice of 1940. The Vichy Secretary of the Navy, Admiral François Darlan, defected to the Allies, who were gaining increasing support from servicemen and civilians. His replacement, Admiral Gabriel Auphan, guessed correctly that the Germans intended to seize the large fleet at Toulon, and ordered it scuttled.
Nazism, the common name in English for National Socialism, is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism. The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War.
In Romania, the ruling Iron Guard fascist party assassinates over 60 of arrested King Carol II of Romania's aides and other political dissidents.

The Kingdom of Romania was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March (O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I, until 1947 with the abdication of King Michael I of Romania and the Romanian parliament's proclamation of the Romanian People's Republic.

The Iron Guard was a Romanian militant revolutionary fascist movement and political party founded in 1927 by Corneliu Zelea Codreanu as the Legion of the Archangel Michael or the Legionnaire Movement. It was strongly anti-democratic, anti-capitalist, anti-communist, and anti-Semitic. It differed from other European right-wing movements of the period due to its spiritual basis, as the Iron Guard was deeply imbued with Romanian Orthodox Christian mysticism.

The Jilava massacre took place during the night of November 26, 1940, at Jilava penitentiary, near Bucharest, Romania. Sixty-four political detainees were killed by the Iron Guard (Legion), with further high-profile assassinations in the immediate aftermath. It came about halfway through the fascist National Legionary State and led to the first open clash between the Guard and conducător Ion Antonescu, who ousted the Legion from power in January 1941.

Carol II was King of Romania from 8 June 1930 until his forced abdication on 6 September 1940. The eldest son of Ferdinand I, he became crown prince upon the death of his grand-uncle, King Carol I in 1914. He was the first of the Hohenzollern kings of Romania to be born in the country; both of his predecessors had been born in Germany and came to Romania only as adults. As such, he was the first member of the Romanian branch of the Hohenzollerns who spoke Romanian as his first language, and was also the first member of the royal family to be raised in the Orthodox faith.
World War II: At the Battle of Cape Spartivento, the Royal Navy engages the Regia Marina in the Mediterranean Sea.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

The Battle of Cape Spartivento, known as the Battle of Cape Teulada in Italy, was a naval battle during the Battle of the Mediterranean in the Second World War, fought between naval forces of the Royal Navy and the Italian Regia Marina on 27 November 1940.

The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service.

The Regia Marina was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic, the Regia Marina changed its name to Marina Militare.

The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Although the Mediterranean is sometimes considered a part of the Atlantic Ocean, it is usually referred to as a separate body of water. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago.
In New York City, the first Macy's Thanksgiving Day Parade is held.

The Macy's Thanksgiving Day Parade is an annual parade in New York City presented by the U.S.-based department store chain Macy's. The Parade first took place in 1924, tying it for the second-oldest Thanksgiving parade in the United States with America's Thanksgiving Parade in Detroit. The three-hour parade is held in Manhattan, ending outside Macy's Herald Square, takes place from 9:00 a.m. to 12:00 p.m. Eastern Standard Time on Thanksgiving Day, and has been televised nationally on NBC since 1953. The Parade's workforce is made up of Macy's employees and their friends and family, all of whom work as volunteers.
The Makhnovshchina is established.

The Makhnovshchina was an attempt to form a stateless anarchist society in parts of Ukraine during the Russian Revolution of 1917–1923. It existed from 1918 to 1921, during which time free soviets and libertarian communes operated under the protection of Nestor Makhno's Revolutionary Insurgent Army. The area had a population of around seven million.
P. E. Svinhufvud becomes the chairman of his first senate, technically the first Prime Minister of Finland.

Pehr Evind Svinhufvud af Qvalstad was the third president of Finland from 1931 to 1937. Serving as a lawyer, judge, and politician in the Russian Grand Duchy of Finland, he played a major role in the movement for Finnish independence, he was one who presented the Declaration of Independence to the Parliament. In 1917–1918, Svinhufvud was the first Head of State of independent Finland, first as Chairman of the Senate and subsequently as Protector of State or Regent. He also served as Prime Minister from 1930 to 1931.

Pehr Evind Svinhufvud's first senate was the first Senate and de facto Government of independent Finland. Its term spanned November 27, 1917 – May 27, 1918.

The prime minister of Finland is the leader of the Finnish Government. The prime minister and their cabinet exercise executive authority in the state. The prime minister is formally ranked third in the protocol after the president of Finland and the speaker of the Parliament. Finland's first prime minister, Pehr Evind Svinhufvud, was appointed on 27 November 1917, just a few days before the country declared independence from Russia.
Spain declares a protectorate over the north shore of Morocco.

Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country primarily located in southwestern Europe with parts of territory in the Atlantic Ocean and across the Mediterranean Sea. The largest part of Spain is situated on the Iberian Peninsula; its territory also includes the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla in Africa. The country's mainland is bordered to the south by Gibraltar; to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea; to the north by France, Andorra and the Bay of Biscay; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. With an area of 505,990 km2 (195,360 sq mi), Spain is the second-largest country in the European Union (EU) and, with a population exceeding 47.4 million, the fourth-most populous EU member state. Spain's capital and largest city is Madrid; other major urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Zaragoza, Málaga, Murcia, Palma de Mallorca, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Bilbao.

Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of 446,300 km2 (172,300 sq mi) or 710,850 km2 (274,460 sq mi), with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca.
The U.S. Army War College is established.

The United States Army War College (USAWC) is a U.S. Army educational institution in Carlisle, Pennsylvania, on the 500-acre (2 km2) campus of the historic Carlisle Barracks. It provides graduate-level instruction to senior military officers and civilians to prepare them for senior leadership assignments and responsibilities. Each year, a number of Army colonels and lieutenant colonels are considered by a board for admission. Approximately 800 students attend at any one time, half in a two-year-long distance learning program, and the other half in an on-campus, full-time resident program lasting ten months. Upon completion, the college grants its graduates a master's degree in Strategic Studies.
Also sprach Zarathustra by Richard Strauss is first performed.

Also sprach Zarathustra, Op. 30 is a tone poem by Richard Strauss, composed in 1896 and inspired by Friedrich Nietzsche's philosophical 1883–1885 novel Thus Spoke Zarathustra. The composer conducted its first performance on 27 November 1896 in Frankfurt. A typical performance lasts half an hour.

Richard Georg Strauss was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wagner and Franz Liszt. Along with Gustav Mahler, he represents the late flowering of German Romanticism, in which pioneering subtleties of orchestration are combined with an advanced harmonic style.
Swedish chemist and industrialist Alfred Nobel (pictured) signed his last will and testament, setting aside the bulk of his estate to establish the Nobel Prize after his death.

Alfred Bernhard Nobel was a Swedish chemist, engineer, inventor, businessman, and philanthropist. He is best known for having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize, though he also made several important contributions to science, holding 355 patents in his lifetime. Nobel's most famous invention was dynamite, a safer and easier means of harnessing the explosive power of nitroglycerin; it was patented in 1867.

The Nobel Prizes are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfred Nobel was a Swedish chemist, engineer, and industrialist most famously known for the invention of dynamite. He died in 1896. In his will, he bequeathed all of his "remaining realisable assets" to be used to establish five prizes which became known as "Nobel Prizes." Nobel Prizes were first awarded in 1901.
At the Swedish–Norwegian Club in Paris, Alfred Nobel signs his last will and testament, setting aside his estate to establish the Nobel Prize after he dies.

Alfred Bernhard Nobel was a Swedish chemist, engineer, inventor, businessman, and philanthropist. He is best known for having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize, though he also made several important contributions to science, holding 355 patents in his lifetime. Nobel's most famous invention was dynamite, a safer and easier means of harnessing the explosive power of nitroglycerin; it was patented in 1867.

A will or testament is a legal document that expresses a person's (testator) wishes as to how their property (estate) is to be distributed after their death and as to which person (executor) is to manage the property until its final distribution. For the distribution (devolution) of property not determined by a will, see inheritance and intestacy.

The Nobel Prizes are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfred Nobel was a Swedish chemist, engineer, and industrialist most famously known for the invention of dynamite. He died in 1896. In his will, he bequeathed all of his "remaining realisable assets" to be used to establish five prizes which became known as "Nobel Prizes." Nobel Prizes were first awarded in 1901.
American Indian Wars: Battle of Washita River: United States Army Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer leads an attack on Cheyenne living on reservation land.

The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settlers, against various American Indian and First Nation tribes. These conflicts occurred in North America from the time of the earliest colonial settlements in the 17th century until the early 20th century. The various wars resulted from a wide variety of factors, the most common being the desire of settlers and governments for lands that the Indian tribes considered their own. The European powers and their colonies also enlisted allied Indian tribes to help them conduct warfare against each other's colonial settlements. After the American Revolution, many conflicts were local to specific states or regions and frequently involved disputes over land use; some entailed cycles of violent reprisal.

The Battle of Washita River occurred on November 27, 1868, when Lt. Col. George Armstrong Custer's 7th U.S. Cavalry attacked Black Kettle's Southern Cheyenne camp on the Washita River.

The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution. The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the Continental Army, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army. The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be the origin of that armed force in 1775.
Lieutenant colonel is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colonel. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply "colonel" in conversation and in unofficial correspondence. Sometimes, the term 'half-colonel' is used in casual conversation in the British Army. In the United States Air Force, the term 'light bird' or 'light bird colonel' is an acceptable casual reference to the rank but is never used directly towards the rank holder. A lieutenant colonel is typically in charge of a battalion or regiment in the army.

George Armstrong Custer was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars.

The Cheyenne are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes in Oklahoma, and the Northern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Northern Cheyenne Tribe of the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation in Montana. The Cheyenne comprise two Native American tribes, the Só'taeo'o or Só'taétaneo'o and the Tsétsêhéstâhese. The tribes merged in the early 19th century.
American Civil War: Confederate cavalry leader John Hunt Morgan and several of his men escape the Ohio Penitentiary and return safely to the South.

The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union and the Confederacy, the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.

The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States, the Confederacy, or "the South", was an unrecognized breakaway republic in North America that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War. Eleven U.S. states, nicknamed Dixie, declared secession and formed the main part of the CSA. They were South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky, and Missouri also had declarations of secession and full representation in the Confederate Congress during their Union army occupation.

John Hunt Morgan was an American soldier who served as a Confederate general in the American Civil War of 1861–1865.

The Ohio Penitentiary, also known as the Ohio State Penitentiary, was a prison operated from 1834 to 1984 in downtown Columbus, Ohio, in what is now known as the Arena District. The state had built a small prison in Columbus in 1813, but as the state's population grew the earlier facility was not able to handle the number of prisoners sent to it by the courts. When the penitentiary first opened in 1834, not all of the buildings were completed. The prison housed 5,235 prisoners at its peak in 1955. Prison conditions were described as "primitive" and the facility was eventually replaced by the Southern Ohio Correctional Facility, a maximum security facility in Lucasville. During its operation, it housed several well-known inmates, including General John H. Morgan, who famously escaped the prison during the Civil War, "Bugs" Moran, O. Henry, Chester Himes, and Sam Sheppard, whose story is said to have inspired the movie The Fugitive. A separate women's prison was built within its walls in 1837. The buildings were demolished in 1997.
American Civil War: Battle of Mine Run: Union forces under General George Meade take up positions against troops led by Confederate General Robert E. Lee.

The Battle of Mine Run, also known as Payne's Farm, or New Hope Church, or the Mine Run campaign, was conducted in Orange County, Virginia, in the American Civil War.

The United States of America, commonly known as the United States or America, is a country in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. It is the third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. It has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 331 million, it is the most populous country in North America and the third most populous in the world. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City.

George Gordon Meade was a United States Army officer and civil engineer best known for decisively defeating Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. He previously fought with distinction in the Second Seminole War and the Mexican–American War. During the Civil War, he served as a Union general, rising from command of a brigade to that of the Army of the Potomac. Earlier in his career, he was an engineer and was involved in the coastal construction of several lighthouses.

The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States, the Confederacy, or "the South", was an unrecognized breakaway republic in North America that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War. Eleven U.S. states, nicknamed Dixie, declared secession and formed the main part of the CSA. They were South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky, and Missouri also had declarations of secession and full representation in the Confederate Congress during their Union army occupation.

Robert Edward Lee was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Northern Virginia—the Confederacy's most powerful army—from 1862 until its surrender in 1865, earning a reputation as a skilled tactician.
King-Grand Duke William III unilaterally revised the constitution of Luxembourg, greatly expanding his powers.

William III was King of the Netherlands and Grand Duke of Luxembourg from 1849 until his death in 1890. He was also the Duke of Limburg from 1849 until the abolition of the duchy in 1866.

The Luxembourg coup of 1856, also called the putsch of 1856, was a reactionary revision of Luxembourg's constitution on 27 November 1856. Whilst not a true coup d'état or revolution, its detractors dubbed it a 'royal coup', as the reigning Grand Duke of Luxembourg, William III, greatly expanded his powers, and the name has stuck. Aimed at reversing the liberal successes embodied in the 1848 constitution, the major changes enacted by William were undone with the promulgation of a new constitution in 1868, after the Luxembourg Crisis. However, some changes have lasted, such as the creation of the Council of State.
The Constitution of Luxembourg is the supreme law of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The modern constitution was adopted on 17 October 1868.
The Coup of 1856 leads to Luxembourg's unilateral adoption of a new, reactionary constitution.

The Luxembourg coup of 1856, also called the putsch of 1856, was a reactionary revision of Luxembourg's constitution on 27 November 1856. Whilst not a true coup d'état or revolution, its detractors dubbed it a 'royal coup', as the reigning Grand Duke of Luxembourg, William III, greatly expanded his powers, and the name has stuck. Aimed at reversing the liberal successes embodied in the 1848 constitution, the major changes enacted by William were undone with the promulgation of a new constitution in 1868, after the Luxembourg Crisis. However, some changes have lasted, such as the creation of the Council of State.

Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a small landlocked country in Western Europe. It borders Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembourg, is one of the four institutional seats of the European Union and the seat of several EU institutions, notably the Court of Justice of the European Union, the highest judicial authority. Luxembourg's culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its French and German neighbors; while Luxembourgish is legally the only national language of the Luxembourgish people, French and German are also used in administrative and judicial matters and all three are considered administrative languages of the country.
The Constitution of Luxembourg is the supreme law of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The modern constitution was adopted on 17 October 1868.
In Boston, Massachusetts, the American Statistical Association is founded.

Boston, officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th-most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about 48.4 sq mi (125 km2) and a population of 675,647 as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County. The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and including Providence, Rhode Island, is home to approximately 8.2 million people, making it the sixth most populous in the United States.

Massachusetts, officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders on the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Maine to the east, Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, and New York to the west. The state's capital and most populous city, as well as its cultural and financial center, is Boston. Massachusetts is also home to the urban core of Greater Boston, the largest metropolitan area in New England and a region profoundly influential upon American history, academia, and the research economy, Originally dependent on agriculture, fishing, and trade. Massachusetts was transformed into a manufacturing center during the Industrial Revolution. During the 20th century, Massachusetts's economy shifted from manufacturing to services. Modern Massachusetts is a global leader in biotechnology, engineering, higher education, finance, and maritime trade.
The American Statistical Association (ASA) is the main professional organization for statisticians and related professionals in the United States. It was founded in Boston, Massachusetts on November 27, 1839, and is the second oldest continuously operating professional society in the US. The ASA services statisticians, quantitative scientists, and users of statistics across many academic areas and applications. The association publishes a variety of journals and sponsors several international conferences every year.
James Pratt and John Smith became the last people executed in England for sodomy.
James Pratt (1805–1835), also known as John Pratt, and John Smith (1795–1835) were two London men who, in November 1835, became the last two to be executed for sodomy in England. Pratt and Smith were arrested in August of that year after allegedly being spied through a keyhole having sex in the rented room of another man, William Bonill. Bonill, although not present, was transported to Australia as an accessory to the crime, where he died.

Sodomy or buggery is generally anal or oral sex between people, or sexual activity between a person and a non-human animal (bestiality), but it may also mean any non-procreative sexual activity. Originally, the term sodomy, which is derived from the story of Sodom and Gomorrah in the Book of Genesis, was commonly restricted to anal sex. Sodomy laws in many countries criminalized the behavior. In the Western world, many of these laws have been overturned or are routinely not enforced. A person who practices sodomy is sometimes referred to as a sodomite.
James Pratt and John Smith are hanged in London; they are the last two to be executed for sodomy in England.
James Pratt (1805–1835), also known as John Pratt, and John Smith (1795–1835) were two London men who, in November 1835, became the last two to be executed for sodomy in England. Pratt and Smith were arrested in August of that year after allegedly being spied through a keyhole having sex in the rented room of another man, William Bonill. Bonill, although not present, was transported to Australia as an accessory to the crime, where he died.
Saint Catherine Labouré experiences a Marian apparition.

Catherine Labouré was a French member of the Daughters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul and a Marian visionary. She is believed to have relayed the request from the Blessed Virgin Mary to create the famous Miraculous Medal of Our Lady of Graces worn by millions of people around the world. Labouré spent forty years caring for the aged and infirm. For this, she is called the patroness of seniors.

A Marian apparition is a reported supernatural appearance by Mary, the mother of Jesus, or a series of related such appearances during a period of time.
As specified by the Congress of Vienna, the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland was signed for the newly recreated Polish state that was under Russian control.
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers and other stakeholders, chaired by Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815.
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland was granted to the 'Congress' Kingdom of Poland by King of Poland Alexander I of Russia in 1815, who was obliged to issue a constitution to the newly recreated Polish state under his domain as specified by the Congress of Vienna. It was considered among the most liberal constitutions of its time; however, it was never fully respected by the government. It was modified during the November Uprising by the revolutionary government and discarded afterwards by the victorious Russian authorities in 1832.

Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established when the French ceded a part of Polish territory to the Russian Empire following France's defeat in the Napoleonic Wars. In 1915, during World War I, it was replaced by the German-controlled nominal Regency Kingdom until Poland regained independence in 1918.
Adoption of Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland.
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland was granted to the 'Congress' Kingdom of Poland by King of Poland Alexander I of Russia in 1815, who was obliged to issue a constitution to the newly recreated Polish state under his domain as specified by the Congress of Vienna. It was considered among the most liberal constitutions of its time; however, it was never fully respected by the government. It was modified during the November Uprising by the revolutionary government and discarded afterwards by the victorious Russian authorities in 1832.
The Berners Street hoax is perpetrated by Theodore Hook in the City of Westminster, London.

The Berners Street hoax was perpetrated by Theodore Hook in Westminster, London, England, in 1809. Hook had made a bet with his friend Samuel Beazley that he could transform any house in London into the most talked-about address in a week, which he achieved by sending out thousands of letters in the name of Mrs Tottenham, who lived at 54 Berners Street, requesting deliveries, visitors, and assistance.

Theodore Edward Hook was an English man of letters and composer and briefly a civil servant in Mauritius. He is best known for his practical jokes, particularly the Berners Street hoax in 1809. The world's first postcard was received by Hook in 1840; he likely posted it to himself.

The City of Westminster is a city and borough in Inner London. It is the site of the United Kingdom's Houses of Parliament and much of the British government. It occupies a large area of central Greater London, including most of the West End. Many London landmarks are within the borough, including Buckingham Palace, Westminster Abbey, Whitehall, Westminster Cathedral, 10 Downing Street, and Trafalgar Square.
The foundation stone to the Jerusalem Church in Berlin is laid.

Jerusalem Church is one of the churches of the Evangelical Congregation in the Friedrichstadt, a member of the Protestant umbrella organisation Evangelical Church of Berlin-Brandenburg-Silesian Upper Lusatia. The present church building is located in Berlin, borough Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg, in the quarter of Friedrichstadt. Jerusalem Church is fourth in rank of the oldest oratories in the town proper.
The great storm of 1703, one of the most severe storms to strike southern Great Britain, destroyed the first Eddystone Lighthouse off Plymouth.

The great storm of 1703 was a destructive extratropical cyclone that struck central and southern England on 26 November 1703. High winds caused 2,000 chimney stacks to collapse in London and damaged the New Forest, which lost 4,000 oaks. Ships were blown hundreds of miles off-course, and over 1,000 seamen died on the Goodwin Sands alone. News bulletins of casualties and damage were sold all over England – a novelty at that time. The Church of England declared that the storm was God's vengeance for the sins of the nation. Daniel Defoe thought it was a divine punishment for poor performance against Catholic armies in the War of the Spanish Succession.

Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of 209,331 km2 (80,823 sq mi), it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west—together with these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago.

The Eddystone Lighthouse is a lighthouse that is located on the dangerous Eddystone Rocks, 9 statute miles (14 km) south of Rame Head in Cornwall, England. The rocks are submerged below the surface of the sea and are composed of Precambrian gneiss.

Plymouth is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately 36 miles (58 km) south-west of Exeter and 193 miles (311 km) south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
A Song dynasty fleet defeated Jin ships in a naval engagement on the Yangtze river during the Jin–Song Wars.

The Song dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.

The Battle of Caishi was a major naval engagement of the Jin–Song Wars of China that took place on November 26–27, 1161. It ended with a decisive Song victory, aided by their use of gunpowder weapons.

The Jin dynasty or Jin State, officially known as the Great Jin, was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin in English to differentiate it from an earlier Jìn dynasty whose name is rendered identically in Hanyu Pinyin without the tone marking. It is also sometimes called the "Jurchen dynasty" or the "Jurchen Jin", because members of the ruling Wanyan clan were of Jurchen descent.

The Yangtze or Yangzi is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains and flows 6,300 km (3,900 mi) in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the seventh-largest river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population.

The Jin–Song Wars were a series of conflicts between the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty (1115–1234) and the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279). In 1115, Jurchen tribes rebelled against their overlords, the Khitan-led Liao dynasty (916–1125), and declared the formation of the Jin. Allying with the Song against their common enemy the Liao dynasty, the Jin promised to cede to the Song the Sixteen Prefectures that had fallen under Liao control since 938. The Song agreed but the Jin's quick defeat of the Liao combined with Song military failures made the Jin reluctant to cede territory. After a series of negotiations that embittered both sides, the Jurchens attacked the Song in 1125, dispatching one army to Taiyuan and the other to Bianjing, the Song capital.
At the Council of Clermont, Pope Urban II called for the First Crusade, declaring holy war against the Muslims who had occupied the Holy Land and were attacking the Eastern Roman Empire.

The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.

Pope Urban II, otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening the Council of Clermont which served as the catalyst for the Crusades.

The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont, during which Pope Urban II supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem.

A religious war or a war of religion, sometimes also known as a holy war, is a war which is primarily caused or justified by differences in religion. In the modern period, there are frequent debates over the extent to which religious, economic, ethnic or other aspects of a conflict are predominant in a given war. The degree to which a war may be considered religious depends on many underlying questions, such as the definition of religion, the definition of 'religious war', and the applicability of religion to war as opposed to other possible factors. Answers to these questions heavily influence conclusions on how prevalent religious wars have been as opposed to other types of wars.

Muslims are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad (sunnah) as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith).
The Holy Land is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy Land" usually refers to a territory roughly corresponding to the modern State of Israel and the modern State of Palestine. Jews, Christians, and Muslims regard it as holy.

The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians distinguish Byzantium from its earlier incarnation because it was centered on Constantinople and not Rome, oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by Eastern Orthodox Christianity, instead of Roman Catholicism or Paganism.
Pope Urban II declares the First Crusade at the Council of Clermont.

Pope Urban II, otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening the Council of Clermont which served as the catalyst for the Crusades.

The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont, during which Pope Urban II supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem.

The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Byzantine Emperor Maurice is forced to watch as the usurper Phocas executes his five sons before Maurice is beheaded himself.

The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians distinguish Byzantium from its earlier incarnation because it was centered on Constantinople and not Rome, oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by Eastern Orthodox Christianity, instead of Roman Catholicism or Paganism.

Maurice was Eastern Roman emperor from 582 to 602 and the last member of the Justinian dynasty. A successful general, Maurice was chosen as heir and son-in-law by his predecessor Tiberius II.

Phocas was Eastern Roman emperor from 602 to 610. Initially, a middle-ranking officer in the Eastern Roman army, Phocas rose to prominence as a spokesman for dissatisfied soldiers in their disputes with the court of the Emperor Maurice. When the army revolted in 602, Phocas emerged as the natural leader of the mutiny. The revolt proved to be successful and led to the capture of Constantinople and the overthrow of Maurice on 23 November 602 with Phocas declaring himself emperor on the same day.

Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the involuntary functions that are needed for the body to function.
King Clovis I dies at Lutetia and is buried in the Abbey of St Genevieve.

Clovis was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single king and ensuring that the kingship was passed down to his heirs. He is considered to have been the founder of the Merovingian dynasty, which ruled the Frankish kingdom for the next two centuries.

The Gallo-Roman town of Lutetia was the predecessor of the modern-day city of Paris. It was founded in about the middle of the 3rd century BCE by the Parisii, a Gallic tribe. Traces of an earlier Neolithic settlement have also been found at the former site of the city. Lutetia was an important crossing point of the Seine, and was located at the intersection of land and water trade routes. In the 1st century BCE, it was conquered by Romans and was gradually rebuilt into a Roman city. Ruins including a forum, amphitheater, and Roman baths still remain. In the 5th century it became the capital of the Merovingian dynasty of French kings, and thereafter was known simply as Paris.

The Abbey of Saint Genevieve was a monastery in Paris. Reportedly built by Clovis, King of the Franks in 502, it became a centre of religious scholarship in the Middle Ages. It was suppressed at the time of the French Revolution.
Rufinus, praetorian prefect of the East, is murdered by Gothic mercenaries under Gainas.
Flavius Rufinus was a 4th-century East Roman statesman of Aquitanian extraction who served as Praetorian prefect of the East for the emperor Theodosius I, as well as for his son Arcadius, under whom Rufinus exercised significant influence in the state affairs.

The praetorian prefecture of the East, or of the Orient was one of four large praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided. As it comprised the larger part of the Eastern Roman Empire, and its seat was at Constantinople, the praetorian prefect was the second most powerful man in the East, after the Emperor, in essence serving as his first minister.

The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe.
Gainas was a Gothic leader who served the Eastern Roman Empire as magister militum during the reigns of Theodosius I and Arcadius.
Emperor Marcus Aurelius grants his son Commodus the rank of "Imperator" and makes him Supreme Commander of the Roman legions.

Marcus Aurelius Antoninus was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good Emperors, and the last emperor of the Pax Romana, an age of relative peace and stability for the Roman Empire lasting from 27 BC to 180 AD. He served as Roman consul in 140, 145, and 161.

Commodus was a Roman emperor who ruled from 177 to 192. He served jointly with his father Marcus Aurelius from 176 until the latter's death in 180, and thereafter he reigned alone until his assassination. His reign is commonly thought of as marking the end of a golden period of peace in the history of the Roman Empire, known as the Pax Romana.

The Latin word imperator derives from the stem of the verb imperare, meaning 'to order, to command'. It was originally employed as a title roughly equivalent to commander under the Roman Republic. Later it became a part of the titulature of the Roman Emperors as part of their cognomen. The English word emperor derives from imperator via Old French: Empereür. The Roman emperors themselves generally based their authority on multiple titles and positions, rather than preferring any single title. Nevertheless, imperator was used relatively consistently as an element of a Roman ruler's title throughout the Principate and the Dominate.
The Roman legion was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire.
Luoyang is declared capital of the Eastern Han dynasty by Emperor Guangwu of Han.
AD 25 (XXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Agrippa. The denomination AD 25 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up area made of the city's five out of six urban districts and Yanshi District, now being conurbated.

The Han dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China. It followed the Qin dynasty, which had unified the Warring States of China by conquest. It was founded by Liu Bang. The dynasty is divided into two periods: the Western Han and the Eastern Han, interrupted briefly by the Xin dynasty of Wang Mang. These appellations are derived from the locations of the capital cities Chang'an and Luoyang, respectively. The third and final capital of the dynasty was Xuchang, where the court moved in 196 CE during a period of political turmoil and civil war.

The Han dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China, established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han contention, and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period. The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters".

Emperor Guangwu of Han, born Liu Xiu (劉秀), courtesy name Wenshu (文叔), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han dynasty. He ruled over parts of China at first, and through suppression and conquest of regional warlords, the whole of China proper was consolidated by the time of his death in AD 57. During his reign, Taoism was made the official religion of China, and the Chinese folk religion began to decline.
Apetor, Norwegian YouTuber (b. 1964) deaths

Tor Eckhoff, also known as Apetor, was a Norwegian industrial worker and YouTuber known primarily for his videos where he drank vodka while performing daring activities on frozen waters, like ice skating, swimming in ice holes and diving. He died in 2021 after he fell through the ice of a lake west of Kongsberg, Norway, while recording a video. At the time of his death, he lived in Sandefjord where he worked in a paint factory run by the chemicals company Jotun.
Mohsen Fakhrizadeh, Iranian nuclear scientist (b. 1958) deaths

Mohsen Fakhrizadeh Mahabadi was an Iranian nuclear physicist and scientist. He was regarded as the chief of Iran's nuclear program.
Ioannis Grivas, Greek statesman (b. 1923) deaths
Ioannis Grivas was a Greek judge, who served as President of the Court of Cassation and served as the Prime Minister of Greece at the head of a non-party caretaker government in 1989.
Mark Behr, Tanzanian-South African author and academic (b. 1963) deaths
Mark Behr was a Tanzanian-born writer who grew up in South Africa. He was professor of English literature and creative writing at Rhodes College, Memphis, Tennessee. He also taught in the MA program at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, South Africa.
Maurice Strong, Canadian businessman and diplomat (b. 1929) deaths

Maurice Frederick Strong, was a Canadian oil and mineral businessman and a diplomat who served as Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations.
Garrett Swasey, American figure skater and coach (b. 1971) deaths

Garrett Preston Russell Swasey (November 16, 1971 – November 27, 2015) was an American competitive ice skater, figure skating coach, and police officer. As an ice dancer, he won the 1992 U.S. junior ice dance title at the U.S. Figure Skating Championships and went on to participate twice more at the senior level. He coached along with Doreen Denny. Swasey was shot and killed in the line of duty during the Colorado Springs Planned Parenthood shooting in 2015.
Philippe Washer, Belgian tennis player and golfer (b. 1924) deaths

Philippe Washer was a Belgian tennis player. He competed in the Davis Cup a number of times, from 1946 to 1961.
Wanda Błeńska, Polish physician and missionary (b. 1911) deaths

Wanda Błeńska, also spelled Wanda Blenska, was a Polish leprosy expert, AK officer, and missionary who succeeded to develop the Buluba Hospital in Uganda into an internationally recognized centre for leprosy treatment.
Phillip Hughes, Australian cricketer (b. 1988) deaths

Phillip Joel Hughes was an Australian Test and One Day International (ODI) cricketer who played domestic cricket for South Australia and Worcestershire. He was a left-handed opening batsman who played for two seasons with New South Wales before making his Test debut in 2009 at the age of 20. He made his One Day International Debut in 2013.
P. D. James, English author (b. 1920) deaths

Phyllis Dorothy James, Baroness James of Holland Park,, known professionally as P. D. James, was an English novelist and life peer. Her rise to fame came with her series of detective novels featuring the police commander and poet, Adam Dalgliesh.
Jack Kyle, Irish rugby player and humanitarian (b. 1926) deaths

John Wilson Kyle,, commonly referred to as Jack Kyle or Jackie Kyle, was a rugby union player who played for Ireland, the British and Irish Lions and the Barbarians during the 1940s and 1950s. Kyle is best known for leading Ireland to a grand slam in the 1948 Five Nations Championship. In 1950, Kyle was declared one of the six players of the year by the New Zealand Rugby Almanac. Kyle is a member of the International Rugby Hall of Fame, and was inducted into the IRB Hall of Fame before the two halls merged to form the current World Rugby Hall of Fame. He was named the Greatest Ever Irish Rugby Player by the Irish Rugby Football Union in 2002.
Fernance B. Perry, Portuguese-American businessman and philanthropist (b. 1922) deaths

Fernance Bento Perry,, was a Portuguese-Bermudian entrepreneur and business leader, who had a prominent role in the economy of Bermuda from the mid-20th century to the time of his death in 2014. Originally from the Azores, his professional career spanned such diverse fields as retail supermarkets, television and radio broadcasting, real estate management and maritime shipping. His philanthropic works contributed to healthcare improvements and programmes of spiritual enrichment in Bermuda. In recognition of his achievements, Perry was appointed a Member of the Order of the British Empire (MBE) in 2007. He died on November 27, 2014, at age 92.
Lewis Collins, English-American actor (b. 1946) deaths

Lewis Collins was an English actor, best known for his career-defining role playing 'Bodie' in the late 1970s – early 1980s British television series The Professionals.
Herbert F. DeSimone, American lawyer and politician, Attorney General of Rhode Island (b. 1929) deaths
Herbert F. DeSimone was an American lawyer and politician from Rhode Island. He served as the 64th Attorney General of Rhode Island and as President Nixon's Assistant Secretary of Transportation for the Environment and Urban System.

The Attorney General of Rhode Island is the chief legal advisor of the Government of the State of Rhode Island and oversees the State of Rhode Island Department of Law. The attorney general is elected every four years. The current Attorney General is Peter F. Neronha.
Volker Roemheld, German physiologist and biologist (b. 1941) deaths
Volker Roemheld was a German agricultural scientist, plant physiologist and soil biologist at Hohenheim University.
Nílton Santos, Brazilian footballer (b. 1925) deaths

Nílton dos Santos was a Brazilian footballer who primarily played as a wingback. At international level, he was a member of the Brazil squads that won the 1958 and 1962 World Cups.
Manuel F. Segura, Filipino colonel (b. 1919) deaths
Manuel Felimon Segura was a colonel of the Armed Forces of the Philippines with assigned serial number 0-3547 AFP. He was G-1 and Adjutant General in the General Headquarters of the Cebuano guerrillas during World War II, with Col. James M. Cushing as his commanding officer. Segura wrote at least two books on the guerrilla story in Cebu.
Mickey Baker, American guitarist (b. 1925) deaths

MacHouston "Mickey" Baker was an American guitarist, best known for his work as a studio musician and as part of the recording duo Mickey & Sylvia.
Ab Fafié, Dutch footballer and manager (b. 1941) deaths

Ab Fafié was a Dutch professional football player and manager.
Érik Izraelewicz, French journalist and author (b. 1954) deaths

Érik Izraelewicz was a French journalist and author, specialised in economics and finance. From February 2011 he was director and editorial executive of the daily Le Monde, after having held the same position at the financial daily newspapers Les Echos and La Tribune.
Marvin Miller, American businessman and union leader (b. 1917) deaths

Marvin Julian Miller was an American baseball executive who served as the executive director of the Major League Baseball Players Association (MLBPA) from 1966 to 1982. Under Miller's direction, the players' union was transformed into one of the strongest unions in the United States. In 1992, Red Barber said, "Marvin Miller, along with Babe Ruth and Jackie Robinson, is one of the two or three most important men in baseball history." Miller was selected to the National Baseball Hall of Fame in December 2019, for induction in 2020.
Jack Wishna, American photographer and businessman, co-founded Rockcityclub (b. 1958) deaths
Jack Wishna was an American businessman and photographer. He was the president and CEO of CPAmerica, a consulting firm for gambling, hotel, and leisure organizations, based in Las Vegas, Nevada. He was also a founder of Rockrena Inc., which launched Rock City Club, a social music network.

Rock City Club was created by Jack Wishna, Ofek Hayon, Brian Silver, music promoter Don Kirshner, and Michael Jackson The management team, partners, and investors attracted to the business include Internet entrepreneurs and music industry executives. One of the original creators of MTV and co-founder of Internet service provider NetZero are listed among the company's board. It was described by the company as "the music industry's first Social Music Network".
Len Fulford, English photographer and director (b. 1928) deaths
Leonard Alfred Fulford was a British commercial photographer and director, with a specialty for photography of still life. He was one of the founding members of BFCS. With studios in London, New York, Los Angeles and Milan, BFCS was one of the most successful commercial production companies of all time, winning the Palme d'Or at the Cannes Advertising Festival an unprecedented six times. Fulford directed the popular Go to work on an egg television commercials for the Egg Marketing Board during the 1960s. Fulford also directed many of the iconic Guinness television commercials of the 1970s and 1980s, along with other memorable spots like the Courage Best 'Rabbit Rabbit' commercial featuring the specially written song by Chas and Dave, and the iconic Simple skincare commercial in which robotic arms spray a pristine white lily with colouring and perfume.
Ken Russell, English actor, director, producer, and screenwriter (b. 1927) deaths

Henry Kenneth Alfred Russell was a British film director, known for his pioneering work in television and film and for his flamboyant and controversial style. His films in the main were liberal adaptations of existing texts, or biographies, notably of composers of the Romantic era. Russell began directing for the BBC, where he made creative adaptations of composers' lives which were unusual for the time. He also directed many feature films independently and for studios.
Gary Speed, Welsh footballer and manager (b. 1969) deaths

Gary Andrew Speed was a Welsh professional footballer and manager. As manager of Wales, Speed is often credited as being the catalyst for the change in fortunes of the national team and as setting the pathway to future successes.
Irvin Kershner, American actor, director, and producer (b. 1923) deaths

Irvin Kershner was an American film director, actor, and producer of film and television.
Al Alberts, American singer-songwriter (b. 1922) deaths
Al Alberts was an American popular singer and composer.
V. P. Singh, Indian lawyer and politician, 7th Prime Minister of India (b. 1931) deaths

Vishwanath Pratap Singh , shortened to V. P. Singh, was an Indian politician who was the 7th Prime Minister of India from 1989 to 1990 and the 41st Raja Bahadur of Manda. He is India's only prime minister to have been former royalty.

The prime minister of India is the head of government of the Republic of India. Executive authority is vested in the prime minister and their chosen Council of Ministers, despite the president of India being the nominal head of the executive. The prime minister is often the leader of the party or the coalition with a majority in the lower house of the Parliament of India, the Lok Sabha, which is the main legislative body in the Republic of India. The prime minister and their cabinet are at all times responsible to the Lok Sabha.
Bernie Banton, Australian activist (b. 1946) deaths

Bernard Douglas Banton AM was an Australian social justice campaigner. He was the widely recognized face of the legal and political campaign to achieve compensation for the many sufferers of asbestos-related conditions, which they contracted after either working for the company James Hardie or being exposed to James Hardie Industries' products.
Robert Cade, American physician and academic, co-invented Gatorade (b. 1927) deaths

James Robert Cade was an American physician, university professor, research scientist and inventor. Cade, a native of Texas, earned his bachelor and medical degrees at the University of Texas, and became a professor of medicine and nephrology at the University of Florida. Although Cade engaged in many areas of medical research, he is most widely remembered as the leader of the research team that created the sports drink Gatorade. Gatorade would have significant medical applications for treating dehydration in patients, and has generated over $150 million in royalties for the university.

Gatorade is an American brand of sports-themed beverage and food products, built around its signature line of sports drinks. Gatorade is currently manufactured by PepsiCo and is distributed in over 80 countries. The beverage was first developed in 1965 by a team of researchers led by Dr. Robert Cade. It was originally made for the Gators at the University of Florida to replenish the carbohydrates that the school's student-athletes burned and the combination of water and electrolytes that they lost in sweat during rigorous sports activities.
Sean Taylor, American football player (b. 1983) deaths

Sean Michael Maurice Taylor was an American football safety for the Washington Redskins of the National Football League (NFL). He was selected fifth overall in the 2004 NFL Draft by the Redskins, where he played four seasons until his murder in 2007.
Bill Willis, American football player and coach (b. 1921) deaths

William Karnet Willis was an American football defensive tackle who played eight seasons for the Cleveland Browns in the All-America Football Conference (AAFC) and the National Football League (NFL). Known for his quickness and strength despite his small stature, Willis was one of the dominant defensive football players of the 1940s and early 1950s. He was named an All-Pro in every season of his career and reached the NFL's Pro Bowl in three of the four seasons he played in the league. His techniques and style of play were emulated by other teams, and his versatility as a pass-rusher and coverage man influenced the development of the modern-day linebacker position. When he retired, Cleveland coach Paul Brown called him "one of the outstanding linemen in the history of professional football".
Don Butterfield, American tuba player (b. 1923) deaths
Don Kiethly Butterfield was an American jazz and classical tuba player.
Bebe Moore Campbell, American author and educator (b. 1950) deaths

Bebe Moore Campbell was an American author, journalist and teacher. Campbell was the author of three New York Times bestsellers: Brothers and Sisters, Singing in the Comeback Choir, and What You Owe Me, which was also a Los Angeles Times "Best Book of 2001". Her other works include the novel Your Blues Ain't Like Mine, which was a New York Times Notable Book of the Year and the winner of the NAACP Image Award for Literature; her memoir, Sweet Summer: Growing Up With and Without My Dad; and her first nonfiction book, Successful Women, Angry Men: Backlash in the Two-Career Marriage. Her essays, articles, and excerpts appear in many anthologies.
Casey Coleman, American sportscaster (b. 1951) deaths
Kenneth R. "Casey" Coleman Jr. was a sportscaster and radio personality in the Cleveland area for nearly 30 years.
Jocelyn Brando, American actress (b. 1919) deaths
Jocelyn Brando was an American actress and writer. She is best known for her role as Katie Bannion in the film noir The Big Heat (1953).
Joe Jones, American singer-songwriter (b. 1926) deaths
Joseph Charles Jones was an American R&B singer, songwriter and arranger, who was born in New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. Jones is also generally credited with discovering the Dixie Cups. He also worked with B.B. King. As a singer, Jones had his biggest hit in the form of the Top Five 1960 R&B hit "You Talk Too Much", which also reached No. 3 on the Billboard Hot 100 chart.
Billie Bird, American actress (b. 1908) deaths

Billie Bird Sellen, better known professionally as Billie Bird, was an American actress and comedian. She played Margie in Dear John (1988–1992).
Shivmangal Singh Suman, Indian poet and academic (b. 1915) deaths
Shivmangal Singh "Suman" was an Indian poet and academician who wrote in Hindi.
Zoe Colletti, American actress births
Zoe Margaret Colletti is an American actress. She made her acting debut in the television pilot of American Men (2006) and played her first major-film role in Annie (2014). Colletti appeared in 2018 films Wildlife and Skin before garnering critical praise in the lead role of Stella Nicholls in horror film Scary Stories to Tell in the Dark (2019). She achieved further recognition and plaudits as Dakota in the sixth season of horror drama series Fear the Walking Dead (2020–2021) and the Truth Pixie in fantasy film A Boy Called Christmas (2021). In 2022 she portrayed Lucy in the second season of Only Murders in the Building.
Malcolm Bradbury, English author and academic (b. 1932) deaths

Sir Malcolm Stanley Bradbury, was an English author and academic.
Uno Prii, Estonian-Canadian architect (b. 1924) deaths
Uno Prii was an Estonian-born Canadian architect. He designed approximately 250 buildings, many in Toronto, but also around southern Ontario and the United States.
Len Shackleton, English footballer and journalist (b. 1922) deaths
Leonard Francis Shackleton was an English footballer. Known as the "Clown Prince of Football", he is generally regarded as one of English football's finest ever entertainers. He also played cricket in the Minor Counties for Northumberland.
Yasuhiro Kojima, Japanese-American wrestler and trainer (b. 1937) deaths

Yasuhiro Kojima was a Japanese professional wrestler and trainer best known by his ring name Hiro Matsuda . He trained many professional wrestlers including Hulk Hogan, The Great Muta, "Mr. Wonderful" Paul Orndorff, Scott Hall, Lex Luger, "Cowboy" Bob Orton, and Ron Simmons.
Alain Peyrefitte, French scholar and politician, French Minister of Justice (b. 1925) deaths

Alain Peyrefitte was a French scholar and politician. He was a confidant of Charles de Gaulle and had a long career in public service, serving as a diplomat in Germany and Poland. Peyrefitte is remembered for his support for partitioning Algeria amid the Algerian War.

The Ministry of Justice is a ministerial department of the Government of France, also known in French as la Chancellerie. It is headed by the Minister of Justice, also known as the Keeper of the Seals, a member of the Council of Ministers. The ministry's headquarters are on Place Vendôme, Paris.
Elizabeth Gray Vining, American author and librarian (b. 1902) deaths

Elizabeth Janet Gray Vining was an American professional librarian and author who tutored Emperor Akihito of Japan in English while he was crown prince. She was also a noted author, whose children's book Adam of the Road received the Newbery Medal in 1943.
Barbara Acklin, American singer-songwriter (b. 1943) deaths

Barbara Jean Acklin was an American soul singer and songwriter, who was most successful in the 1960s and 1970s. Her biggest hit as a singer was "Love Makes a Woman" (1968). As a songwriter, she is best known for co-writing the multi-million-selling "Have You Seen Her" (1971) with Eugene Record, lead singer of the Chi-Lites.
Gloria Fuertes, Spanish poet and author of children's literature (b. 1917) deaths

Gloria Fuertes García was a Spanish poet and author of children's literature. She was part of the Spanish literary movement known as postismo (post-ism) that began after the Spanish Civil War. Active in the Spanish artistic movement known as Generation of '50, Fuertes is considered a singular voice in Spanish post-war poetry. She was also well-known in Spain for her children's television shows. In her work, Fuertes promoted gender equality, pacifism, and care for the environment.
Buck Leonard, American baseball player and educator (b. 1907) deaths

Walter Fenner "Buck" Leonard was an American first baseman in Negro league baseball and in the Mexican League. After growing up in North Carolina, he played for the Homestead Grays between 1934 and 1950, batting fourth behind Josh Gibson for many years. The Grays teams of the 1930s and 1940s were considered some of the best teams in Negro league history. Leonard and Gibson are two of only nine players in league history to win multiple batting titles.
Mike Williams, Dutch DJ and record producer births

Mike Willemsen, better known by his stage name Mike Williams, is a Dutch DJ, record producer, musician, and remixer. He is best known for working with Tiësto and as an artist of Spinnin' Records, who recognised him as an "artist of the future". He is regarded as one of the pioneers of the future bounce genre, an emerging subgenre of future house, alongside Dutch DJs Justin Mylo, Brooks and Mesto.
Andy Truong, Australian fashion designer births
Andy Truong is an Australian fashion designer of Vietnamese heritage. In 2012, he was known as Australia's youngest fashion designer, at the age of 15, after his launch into the fashion industry at Melbourne Spring Fashion Week.
Suliasi Vunivalu, Fijian rugby league player births

Suliasi Vunivalu is a professional rugby union footballer who plays for the Queensland Reds in the Super Rugby. His regular playing position is Wing.
Fernando Lopes-Graça, Portuguese composer and conductor (b. 1906) deaths
Fernando Lopes-Graça, GOSE, GCIH was a Portuguese composer, conductor and musicologist. Lopes-Graça was born in Tomar, and was influenced by Portuguese popular music, which he also studied, continuing the work of the composer and musicologist Francisco de Lacerda. He was a member of the Portuguese Communist Party and strenuously opposed the Estado Novo and its leader António de Oliveira Salazar. He completed the Dicionário de Música, started by his teacher, Tomás Borba, himself a composer. He died in Parede, near Cascais.
Ala Boratyn, Polish singer-songwriter births
Ala Boratyn, also known mononymously as Ala, born Alicja Julia Boratyn on 27 November 1992, is a Polish singer-songwriter. She rose to fame in 2005 as one of the lead singers of Polish girl duo Blog 27. With Blog 27, Boratyn enjoyed success in her native Poland, Central Europe, and Japan. Having departed from the band in 2006, she embarked on a short-lived solo career before becoming member of the bands Wicked Giant, New People and Ala Zastary.
Park Chanyeol, South Korean rapper, singer, songwriter, actor and model births

Park Chan-yeol, better known mononymously as Chanyeol, is a South Korean rapper, singer, songwriter, producer, actor and model. He is a member of the South Korean-Chinese boy group Exo, its sub-group Exo-K and sub-unit Exo-SC. Apart from his group's activities, Chanyeol has also starred in various television dramas and movies such as So I Married an Anti-fan (2016), and Secret Queen Makers (2018).
Ivan Generalić, Croatian painter (b. 1914) deaths

Ivan Generalić was a Croatian painter in the naïve tradition.
Josh Dubovie, English singer births

Josh James Dubovie is a British singer. Dubovie is most notable for having represented the UK at the 2010 Eurovision Song Contest, held in Oslo, Norway, in May 2010, after winning the UK national selection competition with "That Sounds Good to Me", a song by Mike Stock, Pete Waterman and Steve Crosby.
David White, American actor (b. 1916) deaths

David White was an American stage, film, and television actor best known for playing Darrin Stephens' boss Larry Tate from 1964 to 1972 on the ABC situation comedy Bewitched.
Basilis C. Xanthopoulos, Greek physicist and academic (b. 1951) deaths

Basilis C. Xanthopoulos was a Greek theoretical physicist, well known in the field of general relativity for his contributions to the study of colliding plane waves.
Michael Floyd, American football player births

Michael Floyd Jr. is a former American football wide receiver. He played college football at Notre Dame from 2008 to 2011, finishing with 271 catches for 3,686 yards and 37 touchdowns, all school records. He was drafted by the Arizona Cardinals in the first round of the 2012 NFL Draft, but was dismissed from the Cardinals during the 2016 season, after he was arrested on drinking and driving charges. He has also played for the New England Patriots, Minnesota Vikings, New Orleans Saints, Washington Redskins, and Baltimore Ravens.
Freddie Sears, English footballer births

Frederick David Sears is an English professional footballer who plays as a forward for Colchester United.
Carlos Arias Navarro, Spanish politician, Prime Minister of Spain (b. 1908) deaths

Carlos Arias Navarro, 1st Marquis of Arias-Navarro was one of the best-known Spanish politicians during the Francoist regime.

The prime minister of Spain is the head of government of Spain. There is no specific date as to when the office of Prime Minister first appeared as the role was not created, but rather evolved over a period of time through a merger of duties. Modern historians have not managed to agree who the first prime minister of Spain was, but Francisco Martínez de la Rosa was the first prime minister recognized by a constitutional law.
John Carradine, American actor (b. 1906) deaths

John Carradine was an American actor, considered one of the greatest character actors in American cinema. He was a member of Cecil B. DeMille's stock company and later John Ford's company, best known for his roles in horror films, Westerns, and Shakespearean theatre. In the later decades of his career, he starred mostly in low-budget B-movies, but continued to also appear in higher-profile fare. In total, he holds 351 film and television credits, making him one of the most prolific English-speaking actors of all time.
Jan Hein Donner, Dutch chess player and author (b. 1927) deaths

Johannes Hendrikus (Hein) Donner was a Dutch chess grandmaster (GM) and writer. Donner was born in The Hague and won the Dutch Championship in 1954, 1957, and 1958. He took part in the Internacional Chess Tournament (1956), Donner came third, behind Larsen and Darga. FIDE, the World Chess Federation, awarded him the GM title in 1959. He played for the Netherlands in the Chess Olympiads 11 times. He was the uncle of the former Dutch Minister of Social Affairs and Employment, Piet Hein Donner.
Suresh Kumar Raina, Indian cricketer births

Suresh Raina is an Indian former international cricketer. He occasionally served as stand-in captain for Indian men's national cricket team during the absence of the main captain. He played for Uttar Pradesh (UP) in domestic cricket circuit. He is an aggressive left-handed middle-order batsman and an occasional off-spin bowler. He is the second-youngest player ever to captain India. He was the captain of Gujarat Lions in the Indian Premier League (IPL), and he also served as vice-captain of the Chennai Super Kings. He is the first Indian batsman to hit a century in all three formats of international cricket.
Steven Silva, American-Filipino footballer births
Steven Joseph Silva is a Filipino-American footballer from Team Socceroo FC in the UFL Second Division. He is also an actor, chef, radio disk jockey, and the Ultimate Male Survivor of the fifth season of StarStruck. He is half-Portuguese, one-fourth Chinese and one-fourth Filipino. He is the first Mindanao representative and the oldest male contestant to win the said title.
Xavi Torres, Spanish footballer births

Xavier "Xavi" Torres Buigues is a Spanish professional footballer who plays as a defensive midfielder for CD Lugo.
Oritsé Williams, English singer-songwriter, producer, and dancer births

Oritsé Jolomi Matthew Soloman Williams, professionally as Oritsé, is an English singer-songwriter, dancer and record producer. He is best known as the founding member of the boy band JLS, who were runners-up to Alexandra Burke on the fifth series of The X Factor in 2008. JLS sold over 10 million records before disbanding in December 2013. Williams also won the ITV dancing competition Stepping Out in September 2013.
Steve Tracy, American actor (b, 1952) deaths
Steve Tracy was an American film and television actor. Tracy is best known for his role on Little House on the Prairie as Percival Dalton.
Park Soo-jin, South Korean singer births

Park Soo-jin is a South Korean actress, singer and model. She was a member of K-pop girl group Sugar from 2001 to 2006, then she transitioned to acting in 2007. Park has also hosted Tasty Road since 2010, a cable show that features trendy restaurants in Seoul.
Alison Pill, Canadian actress births

Alison Pill is a Canadian actress. A former child actress, Pill began her career at age 12, appearing in numerous films and television series. She transitioned to adult roles and her breakthrough came with the television series The Book of Daniel (2006). That same year, she was nominated for a Tony Award for Best Featured Actress in a Play for her performance in The Lieutenant of Inishmore (2006). Pill had prominent roles in the films Confessions of a Teenage Drama Queen (2004), Plain Truth (2004), Milk (2008), Scott Pilgrim vs. the World (2010), Midnight in Paris (2011), Hail, Caesar! (2016), Vice (2018), the television series In Treatment (2009), The Pillars of the Earth (2010), The Newsroom (2012–14), American Horror Story: Cult (2017), Star Trek: Picard (2020–2022), Devs (2020), and Them (2021).
Thilo Versick, German footballer births
Thilo Versick is a German former professional footballer who played as a forward. He made two appearances for Arminia Bielefeld in the Bundesliga.
Rendra Karno, Indonesian actor (b. 1920) deaths

Raden Soekarno, better known as Rendra Karno, was an Indonesian actor. Born in Kutoarjo, Central Java, Soekarno entered the film industry in 1941, making his debut appearance in Union Films' Soeara Berbisa. Over the next forty years he appeared in more than fifty films. He was also involved in the theatre during the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies and the Indonesian National Revolution. For his role in 1962's Bajangan di Waktu Fadjar, he was named best supporting actor at the 1963 Asian Film Festival in Tokyo.
Izumi Kitta, Japanese voice actress and singer births

Izumi Kitta is a Japanese voice actress best known as the voice of Cordelia Glauca in the media franchise Tantei Opera Milky Holmes, the voice of Tomoko Kuroki in No Matter How I Look at It, It's You Guys' Fault I'm Not Popular!, and the voice of Rainbow Dash in the Japanese dub of My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic. Her first maxi single, "Colorful Garden" was released on April 6, 2011. Kitta attended Dwango Creative School, a voice actor training school in 2007. After leaving Dwango Artist Production, she is now affiliated with Hibiki Cast. In 2017 she published her first manga, Liberty, in yuri magazine Galette, illustrated by Moto Momono.
Domata Peko, American football player births

Domata Uluaifaasau Peko Sr is an American football nose tackle who is a free agent. Peko was born in Los Angeles and grew up in Pago Pago, American Samoa. He played college football at Michigan State and was drafted by the Cincinnati Bengals in the fourth round of the 2006 NFL Draft.
Leslie Dewan, American entrepreneur births

Leslie Dewan is an American nuclear engineer. She was the co-founder and chief executive officer of Transatomic Power. Dewan was a member of the board of MIT and was named a Young Global Leader by the World Economic Forum.
Professor Green, English rapper births

Stephen Paul Manderson, better known by his stage name Professor Green or simply Pro Green, is an English rapper, singer, songwriter, actor, television personality and mental health activist from London.
Donta Smith, American-Venezuelan basketball player births

Donta Lamont Smith is an American-Venezuelan professional basketball player for Cangrejeros de Santurce of the Baloncesto Superior Nacional. Playing for Maccabi Haifa, he was named the 2014 Israeli Basketball Premier League MVP.
David Bellion, French footballer births

David Bellion is a French former professional footballer who played as a striker. His previous clubs include Cannes, Sunderland, Manchester United, West Ham United, Nice, Bordeaux and Red Star.
Aleksandr Kerzhakov, Russian footballer births

Aleksandr Anatolyevich Kerzhakov is a Russian football manager and former professional football player who played as a striker.
Tommy Robinson, English activist, co-founded the English Defence League births

Stephen Christopher Yaxley-Lennon, better known as Tommy Robinson, is a British far-right, Islamophobic activist, and convicted criminal on multiple counts of violence and fraud as well as other crimes. He is the co-founder and former leader of the English Defence League, and later served as a political advisor to former UKIP leader Gerard Batten.

The English Defence League (EDL) is a far-right, Islamophobic organisation in the United Kingdom. A social movement and pressure group that employs street demonstrations as its main tactic, the EDL presents itself as a single-issue movement opposed to Islamism and Islamic extremism, although its rhetoric and actions target Islam and Muslims more widely. Founded in 2009, its heyday lasted until 2011, after which it entered a decline.
Bruno Alves, Portuguese footballer births

Bruno Eduardo Regufe Alves is a Portuguese former footballer who played as a central defender, currently sporting director of Super League Greece club AEK Athens.
Ryan Jimmo, Canadian mixed martial artist (d. 2016) births
Ryan Jimmo was a Canadian mixed martial artist who competed in the light heavyweight division of the Ultimate Fighting Championship. He mostly fought in Canada and competed on the eighth season of The Ultimate Fighter. Jimmo was the former MFC Light Heavyweight Champion.
Matthew Taylor, English footballer births

Matthew Simon Taylor is an English professional football coach, manager and former player who was most recently head coach of League Two club Walsall.
Lotte Lenya, Austrian singer and actress (b. 1898) deaths

Lotte Lenya was an Austrian-American singer, diseuse, and actress, long based in the United States. In the German-speaking and classical music world, she is best remembered for her performances of the songs of her first husband, Kurt Weill. In English-language cinema, she was nominated for an Academy Award for her role as a jaded aristocrat in The Roman Spring of Mrs. Stone (1961). She also played the murderous and sadistic Rosa Klebb in the James Bond movie From Russia with Love (1963).
Jackie Greene, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Jackie Greene is an American singer-songwriter and musician. He has a solo career and became a member of The Black Crowes in 2013, though the band broke up in 2015 before he could contribute any studio work.
Veronika Portsmuth, Estonian singer and conductor births
Veronika Portsmuth is an Estonian conductor and singer.
Michael Yardy, English cricketer births

Michael Howard Yardy is an English cricket coach and former professional cricketer who played limited over internationals for the England cricket team between 2006 and 2015. He played as a left-handed batsman and captained Sussex County Cricket Club. His unusual batting technique attracted a great deal of attention due to a pronounced shuffle from leg to off immediately prior to the bowler releasing the ball. Yardy also bowled slow left arm with a characteristic round armed action, and was used as a bowling all-rounder in England's One Day International and Twenty20 International teams. Yardy retired from professional cricket at the end of the 2015 season.
F. Burrall Hoffman, American architect, designed the Villa Vizcaya (b. 1882) deaths
Francis Burrall Hoffman was an American-born architect, best known for his work with James Deering’s Villa Vizcaya in Miami, Florida.

The Vizcaya Museum and Gardens, previously known as Villa Vizcaya, is the former villa and estate of businessman James Deering, of the Deering McCormick-International Harvester fortune, on Biscayne Bay in the present-day Coconut Grove neighborhood of Miami, Florida. The early 20th-century Vizcaya estate also includes extensive Italian Renaissance gardens, native woodland landscape, and a historic village outbuildings compound.
Ricky Carmichael, American motocross racer births

Richard Joseph Carmichael is an American former professional motocross and stock car racing driver. He competed in the AMA Motocross Championships from 1997 to 2007 and in NASCAR from 2008 to 2011. Carmichael is notable for winning the AMA 450cc motocross national championship seven times and, the AMA Supercross Championship 450cc class five times. His unrivaled successes in the sport of motocross have given him the nickname "The GOAT"; standing for Greatest of All Time.

Motocross is a form of off-road motorcycle racing held on enclosed off-road circuits. The sport evolved from motorcycle trials competitions held in the United Kingdom.
Hilary Hahn, American violinist births

Hilary Hahn is an American violinist. She has performed throughout the world as a soloist with leading orchestras and conductors and as a recitalist. She is an avid supporter of contemporary classical music, and several composers have written works for her, including concerti by Edgar Meyer and Jennifer Higdon, partitas by Antón García Abril, two serenades for violin and orchestra by Einojuhani Rautavaara, and a violin and piano sonata by Lera Auerbach.
Teemu Tainio, Finnish footballer births

Teemu Mikael Tainio is a Finnish football coach and former player. He is the current head coach of FC Haka.
Eszter Molnár, Hungarian tennis player births
Eszter Molnár is a Hungarian former professional tennis player. In her career, she won a total of 11 ITF titles and reached a doubles ranking high of world No. 192 on 18 February 2002.
Jimmy Rollins, American baseball player births

James Calvin Rollins, nicknamed "J-Roll", is an American former professional baseball shortstop, who played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Philadelphia Phillies (2000–2014), Los Angeles Dodgers (2015), and Chicago White Sox (2016).
Mike Skinner, English rapper and producer births

Michael Geoffrey Skinner is an English rapper, singer-songwriter, musician, and record producer. Best known for the music project the Streets, Skinner has also released music as a solo artist, as part of the D.O.T. with frequent collaborator Rob Harvey, and under the pseudonym The Darker the Shadow the Brighter the Light.
Radek Štěpánek, Czech tennis player births

Radek Štěpánek is a Czech former professional tennis player. His career-high singles ranking was world No. 8 and best doubles ranking was world No. 4. Štěpánek's biggest achievements are reaching two Masters 1000 event finals and the quarterfinals of Wimbledon in 2006, as well as winning the deciding match for Czech Republic's Davis Cup winning team in 2012 and again in 2013. In doubles, he won his first Grand Slam title at the 2012 Australian Open, along with Indian partner Leander Paes, defeating the Bryan Brothers in the final. Paes and Štěpánek also won the men's doubles title at the 2013 US Open, defeating Bruno Soares and Alexander Peya in the final. In November 2017, he became a coach of Novak Djokovic and in May 2019, he joined Andre Agassi as part of Grigor Dimitrov's coaching staff.
Harvey Milk, American lieutenant and politician (b. 1930) deaths

Harvey Bernard Milk was an American politician and the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, as a member of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors. Milk was born and raised in New York where he acknowledged his homosexuality as an adolescent, but chose to pursue sexual relationships with secrecy and discretion well into his adult years. His experience in the counterculture of the 1960s caused him to shed many of his conservative views about individual freedom and the expression of sexuality.
George Moscone, American lawyer and politician, 37th Mayor of San Francisco (b. 1929) deaths

George Richard Moscone was an American attorney and Democratic politician. He was the 37th mayor of San Francisco, California from January 1976 until his assassination in November 1978. He was known as "The People's Mayor", who opened up City Hall and its commissions to reflect the diversity of San Francisco, appointing African Americans, Asian Americans, and homosexuals. Moscone served in the California State Senate from 1967 until becoming Mayor. In the Senate, he served as Majority Leader. Moscone is remembered for being an advocate of civil progressivism.

The mayor of the City and County of San Francisco is the head of the executive branch of the San Francisco city and county government. The officeholder has the duty to enforce city laws, and the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the San Francisco Board of Supervisors, the legislative branch. The mayor serves a four-year term and is limited to two successive terms. Because of San Francisco's status as a consolidated city-county, the mayor also serves as the head of government of the county; both entities have been governed together by a combined set of governing bodies since 1856.
Willie Bloomquist, American baseball player births

Willie Paul Bloomquist is an American baseball coach and former utility player, who is the current head baseball coach of the Arizona State Sun Devils. He played college baseball at Arizona State for coach Pat Murphy from 1997 to 1999 and played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for 14 seasons from 2002 to 2015. In 2021, he returned to his alma mater, Arizona State.
Bendor Grosvenor, British art historian births

Bendor Gerard Robert Grosvenor is a British art historian, writer and former art dealer. He is known for discovering a number of important lost artworks by Old Master artists, including Sir Peter Paul Rubens, Claude Lorrain and Peter Brueghel the Younger. As a dealer he specialised in Old Masters, with a particular interest in Anthony van Dyck.
Mart Laga, Estonian basketball player (b. 1936) deaths
Mart Laga was an Estonian basketball player who competed for the Soviet Union in the EuroBasket 1955 and EuroBasket 1957 events.
Jean Grae, South African-American rapper and producer births

Tsidi Ibrahim, known professionally as Jean Grae, is an American rapper from Manhattan, New York City. Jean rose in the underground hip hop scene in New York City and has built an international fanbase. Grae's unique music and lyrical style have earned the artist recognition as a favorite emcee by many rap artists such as Talib Kweli, Jay-Z, and Black Thought of the Roots.
Chad Kilger, Canadian ice hockey player and firefighter births

Chad William Lawrence Kilger is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player. He played for several National Hockey League teams, most recently the Toronto Maple Leafs.
Jaleel White, American actor and screenwriter births

Jaleel Ahmad White is an American actor. He is best known for his role as Steve Urkel on the sitcom Family Matters.
Bad Azz, American rapper (d. 2019) births

Jamarr Antonio Stamps (November 27, 1975 – November 11, 2019), better known by his stage name Bad Azz, was an American rapper and member of Tha Dogg Pound Gangsta Crips.
Martín Gramática, Argentinian-American football player births

Martín Gramática is an Argentine-born former American football placekicker in the National Football League (NFL) for the Tampa Bay Buccaneers, Indianapolis Colts, Dallas Cowboys, and New Orleans Saints. He played college football at Kansas State University where was recognized twice as an All-American and was drafted by the Tampa Bay Buccaneers in the third round of the 1999 NFL Draft.
Rain Vessenberg, Estonian footballer births
Rain Vessenberg is a retired football (soccer) goalkeeper from Estonia. He played for several clubs in his native country, including JK Nõmme United and JK Viljandi Tulevik.
Alberto Massimino, Italian automotive engineer (b. 1895) deaths

Alberto Massimino was an Italian automotive engineer.
Ross McWhirter, English author and activist, co-founded the Guinness Book of Records (b. 1925) deaths

Alan Ross McWhirter was, with his twin brother, Norris, the cofounder of the 1955 Guinness Book of Records and a contributor to the television programme Record Breakers. He was killed by the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) in 1975.

Guinness World Records, known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as The Guinness Book of Records and in previous United States editions as The Guinness Book of World Records, is a reference book published annually, listing world records both of human achievements and the extremes of the natural world. The brainchild of Sir Hugh Beaver, the book was co-founded by twin brothers Norris and Ross McWhirter in Fleet Street, London, in August 1955.
Wendy Houvenaghel, Northern Irish racing cyclist births

Wendy Louise Houvenaghel is a Northern Irish former racing cyclist from Upperlands, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland, riding on both the road and track, but specialising in the latter. She has represented Great Britain in various World Cycling Championships and in the 2008 Olympic Games, most notably winning the silver medal at the Beijing Olympic Games, and gold in the team pursuit at the 2008, 2009 and 2011 Track World Championships. She has also won many British national titles and represented England at the 2006 Commonwealth Games and Northern Ireland at the 2010 Commonwealth Games. Houvenaghel is based in Cornwall, England.
Alec Newman, Scottish actor births

Alec Newman is a Scottish actor best known for portraying Paul Atreides in the Sci Fi Channel's 2000 miniseries adaptation of Frank Herbert's Dune.
Sharlto Copley, South African actor births

Sharlto Copley is a South African actor. His acting credits include roles in the Academy Award-nominated science fiction film District 9, the 2010 adaptation of The A-Team, the science fiction film Elysium, the science fiction horror film Europa Report and the dark fantasy adventure film Maleficent. He also played the title character in the science fiction film Chappie, Jimmy in Hardcore Henry, and starred in two seasons as Christian Walker of the TV series Powers. Copley is married to fellow South African actress and supermodel Tanit Phoenix.
Samantha Harris, American model and television host births

Samantha Harris is an American television presenter, model, and entertainment reporter and actress, known as the co-host of seasons two through nine of Dancing with the Stars with Tom Bergeron. From 2010–12, she was a correspondent at Entertainment Tonight. In September 2015, she returned to the program as a co-anchor for the weekend edition.
Evan Karagias, American wrestler and actor births
Evan Karagias is an American professional wrestler and actor.
Jin Katagiri, Japanese comedian, actor, sculptor, and potter births
Jin Katagiri is a comedian, actor, sculptor, and potter from Saitama Prefecture, Japan. He graduated from Kasukabe High School and Tama Art University. Outside Japan, he is most well known for playing the PC in the "Get A Mac" advertising campaign in Japan. He is a member of the Rahmens owarai comedy duo.
Twista, American rapper and producer births

Carl Terrell Mitchell, better known by his stage name Twista, is an American rapper and record producer. He is best known for his chopper style of rapping and for once holding the title of fastest English-speaking rapper in the world according to Guinness World Records in 1992, being able to pronounce 598 syllables in 55 seconds.
Frank Christian, American trumpet player (b. 1887) deaths

Frank Joseph Christian was an early jazz trumpeter.
Shane Salerno, American screenwriter and producer births

Shane Salerno is an American screenwriter, producer, and Chief Creative Officer of The Story Factory. His writing credits include the films Avatar: The Way of Water, Armageddon, Savages, Shaft, and the TV series Hawaii Five-0. He was chosen by director James Cameron to co-write the four sequels to Avatar, set to release in 2022, 2024, 2026 and 2028. He spent ten years writing, producing, financing, and directing the documentary Salinger, and co-writing with David Shields the companion book which became a New York Times bestseller.
Kirk Acevedo, American actor births

Kirk M. Acevedo is an American actor. He is primarily known for his work on television for the portrayals of Miguel Alvarez in the HBO series Oz, Joe Toye in Band of Brothers, and FBI Agent Charlie Francis in the science-fiction series Fringe. His best-known films are The Thin Red Line, Dinner Rush and Dawn of the Planet of the Apes. He portrayed comic book villain Ricardo Diaz / The Dragon on Arrow as the main antagonist in seasons six and the first half of season seven.
Larry Allen, American football player births

Larry Christopher Allen Sr. is an American former football guard who played in the National Football League (NFL) for fourteen seasons, primarily with the Dallas Cowboys. He played college football at Sonoma State and was selected by the Cowboys in the second round of the 1994 NFL Draft. Allen is regarded as one of the NFL's physically strongest players ever while also capable of using his speed against defenders.
Iván Rodríguez, Puerto Rican-American baseball player births

Iván Rodríguez Torres, nicknamed "Pudge" and "I-Rod", is a Puerto Rican former Major League Baseball catcher. He played for the Texas Rangers, Florida Marlins, Detroit Tigers, New York Yankees, Houston Astros and Washington Nationals. Rodríguez was awarded the AL MVP award in 1999 and is widely regarded as one of the greatest catchers in MLB history.
Nick Van Exel, American basketball player and coach births

Nickey Maxwell Van Exel is an American professional basketball coach and former player who is an assistant coach for the Atlanta Hawks of the National Basketball Association (NBA). Van Exel played for six NBA teams from 1993 through 2006. He was an NBA All-Star with the Los Angeles Lakers in 1998.
Helene Madison, American swimmer and nurse (b. 1913) deaths

Helene Emma Madison was an American competition swimmer, Olympic champion, and former world record-holder.
Ruth George, English politician births

Ruth Stephanie Nicole George is a British politician who served as Member of Parliament (MP) for High Peak from 2017 to 2019. A member of the Labour Party, she has been a Member of Derbyshire County Council since 2020.
Damian Hinds, English politician births

Damian Patrick George Hinds is a British politician serving as Minister of State for Prisons, Parole and Probation since October 2022. He served as Secretary of State for Education from 2018 to 2019 and Minister of State for Security and Borders from 2021 to 2022. A member of the Conservative Party, he has been Member of Parliament (MP) for East Hampshire since 2010.
Myles Kennedy, American singer-songwriter births

Myles Richard Bass, known professionally as Myles Kennedy, is an American singer, guitarist, and songwriter. He is the lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of the rock band Alter Bridge and the lead vocalist in guitarist Slash's backing band, known as Myles Kennedy and the Conspirators. A former guitar instructor from Spokane, Washington, Kennedy has worked as a session musician and songwriter, making both studio and live appearances with several artists, and has been involved with several projects throughout his career.
May Gibbs, English Australian children's author, illustrator, and cartoonist, (b. 1877) deaths

Cecilia May Gibbs MBE was an Australian children's author, illustrator, and cartoonist. She is best known for her gumnut babies, and the book Snugglepot and Cuddlepie.
Michael Vartan, French-American actor births

Michael S. Vartan is a French-American actor, known for his role as Michael Vaughn on the ABC television action drama Alias, his role on the TNT medical drama Hawthorne, and his role on the E! drama The Arrangement as Terence Anderson. His film roles include The Pallbearer, Never Been Kissed, The Next Best Thing, One Hour Photo, Monster-in-Law, Rogue, Colombiana, and Small Town Crime.
Al Barrow, English bass guitarist births

Al Barrow is an English bassist best known as the former member of the hard rock band Magnum.
Léon M'ba, Gabonese politician, 1st President of Gabon (b. 1902) deaths

Gabriel Léon M'ba was a Gabonese politician who served as both the first Prime Minister (1959–1961) and President (1961–1967) of Gabon.

The president of Gabon is the head of state of Gabon. A total of three people have served as president since the post was formed in 1960.
Andy Merrill, American television writer, producer and voice actor births

Andrew Merrill is an American voice actor best known for his portrayal of the character Brak on Space Ghost Coast to Coast and Cartoon Planet.
Danielle Ammaccapane, American golfer births
Danielle Ammaccapane is an American professional golfer playing on the LPGA Tour. Her daughter, with husband Rod Kesling, is child actor Laura Ann Kesling.
Robin Givens, American actress births
Robin Givens is an American actress, model and director.
Roberto Mancini, Italian footballer and manager births

Roberto Mancini is an Italian football manager and former player. He is currently the manager of the Italy national team.
Hisayuki Sasaki, Japanese golfer (d. 2013) births
Hisayuki Sasaki was a Japanese professional golfer.
Fisher Stevens, American actor, director, and producer births

Fisher Stevens is an American actor, director, producer and writer. As an actor, he is best known for his portrayals of Ben in Short Circuit and Short Circuit 2, Chuck Fishman on the 1990s television series Early Edition, and villainous computer genius Eugene "The Plague" Belford in Hackers. He portrays Marvin Gerard on NBC’s The Blacklist. His most recent successes include winning the 2010 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature for The Cove and the 2008 Independent Spirit Award for Best Documentary Feature for Crazy Love. In addition, he has directed the documentary Before the Flood, which screened at the Toronto International Film Festival and by National Geographic on October 21, 2016. He stars as Hugo Baker on the HBO satirical drama series Succession.
Charlie Benante, American drummer and songwriter births

Charles Lee Benante is an American musician best known as the drummer for thrash metal band Anthrax, as well as crossover thrash band Stormtroopers of Death. Alongside rhythm guitarist and band leader Scott Ian, Benante has composed the majority of the music throughout Anthrax's discography. He joined the reunited Pantera in 2022, filling-in for original drummer Vinnie Paul for their upcoming 2023 tour.
Mike Bordin, American drummer births

Michael Andrew Bordin is an American musician, best known as the drummer for the rock band Faith No More. He has amicably been known as "Puffy", "Puffster" or "The Puff", in reference to the afro hair style he wore in the early 1980s. The nicknames were coined by Faith No More guitarist Jim Martin, and they stuck around even after he grew out his hair and tied it in dreadlocks, a trademark look he has worn for most of his career.
Davey Boy Smith, English-Canadian wrestler (d. 2002) births

David Smith was an English professional wrestler. Born in Golborne, Lancashire, Smith is best known for his appearances in the United States with the World Wrestling Federation under the ring names Davey Boy Smith and The British Bulldog. He was trained by Ted Betley in Winwick, England before relocating to Calgary, Alberta, Canada to further his training under Stu Hart. While training with Hart, Smith met Stu and Helen Hart's youngest daughter Diana, whom he married on 7 October 1984. Their son Harry is also an accomplished professional wrestler who wrestled and won tag-team gold in WWE NJPW, Pro Wrestling NOAH,
August Lass, Estonian footballer (b. 1903) deaths
August Lass was an Estonian footballer.
Samantha Bond, English actress births
Samantha Jane Bond is an English actress, who is best known for playing Miss Moneypenny in four James Bond films during the Pierce Brosnan years, and for her role on Downton Abbey as the wealthy widow Lady Rosamund Painswick, sister of Robert Crawley, the Earl of Grantham. She is also known for originating the role of "Miz Liz" Probert in the Rumpole of the Bailey series. Bond is a member of the Royal Shakespeare Company. In her television career, she is known for her role as "Auntie Angela" in the sitcom Outnumbered and the villain Mrs Wormwood in the CBBC Doctor Who spin-off, The Sarah Jane Adventures.
Steve Oedekerk, American actor, director, and screenwriter births
Steven Brent Oedekerk is an American actor, stand-up comedian, director, editor, producer, and screenwriter. He is best known for his collaborations with actor and comedian Jim Carrey and director Tom Shadyac, his series of "Thumbmation" shorts and his film Kung Pow! Enter the Fist (2002), along with his films Jimmy Neutron: Boy Genius, Santa vs. the Snowman 3D, Barnyard and The Nutty Professor remake.
Kevin Henkes, American author and illustrator births

Kevin Henkes is an American writer and illustrator of children's books. As an illustrator he won the Caldecott Medal for Kitten's First Full Moon (2004). Two of his books were Newbery Medal Honor Books, Olive's Ocean in 2004 and The Year of Billy Miller in 2014. His picture book Waiting was named both a 2016 Caldecott Honor Book and a Geisel Honor Book. It was only the second time any author has won that combination of awards.
Ken O'Brien, American football player and coach births
Kenneth John O'Brien Jr. is a former American football quarterback who played in the National Football League for the New York Jets and Philadelphia Eagles. When he retired he was the only Jets quarterback to have ever been the top ranked passer in a season. He held the team record for most consecutive pass completions (17) in a game. O'Brien was one of the six quarterbacks in the famed Quarterback class of 1983 and in 1997 he was inducted into the College Football Hall of Fame.
Tim Pawlenty, American lawyer and politician, 39th Governor of Minnesota births

Timothy James Pawlenty is an American attorney, businessman, and politician who served as the 39th governor of Minnesota from 2003 to 2011. A member of the Republican Party, Pawlenty served in the Minnesota House of Representatives from 1993 to 2003, and as House Majority Leader from 1999 to 2003. He unsuccessfully ran for the Republican presidential nomination in the 2012 presidential election. As of 2022, he is the most recent Republican to serve as governor of Minnesota.

The governor of Minnesota is the head of government of the U.S. state of Minnesota, leading the state's executive branch. Forty people have been governor of Minnesota, though historically there were also three governors of Minnesota Territory. Alexander Ramsey, the first territorial governor, also served as state governor several years later. State governors are elected to office by popular vote, but territorial governors were appointed to the office by the United States president. The current governor of Minnesota is Tim Walz of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party (DFL).
Yulia Tymoshenko, Ukrainian economist and politician, 10th Prime Minister of Ukraine births

Yulia Volodymyrivna Tymoshenko is a Ukrainian politician, people's Deputy of Ukraine, Vice Prime Minister of Ukraine for the fuel and energy complex (1999–2001), Prime Minister of Ukraine from February to September 2005 and from December 2007 to March 2010. She was the first and so far the only woman to serve as prime minister of Ukraine. She has the degree of Candidate of Economic Sciences.

The prime minister of Ukraine is the head of government of Ukraine. The prime minister presides over the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, which is the highest body of the executive branch of the Ukrainian government. The position replaced the Soviet post of chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Ukrainian SSR, which was established on March 25, 1946.
Gianni Vernetti, Italian lawyer and politician births

Gianni Vernetti is a writer and Italian politician.
Frederick Fane, Irish-English cricketer (b. 1875) deaths

Frederick Luther Fane, played cricket for the England cricket team in 14 Test matches. He also played for Essex, Oxford University and London County.
Dirk Jan de Geer, Dutch lawyer and politician, Prime Minister of the Netherlands (b. 1870) deaths

Jonkheer Dirk Jan de Geer was a Dutch politician of the defunct Christian Historical Union (CHU) now merged into the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA). He served as Prime Minister of the Netherlands from 8 March 1926 until 10 August 1929 and from 10 August 1939 until 3 September 1940.

The prime minister of the Netherlands is the head of the executive branch of the Government of the Netherlands. Although the monarch is the de jure head of government, the prime minister de facto occupies this role as the officeholder chairs the Council of Ministers and coordinates its policy with the rest of the cabinet. The current prime minister has been Mark Rutte since 14 October 2010, whose fourth cabinet was inaugurated on 10 January 2022.
Charlie Burchill, Scottish guitarist and songwriter births

Charles Burchill is a Scottish musician and composer, best known as the guitarist of Simple Minds. He is one of the founders of the group.
Viktoria Mullova, Russian violinist births
Viktoria Yurievna Mullova is a Russian-born British violinist. She is best known for her performances and recordings of a number of violin concerti, compositions by J.S. Bach, and her innovative interpretations of popular and jazz compositions by Miles Davis, Duke Ellington, The Beatles, and others.
Tetsuya Komuro, Japanese singer-songwriter, and producer births

Tetsuya Komuro is a Japanese musician, songwriter and record producer. He is recognized as the most successful producer in Japanese music history and introduced contemporary electronic dance music to the Japanese mainstream. He was also a former owner of the disco Velfarre located in Roppongi, Tokyo.
Mike Scioscia, American baseball player and manager births

Michael Lorri Scioscia, nicknamed "Sosh" and "El Jefe", is an American former Major League Baseball catcher and manager in Major League Baseball (MLB). He managed the Anaheim / Los Angeles Angels of Anaheim / Los Angeles Angels from the 2000 season through the 2018 season, and was the longest-tenured manager in Major League Baseball and second-longest-tenured coach/manager in the "Big Four", behind only Gregg Popovich at the time of his retirement. As a player, Scioscia made his major league debut with the Los Angeles Dodgers in 1980. He was selected to two All-Star Games and won two World Series over the course of his 13-year MLB career, which was spent entirely with the Dodgers; this made him the only person in MLB history to spend his entire playing career with one team and entire managing career with another team with 10+ years in both places. He was signed by the San Diego Padres and Texas Rangers late in his career, but never appeared in a major league game for either team due to injury.
Georgi Damyanov, Bulgarian politician, Head of State of Bulgaria (b. 1892) deaths
Georgi Purvanov Damyanov was a Bulgarian communist politician.

This is a list of the heads of the modern Bulgarian state, from the establishment of the Principality of Bulgaria to the present day.
Artur Rodziński, Polish-American conductor (b. 1892) deaths

Artur Rodziński was a Polish-American conductor of orchestral music and opera. He began his career after World War I in Poland, where he was discovered by Leopold Stokowski, who invited him to be his assistant with the Philadelphia Orchestra. This engagement led to Rodziński becoming music director of the Los Angeles Philharmonic, Cleveland Orchestra, New York Philharmonic, and the Chicago Symphony Orchestra. He also prepared the NBC Symphony Orchestra for Arturo Toscanini before the Italian conductor's debut with them. A dispute in Chicago led to Rodziński's dismissal in 1948, whereupon he shifted his career to Europe, eventually settling in Italy, although continuing to maintain a home in Lake Placid, New York. In November 1958, beset by heart disease, he made his professional return to the United States for the first time in a decade, conducting acclaimed performances of Richard Wagner's Tristan und Isolde with the Lyric Opera of Chicago. Exhausted, he checked into Massachusetts General Hospital where he died 11 days later.
Kenny Acheson, Northern Irish race car driver births
Kenneth Henry Acheson is a British former racing driver from Northern Ireland who competed for RAM Racing in the 1983 and 1985 Formula One seasons. He completed only one of his three race starts, finishing in 12th position in the 1983 South African Grand Prix. In 1985, he was a substitute for Manfred Winkelhock, who was killed in a sportscar race during the season.
Frank Boeijen, Dutch singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Franciscus Johannes Maria (Frank) Boeijen is a Dutch singer and guitarist. His best known songs are Kronenburg Park about a prostitute, Zwart Wit about the racial murder of Kerwin Duinmeijer in Amsterdam and Twee gezichten about a split personality. Having been in the music business for 25 years, he received the Edison award for his career achievements in 2005.
Caroline Kennedy, American lawyer and diplomat, 29th United States Ambassador to Japan, daughter of President John F. Kennedy births

Caroline Bouvier Kennedy is an American author, attorney, and diplomat serving in the Biden administration as the United States Ambassador to Australia since 2022. She previously served in the Obama administration as the United States Ambassador to Japan from 2013 to 2017. A prominent member of the Kennedy family, she is the only surviving child of former U.S. president John F. Kennedy and former first lady Jacqueline Kennedy.

The ambassador of the United States of America to Japan is the ambassador from the United States of America to Japan.
Callie Khouri, American director, producer, and screenwriter births

Carolyn Ann "Callie" Khouri is an American film and television screenwriter, producer, and director. In 1992, she won the Academy Award for Best Screenplay Written Directly for the Screen for the film Thelma & Louise, which was controversial upon its release, but which subsequently became a classic. It was inducted into the Library of Congress National Film Registry in December 2016.
Michael A. Stackpole, American game designer and author births

Michael Austin Stackpole is an American science fiction and fantasy author best known for his Star Wars and BattleTech books. He was born in Wausau, Wisconsin, but raised in Vermont. He has a BA in history from the University of Vermont. From 1977 on, he worked as a designer of role-playing games for various gaming companies, and wrote dozens of magazine articles with limited distribution within the industry. He lives in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Edda Heiðrún Backman, Icelandic actress, singer, director and artist (d. 2016) births
Edda Heiðrún Backman was an Icelandic actress, voice actress, singer, painter and director.
William Fichtner, American actor births

William Edward Fichtner is an American actor. He is known for his television roles as Sheriff Tom Underlay on Invasion, Alexander Mahone on Prison Break, Carl Hickman on Crossing Lines, and Adam Janikowski on Mom. His film appearances include Heat, Contact, Armageddon, The Perfect Storm, Go, Crash, Black Hawk Down, and Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles.
John McCarthy, English journalist and author births
John Patrick McCarthy is a British journalist, writer and broadcaster, and one of the hostages in the Lebanon hostage crisis. McCarthy was the United Kingdom's longest-held hostage in Lebanon, where he was a prisoner for more than five years.
Nazrin Shah of Perak, Sultan of Perak births

Sultan Nazrin Muizzuddin Shah ibni Almarhum Sultan Azlan Muhibbuddin Shah Al-Maghfur-Lah is the 35th and current Sultan of Perak since May 2014. Co-currently, he is serving as the Deputy Yang di-Pertuan Agong since 13 December 2016. Additionally, he served as the Acting Yang di-Pertuan Agong from November 2018 to December 2018 and again in January 2019.
Pierre Mondou, Canadian ice hockey player births
Joseph Julien Claude Pierre Mondou is a former Canadian ice hockey forward.
Bill Nye, American engineer, educator, and television host births

William Sanford Nye, popularly known as Bill Nye the Science Guy, is an American mechanical engineer, science communicator, and television presenter. He is best known as the host of the science television show Bill Nye the Science Guy (1993–1999) and the Netflix show Bill Nye Saves the World (2017–2018), and for his many appearances in popular media as a science educator.
Arthur Honegger, French-Swiss composer and academic (b. 1892) deaths
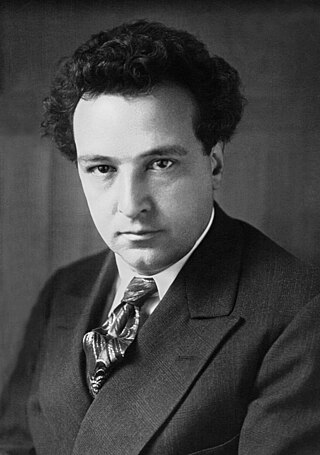
Arthur Honegger was a Swiss composer who was born in France and lived a large part of his life in Paris. A member of Les Six, his best known work is probably Antigone, composed between 1924 and 1927 to the French libretto by Jean Cocteau based on the tragedy Antigone by Sophocles. It premiered on 28 December 1927 at the Théâtre Royal de la Monnaie with sets designed by Pablo Picasso and costumes by Coco Chanel. However, his most frequently performed work is probably the orchestral work Pacific 231, which was inspired by the sound of a steam locomotive.
Arthur Smith, English comedian, actor, and screenwriter births

Brian Arthur John Smith is an English alternative comedian, presenter and writer.
Curtis Armstrong, American actor, singer, and producer births

Curtis Armstrong is an American actor and singer best known for playing the role of Booger in the Revenge of the Nerds movies, Herbert Viola on the TV series Moonlighting, Miles Dalby in the film Risky Business, and record producer Ahmet Ertegun in the film Ray as well as for playing the role of Metatron on the TV series Supernatural.
Steve Bannon, American media executive and political figure births

Stephen Kevin Bannon is an American media executive, political strategist, and former investment banker. He served as the White House's chief strategist in the administration of U.S. president Donald Trump during the first seven months of Trump's term. He is a former executive chairman of Breitbart News and previously served on the board of the now-defunct data-analytics firm Cambridge Analytica.
Boris Grebenshchikov, Russian singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Boris Borisovich Grebenshchikov is a prominent member of the generation which is widely considered to be the "founding fathers" of Russian rock music. He is the founder and lead singer of the band Aquarium which has been active from 1972 until today. Grebenshchikov is frequently referred to as BG, after his initials. On 5 October 2022, he appeared on BBC Hardtalk talking about his opposition to the Russian intervention in Ukraine, his self-imposed exile to London, and his involvement with Dave Stewart to produce an antiwar record to support the people of Ukraine.
Tarmo Kõuts, Estonian admiral and politician births

Tarmo Kõuts is an Estonian politician and former Commander of the Estonian Defence Forces.
Lyle Mays, American keyboardist and composer (d. 2020) births
Lyle David Mays was an American jazz pianist, composer, and member of the Pat Metheny Group. Metheny and Mays composed and arranged nearly all of the group's music, for which Mays won eleven Grammy Awards.
Richard Stone, American composer (d. 2001) births
Richard Stone was an American composer. He played an important part in the revival of Warner Bros. animation in the 1990s, composing music and songs for Looney Tunes, Tiny Toon Adventures, Taz-Mania, The Plucky Duck Show, Animaniacs, Pinky and the Brain, Pinky, Elmyra & the Brain, Histeria!, The Sylvester & Tweety Mysteries, Freakazoid!, and Road Rovers, as well as the Warner Bros. Family Entertainment fanfare. Many consider him to be an heir to the style of Carl W. Stalling.
Eugene O'Neill, American playwright, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1888) deaths

Eugene Gladstone O'Neill was an American playwright and Nobel laureate in literature. His poetically titled plays were among the first to introduce into the U.S. the drama techniques of realism, earlier associated with Russian playwright Anton Chekhov, Norwegian playwright Henrik Ibsen, and Swedish playwright August Strindberg. The tragedy Long Day's Journey into Night is often included on lists of the finest U.S. plays in the 20th century, alongside Tennessee Williams's A Streetcar Named Desire and Arthur Miller's Death of a Salesman.

The Nobel Prize in Literature is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in the field of literature, produced the most outstanding work in an idealistic direction". Though individual works are sometimes cited as being particularly noteworthy, the award is based on an author's body of work as a whole. The Swedish Academy decides who, if anyone, will receive the prize. The academy announces the name of the laureate in early October. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895. Literature is traditionally the final award presented at the Nobel Prize ceremony. On some occasions the award has been postponed to the following year, most recently in 2018 as of May 2022.
Sheila Copps, Canadian journalist and politician, 6th Deputy Prime Minister of Canada births

Sheila Maureen Copps is a former Canadian politician who also served as the sixth deputy prime minister of Canada from November 4, 1993, to April 30, 1996, and June 19, 1996, to June 11, 1997. Her father, Victor Copps, was once mayor of Hamilton, Ontario.

The deputy prime minister of Canada is a minister of the Crown and a member of the Canadian Cabinet. The office is conferred at the discretion of the prime minister and does not have an associated departmental portfolio. Canadian deputy prime ministers are appointed to the Privy Council and styled as the Honourable, a privilege maintained for life.
Bappi Lahiri, Indian singer-songwriter and producer births

Bappi Aparesh Lahiri, also known as Bappi Da was an Indian singer, composer and record producer. He popularised the use of synthesised disco music in Indian music industry and sang some of his own compositions. He was popular in the 1980s and 1990s with filmi soundtracks. He also delivered major box office successes in Bengali, Telugu, and Kannada films. His music was well received into the 21st century.
Jim Wetherbee, American captain, engineer, and astronaut births

James Donald "Wxb" Wetherbee, is a retired United States Navy officer and aviator, test pilot, aerospace engineer, and NASA astronaut. He is a veteran of six Space Shuttle missions and is the only American to have commanded five spaceflight missions.
Kathryn Bigelow, American director, producer, and screenwriter births

Kathryn Ann Bigelow is an American filmmaker. Covering a wide range of genres, her films include Near Dark (1987), Point Break (1991), Strange Days (1995), K-19: The Widowmaker (2002), The Hurt Locker (2008), Zero Dark Thirty (2012), and Detroit (2017).
Vera Fischer, Brazilian actress, winner from Miss Brasil 1969 contest births

Vera Fischer is a Brazilian actress, known for acting in telenovelas, and former beauty pageant titleholder.
Gunnar Graps, Estonian singer and guitarist (d. 2004) births

Gunnar Graps-Grāfs was a popular Estonian musician and one of the pioneers of hard rock in Estonia and Soviet Union. He has sold hundreds of thousands of records all over the world and in 2004 Graps was given a lifetime award at Estonian Music Awards. He has been compared to Mick Jagger and Alice Cooper, both who were his own personal idols, and is often called Raudmees.
Gavyn Davies, English journalist and businessman births

Gavyn Davies, OBE is a former Goldman Sachs partner who was the chairman of the BBC from 2001 until 2004. On 28 January 2004 he announced that he was resigning his BBC post following the publication of the Hutton Inquiry report which heavily criticised the organisation.
Masanori Sekiya, Japanese race car driver births
Masanori Sekiya is a racing car driver, most famous for being the first Japanese driver to win the 24 Hours of Le Mans, in 1995.
Don Adams, American basketball player (d. 2013) births
Don Lamar Adams was an American professional basketball small forward. He was 6 ft 6 in 210 lb.
Neil Rosenshein, American tenor and actor births
Neil Rosenshein is an American operatic tenor, who sang leading tenor roles in the major American and European opera houses. He created the roles of Aspern in Dominick Argento's The Aspern Papers and Léon in Corigliano's The Ghosts of Versailles.
Richard Codey, American politician, 53rd Governor of New Jersey births

Richard James Codey is an American Democratic Party politician who served as the 53rd governor of New Jersey from 2004 to 2006. He has served in the New Jersey Senate since 1982 and served as the President of the Senate from 2002 to 2010. He represents the 27th Legislative District, which covers the western portions of Essex County and the southeastern portion of Morris County. Codey is the longest-serving state legislator in New Jersey history, having served in the New Jersey Legislature continuously since January 8, 1974. He has served as the Deputy Senate President Pro Tem since 2022.

The governor of New Jersey is the head of government of New Jersey. The office of governor is an elected position with a four-year term. There is a two consecutive term term limit, with no limitation on non-consecutive terms. The official residence of the governor is Drumthwacket, a mansion located in Princeton, New Jersey. The governor’s office is located inside of the New Jersey State House in Trenton, making New Jersey notable as the executive’s office is located in the same building as the legislature. New Jersey is also notable for being one of the few states in which the governor’s official residence is not located in the state capital.
Ismaïl Omar Guelleh, Ethiopian-Djiboutian lawyer and politician, President of Djibouti births

Ismaïl Omar Guelleh is the current President of Djibouti. He has been in office since 1999, making him one of the longest-serving rulers in Africa. He is often referred to by his initials, IOG.

This is a list of presidents of Djibouti. Since the establishment of the office of president in 1977, there have been two presidents. The president is both head of state and head of government of Djibouti and the commander-in-chief of the Djibouti Armed Forces. The current president is Ismaïl Omar Guelleh, since 1999.
James Avery, American actor (d. 2013) births

James La Rue Avery was an American actor. He was best known for his roles as Philip Banks in The Fresh Prince of Bel-Air, Shredder in Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles, Judge Michael Conover on L.A. Law, Steve Yeager in The Brady Bunch Movie, Haroud Hazi Bin in Aladdin, and Dr. Crippen on The Closer (2005–2007).
Phil Bloom, Dutch model and actress births

Phil Bloom is a Dutch artist, graphic designer and performer. She was the first person to appear completely nude on Dutch television, on 28 July 1967 during the show Hoepla, which caused scandal and controversy at the time. Afterwards, she followed a passionate career in painting, photography and performance art. She was a member of the Fluxus network in 1967. A notable performance of hers is titled "Lemniscaat" which takes place in Lapland.
Randy Brecker, American trumpeter and flugelhornist births

Randal Edward Brecker is an American trumpeter, flugelhornist, and composer. His versatility has made him a popular studio musician who has recorded with acts in jazz, rock, and R&B.
Alain de Cadenet, English race car driver births

Alain de Cadenet was an English television presenter and racing driver. He was noted for racing in 15 editions of the 24 Hours of Le Mans during the 1970s and 1980s, achieving one podium finish with third place in 1976.
Benigno Fitial, Mariana Islander businessman and politician, 7th Governor of the Northern Mariana Islands births

Benigno Repeki Fitial is a Northern Marianan politician who served was the seventh governor of the Northern Mariana Islands. The second longest-serving governor in CNMI history, Fitial was elected on November 6, 2005, assumed office on January 9, 2006, and was re-elected to a (five-year) second term in 2009. He was impeached by the CNMI House of Representatives on February 11, 2013, and was scheduled to face trial before the CNMI Senate to determine if he should be removed from office. He resigned on February 20, 2013, after 7 years, 1 month, and 11 days in office.

The following is a list of persons who served as governor of Northern Mariana Islands. The term of office is 4 years. The longest-serving governors in CNMI history are Pedro Tenorio, who served 12 years in office from 1982 to 1990 and from 1998 to 2002, and Benigno Fitial, who served 7 years, one month, and 11 days from 2006 to 2013.
Simon Townsend, Australian journalist and television host births
Simon Townsend is an Australian journalist who became a popular television host during the 1980s. He is now retired.
Mickey Leland, American activist and politician (d. 1989) births

George Thomas "Mickey" Leland III was an anti-poverty activist who later became a congressman from the Texas 18th District and chair of the Congressional Black Caucus. He was a Democrat.
Leonid Mandelstam, Russian physicist and academic (b. 1879) deaths

Leonid Isaakovich Mandelstam or Mandelshtam was a Soviet physicist of Belarusian-Jewish background.
Nicole Brossard, Canadian author and poet births

Nicole Brossard is a leading French-Canadian formalist poet and novelist. Her work is known for exploration of feminist themes and for challenging masculine-oriented language and points of view in French literature.
Jil Sander, German fashion designer births
Heidemarie Jiline "Jil" Sander is a German Minimalist fashion designer and the founder of the Jil Sander fashion house.
Ivo Lola Ribar, Croatian soldier and politician (b. 1916) deaths

Ivan Ribar, known as Ivo Lola or Ivo Lolo, was a Yugoslav communist politician and military leader of Croatian descent. In the 1930s, he became one of the closest associates of Josip Broz Tito, leader of the Yugoslav Communist Party. In 1936, Ribar became secretary of the Central Committee of SKOJ. During World War II in Yugoslavia, Ribar was among the main leaders of the Yugoslav Partisans and was a member of the Partisan Supreme Headquarters. During the war, he founded and ran several leftist youth magazines. In 1942, Ribar was among the founders of the Unified League of Anti-Fascist Youth of Yugoslavia (USAOJ). He was killed by a German bomb in 1943 near Glamoč while boarding an airplane for Cairo, where he was to become the first representative of Communist Yugoslavia to the Middle East Command.
Henry Carr, American football player and sprinter (d. 2015) births

Henry Carr was an American track and field athlete who won two gold medals at the 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, Japan.
Marilyn Hacker, American poet and critic births
Marilyn Hacker is an American poet, translator and critic. She is Professor of English emerita at the City College of New York.
Jimi Hendrix, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and producer (d. 1970) births

James Marshall "Jimi" Hendrix was an American guitarist, singer and songwriter. Although his mainstream career spanned only four years, he is widely regarded as one of the most influential electric guitarists in the history of popular music, and one of the most celebrated musicians of the 20th century. The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame describes him as "arguably the greatest instrumentalist in the history of rock music."
Aimé Jacquet, French footballer, coach, and manager births

Aimé Étienne Jacquet is a French former professional football manager and player. He was manager of the France national football team that won the 1998 FIFA World Cup.
Eddie Rabbitt, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 1998) births

Edward Thomas Rabbitt was an American country music singer and songwriter. His career began as a songwriter in the late 1960s, springboarding to a recording career after composing hits such as "Kentucky Rain" for Elvis Presley in 1970 and "Pure Love" for Ronnie Milsap in 1974. Later in the 1970s, Rabbitt helped to develop the crossover-influenced sound of country music prevalent in the 1980s with such hits as "Suspicions", "I Love a Rainy Night", and "Every Which Way but Loose". His duets "Both to Each Other " with Juice Newton and "You and I" with Crystal Gayle later appeared on the soap operas Days of Our Lives and All My Children.
Louis van Dijk, Dutch pianist (d. 2020) births

Louis van Dijk, also spelled Louis van Dyke, was a beloved Dutch pianist.
Bruce Lee, American-Chinese actor, martial artist, and screenwriter (d. 1973) births

Bruce Lee was a Hong Kong and American martial artist and actor. He was the founder of Jeet Kune Do, a hybrid martial arts philosophy drawing from different combat disciplines that is often credited with paving the way for modern mixed martial arts (MMA). Lee is considered by critics, media, and other martial artists to be the most influential martial artist of all time and a pop culture icon of the 20th century, who bridged the gap between East and West. He is credited with promoting Hong Kong action cinema and helping to change the way Asians were presented in American films.
Nicolae Iorga, Romanian historian and politician, 34th Prime Minister of Romania (b. 1871) deaths

Nicolae Iorga was a Romanian historian, politician, literary critic, memoirist, Albanologist, poet and playwright. Co-founder of the Democratic Nationalist Party (PND), he served as a member of Parliament, President of the Deputies' Assembly and Senate, cabinet minister and briefly (1931–32) as Prime Minister. A child prodigy, polymath and polyglot, Iorga produced an unusually large body of scholarly works, establishing his international reputation as a medievalist, Byzantinist, Latinist, Slavist, art historian and philosopher of history. Holding teaching positions at the University of Bucharest, the University of Paris and several other academic institutions, Iorga was founder of the International Congress of Byzantine Studies and the Institute of South-East European Studies (ISSEE). His activity also included the transformation of Vălenii de Munte town into a cultural and academic center.

This is a table list consisting of all the heads of government, of the modern and contemporary Romanian state, since the establishment of the United Principalities in 1859 to the present-day during the early 21st century.
Dave Giusti, American baseball player and manager births

David John Giusti, Jr. is an American former professional baseball player. He played in Major League Baseball as a right-handed pitcher from 1962 to 1977, most notably as a member of the Pittsburgh Pirates teams that won five National League Eastern Division titles in six years between 1970 and 1975 and, won the World Series in 1971.
Laurent-Désiré Kabila, Congolese politician, President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (d. 2001) births

Laurent-Désiré Kabila or simply Laurent Kabila, was a Congolese revolutionary and politician who was the third President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from 1997 until his assassination in 2001.

This is a list of presidents of the Democratic Republic of the Congo since the country's independence in 1960.
John Ashworth, English biologist and academic births

Sir John Ashworth is a scientist and educationalist.
Apolo Nsibambi, Ugandan academic and politician, Prime Minister of Uganda (d. 2019) births

Apolo Robin Nsibambi was a Ugandan academic and politician who served as the 8th Prime Minister of Uganda from 5 April 1999 until 24 May 2011, when Amama Mbabazi succeeded him.

The prime minister of Uganda chairs the Cabinet of Uganda, although the president is the effective head of government. Robinah Nabbanja has been the prime minister since 21 June 2021.
Gail Sheehy, American journalist and author (d. 2020) births

Gail Sheehy was an American author, journalist, and lecturer. She was the author of seventeen books and numerous high-profile articles for magazines such as New York and Vanity Fair. Sheehy played a part in the movement Tom Wolfe called the New Journalism, sometimes known as creative nonfiction, in which journalists and essayists experimented with adopting a variety of literary techniques such as scene setting, dialogue, status details to denote social class, and getting inside the story and sometimes reporting the thoughts of a central character.
Basil Zaharoff, Greek-French businessman and philanthropist (b. 1849) deaths

Sir Basil Zaharoff, GCB, GBE was a Greek arms dealer and industrialist. One of the richest men in the world during his lifetime, Zaharoff was described as both a "merchant of death" and a "mystery man of Europe". His success was forged through his cunning, often aggressive and sharp, business tactics. These included the sale of arms to opposing sides in conflicts, sometimes delivering fake or faulty machinery and skilfully using the press to attack business rivals.
Les Blank, American director and producer (d. 2013) births

Les Blank was an American documentary filmmaker best known for his portraits of American traditional musicians.
Daniel Charles, French musicologist and philosopher (d. 2008) births

Daniel Paul Charles was a French musician, musicologist and philosopher. He was born on 27 November 1935 in Oran (Algeria) and died on 21 August 2008 in Antibes (France).
Willie Pastrano, American boxer (d. 1997) births
Wilfred Raleigh Pastrano was an American former professional boxer who competed from 1951 to 1965. He held the undisputed WBA, WBC, and The Ring light heavyweight titles between 1963 and 1965.
Ammo Baba, Iraqi footballer and manager (d. 2009) births

Emmanuel Baba Dawud, better known as Ammo Baba, was an Iraqi Assyrian football player and coach of the Iraq national football team.
Al Jackson, Jr., American drummer, songwriter, and producer (d. 1975) births

Albert J. Jackson Jr. was an American drummer, producer, and songwriter. He was a founding member of Booker T. & the M.G.'s, a group of session musicians who worked for Stax Records and produced their own instrumentals. Jackson was affectionately dubbed "The Human Timekeeper" for his drumming ability. He was inducted into the Memphis Music Hall of Fame in 2015, and the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame as a member of Booker T. & the M.G.'s in 1992.
Gilbert Strang, American mathematician and academic births

William Gilbert Strang, usually known as simply Gilbert Strang or Gil Strang, is an American mathematician, with contributions to finite element theory, the calculus of variations, wavelet analysis and linear algebra. He has made many contributions to mathematics education, including publishing seven mathematics textbooks and one monograph. Strang is the MathWorks Professor of Mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He teaches Introduction to Linear Algebra, Computational Science and Engineering, and Matrix Methods, and his lectures are freely available through MIT OpenCourseWare.
Baby Face Nelson, American criminal (b. 1908) deaths

Lester Joseph Gillis, also known as George Nelson and Baby Face Nelson, was an American bank robber who became a criminal partner of John Dillinger, when he helped Dillinger escape from prison, in Crown Point, Indiana. Later, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) announced Nelson and the remaining gang of bank robbers were collectively "Public Enemy Number One."
Jacques Godbout, Canadian journalist, author, director, and screenwriter births

Jacques Godbout, OC, CQ is a Canadian novelist, essayist, children's writer, journalist, filmmaker and poet. By his own admission a bit of a dabbler (touche-à-tout), Godbout has become one of the most important writers of his generation, with a major influence on post-1960 Quebec intellectual life.
Gordon S. Wood, American historian and academic births

Gordon Stewart Wood is an American historian and professor at Brown University. He is a recipient of the 1993 Pulitzer Prize for History for The Radicalism of the American Revolution (1992). His book The Creation of the American Republic, 1776–1787 (1969) won a 1970 Bancroft Prize. In 2010, he was awarded the National Humanities Medal.
Benigno Aquino Jr., Filipino journalist and politician (d. 1983) births

Benigno "Ninoy" Simeon Aquino Jr., was a Filipino politician who served as a senator of the Philippines (1967–1972) and governor of the province of Tarlac. Aquino was the husband of Corazon Aquino, who became the 11th president of the Philippines after his assassination, and father of Benigno Aquino III, who became the 15th president of the Philippines. Aquino, together with Gerardo Roxas and Jovito Salonga, helped form the leadership of the opposition towards then President Ferdinand Marcos. He was the aggressive leader who together with the intellectual leader Sen. Jose W. Diokno led the overall opposition.
Lya De Putti, Slovak-American actress (b. 1899) deaths

Lya de Putti was a Hungarian film actress during the silent era. She was noted for her portrayals of vamp characters.
Joe DeNardo, American meteorologist (d. 2018) births
Joseph William DeNardo was an American meteorologist best known for his work at WTAE-TV in Pittsburgh. He was known for his 1994 campaign, "Joe Said It Would." DeNardo resided in Moon Township, Pennsylvania, with his wife of almost 60 years. When he retired in 2005, after 45 years on the air, he enjoyed "iconic" status among Pittsburghers.
Dick Poole, Australian rugby league player and coach births

Herbert Richard Poole is an Australian former rugby league footballer and coach. He was a centre for the Australian national team. He played in ten Tests and three World Cup games between 1955 and 1957, as captain on three occasions.
Rex Shelley, Singaporean engineer and author (d. 2009) births

Rex Anthony Shelley was a Singaporean author. A graduate of the University of Malaya in Malaysia and Cambridge trained in engineering and economics, Shelley managed his own business and also worked as member of the Public Service Commission (PSC) for over 30 years. For his service, he was conferred the Bintang Bakti Masyarakat by the Government of Singapore in 1978, and an additional Bar the next year.
Simon Kahquados, Potawatomi political activist (b. 1851) deaths

Simon Kahquados, born Kakanisaiga, was a leader of the Potawatomi people in Wisconsin, United States, and played a pivotal role in creating the federally recognized Forest County Potawatomi Community.
Alan Simpson, English screenwriter and producer (d. 2017) births

Alan Francis Simpson was an English scriptwriter, best known for the Galton and Simpson comedy writing partnership with Ray Galton. Together they devised and wrote the BBC sitcom Hancock's Half Hour (1954–1961), the first two series of Comedy Playhouse (1961–1963), and Steptoe and Son (1962–1974).
Alekos Alexandrakis, Greek actor and director (d. 2005) births
Alekos Alexandrakis was a famous Greek actor. He was known for his theatrical work as well as work in film and television. He died of lung cancer.
Josh Kirby, English painter and illustrator (d. 2001) births

Ronald William "Josh" Kirby was a British commercial artist. Over a career spanning 60 years, he was the artist for the covers of many science fiction books including Terry Pratchett's Discworld novels.
Carlos José Castilho, Brazilian footballer and manager (d. 1987) births

Carlos José Castilho was a Brazilian football goalkeeper. He was born in Rio de Janeiro and played for Fluminense from 1947 to 1964 and for Brazil. He was a member of the Brazil squad in four World Cups: 1950, 1954, 1958 and 1962, but he only actually played three games, all of them in the 1954 finals.
William E. Simon, American soldier and politician, 63rd United States Secretary of the Treasury (d. 2000) births

William Edward Simon was an American businessman and philanthropist who served as the 63rd United States Secretary of the Treasury. He became the Secretary of the Treasury on May 9, 1974, during the Nixon administration. After Nixon resigned, Simon was reappointed by President Gerald Ford and served until 1977 when President Jimmy Carter took office. Outside of government, he was a successful businessman and philanthropist. The William E. Simon Foundation carries on this legacy. He styled himself as a strong advocate of laissez-faire capitalism. He wrote, "There is only one social system that reflects the sovereignty of the individual: the free-market, or capitalist, system".

The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters pertaining to economic and fiscal policy. The secretary is a statutory member of the Cabinet of the United States, and is fifth in the presidential line of succession.
Chae Myung-shin, South Korean general (d. 2013) births

Chae Myung-shin was a South Korean army officer who commanded South Korean military forces in the Vietnam War. He was also the co-founder of the Korean Taekwondo Association.
John Maddox, Welsh chemist, physicist, and journalist (d. 2009) births

Sir John Royden Maddox, FRS was a Welsh theoretical chemist, turned physicist, and science writer. He was an editor of Nature for 22 years, from 1966 to 1973 and 1980 to 1995.
Marshall Thompson, American actor, director, and screenwriter (d. 1992) births

James Marshall Thompson was an American film and television actor.
Derroll Adams, American folk singer-songwriter and musician (d. 2000) births
Derroll Adams was an American folk musician.
Ernie Wise, English actor, comedian, singer, and screenwriter (d. 1999) births

Ernest Wiseman,, known by his stage name Ernie Wise, was an English comedian, best known as one half of the comedy duo Morecambe and Wise, who became a national institution on British television, especially for their Christmas specials.
J. Ernest Wilkins Jr., American nuclear scientist, mechanical engineer and mathematician (d. 2011) births

Jesse Ernest Wilkins Jr. was an African American nuclear scientist, mechanical engineer and mathematician. A child prodigy, he attended the University of Chicago at the age of 13, becoming its youngest ever student. His graduation at a young age resulted in him being hailed as "the Negro Genius" in the national media.
Hall Bartlett, American director, producer, and screenwriter (d. 1993) births
Hall Bartlett was an American film producer, director, and screenwriter.
Nicholas Magallanes, American principal dancer and charter member of the New York City Ballet (d. 1977) births

Nicholas Magallanes was a principal dancer and charter member of the New York City Ballet. Along with Francisco Moncion, Maria Tallchief, and Tanaquil Le Clercq, Magallanes was among the core group of dancers with which George Balanchine and Lincoln Kirstein formed Ballet Society, the immediate predecessor of the New York City Ballet.

New York City Ballet (NYCB) is a ballet company founded in 1948 by choreographer George Balanchine and Lincoln Kirstein. Balanchine and Jerome Robbins are considered the founding choreographers of the company. Léon Barzin was the company's first music director. City Ballet grew out of earlier troupes: the Producing Company of the School of American Ballet, 1934; the American Ballet, 1935, and Ballet Caravan, 1936, which merged into American Ballet Caravan, 1941; and directly from the Ballet Society, 1946.
Dora Dougherty Strother, American pilot and academic (d. 2013) births

Dora Jean Dougherty Strother was an American aviator best known as a Woman Airforce Service Pilots (WASP) and B-29 Superfortress demonstration pilot. She was a U.S. military pilot, human factors engineer with Bell Aircraft, instructor at the University of Illinois and helicopter test pilot for Bell Aircraft.
Alexander Dubček, Slovak soldier and politician (d. 1992) births

Alexander Dubček was a Slovak politician who served as the First Secretary of the Presidium of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia (KSČ) from January 1968 to April 1969. He attempted to reform the communist government during the Prague Spring but was forced to resign following the Warsaw Pact invasion in August 1968.
Douglas Cameron, Canadian contractor and politician, 8th Lieutenant Governor of Manitoba (b. 1854) deaths

Sir Douglas Colin Cameron was a Canadian politician. He served in the Ontario Legislature from 1902 to 1905, and was the eighth Lieutenant Governor of Manitoba from 1911 to 1916.

The lieutenant governor of Manitoba is the viceregal representative in Manitoba of the Canadian monarch, King Charles III, who operates distinctly within the province but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada, as well as the other Commonwealth realms and any subdivisions thereof, and resides predominantly in his oldest realm, the United Kingdom. The lieutenant governor of Manitoba is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties. The present, and 26th, lieutenant governor of Manitoba is Anita Neville, who has served in the role since 24 October 2022.
Mary Grant Roberts, Australian zoo owner (b. 1841) deaths
Mary Grant Roberts was an Australian zoo owner. Roberts owned Hobart Zoo from when it opened in 1895 until her death in 1921. The zoo was closed in 1937.
Abe Lenstra, Dutch footballer (d. 1985) births

Abe Minderts Lenstra was a Dutch footballer and national football icon in the 1950s who played as a forward. He is regarded as one of the greatest players ever to hail from the Netherlands. He was also a Frisian legend, most notably with the club where he made his name as a football player, Heerenveen.
Buster Merryfield, English actor (d. 1999) births

Harry "Buster" Merryfield was an English actor best known for starring as Uncle Albert in the BBC comedy Only Fools and Horses.
Cal Worthington, Automobile dealer and television personality (d. 2013) births
Calvin Coolidge Worthington was an American car dealer, best known on the West Coast of the United States, and to a more limited extent elsewhere, from minor appearances and parodies in a number of movies. He was best known for his unique radio and television advertisements for the Worthington Dealership Group, most of which began with the announcement "Here's Cal Worthington and his dog Spot!"—though "Spot" was never a dog. Often, Spot was a tiger, a seal, an elephant, a chimpanzee, or a bear. In one ad, "Spot" was a hippopotamus, which Worthington rode in the commercial. On some occasions, "Spot" was a vehicle, such as an airplane on whose wings Worthington would be seen standing while airborne. "Spot" was officially retired in the mid-1980s; however he was mentioned occasionally in later commercials.
Alexius Meinong, Ukrainian-Austrian philosopher and author (b. 1853) deaths

Alexius Meinong Ritter von Handschuchsheim was an Austrian philosopher, a realist known for his unique ontology. He also made contributions to philosophy of mind and theory of value.
Manuel Espinosa Batista, Panamanian pharmacist and politician (b. 1857) deaths

Manuel Espinosa Batista was a Colombian pharmacist turned politician who campaigned for a separate Panama state and became one of "Founders of the Republic". He is known for his philanthropy.
Stephen Elliott, American actor (d. 2005) births

Elliott Pershing Stitzel, better known by his stage name Stephen Elliott, was an American actor. His best known roles were that of the prospective father-in-law, Burt Johnson, in the hit 1981 film Arthur and as Chief Hubbard in the 1984 blockbuster Beverly Hills Cop.
Buffalo Bob Smith, American actor and television host (d. 1998) births

Robert Emil Schmidt, nicknamed Buffalo Bob, was the host of the children's show Howdy Doody.
Chick Hearn, American sportscaster and actor (d. 2002) births

Francis Dayle "Chick" Hearn was an American sportscaster who was the play-by-play announcer for the Los Angeles Lakers of the National Basketball Association for 41 years. Hearn is remembered for his rapid fire, staccato broadcasting style, associated with colorful phrases such as slam dunk, air ball, and no harm, no foul that have become common basketball vernacular. Hearn broadcast 3,338 consecutive Lakers games starting on November 21, 1965. Most of Hearn's games in the television era were simulcast on both radio and television, even after most teams chose to use different announcers for the different media.
Emile Verhaeren, Belgian poet and playwright (b. 1855) deaths

Émile Adolphe Gustave Verhaeren was a Belgian poet and art critic who wrote in the French language. He was one of the founders of the school of Symbolism and was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature on six occasions.
Connie Sawyer, American actress (d. 2018) births

Connie Sawyer was an American stage, film, and television actress, affectionately nicknamed "The Clown Princess of Comedy". She had over 140 film and television credits to her name, but was best known for her appearances in Pineapple Express, Dumb and Dumber, and When Harry Met Sally.... At the time of her death at age 105, she was the oldest working actress in Hollywood, with a career spanning an impressive 85 years, and was the oldest member of the Screen Actors Guild and the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences.
Fe del Mundo, Filipino pediatrician and educator (d. 2011) births

Fe Villanueva del Mundo,, was a Filipina pediatrician. She founded the first pediatric hospital in the Philippines and is known for shaping the modern child healthcare system in the Philippines. Her pioneering work in pediatrics in the Philippines while in active medical practice spanned eight decades. She gained international recognition, including the Ramon Magsaysay Award for Public Service in 1977. In 1980, she was conferred the rank and title of National Scientist of the Philippines, and in 2010, she was conferred the Order of Lakandula. She was the first female president of the Philippine Pediatric Society and the first woman to be named National Scientist of the Philippines in 1980. She was also the founder and the first president of the Philippine Pediatric Society, the first Asian to be elected president of the Philippine Medical Association in its 65-years existence, and the first Asian to be voted president of the Medical Woman's International Association.
David Merrick, American director and producer (d. 2000) births

David Merrick was an American theatrical producer who won a number of Tony Awards.
James Agee, American novelist, screenwriter, and critic (d. 1955) births

James Rufus Agee was an American novelist, journalist, poet, screenwriter and film critic. In the 1940s, writing for Time Magazine, he was one of the most influential film critics in the United States. His autobiographical novel, A Death in the Family (1957), won the author a posthumous 1958 Pulitzer Prize. Agee is also known as a co-writer of the book Let Us Now Praise Famous Men and as the screenwriter of the film classics The African Queen and The Night of the Hunter.
Anatoly Maltsev, Russian mathematician and theorist (d. 1967) births
Anatoly Ivanovich Maltsev was born in Misheronsky, near Moscow, and died in Novosibirsk, USSR. He was a mathematician noted for his work on the decidability of various algebraic groups. Malcev algebras, as well as Malcev Lie algebras are named after him.
Jean Albert Gaudry, French geologist and palaeontologist (b. 1827) deaths

Jean Albert Gaudry was a French geologist and palaeontologist. He was born at St Germain-en-Laye, and was educated at the Catholic Collège Stanislas de Paris. He was a notable proponent of theistic evolution.
Harivansh Rai Bachchan, Indian poet and author (d. 2003) births

Harivansh Rai Bachchan was an Indian poet and writer of the Nayi Kavita literary movement of early 20th century Hindi literature. He was also a poet of the Hindi Kavi Sammelan. He is best known for his early work Madhushala. He was also the husband of social activist, Teji Bachchan, father of Amitabh Bachchan and Ajitabh Bachchan, and grandfather of Abhishek Bachchan. In 1976, he received the Padma Bhushan for his service to Hindi literature.
L. Sprague de Camp, American historian and author (d. 2000) births

Lyon Sprague de Camp was an American writer of science fiction, fantasy and non-fiction. In a career spanning 60 years, he wrote over 100 books, including novels and works of non-fiction, including biographies of other fantasy authors. He was a major figure in science fiction in the 1930s and 1940s.
Astrid Allwyn, American actress (d. 1978) births

Astrid Allwyn was an American stage and film actress.
Lars Onsager, Norwegian-American chemist and physicist, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1976) births

Lars Onsager was a Norwegian-born American physical chemist and theoretical physicist. He held the Gibbs Professorship of Theoretical Chemistry at Yale University. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1968.

The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation, and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences on proposal of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry which consists of five members elected by the Academy. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death.
Ted Husing, American sportscaster (d. 1962) births

Edward Britt Husing was an American sportscaster. He was among the first to lay the groundwork for the structure and pace of modern sports reporting on television and radio.
Clement Studebaker, American businessman, co-founded Studebaker (b. 1831) deaths

Clement Studebaker was an American wagon and carriage manufacturer. With his brother Henry, he co-founded the H & C Studebaker Company, precursor of the Studebaker Corporation, which built Pennsylvania-German Conestoga wagons and carriages during his lifetime, and automobiles after his death, in South Bend, Indiana.

Studebaker was an American wagon and automobile manufacturer based in South Bend, Indiana, with a building at 1600 Broadway, Times Square, Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 1852 and incorporated in 1868 as the Studebaker Brothers Manufacturing Company, the firm was originally a coachbuilder, manufacturing wagons, buggies, carriages and harnesses.
Jovette Bernier, Canadian journalist, author, and radio show host (d. 1981) births

Marie-Angèle "Jovette" Alice Bernier was a journalist and writer in Quebec. Because of extensive exposure in the print media and on radio, she was often referred to simply as Jovette.
Constant Fornerod, Swiss academic and politician, 10th President of the Swiss Council of States (b. 1819) deaths

Constant Fornerod was a Swiss politician, originally from Avenches, and member of the Swiss Federal Council (1855-1867).
This is a list of presidents of the Swiss Council of States, the upper house of the Federal Assembly.
Fredric Warburg, English author and publisher (d. 1981) births

Fredric John Warburg was a British publisher best known for his association with the author George Orwell. During a career spanning a large part of the 20th century and ending in 1971, Warburg published Orwell's major books Animal Farm (1945) and Nineteen Eighty-Four (1949), as well as works by other leading figures such as Thomas Mann and Franz Kafka. Other notable publications included The Third Eye by Lobsang Rampa, Pierre Boulle's The Bridge over the River Kwai, Adolf Hitler's Mein Kampf and William Shirer's The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich.
Alexandre Dumas, fils, French novelist and playwright (b. 1824) deaths

Alexandre Dumas fils was a French author and playwright, best known for the romantic novel La Dame aux Camélias, published in 1848, which was adapted into Giuseppe Verdi's 1853 opera La traviata, as well as numerous stage and film productions, usually titled Camille in English-language versions.
Konosuke Matsushita, Japanese businessman, founded Panasonic (d. 1989) births

Kōnosuke Matsushita was a Japanese industrialist who founded Panasonic, the largest Japanese consumer electronics company. Matsushita is referred to as the "God of Management" in Japan.

Panasonic Holdings Corporation, formerly Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. between 1935 and 2008 and the first incarnation of Panasonic Corporation between 2008 and 2022, is a major Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka. It was founded by Kōnosuke Matsushita in 1918 as a lightbulb socket manufacturer. In addition to consumer electronics, of which it was the world's largest maker in the late 20th century, Panasonic offers a wide range of products and services, including rechargeable batteries, automotive and avionic systems, industrial systems, as well as home renovation and construction.
Katherine Milhous, American author and illustrator (d. 1977) births

Katherine Milhous (1894–1977) was an American artist, illustrator, and writer. She is known best as the author and illustrator of The Egg Tree, which won the 1951 Caldecott Medal for U.S. picture book illustration. Born into a Quaker family active in the printing industry in Philadelphia, Milhous is also known for her graphic designs for the Works Progress Administration (WPA). Her work has been exhibited at the 1939 New York World's Fair and at the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts.
Amphilochius of Pochayiv, Ukrainian monk and saint (d. 1971) births

Amphilochius of Pochayiv was a 20th-century Ukrainian Orthodox saint, from Ternopil Oblast of western Ukraine.
Mahatma Phule, Indian Activist (b. 1827) deaths

Jyotirao Govindrao Phule, also known as Mahatma Jyotiba Phule was an Indian social activist, thinker, anti-caste social reformer and writer from Maharashtra. His work extended to many fields, including eradication of untouchability and the caste system and for his efforts in educating women and oppressed caste people. He and his wife, Savitribai Phule, were pioneers of women's education in India. Phule started his first school for girls in 1848 in Pune at Tatyasaheb Bhide's residence or Bhidewada. He, along with his followers, formed the Satyashodhak Samaj to attain equal rights for people from lower castes. People from all religions and castes could become a part of this association which worked for the upliftment of the oppressed classes. Phule is regarded as an important figure in the social reform movement in Maharashtra. He was bestowed with honorific Mahātmā title by Maharashtrian social activist Vithalrao Krishnaji Vandekar in 1888.
Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar, Indian activist and politician, 1st Speaker of the Lok Sabha (d. 1956) births

Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar popularly known as Dadasaheb was an independence activist, the President of the Central Legislative Assembly, then Speaker of the Constituent Assembly of India, and later the first Speaker of the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India. His son Purushottam Mavalankar was later elected to the Lok Sabha twice from Gujarat.

The speaker of the Lok Sabha is the presiding officer and the highest authority of the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India. The speaker is elected generally in the first meeting of the Lok Sabha following general elections. Serving for a term of five years, the speaker chosen from sitting members of the Lok Sabha.
Masaharu Homma, Japanese general (d. 1946) births

Masaharu Homma was a lieutenant general in the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. Homma commanded the Japanese 14th Army, which invaded the Philippines and perpetrated the Bataan Death March. After the war, Homma was convicted of war crimes relating to the actions of troops under his direct command and executed by firing squad on April 3, 1946.
Tsuguharu Foujita, Japanese–French painter and printmaker (d. 1968) births

Léonard Tsuguharu Foujita was a Japanese–French painter and printmaker born in Tokyo, Japan, who applied Japanese ink techniques to Western style paintings. At the height of his fame in Paris, during the 1920s, he was known for his portraits of nudes using an opalescent white ink with fine black outlines and his pictures of cats. He returned to Japan in 1933, and served as a war artist for the Imperial Japan during World War II. After the war, Foujita returned to France, where he became a French citizen and converted to Christianity. He was buried in The Chapel of our Lady of Peace, which he had helped build and is painted with his frescoes. Since his death, Foujita's work has become increasingly appreciated in Japan.
Daniel Mendaille, French actor (d. 1963) births
Daniel Mendaille was a French stage and film actor whose career spanned nearly sixty years.
Liviu Rebreanu, Romanian author and playwright (d. 1944) births

Liviu Rebreanu was a Romanian novelist, playwright, short story writer, and journalist.
Fanny Elssler, Austrian ballerina (b. 1810) deaths

Fanny Elssler was an Austrian ballerina of the Romantic Period.
Theobald Boehm, German flute player and composer (b. 1794) deaths

Theobald Böhm was a German inventor and musician, who perfected the modern Western concert flute and improved its fingering system. He was a Bavarian court musician, a virtuoso flautist and a renowned composer.
Jatindramohan Bagchi, Indian poet and critic (d. 1948) births

Jatindramohan Bagchi was a Bengali poet and editor.
Charles Dvorak, American pole vaulter and coach (d. 1969) births

Charles Edward Dvorak was an American track and field athlete who specialized in the pole vault. He attended the University of Michigan where he competed for the Michigan Wolverines men's track and field team from 1900 to 1904. He participated in the 1900 Summer Olympics where he was a favorite in the pole vault. However, he missed the competition after being told by officials that the finals would not be held on a Sunday. He won a special silver medal in a consolation competition. In 1903, he set a world's record in the pole vault with a jump of 11 feet, 11 inches.(This mark doesn't appear in the progression of World or American Records). Dvorak returned to international competition and won the gold medal in the pole vault at the 1904 Summer Olympics. Dvorak later served as a high school football, basketball and track coach in Seattle, Washington, where he died in 1969 at age 91.
Katharine Anthony, American biographer (d. 1965) births

Katharine Susan Anthony, sometimes also spelled Katherine, was a US biographer best known for The Lambs (1945), a controversial study of the British writers Charles and Mary Lamb.
Julius Lenhart, Austrian gymnast (d. 1962) births
Julius Lenhart was an Austrian gymnast who competed in the 1904 Summer Olympics. He won two gold medals and one silver medal, making him the most successful Austrian competitor ever at the Summer Olympic Games.
Richard Christopher Carrington, English astronomer and educator (b. 1826) deaths
Richard Christopher Carrington was an English amateur astronomer whose 1859 astronomical observations demonstrated the existence of solar flares as well as suggesting their electrical influence upon the Earth and its aurorae; and whose 1863 records of sunspot observations revealed the differential rotation of the Sun.
Charles A. Beard, American historian, author, and educator, co-founded The New School (d. 1948) births

Charles Austin Beard (1874–1948) was an American historian and professor, who wrote primarily during the first half of the 20th century. A history professor at Columbia University, Beard's influence is primarily due to his publications in the fields of history and political science. His works included a radical re-evaluation of the Founding Fathers of the United States, whom he believed to be more motivated by economics than by philosophical principles. Beard's most influential book, An Economic Interpretation of the Constitution of the United States (1913), has been the subject of great controversy ever since its publication. While it has been frequently criticized for its methodology and conclusions, it was responsible for a wide-ranging reinterpretation of early American history.

The New School is a private research university in New York City. It was founded in 1919 as The New School for Social Research with an original mission dedicated to academic freedom and intellectual inquiry and a home for progressive thinkers. Since then, the school has grown to house five divisions within the university. These include the Parsons School of Design, the Eugene Lang College of Liberal Arts, the College of Performing Arts, The New School for Social Research, and the Schools of Public Engagement.
Chaim Weizmann, Belarusian-Israeli chemist and politician, 1st President of Israel (d. 1952) births

Chaim Azriel Weizmann was a Russian-born biochemist, Zionist leader and Israeli statesman who served as president of the Zionist Organization and later as the first president of Israel. He was elected on 16 February 1949, and served until his death in 1952. Weizmann was fundamental in obtaining the Balfour Declaration and later convincing the United States government to recognize the newly formed State of Israel.

The president of the State of Israel is the head of state of Israel. The position is largely a ceremonial role, with executive power vested in the cabinet led by the prime minister. The incumbent president is Isaac Herzog, who took office on 7 July 2021. Presidents are elected by the Knesset for a single seven-year term.
Giovanni Giorgi, Italian physicist and engineer (d. 1950) births

Giovanni Giorgi was an Italian physicist and electrical engineer who proposed the Giorgi system of measurement, the precursor to the International System of Units (SI).
Juho Kusti Paasikivi, Finnish academic and politician, 7th President of Finland (d. 1956) births

Juho Kusti Paasikivi was the seventh president of Finland (1946–1956). Representing the Finnish Party until its dissolution in 1918 and then the National Coalition Party, he also served as Prime Minister of Finland. In addition to the above, Paasikivi held several other positions of trust, and was an influential figure in Finnish economics and politics for over fifty years.

The president of the Republic of Finland is the head of state of Finland. Under the Constitution of Finland, executive power is vested in the Finnish Government and the president, with the latter possessing only residual powers. The president is directly elected by universal suffrage for a term of six years. Since 1994, no president may be elected for more than two consecutive terms. The president must be a natural-born Finnish citizen. The presidential office was established in the Constitution Act of 1919. The incumbent president is Sauli Niinistö. He was elected for the first time in 2012 and was re-elected in 2018.
Charles Koechlin, French composer and educator (d. 1950) births

Charles-Louis-Eugène Koechlin, commonly known as Charles Koechlin, was a French composer, teacher and musicologist. He was a political radical all his life and a passionate enthusiast for such diverse things as medieval music, The Jungle Book of Rudyard Kipling, Johann Sebastian Bach, film stars, traveling, stereoscopic photography and socialism. He once said: "The artist needs an ivory tower, not as an escape from the world, but as a place where he can view the world and be himself. This tower is for the artist like a lighthouse shining out across the world." Among his better known works is Les Heures persanes, a set of piano pieces based on the novel Vers Ispahan by Pierre Loti and The Seven Stars Symphony, a 7 movement symphony where each movement is themed around a different film star who were popular at the time of the piece's writing (1933).
Janez Evangelist Krek, Slovene priest, journalist, and politician (d. 1917) births

Janez Evangelist Krek was a Slovene Christian Socialist politician, priest, journalist, and author.
William Bliss Baker, American painter (d. 1886) births

William Bliss Baker was an American artist who began painting just as the Hudson River School was winding down. Baker began his studies in 1876 at the National Academy of Design, where he studied with Bierstadt and de Haas. He later maintained studios in Clifton Park, New York and New York City, where he painted in oils and watercolors. He completed more than 130 paintings, including several in black and white.
Charles Scott Sherrington, English physiologist, bacteriologist, and pathologist, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1952) births

Sir Charles Scott Sherrington was an eminent English neurophysiologist. His experimental research established many aspects of contemporary neuroscience, including the concept of the spinal reflex as a system involving connected neurons, and the ways in which signal transmission between neurons can be potentiated or depotentiated. Sherrington himself coined the word "synapse" to define the connection between two neurons. His book The Integrative Action of the Nervous System (1906) is a synthesis of this work, in recognition of which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1932.

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
Frank Dicksee, English painter and illustrator (d. 1928) births

Sir Francis Bernard Dicksee was an English Victorian painter and illustrator, best known for his pictures of dramatic literary, historical, and legendary scenes. He also was a noted painter of portraits of fashionable women, which helped to bring him success in his own time.
Ada Lovelace, English mathematician and computer scientist (b. 1815) deaths

Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognise that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
Frederic Crowninshield, American artist and author (d. 1918) births

Frederic Crowninshield (1845–1918) was an American artist and author.
Cornelius Vanderbilt II, American businessman (d. 1899) births

Cornelius "Corneil" Vanderbilt II was an American socialite and a member of the prominent United States Vanderbilt family.
Princess Mary Adelaide of Cambridge (d. 1897) births

Princess Mary Adelaide Wilhelmina Elizabeth of Cambridge, later Duchess of Teck, was a member of the British royal family. She was one of the first royals to patronise a wide range of charities.
André Parmentier, Belgian-American architect (b. 1780) deaths
André Joseph Ghislain Parmentier, also known as Andrew Parmentier is one of a generation of American landscape designers who arrived from Europe in the early years after Independence. Many of these designers, including William Russell Birch and George Isham Parkyns, also practiced landscape depiction, reinforcing the picturesque connection of landscape art as both making and representing places.
James Service, Scottish-Australian politician, 12th Premier of Victoria (d. 1899) births

James Service, Australian colonial politician, was the 12th Premier of Victoria, Australia.

The premier of Victoria is the head of government in the Australian state of Victoria. The premier is appointed by the governor of Victoria, and is the leader of the political party able to secure a majority in the Victorian Legislative Assembly.
Rachel Brooks Gleason, fourth woman to earn a medical degree in the United States (d. 1905) births

Rachel Brooks Gleason was an American physician, the fourth woman to earn a medical degree in the United States.
Gustavus Conyngham, Irish-born American merchant sea captain, an officer in the Continental Navy and a privateer. deaths

Gustavus Conyngham was an Irish-born American merchant sea captain, an officer in the Continental Navy and a privateer. As a commissioned captain fighting the British in the American Revolutionary War, he captured 24 ships in the eastern Atlantic between May 1777 and May 1778, bringing the expenses associated with British shipping to a then all-time high. He has been called "the most successful of all Continental Navy captains".
The Continental Navy was the navy of the United States during the American Revolutionary War and was founded October 13, 1775. The fleet cumulatively became relatively substantial through the efforts of the Continental Navy's patron John Adams and vigorous Congressional support in the face of stiff opposition, when considering the limitations imposed upon the Patriot supply pool.

A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission.
Charles-François-Frédéric, marquis de Montholon-Sémonville, French politician and diplomat, French ambassador to the United States (d. 1886) births

Charles François Frédéric de Montholon-Sémonville was a French senator, diplomat, and French ambassador to the United States from 1864 to 1866.
The French ambassador to the United States is the diplomatic representation of the French Republic to the United States. They reside in Washington, D.C. The current ambassador is Philippe Étienne.
Andrew Meikle, Scottish engineer, designed the threshing machine (b. 1719) deaths

Andrew Meikle was a Scottish mechanical engineer credited with inventing the threshing machine, a device used to remove the outer husks from grains of wheat. He also had a hand in assisting Firbeck in the invention of the Rotherham Plough. This was regarded as one of the key developments of the British Agricultural Revolution in the late 18th century. The invention was made around 1786, although some say he only improved on an earlier design by a Scottish farmer named Leckie. Michael Stirling is said to have invented a rotary threshing machine in 1758 which for forty years was used to process all the corn on his farm at Gateside, no published works have yet been found but his son William made a sworn statement to his minister to this fact, he also gave him the details of his father's death in 1796.

A threshing machine or a thresher is a piece of farm equipment that threshes grain, that is, it removes the seeds from the stalks and husks. It does so by beating the plant to make the seeds fall out.
Fanny Kemble, English actress, playwright, and poet (d. 1893) births

Frances Anne "Fanny" Kemble was a British actress from a theatre family in the early and mid-19th century. She was a well-known and popular writer and abolitionist, whose published works included plays, poetry, eleven volumes of memoirs, travel writing and works about the theatre.
Julius Benedict, German-English conductor and composer (d. 1885) births

Sir Julius Benedict was a German-born composer and conductor, resident in England for most of his career.
Aimé, duc de Clermont-Tonnerre, French general and politician, French Minister of Defence (d. 1865) births
Aimé-Marie-Gaspard, comte de Clermont-Tonnerre was a French general and statesman.

The Minister of the Armed Forces is the leader and most senior official of the French Ministry of the Armed Forces, tasked with running the French Armed Forces. The minister is the third highest civilian having authority over France's military, behind only the President of the Republic and the Prime Minister. Based on the governments, they may be assisted by a minister or state secretary for veterans' affairs.
Franz Krommer, Czech violinist and composer (d. 1831) births

Franz Krommer was a Czech composer of classical music and violinist. He was one of the most popular composers in the 19th century Vienna. Today he is mostly known for his clarinet concertos.
Georg Forster, German-Polish ethnologist and journalist (d. 1794) births

Johann George Adam Forster, also known as Georg Forster, was a German naturalist, ethnologist, travel writer, journalist and revolutionary. At an early age, he accompanied his father, Johann Reinhold Forster, on several scientific expeditions, including James Cook's second voyage to the Pacific. His report of that journey, A Voyage Round the World, contributed significantly to the ethnology of the people of Polynesia and remains a respected work. As a result of the report, Forster, who was admitted to the Royal Society at the early age of twenty-two, came to be considered one of the founders of modern scientific travel literature.
Abraham de Moivre, French-English mathematician and theorist (b. 1667) deaths

Abraham de Moivre FRS was a French mathematician known for de Moivre's formula, a formula that links complex numbers and trigonometry, and for his work on the normal distribution and probability theory.
Robert R. Livingston, American lawyer and politician, 1st United States Secretary for Foreign Affairs (d. 1813) births

Robert Robert Livingston was an American lawyer, politician, and diplomat from New York, as well as a Founding Father of the United States. He was known as "The Chancellor", after the high New York state legal office he held for 25 years. He was a member of the Committee of Five that drafted the Declaration of Independence, along with Thomas Jefferson, Benjamin Franklin, John Adams, and Roger Sherman. Livingston administered the oath of office to George Washington when he assumed the presidency April 30, 1789. Livingston was also elected as a member of the American Philosophical Society in 1801.

This is a list of secretaries of state of the United States.
Increase Sumner, American lawyer, jurist, and politician, 5th Governor of Massachusetts (d. 1799) births

Increase Sumner was an American lawyer, jurist, and politician from Massachusetts. He was the fifth governor of Massachusetts, serving from 1797 to 1799. Trained as a lawyer, he served in the provisional government of Massachusetts during the American Revolutionary War, and was elected to the Confederation Congress in 1782. Appointed to the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court the same year, he served there as an associate justice until 1797.

The governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the chief executive officer of the government of Massachusetts. The governor is the head of the state cabinet and the commander-in-chief of the commonwealth's military forces.
Robert Lowth, English bishop and academic (d. 1787) births

Robert Lowth was a Bishop of the Church of England, Oxford Professor of Poetry and the author of one of the most influential textbooks of English grammar.
Henry Winstanley, English painter and engineer (b. 1644) deaths

Henry Winstanley was an English painter, engineer and merchant, who constructed the first Eddystone lighthouse after losing two of his ships on the Eddystone rocks. He died while working on the project during the Great Storm of 1703.
Anders Celsius, Swedish astronomer, physicist, and mathematician (d. 1744) births

Anders Celsius was a Swedish astronomer, physicist and mathematician. He was professor of astronomy at Uppsala University from 1730 to 1744, but traveled from 1732 to 1735 visiting notable observatories in Germany, Italy and France. He founded the Uppsala Astronomical Observatory in 1741, and in 1742 proposed the Centigrade temperature scale which was later renamed Celsius in his honour.
Barbara Palmer, 1st Duchess of Cleveland (d. 1709) births

Barbara Palmer, 1st Duchess of Cleveland, Countess of Castlemaine, was an English royal mistress of the Villiers family and perhaps the most notorious of the many mistresses of King Charles II of England, by whom she had five children, all of them acknowledged and subsequently ennobled. Barbara was the subject of many portraits, in particular by court painter Sir Peter Lely.
Françoise d'Aubigné, Marquise de Maintenon, second wife of Louis XIV of France (d. 1719) births

Françoise d'Aubigné, known first as Madame Scarron and subsequently as Madame de Maintenon, was a French noblewoman who secretly married King Louis XIV. Although she was never considered queen of France, she was one of the King's closest advisers and the royal children's governess. In 1686, she founded the Maison royale de Saint-Louis, a school for girls from poorer noble families.

Louis XIV, also known as Louis the Great or the Sun King, was King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign in history whose date is verifiable. Although Louis XIV's France was emblematic of the age of absolutism in Europe, the King surrounded himself with a variety of significant political, military, and cultural figures, such as Bossuet, Colbert, Le Brun, Le Nôtre, Lully, Mazarin, Molière, Racine, Turenne, and Vauban.
John Eliot, English politician (b. 1592) deaths

Sir John Eliot was an English statesman who was serially imprisoned in the Tower of London, where he eventually died, by King Charles I for advocating the rights and privileges of Parliament.
Sigismund Francis, Archduke of Austria (d. 1665) births

Sigismund Francis, Archduke of Further Austria was the ruler of Further Austria including Tyrol from 1662 to 1665.
Francis, Duke of Pomerania-Stettin, Bishop of Cammin (b. 1577) deaths

Francis of Pomerania was Duke of Pomerania-Stettin and Bishop of Cammin.
Nakagawa Hidemasa, Japanese commander (b. 1568) deaths
Nakagawa Hidemasa was a samurai commander in the Azuchi–Momoyama period. He was the eldest son of Nakagawa Kiyohide. His young brother was Nakagawa Hidenari. His wife was Tsuruhime who was the daughter of Oda Nobunaga.
Pierre Dupuy, French historian and scholar (d. 1651) births

Pierre Dupuy, otherwise known as Puteanus, was a French scholar, the son of the humanist and bibliophile Claude Dupuy.
Shimazu Tadatsune, Japanese daimyō (d. 1638) births

Shimazu Tadatsune was a tozama daimyō of Satsuma, the first to hold it as a formal fief (han) under the Tokugawa shogunate, and the first Japanese to rule over the Ryūkyū Kingdom. As lord of Satsuma, he was among the most powerful lords in Japan at the time, and formally submitted to Tokugawa Ieyasu in 1602, to prove his loyalty, being rewarded as a result with the name Matsudaira Iehisa; Matsudaira being a branch family of the Tokugawa, and "Ie" of "Iehisa" being taken from "Ieyasu", this was a great honor. As of 1603, his holdings amounted to 605,000 koku.
Jacopo Sansovino, Italian sculptor and architect (b. 1486) deaths

Jacopo d'Antonio Sansovino was an Italian Renaissance sculptor and architect, best known for his works around the Piazza San Marco in Venice. These are crucial works in the history of Venetian Renaissance architecture. Andrea Palladio, in the Preface to his Quattro Libri was of the opinion that Sansovino's Biblioteca Marciana was the best building erected since Antiquity. Giorgio Vasari uniquely printed his Vita of Sansovino separately.
Mingyi Swa, Crown Prince of Burma (d. 1593) births
Mingyi Swa was heir apparent of Burma from 1581 to 1593. The eldest son of King Nanda of the Toungoo Dynasty led three out of the five Burmese invasions of Siam between 1584 and 1593, all of which ended in complete failure. He died in action during the fifth invasion in 1593. In prevailing Thai history, he was killed in single combat by King Naresuan. However no other accounts, including the earliest Siamese records and European accounts, mention a formal duel between the two. The Burmese chronicles say Swa was felled by a Siamese mortar round.
Jacopo Mazzoni, Italian philosopher (d. 1598) births

Jacopo Mazzoni was an Italian philosopher, a professor in Pisa, and friend of Galileo Galilei. His first name is sometimes reported as "Giacomo".
Guillaume Du Fay, French composer and music theorist (b. 1397) deaths

Guillaume Du Fay was a French composer and music theorist of the early Renaissance. Considered the leading European composer of his time, his music was widely performed and reproduced. Du Fay was well-associated with composers of the Burgundian School, particularly his colleague Gilles Binchois, but was never a regular member of the Burgundian chapel himself.
Gaston IV, Count of Foix, French nobleman (d. 1472) births

Gaston IV was the sovereign Viscount of Béarn and the Count of Foix and Bigorre in France from 1436 to 1472. He also held the viscounties of Marsan, Castelbon, Nébouzan, Villemeur and Lautrec and was, by virtue of the county of Foix, co-prince of Andorra. From 1447 he was also Viscount of Narbonne. Through his marriage to Eleonor, heiress of the Kingdom of Navarre, he also held the title of Prince of Navarre.
Philip van Artevelde, Flemish patriot (b. 1340) deaths

Philip van Artevelde was a Flemish patriot, the son of Jacob van Artevelde. Because of his father's prominence he was godson of English queen Philippa of Hainault, who held him in her arms during his baptism.
King Ferdinand I of Aragon (d. 1416) births

Ferdinand I named Ferdinand of Antequera and also the Just was king of Aragon, Valencia, Majorca, Sardinia and (nominal) Corsica and king of Sicily, duke (nominal) of Athens and Neopatria, and count of Barcelona, Roussillon and Cerdanya (1412–1416). He was also regent of Castile (1406–1416).
Saint Gregory of Sinai (b. c. 1260) deaths
Gregory of Sinai, or in Serbian and Bulgarian Grigorije Sinaita, was a Greek Christian monk and writer from Smyrna. He was instrumental in the emergence of hesychasm on Mount Athos in the early 14th century.
Blanche of Castile (b. 1188) deaths

Blanche of Castile was Queen of France by marriage to Louis VIII. She acted as regent twice during the reign of her son, Louis IX: during his minority from 1226 until 1234, and during his absence from 1248 until 1252. She was born in Palencia, Spain, in 1188, the third daughter of Alfonso VIII, King of Castile, and Eleanor of England, sister of King Richard I of England and King John of England.
Constance, Queen of Sicily (b. 1154) deaths

Constance I was reigning Queen of Sicily from 1194–98, jointly with her spouse from 1194 to 1197, and with her infant son Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, in 1198, as the heiress of the Norman kings of Sicily. She was also Holy Roman Empress and later Dowager by marriage to Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor.
Emperor Xiaozong of Song (d. 1194) births

Emperor Xiaozong of Song, personal name Zhao Shen, courtesy name Yuanyong, was the 11th emperor of the Song dynasty of China and the second emperor of the Southern Song dynasty. He started his reign in 1162 when his adoptive father and predecessor, Emperor Gaozong, abdicated and passed the throne to him. Even though Emperor Gaozong became a Taishang Huang after his abdication, he remained the de facto ruler, so Emperor Xiaozong only took full power in 1187 after Emperor Gaozong's death. After ruling for about a year, Emperor Xiaozong followed in his predecessor's footsteps and abdicated in favour of his third son Zhao Dun, while he became Taishang Huang and still remained in power until his death in 1194.
Acarius, bishop of Doornik and Noyon deaths
Saint Acarius was a monk of Luxeuil Abbey, who became bishop of Doornik and Noyon, which today are located on either side of the Franco-Belgian border.

The Diocese of Tournai is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Belgium. The diocese was formed in 1146, upon the dissolution of the Diocese of Noyon & Tournai, which had existed since the 7th Century. It is now suffragan in the ecclesiastical province of the metropolitan Archdiocese of Mechelen-Brussels. The cathedra is found within the Cathedral of Notre-Dame de Tournai, which has been classified both as a major site for Wallonia's heritage since 1936 and as a World Heritage Site since 2000.
Maurice, Byzantine emperor (b. 539) deaths

Maurice was Eastern Roman emperor from 582 to 602 and the last member of the Justinian dynasty. A successful general, Maurice was chosen as heir and son-in-law by his predecessor Tiberius II.
Clovis I, king of the Franks deaths

Clovis was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single king and ensuring that the kingship was passed down to his heirs. He is considered to have been the founder of the Merovingian dynasty, which ruled the Frankish kingdom for the next two centuries.

The Franks were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire. Later the term was associated with Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire.
Galla Placidia, Roman Empress (b. 392) deaths

Galla Placidia, daughter of the Roman emperor Theodosius I, was a mother, tutor, and advisor to emperor Valentinian III, and a major force in Roman politics for most of her life. She was queen consort to Ataulf, king of the Visigoths from 414 until his death in 415, briefly empress consort to Constantius III in 421, and managed the government administration as a regent during the early reign of Valentinian III, until her death.

This is a list of Roman and Byzantine empresses. A Roman empress was a woman who was the wife of a Roman emperor, the ruler of the Roman Empire.
Rufinus, Roman politician (b. 335) deaths
Flavius Rufinus was a 4th-century East Roman statesman of Aquitanian extraction who served as Praetorian prefect of the East for the emperor Theodosius I, as well as for his son Arcadius, under whom Rufinus exercised significant influence in the state affairs.
Antinous, Greek favourite of Hadrian (d. 130) births
Year 111 (CXI) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Piso and Bolanus. The denomination 111 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Antinous, also called Antinoös, was a Greek youth from Bithynia and a favourite and probable lover of the Roman emperor Hadrian. Following his premature death before his twentieth birthday, Antinous was deified on Hadrian's orders, being worshipped in both the Greek East and Latin West, sometimes as a god and sometimes merely as a hero.

Hadrian was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica, a Roman municipium founded by Italic settlers in Hispania Baetica and he came from a branch of the gens Aelia that originated in the Picenean town of Hadria, the Aeli Hadriani. His father was of senatorial rank and was a first cousin of Emperor Trajan. Hadrian married Trajan's grand-niece Vibia Sabina early in his career before Trajan became emperor and possibly at the behest of Trajan's wife Pompeia Plotina. Plotina and Trajan's close friend and adviser Lucius Licinius Sura were well disposed towards Hadrian. When Trajan died, his widow claimed that he had nominated Hadrian as emperor immediately before his death.
Horace, Roman soldier and poet (b. 65 BC) deaths

Quintus Horatius Flaccus, known in the English-speaking world as Horace, was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus. The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his Odes as just about the only Latin lyrics worth reading: "He can be lofty sometimes, yet he is also full of charm and grace, versatile in his figures, and felicitously daring in his choice of words."
Christian feast day: Acarius of Tournai
Saint Acarius was a monk of Luxeuil Abbey, who became bishop of Doornik and Noyon, which today are located on either side of the Franco-Belgian border.
Christian feast day: Barlaam and Josaphat

Barlaam and Josaphat, also known as Bilawhar and Budhasaf, are legendary Christian saints. Their life story was based on the life of the Gautama Buddha, and tells of the conversion of Josaphat to Christianity. According to the legend, an Indian king persecuted the Christian Church in his realm. After astrologers predicted that his own son would some day become a Christian, the king imprisoned the young prince Josaphat, who nevertheless met the hermit Saint Barlaam and converted to Christianity. After much tribulation the young prince's father accepted the Christian faith, turned over his throne to Josaphat, and retired to the desert to become a hermit. Josaphat himself later abdicated and went into seclusion with his old teacher Barlaam.
Christian feast day: Bilihildis

Bilihildis was a Frankish noblewoman, remembered as the founder and abbess of the monastery of Altmünster near Mainz, and venerated locally as a saint, on Nov. 27.
Christian feast day: Congar of Congresbury

Saint Congar, was a Welsh abbot and supposed bishop in Somerset, then in the British kingdom of Somerset, now in England.
Christian feast day: Facundus and Primitivus

Saints Facundus and Primitivus are venerated as Christian martyrs. According to tradition, they were Christian natives of León who were tortured and then beheaded on the banks of the River Cea. According to an account of their martyrdom, after the two saints were beheaded, lac et sanguis gushed from their necks.
Christian feast day: Humilis of Bisignano
Humilis of Bisignano was a Franciscan friar who was widely known in his day as a mystic and wonderworker. He has been declared a saint by the Catholic Church.
Christian feast day: James Intercisus

Saint James Intercisus, also called James the Mutilated or James the Persian, was a Syriac Christian saint born in Beth Huzaye in Persia. His epithet, Intercisus, is derived from the Latin word for "cut into pieces," which refers to the manner of his martyrdom: he was slowly cut into twenty-eight pieces. His death, along with the persecution of other Christians in the Sasanid Empire, started the Roman-Sassanid War (421-422).
Christian feast day: Leonard of Port Maurice

Leonard of Port Maurice, O.F.M., was an Italian Franciscan preacher and ascetic writer.
Christian feast day: Our Lady of the Miraculous Medal (Roman Catholic)

The Miraculous Medal, also known as the Medal of Our Lady of Graces, is a devotional medal, the design of which was originated by Catherine Labouré following her apparitions of the Blessed Virgin Mary in the Chapel of Our Lady of the Miraculous Medal of Paris, France. It was made by goldsmith Adrien Vachette.

The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2019. As the world's oldest and largest continuously functioning international institution, it has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. The church consists of 24 sui iuris churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state.
Christian feast day: Secundinus

Secundinus, or Sechnall as he was known in Irish, was founder and patron saint of Domhnach Sechnaill, Co. Meath, who went down in medieval tradition as a disciple of St Patrick and one of the first bishops of Armagh. Historians have suggested, however, that the connection with St Patrick was a later tradition invented by Armagh historians in favour of their patron saint and that Secundinus is more likely to have been a separate missionary, possibly a companion of Palladius.
Christian feast day: Siffredus of Carpentras

Saint Siffredus of Carpentras was a bishop of Carpentras who is venerated as a saint by the Catholic Church.
Christian feast day: Vergilius of Salzburg

Virgil, also spelled Vergil, Vergilius, Virgilius, Feirgil or Fearghal, was an Irish churchman and early astronomer. He left Ireland around 745, intending to visit the Holy Land; but, like many of his countrymen, he settled in Francia. Virgil served as abbot of Aghaboe, bishop of Ossory and later bishop of Salzburg. He was called "the Apostle of Carinthia" and "the geometer".
Christian feast day: Clovis I

Clovis was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single king and ensuring that the kingship was passed down to his heirs. He is considered to have been the founder of the Merovingian dynasty, which ruled the Frankish kingdom for the next two centuries.
Christian feast day: November 27 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)

November 26 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar - November 28
Lancashire Day (United Kingdom)

Lancashire Day is the county day of historic Lancashire in England. It is held on 27 November to commemorate the day in 1295 when Lancashire first sent representatives to Parliament, to attend the Model Parliament of King Edward I. Lancashire Day was first held in 1996.

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is 242,495 square kilometres (93,628 sq mi), with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people.
Maaveerar Day (Tamil Eelam, Sri Lanka)

Maaveerar Naal is a remembrance day observed by Sri Lankan Tamils to remember the deaths of militants who fought for the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). It is held each year on 27 November, the date on which the first LTTE cadre, Lt. Shankar, died in combat in 1982. Traditionally oil lamps are lit for the three days ending on 27 November and the Tamil Eelam flag is raised at ceremonies. The symbol for Maaveerar Naal is the Gloriosa superba which blooms during November.

Tamil Eelam is a proposed independent state that many Tamils in Sri Lanka and the Sri Lankan Tamil diaspora aspire to create in the north and east of Sri Lanka. The name is derived from the ancient Tamil name for Sri Lanka, Eelam. Tamil Eelam, although encompassing the traditional homelands of Sri Lankan Tamils, does not have official status or recognition by world states. Large sections of the North-East were under de facto control of the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) for most of the 1990s–2000s during the Sri Lankan Civil War.

Sri Lanka, formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, and southeast of the Arabian Sea; it is separated from the Indian subcontinent by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait. Sri Lanka shares a maritime border with India and the Maldives. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is its legislative capital, and Colombo is its largest city and financial centre.
Naval Infantry Day (Russia)

The following is the list of official public holidays recognized by the Government of Russia. On these days, government offices, embassies and some shops, are closed. If the date of observance falls on a weekend, the following Monday will be a day off in lieu of the holiday.

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering 17,098,246 square kilometres (6,601,670 sq mi), and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan.
Teacher's Day (Spain)
Teachers' Day is a special day for the appreciation of teachers, and may include celebrations to honor them for their special contributions in a particular field area, or the community tone in education. This is the primary reason why countries celebrate this day on different dates, unlike many other International Days. For example, Argentina has commemorated Domingo Faustino Sarmiento's death on 11 September as Teachers' Day since 1915. In India the birthday of the second president Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, 5 September, is celebrated as Teachers' Day since 1962, while Guru Purnima has been traditionally observed as a day to worship teachers/gurus by Hindus. Many countries celebrate their Teachers' Day on 5 October in conjunction with World Teachers' Day, which was established by UNESCO in 1994.

Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country primarily located in southwestern Europe with parts of territory in the Atlantic Ocean and across the Mediterranean Sea. The largest part of Spain is situated on the Iberian Peninsula; its territory also includes the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla in Africa. The country's mainland is bordered to the south by Gibraltar; to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea; to the north by France, Andorra and the Bay of Biscay; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. With an area of 505,990 km2 (195,360 sq mi), Spain is the second-largest country in the European Union (EU) and, with a population exceeding 47.4 million, the fourth-most populous EU member state. Spain's capital and largest city is Madrid; other major urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Zaragoza, Málaga, Murcia, Palma de Mallorca, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Bilbao.