Scott S. Sheppard
Scott Sander Sheppard is an American astronomer and a discoverer of numerous moons, comets and minor planets in the outer Solar System.
Scott S. Sheppard announces that his team has discovered a dozen irregular moons of Jupiter.
Scott Sander Sheppard is an American astronomer and a discoverer of numerous moons, comets and minor planets in the outer Solar System.

There are 80 known moons of Jupiter, not counting a number of moonlets likely shed from the inner moons. All together, they form a satellite system which is called the Jovian system. The most massive of the moons are the four Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto, which were independently discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and Simon Marius and were the first objects found to orbit a body that was neither Earth nor the Sun. Much more recently, beginning in 1892, dozens of far smaller Jovian moons have been detected and have received the names of lovers or daughters of the Roman god Jupiter or his Greek equivalent Zeus. The Galilean moons are by far the largest and most massive objects to orbit Jupiter, with the remaining 76 known moons and the rings together composing just 0.003% of the total orbiting mass.
At least 120 people are killed and 130 injured by a suicide bombing in Diyala Governorate, Iraq.
A suicide car bombing occurred on 17 July 2015 in the Iraqi city of Khan Bani Saad, targeting a local marketplace. As of 19 July 2015 approximately 130 people were killed in the bombing, with a similar number of injured. Several people were killed by collapsed buildings. The bomb was hidden under an ice truck in an attempt to attract more people amid the heat. Responsibility for the attack was claimed by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL).
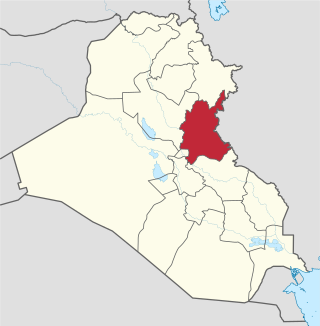
Diyala Governorate or Diyala Province is a governorate in central-eastern Iraq.
Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 was shot down over eastern Ukraine, killing all 298 people on board.

Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 (MH17/MAS17) was a scheduled passenger flight from Amsterdam to Kuala Lumpur that was shot down by Russian forces on 17 July 2014, while flying over eastern Ukraine. All 283 passengers and 15 crew were killed. Contact with the aircraft, a Boeing 777-200ER, was lost when it was about 50 km (31 mi) from the Ukraine–Russia border, and wreckage from the aircraft fell near Hrabove in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine, 40 km (25 mi) from the border. The shoot-down occurred during the war in Donbas over territory controlled by Russian separatist forces.
Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, a Boeing 777, crashes near the border of Ukraine and Russia after being shot down. All 298 people on board are killed.

Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 (MH17/MAS17) was a scheduled passenger flight from Amsterdam to Kuala Lumpur that was shot down by Russian forces on 17 July 2014, while flying over eastern Ukraine. All 283 passengers and 15 crew were killed. Contact with the aircraft, a Boeing 777-200ER, was lost when it was about 50 km (31 mi) from the Ukraine–Russia border, and wreckage from the aircraft fell near Hrabove in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine, 40 km (25 mi) from the border. The shoot-down occurred during the war in Donbas over territory controlled by Russian separatist forces.

The Boeing 777, commonly referred to as the Triple Seven, is an American long-range wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. It is the world's largest twinjet. The 777 was designed to bridge the gap between Boeing's other wide body airplanes, the twin-engined 767 and quad-engined 747, and to replace older DC-10s and L-1011 trijets. Developed in consultation with eight major airlines, with a first meeting in January 1990, the program was launched in October, with an order from United Airlines. The prototype was rolled out in April 1994, and first flew in June. The 777 entered service with the launch customer, United Airlines, in June 1995. Longer range variants were launched in 2000, and were first delivered in 2004.

Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately 600,000 square kilometres (230,000 sq mi). Prior to the ongoing Russo-Ukrainian War, it was the eighth-most populous country in Europe, with a population of around 41 million people. It is also bordered by Belarus to the north; by Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary to the west; and by Romania and Moldova to the southwest; with a coastline along the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and largest city. Ukraine's official and national language is Ukrainian; most people are also fluent in Russian.
A French regional train on the Pau-Bayonne line crashes into a high-speed train near the town of Denguin, resulting in at least 25 injuries.

Transport express régional is the brand name used by the SNCF, the French national railway company, to denote rail service run by the regional councils of France, specifically their organised transport authorities. The network serves French regions; Île-de-France (Transilien) and Corsica (CFC) have their own specific transport systems. Every day, over 800,000 passengers are carried on 5,700 TER-branded trains.
The Denguin rail crash occurred on 17 July 2014 when a TER passenger train collided with a SNCF TGV express train near Denguin, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France. Forty people were injured, four seriously.

The TGV is France's intercity high-speed rail service, operated by SNCF. SNCF worked on a high-speed rail network from 1966 to 1974 and presented the project to President Georges Pompidou who approved it. Originally designed as turbotrains to be powered by gas turbines, TGV prototypes evolved into electric trains with the 1973 oil crisis. In 1976 the SNCF ordered 87 high-speed trains from Alstom. Following the inaugural service between Paris and Lyon in 1981 on the LGV Sud-Est, the network, centered on Paris, has expanded to connect major cities across France and in neighbouring countries on a combination of high-speed and conventional lines. The TGV network in France carries about 110 million passengers a year.

Denguin is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department, southwestern France. It is located 14 km from Pau, Pyrenees-Atlantiques, the prefecture of the Department.
TAM Airlines Flight 3054 crash-landed at Congonhas Airport in São Paulo, Brazil, killing 199 people, the highest death toll of any aviation accident in Brazil and the highest death toll of any accident involving an Airbus A320 airliner.

TAM Airlines Flight 3054 (JJ3054/TAM3054) was a regularly scheduled domestic passenger flight of TAM Airlines from Porto Alegre to São Paulo, Brazil. On the evening of July 17, 2007, the Airbus A320-233 serving the flight overran runway 35L at São Paulo during moderate rain and crashed into a nearby TAM Express warehouse adjacent to a Shell gas station. The plane exploded on impact, killing all 187 passengers and crew on board and 12 people on the ground. The crash surpassed Gol Transportes Aéreos Flight 1907 as the deadliest aviation accident in Brazilian territory and in South American history, and remains the deadliest aviation accident involving the A320 proper worldwide, and the second-deadliest air disaster involving the A320 family, surpassed by the bombing of Metrojet Flight 9268, an A321-231, which crashed in Egypt in October 2015 with 224 fatalities.

São Paulo/Congonhas–Deputado Freitas Nobre Airport [kõˈɡõɲɐs] is one of the four commercial airports serving São Paulo, Brazil. The airport is named after the neighborhood where it is located, called Vila Congonhas, property of the descendants of Lucas Antônio Monteiro de Barros (1767–1851), Viscount of Congonhas do Campo, first president of the Province of São Paulo after the independence of Brazil in 1822, during the Empire. In turn, the Viscount's domain was named after the plural of a shrub known in Brazil as congonha-do-campo. Since June 19, 2017, it is officially named after Deputy Freitas Nobre. The name Congonhas, however, remains mostly used. It is owned by the City of São Paulo.

The Airbus A320 family is a series of narrow-body airliners developed and produced by Airbus. The A320 was launched in March 1984, first flew on 22 February 1987, and was introduced in April 1988 by Air France. The first member of the family was followed by the longer A321, the shorter A319, and the even shorter A318 . Final assembly takes place in Toulouse in France; Hamburg in Germany; Tianjin in China since 2009; and in Mobile, Alabama in the United States since April 2016.
TAM Airlines Flight 3054, an Airbus A320, crashes into a warehouse after landing too fast and missing the end of the São Paulo–Congonhas Airport runway, killing 199 people.

TAM Airlines Flight 3054 (JJ3054/TAM3054) was a regularly scheduled domestic passenger flight of TAM Airlines from Porto Alegre to São Paulo, Brazil. On the evening of July 17, 2007, the Airbus A320-233 serving the flight overran runway 35L at São Paulo during moderate rain and crashed into a nearby TAM Express warehouse adjacent to a Shell gas station. The plane exploded on impact, killing all 187 passengers and crew on board and 12 people on the ground. The crash surpassed Gol Transportes Aéreos Flight 1907 as the deadliest aviation accident in Brazilian territory and in South American history, and remains the deadliest aviation accident involving the A320 proper worldwide, and the second-deadliest air disaster involving the A320 family, surpassed by the bombing of Metrojet Flight 9268, an A321-231, which crashed in Egypt in October 2015 with 224 fatalities.

The Airbus A320 family is a series of narrow-body airliners developed and produced by Airbus. The A320 was launched in March 1984, first flew on 22 February 1987, and was introduced in April 1988 by Air France. The first member of the family was followed by the longer A321, the shorter A319, and the even shorter A318 . Final assembly takes place in Toulouse in France; Hamburg in Germany; Tianjin in China since 2009; and in Mobile, Alabama in the United States since April 2016.

São Paulo/Congonhas–Deputado Freitas Nobre Airport [kõˈɡõɲɐs] is one of the four commercial airports serving São Paulo, Brazil. The airport is named after the neighborhood where it is located, called Vila Congonhas, property of the descendants of Lucas Antônio Monteiro de Barros (1767–1851), Viscount of Congonhas do Campo, first president of the Province of São Paulo after the independence of Brazil in 1822, during the Empire. In turn, the Viscount's domain was named after the plural of a shrub known in Brazil as congonha-do-campo. Since June 19, 2017, it is officially named after Deputy Freitas Nobre. The name Congonhas, however, remains mostly used. It is owned by the City of São Paulo.
The 7.7 Mw Pangandaran tsunami earthquake severely affects the Indonesian island of Java, killing 668 people, and leaving more than 9,000 injured.

An earthquake occurred on July 17, 2006 at 15:19:27 local time along a subduction zone off the coast of west and central Java, a large and densely populated island in the Indonesian archipelago. The shock had a moment magnitude of 7.7 and a maximum perceived intensity of IV (Light) in Jakarta, the capital and largest city of Indonesia. There were no direct effects of the earthquake's shaking due to its low intensity, and the large loss of life from the event was due to the resulting tsunami, which inundated a 300 km (190 mi) portion of the Java coast that had been unaffected by the earlier 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami that was off the coast of Sumatra. The July 2006 earthquake was also centered in the Indian Ocean, 180 kilometers (110 mi) from the coast of Java, and had a duration of more than three minutes.
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Indonesian population.
Concorde is brought back into service nearly a year after the July 2000 crash.

The Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde is a Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC). Studies started in 1954, and France and the UK signed a treaty establishing the development project on 29 November 1962, as the programme cost was estimated at £70 million . Construction of the six prototypes began in February 1965, and the first flight took off from Toulouse on 2 March 1969. The market was predicted for 350 aircraft, and the manufacturers received up to 100 option orders from many major airlines. On 9 October 1975, it received its French Certificate of Airworthiness, and from the UK CAA on 5 December.

On 25 July 2000, Air France Flight 4590, a Concorde passenger jet on an international charter flight from Paris to New York, crashed shortly after takeoff, killing all 109 people on board and four on the ground. It was the only fatal Concorde accident during its 27-year operational history.
During approach to Lok Nayak Jayaprakash Airport, Alliance Air Flight 7412 suddenly crashes into a residential neighborhood in Patna, killing 60 people.

Jayprakash Narayan Airport is an international airport located in Patna, the state capital of Bihar in India. It is named after the independence activist and political leader, Jayprakash Narayan. It is the 14th busiest airport in India, in April 2021 - March 2022. To meet demand, the Airports Authority of India (AAI) is working to expand and modernise airport infrastructure. The airport is currently undergoing an ambitious expansion project that includes a new two-level passenger terminal, which will be completed by December 2023.

Alliance Air Flight 7412 was a scheduled Indian domestic passenger flight from Calcutta to Delhi, operated by Indian regional airliner Alliance Air. On 17 July 2000, while on approach to its first stopover in Patna, the Boeing 737-2A8 operating the route nose-dived and crashed into a residential area in Patna, killing 60 people including 5 on the ground.

Patna, historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. Covering 250 square kilometres (97 sq mi) and over 2.5 million people, its urban agglomeration is the 18th largest in India. Patna serves as the seat of Patna High Court. The Buddhist, Hindu and Jain pilgrimage centres of Vaishali, Rajgir, Nalanda, Bodh Gaya and Pawapuri are nearby and Patna City is a sacred city for Sikhs as the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh was born here. The modern city of Patna is mainly on the southern bank of the river Ganges. The city also straddles the rivers Sone, Gandak and Punpun. The city is approximately 35 kilometres (22 mi) in length and 16 to 18 kilometres wide.
A tsunami triggered by an undersea earthquake devastated several villages in Papua New Guinea, killing more than 2,100 people, and destroying the homes of thousands more.

A tsunami is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event.
The 1998 Papua New Guinea earthquake occurred on July 17 with a moment magnitude of 7.0 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The event occurred on a reverse fault near the north coast region of Papua New Guinea, 25 kilometers (16 mi) from the coast near Aitape, and caused a large undersea landslide which caused a tsunami that hit the coast, killing between at least 2,183 and 2,700 people and injuring thousands.

Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).
The 7.0 Mw Papua New Guinea earthquake triggers a tsunami that destroys ten villages in Papua New Guinea, killing up to 2,700 people, and leaving several thousand injured.
The 1998 Papua New Guinea earthquake occurred on July 17 with a moment magnitude of 7.0 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The event occurred on a reverse fault near the north coast region of Papua New Guinea, 25 kilometers (16 mi) from the coast near Aitape, and caused a large undersea landslide which caused a tsunami that hit the coast, killing between at least 2,183 and 2,700 people and injuring thousands.

A tsunami is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event.

Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).
A diplomatic conference adopts the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, establishing a permanent international court to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression.

The Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court is the treaty that established the International Criminal Court (ICC). It was adopted at a diplomatic conference in Rome, Italy on 17 July 1998 and it entered into force on 1 July 2002. As of November 2019, 123 states are party to the statute. Among other things, the statute establishes the court's functions, jurisdiction and structure.

The International Criminal Court is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals for the international crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes and the crime of aggression. It is distinct from the International Court of Justice, an organ of the United Nations that hears disputes between states. While praised as a major step towards justice, and as an innovation in international law and human rights, the ICC has faced a number of criticisms from governments and civil society, including objections to its jurisdiction, accusations of bias, Eurocentrism and racism, questioning of the fairness of its case-selection and trial procedures, and doubts about its effectiveness.

Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word γένος with the Latin suffix -caedo.

Crimes against humanity are widespread or systemic acts committed by or on behalf of a de facto authority, usually a state, that grossly violate human rights. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity do not have to take place within the context of war, and apply to widespread practices rather than acts committed by individuals. Although crimes against humanity apply to acts committed by or on behalf of authorities, they need not be official policy, and require only tolerance rather than explicit approval. The first prosecution for crimes against humanity took place at the Nuremberg trials. Initially being considered for legal use, widely in international law, following the Holocaust a global standard of human rights was articulated in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948). Political groups or states that violate or incite violation of human rights norms, as found in the Declaration, are an expression of the political pathologies associated with crimes against humanity.

A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hostages, unnecessarily destroying civilian property, deception by perfidy, wartime sexual violence, pillaging, and for any individual that is part of the command structure who orders any attempt to committing mass killings including genocide or ethnic cleansing, the granting of no quarter despite surrender, the conscription of children in the military and flouting the legal distinctions of proportionality and military necessity.

A crime of aggression or crime against peace is the planning, initiation, or execution of a large-scale and serious act of aggression using state military force. The definition and scope of the crime is controversial. The Rome Statute contains an exhaustive list of acts of aggression that can give rise to individual criminal responsibility, which include invasion, military occupation, annexation by the use of force, bombardment, and military blockade of ports. Aggression is generally a leadership crime that can only be committed by those with the power to shape a state's policy of aggression, rather than those who carry it out.
TWA Flight 800 exploded in mid-air and crashed into the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York.

Trans World Airlines Flight 800 (TWA800) was a Boeing 747-100 that exploded and crashed into the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York, on July 17, 1996, at about 8:31 pm. EDT, 12 minutes after takeoff from John F. Kennedy International Airport, on a scheduled international passenger flight to Rome, with a stopover in Paris. All 230 people on board died in the crash; it is the third-deadliest aviation accident in U.S. history. Accident investigators from the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) traveled to the scene, arriving the following morning amid speculation that a terrorist attack was the cause of the crash. Consequently, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and New York Police Department Joint Terrorism Task Force (JTTF) initiated a parallel criminal investigation. Sixteen months later, the JTTF announced that no evidence of a criminal act had been found and closed its active investigation.

East Moriches is a hamlet and census-designated place in the Town of Brookhaven, Suffolk County, New York, United States. The population was 5,249 at the 2010 census.
TWA Flight 800: Off the coast of Long Island, New York, a Paris-bound TWA Boeing 747 explodes, killing all 230 on board.

Trans World Airlines Flight 800 (TWA800) was a Boeing 747-100 that exploded and crashed into the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York, on July 17, 1996, at about 8:31 pm. EDT, 12 minutes after takeoff from John F. Kennedy International Airport, on a scheduled international passenger flight to Rome, with a stopover in Paris. All 230 people on board died in the crash; it is the third-deadliest aviation accident in U.S. history. Accident investigators from the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) traveled to the scene, arriving the following morning amid speculation that a terrorist attack was the cause of the crash. Consequently, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and New York Police Department Joint Terrorism Task Force (JTTF) initiated a parallel criminal investigation. Sixteen months later, the JTTF announced that no evidence of a criminal act had been found and closed its active investigation.

Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United States and the 18th-most populous in the world. The island begins at New York Harbor approximately 0.35 miles (0.56 km) east of Manhattan Island and extends eastward about 118 miles (190 km) into the Atlantic Ocean and 23 miles wide at its most distant points. The island comprises four counties: Kings and Queens counties and Nassau County share the western third of the island, while Suffolk County occupies the eastern two thirds of the island. More than half of New York City's residents (58.4%) lived on Long Island as of 2020, in Brooklyn and in Queens. Culturally, many people in the New York metropolitan area colloquially use the term "Long Island" to refer exclusively to Nassau and Suffolk counties, and conversely, employ the term "the City" to mean Manhattan alone. The Nassau-and-Suffolk-only definition of Long Island is recognized as a "region" by the state of New York. Although geographically an island, the Supreme Court of the United States has held that given the island's extensive ties to the mainland, it should be treated like a peninsula, allowing the state to have jurisdiction within its maritime boundaries.

The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022. After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet 2+1⁄2 times its size, to reduce its seat cost by 30% to democratize air travel. In 1965, Joe Sutter left the 737 development program to design the 747, the first twin-aisle airliner. In April 1966, Pan Am ordered 25 Boeing 747-100 aircraft and in late 1966, Pratt & Whitney agreed to develop its JT9D engine, a high-bypass turbofan. On September 30, 1968, the first 747 was rolled out of the custom-built Everett Plant, the world's largest building by volume. The first flight took place on February 9, 1969, and the 747 was certified in December of that year. It entered service with Pan Am on January 22, 1970. The 747 was the first airplane dubbed "Jumbo Jet", the first wide-body airliner.
Queen Elizabeth II officially opened the Manchester Metrolink, the first modern street-running light-rail system in the United Kingdom.

Elizabeth II was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during her lifetime, and was head of state of 15 realms at the time of her death. Her reign of 70 years and 214 days was the longest of any British monarch and the longest verified reign of any female monarch in history.

Manchester Metrolink is a tram/light rail system in Greater Manchester, England. The network has 99 stops along 64 miles (103 km) of standard-gauge route, making it the most extensive light rail system in the United Kingdom. Metrolink is owned by the public body Transport for Greater Manchester (TfGM) and operated and maintained under contract by a Keolis/Amey consortium. In 2021/22, 26 million passenger journeys were made on the system.

Light rail transit (LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit characterized by a combination of tram and rapid transit features. While its rolling stock is more similar to a traditional tram, it operates at a higher capacity and speed, and often on an exclusive right-of-way. In many cities, light rail transit systems more closely resemble, and are therefore indistinguishable from, traditional underground or at-grade subways and heavy-rail metros.
First flight of the B-2 Spirit Stealth Bomber.

The Northrop B-2 Spirit, also known as the Stealth Bomber, is an American heavy strategic bomber, featuring low observable stealth technology designed for penetrating dense anti-aircraft defenses. Designed during the Cold War, it is a flying wing design with a crew of two. The bomber is subsonic and can deploy both conventional and thermonuclear weapons, such as up to eighty 500-pound class (230 kg) Mk 82 JDAM GPS-guided bombs, or sixteen 2,400-pound (1,100 kg) B83 nuclear bombs. The B-2 is the only acknowledged aircraft that can carry large air-to-surface standoff weapons in a stealth configuration.
Holy See–Poland relations are restored.

Holy See–Poland relations are foreign relations between the Holy See and the Republic of Poland. As of 2015, approximately 92.9 percent of Poles belong to the Catholic Church.
Founding of the EUREKA Network by former head of states François Mitterrand (France) and Helmut Kohl (Germany).

Eureka is an intergovernmental organisation for research and development funding and coordination. Eureka is an open platform for international cooperation in innovation. Organisations and companies applying through Eureka programmes can access funding and support from national and regional ministries or agencies for their international R&D projects.

François Marie Adrien Maurice Mitterrand was President of France, serving under that position from 1981 to 1995, the longest time in office in the history of France. As First Secretary of the Socialist Party, he was the first left-wing politician to assume the presidency under the Fifth Republic.

Helmut Josef Michael Kohl was a German politician who served as Chancellor of Germany from 1982 to 1998 and Leader of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) from 1973 to 1998. Kohl's 16-year tenure is the longest of any German chancellor since Otto von Bismarck, and oversaw the end of the Cold War, the German reunification and the creation of the European Union (EU). Further, Kohl's 16 years and 30 day tenure is the longest for any democratically elected Chancellor of Germany.
The national drinking age in the United States was changed from 18 to 21.

The National Minimum Drinking Age Act of 1984 was passed by the United States Congress and was later signed into law by President Ronald Reagan on July 17, 1984. The act would punish any state that allowed persons under 21 years to purchase alcoholic beverages by reducing its annual federal highway apportionment by 10 percent. The law was later amended, lowering the penalty to 8 percent from fiscal year 2012 and beyond.
A structural failure caused a walkway at the Hyatt Regency hotel in Kansas City, Missouri, U.S., to collapse (damage pictured), killing 114 people and injuring 216 others.

Structural integrity and failure is an aspect of engineering that deals with the ability of a structure to support a designed structural load without breaking and includes the study of past structural failures in order to prevent failures in future designs.

The Sheraton Kansas City Hotel at Crown Center is a 504.0 ft (153.62 m), 45-story hotel located in the Crown Center complex in Kansas City, Missouri. It was Missouri's tallest building from 1980 to 1986. It is now the state's sixth-tallest building and Kansas City's third-tallest building.

Kansas City is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central city of the Kansas City metropolitan area, which straddles the Missouri–Kansas state line and has a population of 2,392,035. Most of the city lies within Jackson County, with portions spilling into Clay, Cass, and Platte counties. Kansas City was founded in the 1830s as a port on the Missouri River at its confluence with the Kansas River coming in from the west. On June 1, 1850, the town of Kansas was incorporated; shortly after came the establishment of the Kansas Territory. Confusion between the two ensued, and the name Kansas City was assigned to distinguish them soon after.

On July 17, 1981, the Hyatt Regency Hotel in Kansas City, Missouri, suffered the structural collapse of two overhead walkways. Loaded with partygoers, the concrete and glass platforms cascaded down, crashing onto a tea dance in the lobby, killing 114 and injuring 216. Kansas City society was affected for years, with the collapse resulting in billions of dollars of insurance claims, legal investigations and city government reforms.
A structural failure leads to the collapse of a walkway at the Hyatt Regency in Kansas City, Missouri, killing 114 people and injuring more than 200.

On July 17, 1981, the Hyatt Regency Hotel in Kansas City, Missouri, suffered the structural collapse of two overhead walkways. Loaded with partygoers, the concrete and glass platforms cascaded down, crashing onto a tea dance in the lobby, killing 114 and injuring 216. Kansas City society was affected for years, with the collapse resulting in billions of dollars of insurance claims, legal investigations and city government reforms.

Kansas City is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central city of the Kansas City metropolitan area, which straddles the Missouri–Kansas state line and has a population of 2,392,035. Most of the city lies within Jackson County, with portions spilling into Clay, Cass, and Platte counties. Kansas City was founded in the 1830s as a port on the Missouri River at its confluence with the Kansas River coming in from the west. On June 1, 1850, the town of Kansas was incorporated; shortly after came the establishment of the Kansas Territory. Confusion between the two ensued, and the name Kansas City was assigned to distinguish them soon after.
Nicaraguan dictator General Anastasio Somoza Debayle resigns and flees to Miami, Florida, United States.

Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the largest country in the Central American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the northwest, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. As of 2015, it was estimated to be the second largest city in Central America. The multi-ethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English.

Anastasio "Tachito" Somoza Debayle was the President of Nicaragua from 1 May 1967 to 1 May 1972 and from 1 December 1974 to 17 July 1979. As head of the National Guard, he was de facto ruler of the country between 1972 and 1974, even during the period when he was not the de jure ruler.

Miami, officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 as of the 2020 census, it is the second-most populous city in Florida and the eleventh-most populous city in the Southeastern United States. The Miami metropolitan area is the ninth largest in the U.S. with a population of 6.138 million people as of 2020. The city has the third-largest skyline in the U.S. with over 300 high-rises, 58 of which exceed 491 ft (150 m).
East Timor is annexed and becomes the 27th province of Indonesia.

East Timor, also known as Timor-Leste, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-western half, and the minor islands of Atauro and Jaco. Australia is the country's southern neighbour, separated by the Timor Sea. The country's size is 14,874 square kilometres (5,743 sq mi). Dili is its capital and largest city.

The Indonesian invasion of East Timor, known in Indonesia as Operation Lotus, began on 7 December 1975 when the Indonesian military (ABRI/TNI) invaded East Timor under the pretext of anti-colonialism and anti-communism to overthrow the Fretilin regime that had emerged in 1974. The overthrow of the popular and briefly Fretilin-led government sparked a violent quarter-century occupation in which approximately 100,000–180,000 soldiers and civilians are estimated to have been killed or starved to death. The Commission for Reception, Truth and Reconciliation in East Timor documented a minimum estimate of 102,000 conflict-related deaths in East Timor throughout the entire period 1974 to 1999, including 18,600 violent killings and 84,200 deaths from disease and starvation; Indonesian forces and their auxiliaries combined were responsible for 70% of the killings.
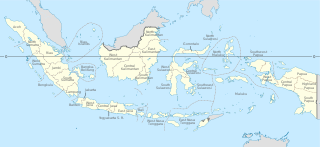
Provinces of Indonesia are the 38 administrative divisions of Indonesia and the highest tier of the local government. Provinces are further divided into regencies and cities, which are in turn subdivided into districts (kecamatan).

Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at 1,904,569 square kilometres. With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population.
The opening of the Summer Olympics in Montreal is marred by 25 African teams boycotting the games because of New Zealand's participation. Contrary to rulings by other international sports organizations, the IOC had declined to exclude New Zealand because of their participation in South African sporting events during apartheid.

The 1976 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XXI Olympiad and commonly known as Montreal 1976, were an international multi-sport event held from July 17 to August 1, 1976 in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Montreal was awarded the rights to the 1976 Games at the 69th IOC Session in Amsterdam on May 12, 1970, over the bids of Moscow and Los Angeles. It was the first and, so far, only Summer Olympic Games to be held in Canada. Toronto hosted the 1976 Summer Paralympics the same year as the Montreal Olympics, which still remains the only Summer Paralympics to be held in Canada. Calgary and Vancouver later hosted the Winter Olympic Games in 1988 and 2010, respectively.

Montreal is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as Ville-Marie, or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked hill around which the early city of Ville-Marie is built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal, which obtained its name from the same origin as the city, and a few much smaller peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is 196 km (122 mi) east of the national capital Ottawa, and 258 km (160 mi) southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City.

New Zealand is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island and the South Island —and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering 268,021 square kilometres (103,500 sq mi). New Zealand is about 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland.

The International Olympic Committee is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss Civil Code. Founded by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas in 1894, it is the authority responsible for organising the modern Olympic Games.

South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by 2,798 kilometres (1,739 mi) of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves the country Lesotho. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World, and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania. South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes, plant and animal life. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 24th-most populous nation and covers an area of 1,221,037 square kilometres. South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein, and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg.

Apartheid was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was characterised by an authoritarian political culture based on baasskap, which ensured that South Africa was dominated politically, socially, and economically by the nation's minority white population. According to this system of social stratification, white citizens had the highest status, followed by Indians and Coloureds, then black Africans. The economic legacy and social effects of apartheid continue to the present day.
Apollo–Soyuz Test Project: An American Apollo and a Soviet Soyuz spacecraft dock with each other in orbit marking the first such link-up between spacecraft from the two nations.

Apollo–Soyuz was the first crewed international space mission, carried out jointly by the United States and the Soviet Union in July 1975. Millions of people around the world watched on television as a United States Apollo spacecraft docked with a Soviet Soyuz capsule. The project, and its handshake in space, was a symbol of détente between the two superpowers during the Cold War.

The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the third United States human spaceflight program carried out by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which succeeded in preparing and landing the first humans on the Moon from 1968 to 1972. It was first conceived in 1960 during President Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration as a three-person spacecraft to follow the one-person Project Mercury, which put the first Americans in space. Apollo was later dedicated to President John F. Kennedy's national goal for the 1960s of "landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth" in an address to Congress on May 25, 1961. It was the third US human spaceflight program to fly, preceded by the two-person Project Gemini conceived in 1961 to extend spaceflight capability in support of Apollo.

Soyuz is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau. The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS.

In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a planet, moon, asteroid, or Lagrange point. Normally, orbit refers to a regularly repeating trajectory, although it may also refer to a non-repeating trajectory. To a close approximation, planets and satellites follow elliptic orbits, with the center of mass being orbited at a focal point of the ellipse, as described by Kepler's laws of planetary motion.
King Mohammed Zahir Shah of Afghanistan, while having surgery in Italy, is deposed by his cousin Mohammed Daoud Khan.

Mohammed Zahir Shah was the last king of Afghanistan, reigning from 8 November 1933 until he was deposed on 17 July 1973. Serving for 40 years, Zahir was the longest-serving ruler of Afghanistan since the foundation of the Durrani Empire in the 18th century. He expanded Afghanistan's diplomatic relations with many countries, including with both sides of the Cold War. In the 1950s, Zahir Shah began modernizing the country, culminating in the creation of a new constitution and a constitutional monarchy system. Demonstrating nonpartisanship, his long reign was marked by peace in the country that was lost afterwards.

Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east. Occupying 652,864 square kilometers (252,072 sq mi) of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains in the north and the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. As of 2021, its population is 40.2 million, composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and serves as its capital.

Mohammed Daoud Khan, also romanized as Daud Khan or Dawood Khan, was an Afghan politician and general who served as prime minister of Afghanistan from 1953 to 1963 and, as leader of the 1973 Afghan coup d'état which overthrew the monarchy, served as the first president of Afghanistan from 1973 to 1978, establishing an autocratic one-party system.
Led by Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr, the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party overthrew Iraqi president Abdul Rahman Arif.

Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was the fourth president of Iraq, from 17 July 1968 to 16 July 1979. He was a leading member of the revolutionary Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party and later the Baghdad-based Ba'ath Party and its regional organisation Ba'ath Party – Iraq Region, which espoused Ba'athism, a mix of Arab nationalism and Arab socialism.

The Arab Socialist Baʿath Party was a political party founded in Syria by Mishel ʿAflaq, Ṣalāḥ al-Dīn al-Bītār, and associates of Zaki al-ʾArsūzī. The party espoused Baʿathism, which is an ideology mixing Arab nationalist, pan-Arabism, Arab socialist, and anti-imperialist interests. Baʿathism calls for unification of the Arab world into a single state. Its motto, "Unity, Liberty, Socialism", refers to Arab unity, and freedom from non-Arab control and interference.

The 17 July Revolution was a bloodless coup in Iraq in 1968 led by Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr, Abd ar-Razzaq an-Naif, and Abd ar-Rahman al-Dawud that ousted President Abdul Rahman Arif and Prime Minister Tahir Yahya and brought the Iraqi Regional Branch of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party to power. Ba'athists involved in the coup as well as the subsequent purge of the moderate faction led by Naif included Hardan al-Tikriti, Salih Mahdi Ammash, and Saddam Hussein, the future President of Iraq. The coup was primarily directed against Yahya, an outspoken Nasserist who exploited the political crisis created by the June 1967 Six-Day War to push Arif's moderate government to nationalize the Western-owned Iraq Petroleum Company (IPC) in order to use Iraq's "oil as a weapon in the battle against Israel." Full nationalization of the IPC did not occur until 1972, under the Ba'athist administration. In the aftermath of the coup, the new Iraqi government consolidated power by denouncing alleged American and Israeli machinations, publicly executing 14 people including 9 Iraqi Jews on fabricated espionage charges amidst a broader purge, and working to expand Iraq's traditionally close relations with the Soviet Union.

Hajj ʿAbd al-Rahman Mohammed ʿArif al-Jumayli was a career soldier and the third president of Iraq from 16 April 1966 to 17 July 1968.
Abdul Rahman Arif is overthrown and the Ba'ath Party is installed as the governing power in Iraq with Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr as the new Iraqi President.

Hajj ʿAbd al-Rahman Mohammed ʿArif al-Jumayli was a career soldier and the third president of Iraq from 16 April 1966 to 17 July 1968.

The 17 July Revolution was a bloodless coup in Iraq in 1968 led by Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr, Abd ar-Razzaq an-Naif, and Abd ar-Rahman al-Dawud that ousted President Abdul Rahman Arif and Prime Minister Tahir Yahya and brought the Iraqi Regional Branch of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party to power. Ba'athists involved in the coup as well as the subsequent purge of the moderate faction led by Naif included Hardan al-Tikriti, Salih Mahdi Ammash, and Saddam Hussein, the future President of Iraq. The coup was primarily directed against Yahya, an outspoken Nasserist who exploited the political crisis created by the June 1967 Six-Day War to push Arif's moderate government to nationalize the Western-owned Iraq Petroleum Company (IPC) in order to use Iraq's "oil as a weapon in the battle against Israel." Full nationalization of the IPC did not occur until 1972, under the Ba'athist administration. In the aftermath of the coup, the new Iraqi government consolidated power by denouncing alleged American and Israeli machinations, publicly executing 14 people including 9 Iraqi Jews on fabricated espionage charges amidst a broader purge, and working to expand Iraq's traditionally close relations with the Soviet Union.

The Arab Socialist Baʿath Party was a political party founded in Syria by Mishel ʿAflaq, Ṣalāḥ al-Dīn al-Bītār, and associates of Zaki al-ʾArsūzī. The party espoused Baʿathism, which is an ideology mixing Arab nationalist, pan-Arabism, Arab socialist, and anti-imperialist interests. Baʿathism calls for unification of the Arab world into a single state. Its motto, "Unity, Liberty, Socialism", refers to Arab unity, and freedom from non-Arab control and interference.

Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to the southwest and Syria to the west. The capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraq is home to diverse ethnic groups including Iraqi Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Yazidis, Mandaeans, Persians and Shabakis with similarly diverse geography and wildlife. The vast majority of the country's 44 million residents are Muslims – the notable other faiths are Christianity, Yazidism, Mandaeism, Yarsanism and Zoroastrianism. The official languages of Iraq are Arabic and Kurdish; others also recognised in specific regions are Neo-Aramaic, Turkish and Armenian.

Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was the fourth president of Iraq, from 17 July 1968 to 16 July 1979. He was a leading member of the revolutionary Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party and later the Baghdad-based Ba'ath Party and its regional organisation Ba'ath Party – Iraq Region, which espoused Ba'athism, a mix of Arab nationalism and Arab socialism.
Nuclear weapons testing: The "Small Boy" test shot Little Feller I becomes the last atmospheric test detonation at the Nevada National Security Site.

Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test.

Little Feller II and Little Feller I were code names for a set of nuclear tests undertaken by the United States at the Nevada Test Site on July 7 and 17, 1962 as part of Operation Sunbeam. They were both tests of stockpiled W54 warheads, the smallest nuclear warheads known to have been produced by the United States, used in both the Davy Crockett warhead and the Special Atomic Demolition Munition.

The Nevada National Security Site, known as the Nevada Test Site (NTS) until 2010, is a United States Department of Energy (DOE) reservation located in southeastern Nye County, Nevada, about 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas. Formerly known as the Nevada Proving Grounds, the site was established in 1951 for the testing of nuclear devices. It covers approximately 1,360 square miles (3,500 km2) of desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear weapons testing at the site began with a 1-kiloton-of-TNT (4.2 TJ) bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. Over the subsequent four decades, over 1,000 nuclear explosions were detonated at the site. Many of the iconic images of the nuclear era come from the site.
Disneyland is dedicated and opened by Walt Disney in Anaheim, California.

Disneyland is a theme park in Anaheim, California. Opened in 1955, it was the first theme park opened by The Walt Disney Company and the only one designed and constructed under the direct supervision of Walt Disney. Disney initially envisioned building a tourist attraction adjacent to his studios in Burbank to entertain fans who wished to visit; however, he soon felt that the proposed site was too small. After hiring the Stanford Research Institute to perform a feasibility study determining an appropriate site for his project, Disney bought a 160-acre (65 ha) site near Anaheim in 1953. The park was designed by a creative team hand-picked by Walt from internal and outside talent. They founded WED Enterprises, the precursor to today's Walt Disney Imagineering. Construction began in 1954 and the park was unveiled during a special televised press event on the ABC Television Network on July 17, 1955. Since its opening, Disneyland has undergone expansions and major renovations, including the addition of New Orleans Square in 1966, Bear Country in 1972, Mickey's Toontown in 1993, and Star Wars: Galaxy's Edge in 2019; Disney California Adventure Park also opened in 2001 at the site of Disneyland's original parking lot.

Anaheim is a city in northern Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area. As of the 2020 United States Census, the city had a population of 346,824, making it the most populous city in Orange County, the 10th-most populous city in California, and the 56th-most populous city in the United States. Anaheim is the second-largest city in Orange County in terms of land area, and is known for being the home of the Disneyland Resort, the Anaheim Convention Center, and two major sports teams: the Los Angeles Angels baseball team and the Anaheim Ducks ice hockey club.
The largest number of United States midshipman casualties in a single event results from an aircraft crash in Florida, killing 44.
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada, Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Kenya.

USMC R4Q Packet BuNo 131663 was one of twenty aircraft airlifting 1,600 Naval Reserve Officer Training Corps (NROTC) second-class (2/c) midshipmen between summer aviation training in Texas and amphibious warfare training in Virginia in July 1953. Shortly after midnight, the plane crashed and burned following a refueling stop in Florida.
World War II: The main three leaders of the Allied nations, Winston Churchill, Harry S. Truman and Joseph Stalin, meet in the German city of Potsdam to decide the future of a defeated Germany.

The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy. Its principal members by 1941 were the United Kingdom, United States, Soviet Union, and China.

Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1951 to 1955. Apart from two years between 1922 and 1924, he was a Member of Parliament (MP) from 1900 to 1964 and represented a total of five constituencies. Ideologically an economic liberal and imperialist, he was for most of his career a member of the Conservative Party, which he led from 1940 to 1955. He was a member of the Liberal Party from 1904 to 1924.

Harry S. Truman was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin Roosevelt and as a United States senator from Missouri from 1935 to January 1945. Assuming the presidency after Roosevelt's death, Truman implemented the Marshall Plan to rebuild the economy of Western Europe and established both the Truman Doctrine and NATO to contain the expansion of Soviet communism. He proposed numerous liberal domestic reforms, but few were enacted by the Conservative Coalition which dominated the Congress.

Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1922–1952) and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (1941–1953). Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, he consolidated power to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically adhering to the Leninist interpretation of Marxism, he formalised these ideas as Marxism–Leninism, while his own policies are called Stalinism.

The Potsdam Conference was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris Peace Conference of 1919. The participants were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States. They were represented respectively by General Secretary Joseph Stalin, Prime Ministers Winston Churchill and Clement Attlee, and President Harry S. Truman. They gathered to decide how to administer Germany, which had agreed to an unconditional surrender nine weeks earlier. The goals of the conference also included establishing the postwar order, solving issues on the peace treaty, and countering the effects of the war.

Potsdam is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of Berlin, and lies embedded in a hilly morainic landscape dotted with many lakes, around 20 of which are located within Potsdam's city limits. It lies some 25 kilometres southwest of Berlin's city centre. The name of the city and of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin.
Laden with munitions for World War II, two ships exploded at the Port Chicago Naval Magazine in California, killing 320 people and injuring more than 400 others.

The Port Chicago disaster was a deadly munitions explosion of the ship SS E. A. Bryan that occurred on July 17, 1944, at the Port Chicago Naval Magazine in Port Chicago, California, United States. Munitions detonated while being loaded onto a cargo vessel bound for the Pacific Theater of Operations, killing 320 sailors and civilians and injuring 390 others. Approximately two-thirds of the dead and injured were enlisted African American sailors.

The Port Chicago Naval Magazine National Memorial is a memorial dedicated in 1994 recognizing the dead of the Port Chicago disaster, and the critical role played by Port Chicago, California during World War II, in serving as the main facility for the Pacific Theater of Operations. The national memorial is located at the Concord Naval Weapons Station near Concord, California, in the United States.
Port Chicago disaster: Near the San Francisco Bay, two ships laden with ammunition for the war explode in Port Chicago, California, killing 320.

The Port Chicago disaster was a deadly munitions explosion of the ship SS E. A. Bryan that occurred on July 17, 1944, at the Port Chicago Naval Magazine in Port Chicago, California, United States. Munitions detonated while being loaded onto a cargo vessel bound for the Pacific Theater of Operations, killing 320 sailors and civilians and injuring 390 others. Approximately two-thirds of the dead and injured were enlisted African American sailors.

San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.

Ammunition is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons and the component parts of other weapons that create the effect on a target.

Port Chicago was a town on the southern banks of Suisun Bay, in Contra Costa County, California. It was located 6.5 miles (10 km) east-northeast of Martinez, at an elevation of 13 feet. It is best known as the site of a devastating explosion at its Naval Munitions Depot during World War II.
World War II: At Sainte-Foy-de-Montgommery in Normandy Field Marshal Erwin Rommel is seriously injured by allied aircraft while returning to his headquarters.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

Sainte-Foy-de-Montgommery is a former commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Val-de-Vie.

Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel was a German field marshal during World War II. Popularly known as the Desert Fox, he served in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany, as well as serving in the Reichswehr of the Weimar Republic, and the army of Imperial Germany.
Douglas Corrigan takes off from Brooklyn to fly the "wrong way" to Ireland and becomes known as "Wrong Way" Corrigan.

Douglas Corrigan was an American aviator, nicknamed "Wrong Way" in 1938. After a transcontinental flight in July from Long Beach, California, to New York City, he then flew from Floyd Bennett Field in Brooklyn to Ireland, though his flight plan was filed to return to Long Beach.

Floyd Bennett Field is an airfield in the Marine Park neighborhood of southeast Brooklyn in New York City, along the shore of Jamaica Bay. The airport originally hosted commercial and general aviation traffic before being used as a naval air station. Floyd Bennett Field is currently part of the Gateway National Recreation Area's Jamaica Bay Unit, and is managed by the National Park Service (NPS). While no longer used as an operational commercial, military, or general aviation airfield, a section is still used as a helicopter base by the New York City Police Department (NYPD), and one runway is reserved for hobbyists flying radio-controlled aircraft.
Spanish Civil War: An Armed Forces rebellion against the recently elected leftist Popular Front government of Spain starts the civil war.

The Spanish Civil War was a civil war in Spain fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republicans and the Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the left-leaning Popular Front government of the Second Spanish Republic, and consisted of various socialist, communist, separatist, anarchist, and republican parties, some of which had opposed the government in the pre-war period. The opposing Nationalists were an alliance of Falangists, monarchists, conservatives, and traditionalists led by a military junta among whom General Francisco Franco quickly achieved a preponderant role. Due to the international political climate at the time, the war had many facets and was variously viewed as class struggle, a religious struggle, a struggle between dictatorship and republican democracy, between revolution and counterrevolution, and between fascism and communism. According to Claude Bowers, U.S. ambassador to Spain during the war, it was the "dress rehearsal" for World War II. The Nationalists won the war, which ended in early 1939, and ruled Spain until Franco's death in November 1975.

The Spanish coup of July 1936 was a nationalist and military uprising that was designed to overthrow the Spanish Second Republic but precipitated the Spanish Civil War; Nationalists fought against Republicans for control of Spain. The coup itself was organised for 18 July 1936, although it started the previous day in Spanish Morocco, and would result in a split of the Spanish military and territorial control, rather than a prompt transfer of power. Although drawn out, the resulting war would ultimately lead to one of its leaders, Francisco Franco, becoming ruler of Spain as a dictator.

The Popular Front in Spain's Second Republic was an electoral alliance and pact signed in January 1936 by various left-wing political organizations, instigated by Manuel Azaña for the purpose of contesting that year's election. In Catalonia and today's Valencian Community the name of the coalition was Front d'Esquerres.
Altona Bloody Sunday: A riot between the Nazi Party paramilitary forces, the SS and SA, and the German Communist Party ensues.
Altona Bloody Sunday is the name given to the events of 17 July 1932 when a recruitment march by the Nazi SA led to violent clashes between the police, the SA and supporters of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) in Altona, which at the time belonged to the Prussian province of Schleswig-Holstein but is now part of Hamburg. Eighteen people were killed. The national government under Reich Chancellor Franz von Papen and Reich President Paul von Hindenburg used the incident as a rationale to depose the acting government of the Free State of Prussia by means of an emergency decree in what came to be known as the Prussian coup d'état of 20 July 1932.

The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party, was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor, the German Workers' Party, existed from 1919 to 1920. The Nazi Party emerged from the extremist German nationalist, racist and populist Freikorps paramilitary culture, which fought against the communist uprisings in post–World War I Germany. The party was created to draw workers away from communism and into völkisch nationalism. Initially, Nazi political strategy focused on anti–big business, anti-bourgeois, and anti-capitalist rhetoric. This was later downplayed to gain the support of business leaders, and in the 1930s, the party's main focus shifted to antisemitic and anti-Marxist themes. The party had little popular support until the Great Depression.

The Schutzstaffel was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, and later throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II.
The Sturmabteilung was the original paramilitary wing of the Nazi Party. It played a significant role in Adolf Hitler's rise to power in the 1920s and 1930s. Its primary purposes were providing protection for Nazi rallies and assemblies, disrupting the meetings of opposing parties, fighting against the paramilitary units of the opposing parties, especially the Roter Frontkämpferbund of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and the Reichsbanner Schwarz-Rot-Gold of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), and intimidating Romani, trade unionists, and especially Jews.

The Communist Party of Germany was a major political party in the Weimar Republic between 1918 and 1933, an underground resistance movement in Nazi Germany, and a minor party in West Germany in the postwar period until it was banned by the Federal Constitutional Court in 1956.
The form of government in the Republic of Finland is officially confirmed. For this reason, July 17 is known as the Day of Democracy (Kansanvallan päivä) in Finland.

Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland across Estonia to the south. Finland covers an area of 338,455 square kilometres (130,678 sq mi) with a population of 5.6 million. Helsinki is the capital and largest city, forming a larger metropolitan area with the neighbouring cities of Espoo, Kauniainen, and Vantaa. The vast majority of the population are ethnic Finns. Finnish, alongside Swedish, are the official languages. Swedish is the native language of 5.2% of the population. Finland's climate varies from humid continental in the south to the boreal in the north. The land cover is primarily a boreal forest biome, with more than 180,000 recorded lakes.
RMS Carpathia, which had rescued survivors of the 1912 Titanic sinking, was sunk by a German U-boat with the loss of five crew.

RMS Carpathia was a Cunard Line transatlantic passenger steamship built by Swan Hunter & Wigham Richardson in their shipyard in Wallsend, England.

The RMS Titanic sank in the early morning hours of 15 April 1912 in the North Atlantic Ocean, four days into her maiden voyage from Southampton to New York City. The largest ocean liner in service at the time, Titanic had an estimated 2,224 people on board when she struck an iceberg at around 23:40 on Sunday, 14 April 1912. Her sinking two hours and forty minutes later at 02:20 on Monday, 15 April, resulted in the deaths of more than 1,500 people, making it one of the deadliest peacetime maritime disasters in history.

U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare role and enforcing a naval blockade against enemy shipping. The primary targets of the U-boat campaigns in both wars were the merchant convoys bringing supplies from Canada and other parts of the British Empire, and from the United States, to the United Kingdom and to the Soviet Union and the Allied territories in the Mediterranean. German submarines also destroyed Brazilian merchant ships during World War II, causing Brazil to declare war on both Germany and Italy on 22 August 1942.
Russian Revolution: Bolsheviks executed Tsar Nicholas II (pictured) and his family at Yekaterinburg.

The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government following two successive revolutions and a bloody civil war. The Russian Revolution can also be seen as the precursor for the other European revolutions that occurred during or in the aftermath of WWI, such as the German Revolution of 1918.

The Bolsheviks, also known in English as the Bolshevists, were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903.

The Russian Imperial Romanov family were shot and bayoneted to death by Bolshevik revolutionaries under Yakov Yurovsky on the orders of the Ural Regional Soviet in Yekaterinburg on the night of 16–17 July 1918. Also murdered that night were members of the imperial entourage who had accompanied them: court physician Eugene Botkin; lady-in-waiting Anna Demidova; footman Alexei Trupp; and head cook Ivan Kharitonov. The bodies were taken to the Koptyaki forest, where they were stripped, buried, and mutilated with grenades to prevent identification.

Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov, known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer, was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland, ruling from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. During his reign, Nicholas gave support to the economic and political reforms promoted by his prime ministers, Sergei Witte and Pyotr Stolypin. He advocated modernization based on foreign loans and close ties with France, but resisted giving the new parliament major roles. Ultimately, progress was undermined by Nicholas's commitment to autocratic rule, strong aristocratic opposition and defeats sustained by the Russian military in the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. By March 1917, public support for Nicholas had collapsed and he was forced to abdicate the throne, thereby ending the Romanov dynasty's 304-year rule of Russia (1613–1917).

Yekaterinburg, alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk, is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia. The city is located on the Iset River between the Volga-Ural region and Siberia, with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in the Ural Federal District, and one of Russia's main cultural and industrial centres. Yekaterinburg has been dubbed the "Third capital of Russia", as it is ranked third by the size of its economy, culture, transportation and tourism.
Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and his immediate family and retainers are executed by Bolshevik Chekists at the Ipatiev House in Yekaterinburg, Russia.

Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov, known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer, was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland, ruling from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. During his reign, Nicholas gave support to the economic and political reforms promoted by his prime ministers, Sergei Witte and Pyotr Stolypin. He advocated modernization based on foreign loans and close ties with France, but resisted giving the new parliament major roles. Ultimately, progress was undermined by Nicholas's commitment to autocratic rule, strong aristocratic opposition and defeats sustained by the Russian military in the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. By March 1917, public support for Nicholas had collapsed and he was forced to abdicate the throne, thereby ending the Romanov dynasty's 304-year rule of Russia (1613–1917).

The Russian Empire was the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately 22,800,000 square kilometres (8,800,000 sq mi), it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity.

The Russian Imperial Romanov family were shot and bayoneted to death by Bolshevik revolutionaries under Yakov Yurovsky on the orders of the Ural Regional Soviet in Yekaterinburg on the night of 16–17 July 1918. Also murdered that night were members of the imperial entourage who had accompanied them: court physician Eugene Botkin; lady-in-waiting Anna Demidova; footman Alexei Trupp; and head cook Ivan Kharitonov. The bodies were taken to the Koptyaki forest, where they were stripped, buried, and mutilated with grenades to prevent identification.

The Bolsheviks, also known in English as the Bolshevists, were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903.

The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission, abbreviated as VChK, and commonly known as Cheka, was the first of a succession of Soviet secret-police organizations. Established on December 5 1917 by the Sovnarkom, it came under the leadership of Felix Dzerzhinsky, a Polish aristocrat-turned-Bolshevik. By late 1918, hundreds of Cheka committees had sprung up in the RSFSR at the oblast, guberniya, raion, uyezd, and volost levels.

Ipatiev House was a merchant's house in Yekaterinburg where the former Emperor Nicholas II of Russia, his family, and members of his household were executed in July 1918 following the Bolshevik Revolution. Its name is identical to that of the Ipatiev Monastery in Kostroma, from where the Romanovs came to the throne. As an act for the 60th anniversary of the Russian Revolutions, it was demolished in 1977 by orders of the Politburo to the local soviet government, almost 59 years after the Romanov family murder and 14 years before the dissolution of the Soviet Union itself.

Yekaterinburg, alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk, is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia. The city is located on the Iset River between the Volga-Ural region and Siberia, with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in the Ural Federal District, and one of Russia's main cultural and industrial centres. Yekaterinburg has been dubbed the "Third capital of Russia", as it is ranked third by the size of its economy, culture, transportation and tourism.

The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR, previously known as the Russian Soviet Republic and the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic as well as being unofficially known as Soviet Russia, the Russian Federation or simply Russia, was an independent federal socialist state from 1917 to 1922, and afterwards the largest and most populous of the Soviet socialist republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1922 to 1991, until becoming a sovereign part of the Soviet Union with priority of Russian laws over Union-level legislation in 1990 and 1991, the last two years of the existence of the USSR. The Russian Republic was composed of sixteen smaller constituent units of autonomous republics, five autonomous oblasts, ten autonomous okrugs, six krais and forty oblasts. Russians formed the largest ethnic group. The capital of the Russian SFSR was Moscow and the other major urban centers included Leningrad, Stalingrad, Novosibirsk, Sverdlovsk, Gorky and Kuybyshev. It was the first Marxist-Leninist state in the world.
The RMS Carpathia, the ship that rescued the 705 survivors from the RMS Titanic, is sunk off Ireland by the German SM U-55; five lives are lost.

RMS Carpathia was a Cunard Line transatlantic passenger steamship built by Swan Hunter & Wigham Richardson in their shipyard in Wallsend, England.

RMS Titanic was a British passenger liner, operated by the White Star Line, which sank in the North Atlantic Ocean on 15 April 1912 after striking an iceberg during her maiden voyage from Southampton, England, to New York City, United States. Of the estimated 2,224 passengers and crew aboard, more than 1,500 died, making it the deadliest sinking of a single ship up to that time. It remains the deadliest peacetime sinking of a superliner or cruise ship. The disaster drew public attention, provided foundational material for the disaster film genre, and has inspired many artistic works.

SM U-55 was one of the six Type U-51 U-boats of the Imperial German Navy during the First World War.
King George V issues a Proclamation stating that the male line descendants of the British Royal Family will bear the surname Windsor.

George V was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.

The British royal family comprises King Charles III and his close relations. There is no strict legal or formal definition of who is or is not a member, although the Royal Household has issued different lists outlining who is a part of the royal family. They support the monarch in undertaking public engagements and often pursue charitable work and interests. The royal family are regarded as British cultural icons.

The House of Windsor is the reigning royal house of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms. In 1901, a line of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha succeeded the House of Hanover to the British monarchy with the accession of King Edward VII, son of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. In 1917, the name of the British royal house was changed from the German Saxe-Coburg and Gotha to the English Windsor because of anti-German sentiment in the United Kingdom during the First World War. There have been five British monarchs of the House of Windsor since then: George V, Edward VIII, George VI, Elizabeth II, and Charles III. The children and male-line descendants of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip also genealogically belong to the House of Oldenburg since Philip belonged to the Glücksburg branch of that house.
Willis Carrier creates the first air conditioner in Buffalo, New York.

Willis Haviland Carrier was an American engineer, best known for inventing modern air conditioning. Carrier invented the first electrical air conditioning unit in 1902. In 1915, he founded Carrier Corporation, a company specializing in the manufacture and distribution of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.

Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment and in some cases also strictly controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or alternatively a variety of other methods, including passive cooling or ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners, but use a reversing valve to allow them to both heat and also cool an enclosed space.

Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from Southern Ontario. With a population of 278,349 according to the 2020 census, Buffalo is the 78th-largest city in the United States. The city and nearby Niagara Falls together make up the two-county Buffalo–Niagara Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA), which had an estimated population of 1.1 million in 2020, making it the 49th largest MSA in the United States. Buffalo is in Western New York, which is the largest population and economic center between Boston and Cleveland.
Liner Deutschland sets east to west transatlantic record of five days, eleven hours and five minutes.

SS Deutschland was a passenger liner built in Stettin and launched in 1900 by the Hamburg America Line of Germany. The rival North German Lloyd line had launched Germany's first four funnel liner, Kaiser Wilhelm der Grosse in 1897, and SS Deutschland was built by Hamburg America as Germany's second four-funnel liner in order to compete.
NEC Corporation is organized as the first Japanese joint venture with foreign capital.

NEC Corporation is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of things (IoT) platform, and telecommunications equipment and software, to business enterprises, communications services providers and to government agencies, and has also been the biggest PC vendor in Japan since the 1980s, when it launched the PC-8000 series.
Harvard School of Dental Medicine is established in Boston, Massachusetts. It is the first dental school in the U.S. that is affiliated with a university.

The Harvard School of Dental Medicine (HSDM) is the dental school of Harvard University. It is located in the Longwood Medical Area in Boston, Massachusetts. In addition to the DMD degree, HSDM offers specialty training programs, advanced training programs, and a PhD program through the Harvard Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. The program considers dentistry a specialty of medicine. Therefore, all students at HSDM experience dual citizenship between Harvard School of Dental Medicine and Harvard Medical School. Today, HSDM is the smallest school at Harvard University with a total student body of 280.

Boston, officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th-most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about 48.4 sq mi (125 km2) and a population of 675,647 as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County. The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and including Providence, Rhode Island, is home to approximately 8.2 million people, making it the sixth most populous in the United States.
The New Zealand Wars resumed as British forces led by General Duncan Cameron began the Invasion of the Waikato.

The New Zealand Wars took place from 1845 to 1872 between the New Zealand colonial government and allied Māori on one side and Māori and Māori-allied settlers on the other. They were previously commonly referred to as the Land Wars or the Māori Wars, while Māori language names for the conflicts included Ngā pakanga o Aotearoa and Te riri Pākehā. Historian James Belich popularised the name "New Zealand Wars" in the 1980s, although according to Vincent O'Malley, the term was first used by historian James Cowan in the 1920s.

General Sir Duncan Alexander Cameron, was a British Army officer who fought in the Crimean War and part of the New Zealand Wars. He was later a governor of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst.

The Invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century New Zealand Wars. Hostilities took place in the North Island of New Zealand between the military forces of the colonial government and a federation of Māori tribes known as the Kingitanga Movement. The Waikato is a territorial region with a northern boundary somewhat south of the present-day city of Auckland. The campaign lasted for nine months, from July 1863 to April 1864. The invasion was aimed at crushing Kingite power and also at driving Waikato Māori from their territory in readiness for occupation and settlement by European colonists. The campaign was fought by a peak of about 14,000 Imperial and colonial troops and about 4,000 Māori warriors drawn from more than half the major North Island tribal groups.
The first astrophotograph of a star other than the Sun, a daguerreotype of Vega (pictured), was taken by William Cranch Bond and John Adams Whipple.

Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object was taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects invisible to the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is done by long time exposure since both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over these long periods of time. Captured photon data can be edited on platforms such as Adobe Photoshop.

Daguerreotype was the first publicly available photographic process; it was widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process.

Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only 25 light-years from the Sun, and one of the most luminous stars in the Sun's neighborhood. It is the fifth-brightest star in the night sky, and the second-brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus.

William Cranch Bond was an American astronomer, and the first director of Harvard College Observatory.

John Adams Whipple was an American inventor and early photographer. He was the first in the United States to manufacture the chemicals used for daguerreotypes. He pioneered astronomical and night photography. He was a prize-winner for his extraordinary early photographs of the moon and he was the first to produce images of stars other than the sun. Among those was the star Vega and the Mizar-Alcor stellar sextuple system, which was thought to be a double star until 2009.
Vega became the first star (other than the Sun) to be photographed.

Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only 25 light-years from the Sun, and one of the most luminous stars in the Sun's neighborhood. It is the fifth-brightest star in the night sky, and the second-brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus.
The Kingdom of Spain cedes the territory of Florida to the United States.

Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country primarily located in southwestern Europe with parts of territory in the Atlantic Ocean and across the Mediterranean Sea. The largest part of Spain is situated on the Iberian Peninsula; its territory also includes the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla in Africa. The country's mainland is bordered to the south by Gibraltar; to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea; to the north by France, Andorra and the Bay of Biscay; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. With an area of 505,990 km2 (195,360 sq mi), Spain is the second-largest country in the European Union (EU) and, with a population exceeding 47.4 million, the fourth-most populous EU member state. Spain's capital and largest city is Madrid; other major urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, Zaragoza, Málaga, Murcia, Palma de Mallorca, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Bilbao.
The history of Florida can be traced to when the first Native Americans began to inhabit the peninsula as early as 14,000 years ago. They left behind artifacts and archeological evidence. Florida's written history begins with the arrival of Europeans; the Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León in 1513 made the first textual records. The state received its name from that conquistador, who called the peninsula La Pascua Florida in recognition of the verdant landscape and because it was the Easter season, which the Spaniards called Pascua Florida.
The 16 Carmelite Martyrs of Compiègne are executed ten days prior to the end of the French Revolution's Reign of Terror.

The Order of the Brothers of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Mount Carmel, known as the Carmelites or sometimes by synecdoche known simply as Carmel, is a Roman Catholic mendicant religious order for men and women. Historical records about its origin remain uncertain, but it was probably founded in the 12th century on Mount Carmel in the Crusader States. Berthold of Calabria, as well as Albert of Vercelli have traditionally been associated with the founding of the order, but few clear records of early Carmelite history have survived. The order of Carmelite nuns was formalised in 1452.

The Martyrs of Compiègne were the 16 members of the Carmel of Compiègne, France: 11 Discalced Carmelite nuns, three lay sisters, and two externs. They were executed by the guillotine towards the end of the Reign of Terror, at what is now the Place de la Nation in Paris on 17 July 1794, and are venerated as beatified martyrs of the Catholic Church. Ten days after their execution, Maximilien Robespierre himself was executed, ending the Reign of Terror. Their story has inspired a novella, a motion picture, a television movie, and an opera, Dialogues of the Carmelites, written by French composer Francis Poulenc.

The Reign of Terror was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the First Republic, a series of massacres and numerous public executions took place in response to revolutionary fervour, anticlerical sentiment, and accusations of treason by the Committee of Public Safety.
Members of the French National Guard under the command of General Lafayette open fire on a crowd of radical Jacobins at the Champ de Mars, Paris, during the French Revolution, killing scores of people.

The National Guard is a French military, gendarmerie, and police reserve force, active in its current form since 2016 but originally founded in 1789 during the French Revolution.

Marie-Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de La Fayette, known in the United States as Lafayette, was a French aristocrat, freemason and military officer who fought in the American Revolutionary War, commanding American troops in several battles, including the siege of Yorktown. After returning to France, he was a key figure in the French Revolution of 1789 and the July Revolution of 1830. He has been considered a national hero in both countries.

The Champ de Mars massacre took place on 17 July 1791 in Paris at the Champ de Mars against a crowd of republican protesters amid the French Revolution. Two days before, the National Constituent Assembly issued a decree that King Louis XVI would retain his throne under a constitutional monarchy. This decision came after Louis and his family had unsuccessfully tried to flee France in the Flight to Varennes the month before. Later that day, leaders of the republicans in France rallied against this decision.
A Jacobin was a member of the Jacobin Club, a revolutionary political movement that was the most famous political club during the French Revolution (1789–1799). The club got its name from meeting at the Dominican rue Saint-Honoré Monastery of the Jacobins. The Dominicans in France were called Jacobins because their first house in Paris was the Saint Jacques Monastery.

The Champ de Mars is a large public greenspace in Paris, France, located in the seventh arrondissement, between the Eiffel Tower to the northwest and the École Militaire to the southeast. The park is named after the Campus Martius in Rome, a tribute to the Roman god of war. The name alludes to the fact that the lawns here were formerly used as drilling and marching grounds by the French military.

The French Revolution was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like liberté, égalité, fraternité reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day.
Dene men, acting as guides to Samuel Hearne on his exploration of the Coppermine River in present-day Nunavut, Canada, massacred a group of about 20 Copper Inuit.

The Dene people are an indigenous group of First Nations who inhabit the northern boreal and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages. Dene is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term "Dene" has two usages. More commonly, it is used narrowly to refer to the Athabaskan speakers of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut in Canada, especially including the Chipewyan (Denesuline), Tlicho (Dogrib), Yellowknives (T'atsaot'ine), Slavey, and Sahtu. However, it is sometimes also used to refer to all Northern Athabaskan speakers, who are spread in a wide range all across Alaska and northern Canada. The Southern Athabaskan speakers, however, also refer to themselves by similar words: Diné (Navajo) and Indé (Apache).

Samuel Hearne was an English explorer, fur-trader, author, and naturalist. He was the first European to make an overland excursion across northern Canada to the Arctic Ocean, actually Coronation Gulf, via the Coppermine River. In 1774, Hearne built Cumberland House for the Hudson's Bay Company, its second interior trading post after Henley House and the first permanent settlement in present Saskatchewan.

The Coppermine River is a river in the North Slave and Kitikmeot regions of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut in Canada. It is 845 kilometres (525 mi) long. It rises in Lac de Gras, a small lake near Great Slave Lake, and flows generally north to Coronation Gulf, an arm of the Arctic Ocean. The river freezes in winter but may still flow under the ice.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.
The Bloody Falls massacre was an incident believed to have taken place during Hudson Bay Company employee Samuel Hearne's exploration of the Coppermine River for copper deposits near modern-day Kugluktuk, Nunavut, Canada on 17 July 1771. Hearne's original travelogue is now lost, and the narrative that became the famous story was published after Hearne's death with substantial editorializing. The narrative states that Chipewyan and "Copper Indian" Dene men led by Hearne's guide and companion Matonabbee attacked a group of Copper Inuit camped by rapids approximately 15 km (9.3 mi) upstream from the mouth of the Coppermine River.

Copper Inuit, also known as Kitlinermiut and Inuinnait, are a Canadian Inuit group who live north of the tree line, in what is now the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut and in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Most of them historically lived in the area around Coronation Gulf, on Victoria Island, and southern Banks Island.
Bloody Falls massacre: Chipewyan chief Matonabbee, traveling as the guide to Samuel Hearne on his Arctic overland journey, massacres a group of unsuspecting Inuit.
The Bloody Falls massacre was an incident believed to have taken place during Hudson Bay Company employee Samuel Hearne's exploration of the Coppermine River for copper deposits near modern-day Kugluktuk, Nunavut, Canada on 17 July 1771. Hearne's original travelogue is now lost, and the narrative that became the famous story was published after Hearne's death with substantial editorializing. The narrative states that Chipewyan and "Copper Indian" Dene men led by Hearne's guide and companion Matonabbee attacked a group of Copper Inuit camped by rapids approximately 15 km (9.3 mi) upstream from the mouth of the Coppermine River.

The Chipewyan are a Dene Indigenous Canadian people of the Athabaskan language family, whose ancestors are identified with the Taltheilei Shale archaeological tradition. Chipewyan is a Cree exonym (ᒌᐘᔮᐣ) meaning pointed hides, referring to the design of their parkas. They are part of the Northern Athabascan group of peoples, and come from what is now Western Canada.
Matonabbee was a Chipewyan hunter and leader. He was also a trader and a Chipewyan representative at the Prince of Wales Fort. He travelled with Chief Akaitcho's older brother, Keskarrah. After his father died, Matonabbee spent some time living at Prince of Wales Fort where he learned to speak English.

Samuel Hearne was an English explorer, fur-trader, author, and naturalist. He was the first European to make an overland excursion across northern Canada to the Arctic Ocean, actually Coronation Gulf, via the Coppermine River. In 1774, Hearne built Cumberland House for the Hudson's Bay Company, its second interior trading post after Henley House and the first permanent settlement in present Saskatchewan.

Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and Alaska. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.
Former emperor Peter III of Russia is murdered.

Peter III was an emperor of Russia who was overthrown by his wife, Catherine the Great. He was born in Kiel as Charles Peter Ulrich of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp, the only child of Charles Frederick, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp, and Anna Petrovna.
King George I of Great Britain sails down the River Thames with a barge of 50 musicians, where George Frideric Handel's Water Music is premiered.

George I was King of Great Britain and Ireland from 1 August 1714 and ruler of the Electorate of Hanover within the Holy Roman Empire from 23 January 1698 until his death in 1727. He was the first British monarch of the House of Hanover as the most senior Protestant descendant of his great-grandfather James VI and I.
The River Thames, known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At 215 miles (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn.

George Frideric Handel was a German-British Baroque composer well known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concertos. Handel received his training in Halle and worked as a composer in Hamburg and Italy before settling in London in 1712, where he spent the bulk of his career and became a naturalised British subject in 1727. He was strongly influenced both by the middle-German polyphonic choral tradition and by composers of the Italian Baroque. In turn, Handel's music forms one of the peaks of the "high baroque" style, bringing Italian opera to its highest development, creating the genres of English oratorio and organ concerto, and introducing a new style into English church music. He is consistently recognized as one of the greatest composers of his age.

The Water Music is a collection of orchestral movements, often published as three suites, composed by George Frideric Handel. It premiered on 17 July 1717, in response to King George I's request for a concert on the River Thames.
The Battle of Castillon, the last engagement of the Hundred Years' War, ended with the English losing all holdings in France except the Pale of Calais.

The Battle of Castillon between the forces of England and France took place on 17 July 1453 in Gascony near the town of Castillon-sur-Dordogne. Historians regard this decisive French victory as marking the end of the Hundred Years' War.

The Hundred Years' War was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagenet and the French royal House of Valois. Over time, the war grew into a broader power struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides.

The Pale of Calais was a territory in Northern France ruled by the monarchs of England for more than two hundred years from 1347 to 1558. The area, which was taken following the Battle of Crécy in 1346 and the subsequent siege of Calais, was confirmed at the Treaty of Brétigny in 1360. It became an important economic centre for England in Europe’s textile trade centred in Flanders.
Battle of Castillon: The last battle of Hundred Years' War, the French under Jean Bureau defeat the English under the Earl of Shrewsbury, who is killed in the battle in Gascony.

The Battle of Castillon between the forces of England and France took place on 17 July 1453 in Gascony near the town of Castillon-sur-Dordogne. Historians regard this decisive French victory as marking the end of the Hundred Years' War.

The Hundred Years' War was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagenet and the French royal House of Valois. Over time, the war grew into a broader power struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides.

Jean Bureau was a French artillery commander active primarily during the later years of the Hundred Years' War. Along with his brother, Gaspard, he is credited with making French artillery the most effective in the world. As Master Gunner of Artillery in the armies of Charles VII, Bureau acquired a reputation as an effective artillery officer during the Normandy campaign (1449–1450), when his bombardments helped capture the towns of Rouen, Harfleur, and Honfleur, and aided in the French victory at Formigny. Bureau commanded the victorious French army at the decisive Battle of Castillon in 1453.
John Talbot, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury, 1st Earl of Waterford, 7th Baron Talbot, KG, known as "Old Talbot", was an English nobleman and a noted military commander during the Hundred Years' War. He was the most renowned in England and most feared in France of the English captains in the last stages of the conflict. Known as a tough, cruel, and quarrelsome man, Talbot distinguished himself militarily in a time of decline for the English. Called the "English Achilles" and the "Terror of the French", he is lavishly praised in the plays of Shakespeare. The manner of his death, leading an ill-advised charge against field artillery, has come to symbolize the passing of the age of chivalry. He also held the subsidiary titles of 10th Baron Strange of Blackmere and 6th Baron Furnivall jure uxoris.

Gascony was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascony. The region is vaguely defined, and the distinction between Guyenne and Gascony is unclear; by some they are seen to overlap, while others consider Gascony a part of Guyenne. Most definitions put Gascony east and south of Bordeaux.
Hundred Years' War: Charles VII of France is crowned the King of France in the Reims Cathedral after a successful campaign by Joan of Arc.

The Hundred Years' War was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagenet and the French royal House of Valois. Over time, the war grew into a broader power struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides.

Charles VII, called the Victorious or the Well-Served, was King of France from 1422 to his death in 1461.

The accession of the King of France to the royal throne was legitimized by a ceremony performed with the Crown of Charlemagne at the Reims Cathedral. In late medieval and early modern times, the new king did not need to be anointed in order to be recognized as French monarch but ascended upon the previous monarch's death with the proclamation "Le Roi est mort, vive le Roi!"

Notre-Dame de Reims, , is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the French city of the same name, the archiepiscopal see of the Archdiocese of Reims. The cathedral was dedicated to the Virgin Mary and was the traditional location for the coronation of the kings of France.

Joan of Arc is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronation of Charles VII of France during the Hundred Years' War. Stating that she was acting under divine guidance, she became a military leader who transcended gender roles and gained recognition as a savior of France.
Zhu Di, better known by his era name as the Yongle Emperor, assumes the throne over the Ming dynasty of China.
A regnal name, or regnant name or reign name, is the name used by monarchs and popes during their reigns and, subsequently, historically. Since ancient times, some monarchs have chosen to use a different name from their original name when they accede to the monarchy.

The Yongle Emperor, personal name Zhu Di, was the third Emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 1424.
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng, numerous rump regimes ruled by remnants of the Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662.
The Fourth Crusade assaults Constantinople. The Byzantine emperor Alexios III Angelos flees from his capital into exile.

The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid Sultanate, the strongest Muslim state of the time. However, a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army's 1202 siege of Zara and the 1204 sack of Constantinople, the capital of the Greek Christian-controlled Byzantine Empire, rather than Egypt as originally planned. This led to the partitioning of the Byzantine Empire by the Crusaders.

Constantinople was the capital of the Roman Empire, and later, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Officially renamed Istanbul in 1930, the city is today the largest city and financial centre of the Republic of Turkey (1923–present). It is also the largest city in Europe.

This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors (symbasileis) who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title.

Alexios III Angelos was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnenos, associating himself with the Komnenos dynasty. A member of the extended imperial family, Alexios came to the throne after deposing, blinding and imprisoning his younger brother Isaac II Angelos. The most significant event of his reign was the attack of the Fourth Crusade on Constantinople in 1203, on behalf of Alexios IV Angelos. Alexios III took over the defence of the city, which he mismanaged, and then fled the city at night with one of his three daughters. From Adrianople, and then Mosynopolis, he attempted unsuccessfully to rally his supporters, only to end up a captive of Marquis Boniface of Montferrat. He was ransomed and sent to Asia Minor where he plotted against his son-in-law Theodore I Laskaris, but was eventually captured and spent his last days confined to the Monastery of Hyakinthos in Nicaea, where he died.
Damasus II began his 23-day-long papacy, one of the shortest in history.
Pope Damasus II was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 17 July 1048 to his death on 9 August that same year. He was the second of the German pontiffs nominated by Emperor Henry III. A native of Bavaria, he was the third German to become pope and had one of the shortest papal reigns.
Damasus II is elected pope, and dies 23 days later.
Pope Damasus II was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 17 July 1048 to his death on 9 August that same year. He was the second of the German pontiffs nominated by Emperor Henry III. A native of Bavaria, he was the third German to become pope and had one of the shortest papal reigns.
Twelve inhabitants of Scillium (near Kasserine, modern-day Tunisia) in North Africa are executed for being Christians. This is the earliest record of Christianity in that part of the world.
The Scillitan Martyrs were a company of twelve North African Christians who were executed for their beliefs on 17 July 180 AD. The martyrs take their name from Scilla, a town in Numidia. The Acts of the Scillitan Martyrs are considered to be the earliest documents of the church of Africa and also the earliest specimen of Christian Latin.
Scillium is an ancient city in the Roman province of Africa Proconsularis, Scillium must not be confounded with Silli, or Sililli, in Numidia, the situation of which is unknown nor, as Battandier does, identified with Kasrin, which is Cillium, a see of Byzantium. Its episcopal see was a suffragan of the see of Carthage, capital of the province.

Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a part of the Maghreb region of North Africa, bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. It features the archaeological sites of Carthage dating back to the 9th century, as well as the Great Mosque of Kairouan. Known for its ancient architecture, souks and blue coasts, it covers 163,610 km2 (63,170 sq mi), and has a population of 12.1 million. It contains the eastern end of the Atlas Mountains and the northern reaches of the Sahara desert; much of its remaining territory is arable land. Its 1,300 km (810 mi) of coastline include the African conjunction of the western and eastern parts of the Mediterranean Basin. Tunisia is home to Africa's northernmost point, Cape Angela; and its capital and largest city is Tunis, which is located on its northeastern coast, and lends the country its name.
John Lewis, American Politician and Civil Rights Leader. (b. 1940) deaths

John Robert Lewis was an American politician and civil rights activist who served in the United States House of Representatives for Georgia's 5th congressional district from 1987 until his death in 2020. He participated in the 1960 Nashville sit-ins, the Freedom Rides, was the chairman of the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) from 1963 to 1966, and was one of the "Big Six" leaders of groups who organized the 1963 March on Washington. Fulfilling many key roles in the civil rights movement and its actions to end legalized racial segregation in the United States, in 1965 Lewis led the first of three Selma to Montgomery marches across the Edmund Pettus Bridge where, in an incident which became known as Bloody Sunday, state troopers and police attacked Lewis and the other marchers.
Ekaterina Alexandrovskaya, Russian-Australian pair skater (b. 2000) deaths

Ekaterina Dmitriyevna Alexandrovskaya was a Russian-Australian pair skater. With her skating partner, Harley Windsor, she was the 2017 CS Tallinn Trophy champion, the 2017 CS Nebelhorn Trophy bronze medallist, the 2018 CS U.S. Classic bronze medallist, and a two-time Australian national champion.
Bill Arnsparger, American football player and coach (b. 1926) deaths
William Stephen Arnsparger was an American college and professional football coach. He was born and raised in Paris, Kentucky, served in the United States Marine Corps during World War II, and graduated from Miami University (Ohio) in 1950. Immediately upon graduation, Arnsparger was hired as an assistant coach with the Miami football program, beginning a long career in the profession.
Jules Bianchi, French race car driver (b. 1989) deaths

Jules Lucien André Bianchi was a French motor racing driver who drove for the Marussia F1 Team in the FIA Formula One World Championship.
Owen Chadwick, English rugby player, historian, and academic (b. 1916) deaths

William Owen Chadwick was a British Anglican priest, academic, rugby international, writer and prominent historian of Christianity. As a leading academic, Chadwick became Dixie Professor of Ecclesiastical History in 1958, serving until 1968, and from 1968 to 1983 was Regius Professor of History. Chadwick was elected master of Selwyn College, Cambridge, and served from 1956 to 1983.
Van Miller, American sportscaster (b. 1927) deaths

Van Miller was an American radio and television sports announcer from Dunkirk, New York, where he began his career at Dunkirk radio station WFCB calling play-by-play for high school football games. In the 1950s, he moved to Buffalo where he became the chief play-by-play announcer for the Buffalo Bills Radio Network, the official radio broadcasting arm of the Buffalo Bills of the National Football League from the team's inception as an AFL team in 1960 to 1971, and again from 1977 to 2003. At the time of his retirement in 2003, Miller was the longest-tenured commentator with one team in pro football history.
John Taylor, English pianist and educator (b. 1942) deaths

John Taylor was a British jazz pianist, born in Manchester, England, who occasionally performed on the organ and the synthesizer.
Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 victims: deaths

Liam Patrick Davison was an Australian novelist and reviewer. He was born in Melbourne, where, until 2007, he taught creative writing at the Chisholm Institute in Frankston.
Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 victims: deaths

Shubashini "Shuba" Jeyaratnam, also known by stage names Shuba Jay and Shuba Jaya, was a Malaysian entrepreneur, stage performer, and actress who achieved popularity through her roles in several TV shows. Of Tamil descent, she was killed, together with her husband and daughter, in the shootdown of Malaysia Airlines Flight 17.
Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 victims: deaths

Joseph Marie Albert "Joep" Lange was a Dutch clinical researcher specialising in HIV therapy. He served as the president of the International AIDS Society from 2002 to 2004. He was a passenger on Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, which was shot down on 17 July 2014 over Ukraine.
Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 victims: deaths

Willem Johannes Witteveen was a Dutch legal scholar, politician, and author. He was a law professor at Tilburg University (1990–2014) and a Member of the Senate for the Labour Party. He was also the author of several books about law and politics. Witteveen was killed on 17 July 2014 when the flight he was travelling on, Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, was shot down over eastern Ukraine by Russian rebels.
Henry Hartsfield, American colonel, pilot, and astronaut (b. 1933) deaths

Henry Warren Hartsfield Jr. was a United States Air Force Colonel and NASA astronaut who logged over 480 hours in space. He was inducted into the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame in 2006.
Otto Piene, German sculptor and academic (b. 1928) deaths

Otto Piene was a German-American artist specializing in kinetic and technology-based art, often working collaboratively. He lived and worked in Düsseldorf, Germany; Cambridge, Massachusetts; and Groton, Massachusetts.
Elaine Stritch, American actress and singer (b. 1925) deaths

Elaine Stritch was an American actress, best known for her work on Broadway and later television. She made her professional stage debut in 1944 and appeared in numerous stage plays, musicals, feature films and television series. Stritch was inducted into the American Theater Hall of Fame in 1995. She is often considered by critics as one of Broadway’s greatest female performers.
Henri Alleg, English-French journalist and author (b. 1921) deaths

Henri Alleg, born Harry John Salem, was a French-Algerian journalist, director of the Alger républicain newspaper, and a member of the French Communist Party. After Editions de Minuit, a French publishing house, released his memoir La Question in 1958, Alleg gained international recognition for his stance against torture, specifically within the context of the Algerian War (1954–1962).
Peter Appleyard, English-Canadian vibraphone player and composer (b. 1928) deaths

Peter Appleyard, was a British–Canadian jazz vibraphonist, percussionist, and composer.

The vibraphone is a percussion instrument in the metallophone family. It consists of tuned metal bars and is typically played by using mallets to strike the bars. A person who plays the vibraphone is called a vibraphonist, vibraharpist, or vibist.
Vincenzo Cerami, Italian screenwriter and producer (b. 1940) deaths
Vincenzo Cerami was an Italian screenwriter, novelist and poet.
Don Flye, American tennis player (b. 1933) deaths
Donald Guy Flye was an American tennis player.
Ian Gourlay, English general (b. 1920) deaths
General Sir Basil Ian Spencer Gourlay, was a Royal Marines officer who served as Commandant General Royal Marines from 1971 to 1975.
David White, Scottish footballer and manager (b. 1933) deaths

David White was a Scottish football player and manager. He played as a wing half for Clyde for his whole career, before managing Clyde, Rangers and Dundee.
Richard Evatt, English boxer (b. 1973) deaths
Richard Evatt, also called 'tiger', was a British amateur and professional boxer in the super featherweight division who was unsuccessful in his only opportunity to win a world title. He hailed from Coventry, West Midlands, United Kingdom.
Forrest S. McCartney, American general (b. 1931) deaths

Forrest Striplin McCartney was a United States Air Force lieutenant general and former director of NASA's John F. Kennedy Space Center.
İlhan Mimaroğlu, Turkish-American composer and producer (b. 1926) deaths
İlhan Kemaleddin Mimaroğlu was a Turkish American musician and electronic music composer. He was born in Istanbul, Turkey, the son of the famous architect Mimar Kemaleddin Bey depicted on the Turkish lira banknotes, denomination 20 lira, of the 2009 E-9 emission. He graduated from Galatasaray High School in 1945 and the Ankara Law School in 1949. He went to study in New York supported by a Rockefeller Scholarship. He studied musicology at Columbia University under Paul Henry Lang and composition under Douglas Moore.
William Raspberry, American journalist and academic (b. 1935) deaths

William Raspberry was an American syndicated public affairs columnist. He was also the Knight Professor of the Practice of Communications and Journalism at the Sanford Institute of Public Policy at Duke University. An African American, he frequently wrote on racial issues.
Marsha Singh, Indian-English politician (b. 1954) deaths

Marsha Singh was a British Labour Party politician, and the Member of Parliament (MP) for Bradford West from 1997 to 2012. Singh stood down due to ill health.
David Ngoombujarra, Australian actor (b. 1967) deaths
David Ngoombujarra was an Indigenous Australian actor of the Yamatji people. Born David Bernard Starr in Meekatharra, Western Australia, his acting career spanned over two decades from the 1980s to 2010; he won three Australian Film Institute Awards. On 17 July 2011 he was found in a park in Fremantle, and taken to Fremantle Hospital where he was pronounced dead.
Larry Keith, American actor (b. 1931) deaths

Larry Keith was an American actor who was a cast member on the ABC soap opera All My Children and was the first American to play the role of Henry Higgins in the Broadway production of My Fair Lady.
Walter Cronkite, American journalist and actor (b. 1916) deaths

Walter Leland Cronkite Jr. was an American broadcast journalist who served as anchorman for the CBS Evening News for 19 years (1962–1981). During the 1960s and 1970s, he was often cited as "the most trusted man in America" after being so named in an opinion poll. Cronkite reported many events from 1937 to 1981, including bombings in World War II; the Nuremberg trials; combat in the Vietnam War; the Dawson's Field hijackings; Watergate; the Iran Hostage Crisis; and the assassinations of President John F. Kennedy, civil rights pioneer Martin Luther King Jr., and Beatles musician John Lennon. He was also known for his extensive coverage of the U.S. space program, from Project Mercury to the Moon landings to the Space Shuttle. He was the only non-NASA recipient of an Ambassador of Exploration award. Cronkite is known for his departing catchphrase, "And that's the way it is", followed by the date of the broadcast.
Leszek Kołakowski, Polish historian and philosopher (b. 1927) deaths

Leszek Kołakowski was a Polish philosopher and historian of ideas. He is best known for his critical analyses of Marxist thought, especially his three-volume history, Main Currents of Marxism (1976). In his later work, Kołakowski increasingly focused on religious questions. In his 1986 Jefferson Lecture, he asserted that "[w]e learn history not in order to know how to behave or how to succeed, but to know who we are".
Grant Forsberg, American actor and businessman (b. 1959) deaths
Grant Forsberg was an American actor, born in Holden, Massachusetts.
Júlio Redecker, Brazilian politician (b. 1956) deaths

Júlio César Redecker was a Brazilian politician and a member of the opposition party, Brazilian Social Democracy Party (PSDB). Redecker was the leader of the minority in the Brazilian Chamber of Deputies. Redecker died aboard TAM Airlines Flight 3054, which crashed after landing in São Paulo on July 17, 2007. He was married and had three children.
Paulo Rogério Amoretty Souza, Brazilian lawyer and businessman (b. 1945) deaths
Paulo Rogério Amoretty Souza was a Brazilian lawyer and former chairman of the association football team Sport Club Internacional. He was born in Recife. Prior to his death he was an attorney for Sport Club Corinthians Paulista. He was married and had two sons, both of whom are lawyers.
Sam Myers, American singer-songwriter (b. 1936) deaths

Samuel Joseph Myers was an American blues musician and songwriter. He was an accompanist on dozens of recordings by blues artists over five decades. He began his career as a drummer for Elmore James but was most famous as a blues vocalist and blues harp player. For nearly two decades he was the featured vocalist for Anson Funderburgh & the Rockets.
Mickey Spillane, American crime novelist (b. 1918) deaths

Frank Morrison Spillane, better known as Mickey Spillane, was an American crime novelist, whose stories often feature his signature detective character, Mike Hammer. More than 225 million copies of his books have sold internationally. Spillane was also an occasional actor, once even playing Hammer himself.
Geraldine Fitzgerald, Irish-American actress (b. 1913) deaths

Geraldine Mary Fitzgerald was an Irish actress and a member of the American Theater Hall of Fame. In 2020, she was listed at number 30 on The Irish Times list of Ireland's greatest film actors.
Edward Heath, English colonel and politician, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (b. 1916) deaths

Sir Edward Richard George Heath was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1970 to 1974 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1965 to 1975. Heath also served for 51 years as a Member of Parliament from 1950 to 2001. Outside politics, Heath was a yachtsman, a musician, and an author.

The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern prime ministers hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons, they sit as members of Parliament.
Joe Vialls, Australian journalist and theorist (b. 1944) deaths
Joe Vialls was a conspiracy theorist and internet journalist based in Perth, Western Australia. His claims that major incidents such as the Port Arthur massacre, terror attacks in Bali and Jakarta and the 2004 Asian tsunami were the work of Israeli and American secret agents gained a measure of notoriety in Australia, America and Indonesia.
David Kelly, Welsh weapons inspector (b. 1944) deaths

David Christopher Kelly was a Welsh scientist and authority on biological warfare (BW). In July 2003 he had an off-the-record conversation with Andrew Gilligan, a BBC journalist; during their discussion they talked about the 2002 dossier on Iraqi weapons of mass destruction, which stated that some of Iraq's chemical and biological weapons were deployable within 45 minutes. When Gilligan reported this on BBC Radio 4's Today programme, he stated that the 45 minute claim was included at the insistence of Alastair Campbell, the Downing Street Director of Communications—something Kelly denied. The government complained to the BBC about the claim, but they refused to recant on it; political tumult between Downing Street and the BBC developed. Kelly informed his line managers in the Ministry of Defence that he may have been the source, but did not think he was the only one, as Gilligan had reported points he had not mentioned. Kelly's name became known to the media, and he was called to appear on 15 July before the parliamentary Intelligence and Security and Foreign Affairs Select committees. Two days later Kelly was found dead near his home.
Rosalyn Tureck, American pianist and harpsichord player (b. 1914) deaths

Rosalyn Tureck was an American pianist and harpsichordist who was particularly associated with the music of Johann Sebastian Bach. However, she had a wide-ranging repertoire that included works by composers Ludwig van Beethoven, Johannes Brahms and Frédéric Chopin, as well as more modern composers such as David Diamond, Luigi Dallapiccola and William Schuman. Diamond's Piano Sonata No. 1 was inspired by Tureck's playing.

A harpsichord is a musical instrument played by means of a keyboard. This activates a row of levers that turn a trigger mechanism that plucks one or more strings with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic. The strings are under tension on a soundboard, which is mounted in a wooden case; the soundboard amplifies the vibrations from the strings so that the listeners can hear it. Like a pipe organ, a harpsichord may have more than one keyboard manual, and even a pedal board. Harpsichords may also have stop buttons which add or remove additional octaves. Some harpsichords may have a buff stop, which brings a strip of buff leather or other material in contact with the strings, muting their sound to simulate the sound of a plucked lute.
Walter Zapp, Latvian-Swiss inventor, invented the Minox (b. 1905) deaths

Walter Zapp was a Baltic German inventor. His greatest creation was the Minox subminiature camera.

Minox is a manufacturer of cameras, known especially for its subminiature camera.
Joseph Luns, Dutch politician and Dutch Minister of Foreign Affairs (b. 1911) deaths

Joseph Marie Antoine Hubert Luns was a Dutch politician and diplomat of the defunct Catholic People's Party (KVP) now merged into the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) party and jurist. He served as Secretary General of NATO from 1 October 1971 until 25 June 1984.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the Netherlands' ministry responsible for foreign relations, foreign policy, international development, international trade, diaspora and matters dealing with the European Union, NATO and the Benelux Union. The ministry was created in 1798, as the Department of Foreign Affairs of the Batavian Republic. In 1876, it became the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Katharine Graham, American publisher (b. 1917) deaths

Katharine Meyer Graham was an American newspaper publisher. She led her family's newspaper, The Washington Post, from 1963 to 1991. Graham presided over the paper as it reported on the Watergate scandal, which eventually led to the resignation of President Richard Nixon. She was the first 20th century female publisher of a major American newspaper. Graham's memoir, Personal History, won the Pulitzer Prize in 1998.
Rosana Serrano, Cuban rower births
Rosana Serrano is a Cuban rower.
Lillian Hoban, American author and illustrator (b. 1925) deaths

Lillian Hoban was an American illustrator and children's writer best known for picture books created with her husband Russell Hoban. According to OCLC, she has published 326 works in 1,401 publications in 11 languages.
Victims of TWA Flight 800 deaths

Michel Breistroff was a French professional ice hockey defenceman.
Victims of TWA Flight 800 deaths

Marcel Dadi was a Tunisian-born Jewish French virtuoso guitarist known for his finger-picking style which faithfully recreated the instrumental styles of American guitarists such as Chet Atkins, Merle Travis and Jerry Reed. He became a friend of country star Chet Atkins.
Victims of TWA Flight 800 deaths

H. David Hogan was an American composer and musical director of CIGAP, a choir composed of openly gay men.
Victims of TWA Flight 800 deaths

Jed Johnson was an American interior designer and film director. Initially hired by Andy Warhol to sweep floors at The Factory, he subsequently moved in with Warhol, and was his boyfriend for twelve years. As a passenger in the first class cabin, he was killed when TWA Flight 800 came down shortly after takeoff in 1996.
Chas Chandler, English bass player and producer (b. 1938) deaths

Bryan James "Chas" Chandler was an English musician, record producer and manager, best known as the original bassist in The Animals, for which he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1994. He also managed the band Slade, and Jimi Hendrix, about whom he was regularly interviewed until his death in 1996.
Juan Manuel Fangio, Argentinian race car driver (b. 1911) deaths

Juan Manuel Fangio, nicknamed El Chueco or El Maestro, was an Argentine racing car driver. He dominated the first decade of Formula One racing, winning the World Drivers' Championship five times.
Kali Uchis, American singer-songwriter births

Karly-Marina Loaiza, known professionally as Kali Uchis, is an American singer. She released her debut mixtape, Drunken Babble, in 2012, which was followed by her debut EP, Por Vida, released in 2015. In 2018, Uchis released her debut studio album Isolation to widespread acclaim. Uchis's second studio album and her first Spanish language project, Sin Miedo , was released in 2020. The album spawned the single "Telepatía", which became Uchis' first solo charting hit on the US Billboard Hot 100. She won a Grammy Award for Best Dance Recording for her feature on Kaytranada's single "10%".
Jean Borotra, French tennis player (b. 1898) deaths

Jean Laurent Robert Borotra was a French tennis champion. He was one of the "Four Musketeers" from his country who dominated tennis in the late 1920s and early 1930s. Borotra was imprisoned in Itter Castle during the latter years of World War II and subsequently fought in the Battle for Castle Itter.
John Patrick Spiegel, American psychiatrist and academic (b. 1911) deaths
John Paul Spiegel was an American psychiatrist, and expert on violence and combat stress and the 103rd President of the American Psychiatric Association (APA). As president-elect of the APA in 1973, he helped to change the definition of homosexuality in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) which had previously described homosexuality as sexual deviance and that homosexuals were pathological.
Itubwa Amram, Nauruan pastor and politician (b. 1922) deaths
The Reverend Alfred Itubwa Amram was a Nauruan pastor and political figure.
Bruiser Brody, American football player and wrestler (b. 1946) deaths

Frank Donald Goodish was an American professional wrestler who earned his greatest fame under the ring name Bruiser Brody. He also worked as King Kong Brody, The Masked Marauder, and Red River Jack. Over the years Brody became synonymous with the hardcore wrestling brawling style that often saw one or more of the participants bleeding by the time the match was over. In his prime he worked as a "special attraction" wrestler in North America, making select appearances for various promotions such as World Class Championship Wrestling (WCCW), World Wide Wrestling Federation (WWWF), Central States Wrestling (CSW), Championship Wrestling from Florida (CWF), and the American Wrestling Association (AWA) among others. He worked regularly in Japan for All Japan Pro Wrestling (AJPW).
Darius Boyd, Australian rugby league player births

Darius Boyd is a former Australian professional rugby league footballer who played fullback, wing, centre and five-eighth for the Brisbane Broncos in the NRL and has played for Australia at international level and State of Origin for Queensland. Boyd captained the Brisbane Broncos from 2017 to 2019.
Jeremih, American singer, songwriter, and record producer births

Jeremy Phillip Felton, known professionally as Jeremih, is an American singer and record producer. In 2009, he signed a record deal with Def Jam Recordings. Jeremih's commercial debut single, "Birthday Sex", peaked at number four on the US Billboard Hot 100 chart—leading his self-titled debut album released in June that year, reaching number six on the US Billboard 200 chart. Jeremih's success continued with the release of his second album, All About You, led by the single "Down on Me", which also reached the top five of the Billboard Hot 100. In 2014, his single "Don't Tell 'Em" became his third top-ten hit on the Billboard Hot 100. The song became the lead single for his third studio album, Late Nights released in December 2015. A collaborative album between Jeremih and California singer Ty Dolla Sign, titled MihTy, was released in 2018.
DeAngelo Smith, American football player births
DeAngelo Lamar Smith is a former American football safety in the National Football League for the Cleveland Browns, Chicago Bears and Detroit Lions. He was drafted by the Dallas Cowboys in the fifth round of the 2009 NFL Draft. He played college football at the University of Cincinnati.
Loui Eriksson, Swedish ice hockey player births

Loui William Eriksson is a Swedish professional ice hockey forward currently playing for Frölunda HC of the Swedish Hockey League (SHL).
Neil McGregor, Scottish footballer births

Neil McGregor, is a Scottish football defender who has previously played in the Scottish Premier League for Dundee.
Adam Lind, American baseball player births

Adam Alan Lind is an American former professional baseball first baseman. He previously played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Toronto Blue Jays, Milwaukee Brewers, Seattle Mariners and Washington Nationals. Lind has also appeared as a designated hitter and in left field. In 2009, Lind won the Silver Slugger Award and the Edgar Martínez Award.
Omari Banks, Anguillan cricketer births

Omari Ahmed Clement Banks is an Anguillan musician and former cricketer, who appeared in 10 Test matches for the West Indies, as well as domestic matches for the Leeward Islands. In 2011, Banks began to pursue his musical career professionally and has been less involved in playing regional cricket, and officially retired from cricket on 31 January 2012.
Hely Ollarves, Venezuelan runner births
Hely Domingo Ollarves Arias is a male track and field athlete from Venezuela. He competed in the men's 4x100 metres relay at the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney, Australia, where he was eliminated in the first round alongside José Carabalí, Juan Morillo, and José Peña.
Javier Camuñas, Spanish footballer births
Javier Camuñas Gallego is a Spanish retired professional footballer. A versatile midfielder, he could also appear as a second striker.
Brett Goldstein, British actor, comedian and writer births

Brett Goldstein is a British actor, comedian, and writer. He is best known for writing and starring in the Apple TV+ sports comedy series Ted Lasso (2020–present), for which he received the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Comedy Series for each of the first two seasons.
Ryan Miller, American ice hockey player births

Ryan Dean Miller is an American former ice hockey goaltender who played 18 seasons in the National Hockey League (NHL) mostly for the Buffalo Sabres. Miller was drafted 138th overall by the Buffalo Sabres in the 1999 NHL Entry Draft. In 2010, he won the Vezina Trophy as the league's best goaltender. On February 17, 2019, Miller became the winningest American-born goaltender in NHL history, surpassing John Vanbiesbrouck.
Don "Red" Barry, American actor and screenwriter (b. 1912) deaths

Donald Barry de Acosta, also known as Red Barry and Milton Poimboeuf, was an American film and television actor. He was nicknamed "Red" after appearing as the first Red Ryder in the highly successful 1940 film Adventures of Red Ryder with Noah Beery Sr.; the character was played in later films by "Wild Bill" Elliott and Allan Lane. Barry went on to bigger budget films following Red Ryder, but none reached his previous level of success. He played Red Doyle in the 1964 Perry Mason episode 'The Case of the Simple Simon'.
Boris Delaunay, Russian mathematician and academic (b. 1890) deaths

Boris Nikolayevich Delaunay or Delone was a Soviet and Russian mathematician, mountain climber, and the father of physicist, Nikolai Borisovich Delone.
Mike Vogel, American actor births

Michael James Vogel is an American actor and former model. Vogel began acting in 2001 and has appeared in several films and series, including The Texas Chainsaw Massacre, The Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants, Grind, Poseidon, Blue Valentine, The Help, Bates Motel, Cloverfield, Under the Dome and The Case for Christ. He starred as the lead in the NBC military drama series The Brave for the 2017–18 season.
Ricardo Arona, Brazilian mixed martial artist births
Ricardo Arona is a retired Brazilian mixed martial artist. A professional from 2000 until 2009, he competed in PRIDE Fighting Championships and RINGS in his mixed martial arts career, and was a member of Brazilian Top Team. He is the former RINGS Middleweight Champion, as well as the 2001 RINGS Middleweight Championship Tournament Winner, and 2005 PRIDE Middleweight Grand Prix Runner-Up. In submission wrestling, he holds an undefeated record of 13–0, never losing a single point in a match, and is a four-time ADCC Champion. These achievements are what led to Arona being part of the inaugural class inducted into the ADCC Hall of Fame. He has notable wins in both MMA and submission grappling competition over Tito Ortiz, Jeff Monson, Renato Sobral, Vitor Belfort, Mark Kerr, Kazushi Sakuraba, Wanderlei Silva, Dan Henderson, Alistair Overeem, Murilo Rua, Jeremy Horn, Guy Mezger, and Dean Lister.
Panda Bear, American musician and songwriter births

Noah Benjamin Lennox, also known by his moniker Panda Bear, is an American musician, singer-songwriter, multi-instrumentalist, and co-founding member of the band Animal Collective. In addition to his work with that group, Lennox has released six solo LPs since 1999, with his influential 2007 album Person Pitch inspiring numerous subsequent acts. His subsequent albums Tomboy (2011) and Panda Bear Meets the Grim Reaper (2015) both reached the Billboard 200.
Jason Jennings, American baseball player births

Jason Ryan Jennings is an American former professional baseball pitcher. He pitched in Major League Baseball with the Colorado Rockies (2001-2006), Houston Astros (2007) and Texas Rangers (2008-2009).
Andrew Downton, Australian cricketer births
Andrew Graham Downton is an Australian cricketer, who played for the Tasmanian Tigers. He plays club cricket for South Hobart/Sandy Bay Cricket Club.
Leif Hoste, Belgian cyclist births

Leif Hoste is a retired Belgian professional road racing cyclist, who last rode for UCI Professional Continental Team team Accent.jobs–Willems Veranda's. Born in Kortrijk, Hoste's career highlights included winning two stages and the overall title at the 2006 Three Days of De Panne, the 2001, 2006 and 2007 Belgian national time trial championships, and a second-place finish at the 2004, 2006 and 2007 one-day classic Tour of Flanders.
Marc Savard, Canadian ice hockey player births

Marc Savard is a Canadian former professional ice hockey centre and current head coach of the Windsor Spitfires of the Ontario Hockey League (OHL). He played in the National Hockey League (NHL) for the New York Rangers, Calgary Flames, Atlanta Thrashers and Boston Bruins. He was an assistant coach for the St. Louis Blues during the 2019–20 season.
Luke Bryan, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Thomas Luther "Luke" Bryan is an American country singer, songwriter, and television personality. He began his music career writing songs for Travis Tritt and Billy Currington before signing with Capitol Nashville in 2007. He is one of the most successful and awarded country artists of the 2010s and 2020s.
Gino D'Acampo, Italian chef and author births

Gennaro Sheffield D'Acampo is an Italian celebrity chef and media personality based in the United Kingdom, best known for his food-focused television shows and cookbooks.
Dagmara Domińczyk, Polish-American actress births

Dagmara Domińczyk is a Polish-American actress and author. She has appeared in the films Rock Star (2001), The Count of Monte Cristo (2002), Kinsey (2004), Trust the Man (2005), Lonely Hearts (2006), Running with Scissors (2006), Higher Ground (2011), The Letter (2012), The Immigrant (2013), Big Stone Gap (2014), A Woman, a Part (2016), The Assistant (2019), and The Lost Daughter (2021). Domińczyk also has a main role in the HBO comedy-drama television series Succession (2018–present).
Marcos Senna, Brazilian-Spanish footballer births

Marcos Antônio Senna da Silva, known as Senna, is a retired professional footballer who played as a central midfielder.
Anders Svensson, Swedish footballer and sportscaster births

Anders Gunnar Svensson is a Swedish former professional footballer. He was a central midfielder, known for his passing, free kicks, and set piece-taking abilities, who usually operated in a playmaking role. He was capped 148 times for the Swedish national football team, many times as a captain, before he retired from international football in 2013. He is the most capped male player for Sweden, beating Thomas Ravelli's previous record of 143 caps.
Eric Winter, American actor births

Eric Barrett Winter is an American actor and former fashion model. He has appeared in the television roles of Rex Brady on the NBC soap opera Days of our Lives, FBI Special Agent Craig O'Laughlin on the CBS drama series The Mentalist (2010–2012), Dash Gardiner on the Lifetime fantasy-drama series Witches of East End (2013–2014), and Sergeant Tim Bradford on the ABC drama The Rookie. His film appearances include Harold & Kumar Escape from Guantanamo Bay (2008) and The Ugly Truth (2009).
Andre Adams, New Zealand cricketer births

Andre Ryan Adams is a New Zealand cricket coach and former cricketer of Caribbean descent.
Elena Anaya, Spanish actress births

Elena Anaya Gutiérrez is a Spanish actress.
Darude, Finnish DJ and producer births

Toni-Ville Henrik Virtanen, better known by his stage name Darude, is a Finnish DJ and record producer from Eura, Satakunta. His music is characterised by its progressive/uplifting style. He started making music in 1995 and released the platinum-selling hit single "Sandstorm" in late 1999. His debut studio album, Before the Storm, was released on September 18, 2000 and sold 800,000 copies worldwide, earning Darude three Finnish Grammy Awards. It peaked at number one on Finland's Official List and number 6 on the Billboard Dance/Electronic Albums chart in the United States. Darude's second studio album, Rush, reached number 11 on the Billboard dance chart in 2003 and number 4 on weekly album chart in Finland.
Harlette, Australian-English fashion designer births
Harlette De Falaise is an Australian and British designer, media personality and entrepreneur, best known for her work in Britain and Saudi Arabia.
Loretta Harrop, Australian triathlete births
Loretta "Loz" Harrop is an Australian triathlete.
Konnie Huq, English television presenter births

Kanak Asha "Konnie" Huq is a British television and radio presenter, screenwriter and children's author. She became the longest-serving female presenter of the British children's television programme Blue Peter, presenting it from 1997 to 2008. She has been a presenter and guest of shows including the 2010 series of The Xtra Factor on ITV2.
Terence Tao, Australian-American mathematician births

Terence Chi-Shen Tao is an Australian mathematician. He is a professor of mathematics at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), where he holds the James and Carol Collins chair. His research includes topics in harmonic analysis, partial differential equations, algebraic combinatorics, arithmetic combinatorics, geometric combinatorics, probability theory, compressed sensing and analytic number theory.
Konstantine Gamsakhurdia, Georgian author (b. 1893) deaths

Konstantine Gamsakhurdia was a Georgian writer and public figure. Educated and first published in Germany, he married Western European influences to purely Georgian thematic to produce his best works, such as The Right Hand of the Grand Master and David the Builder. Hostile to the Soviet rule, he was, nevertheless, one of the few leading Georgian writers to have survived the Stalin-era repressions, including his exile to a White Sea island and several arrests. His works are noted for their character portrayals of great psychological insight. Another major feature of Gamsakhurdia's writings is a new subtlety he infused into Georgian diction, imitating an archaic language to create a sense of classicism.
Claudio López, Argentine footballer births

Claudio Javier López is an Argentine former footballer, who played as a forward. Nicknamed Piojo (louse), he is best known for his spells with Valencia in Spain and Lazio in Italy. López also had a notable impact in the Argentina national team, participating in two World Cups.
Dizzy Dean, American baseball player and sportscaster (b. 1910) deaths

Jay Hanna "Dizzy" Dean, also known as Jerome Herman Dean, was an American professional baseball pitcher. During his Major League Baseball (MLB) career, he played for the St. Louis Cardinals, Chicago Cubs, and St. Louis Browns.
Eric Moulds, American football player births

Eric Shannon Moulds is a former American football wide receiver who played 12 seasons in the National Football League (NFL). He played college football for Mississippi State University and was drafted by the Buffalo Bills 24th overall in the 1996 NFL Draft. In 2009, Moulds was one of three receivers named to the Buffalo Bills 50th Anniversary All-Time Team.
Elizabeth Cook, American singer and guitarist births

Elizabeth Cook is an American country music singer and radio host. She has made over 400 appearances on the Grand Ole Opry since her debut on March 17, 2000, despite not being a member. Cook, "the daughter of a hillbilly singer married to a moonshiner who played his upright bass while in a prison band", was "virtually unknown to the pop masses" before she made a debut appearance on the Late Show with David Letterman in June 2012. The New York Times called her "a sharp and surprising country singer" and an "idiosyncratic traditionalist".
Donny Marshall, American basketball player and sportscaster births
Donny Marshall is an American former professional basketball player who played five seasons in the National Basketball Association (NBA) for the Cleveland Cavaliers and New Jersey Nets. He is currently a college basketball television analyst for Fox Sports 1, Westwood One National Radio and CBSSN.
Jason Rullo, American drummer births

Jason Rullo is an American drummer, who is one of the founding members of progressive metal band Symphony X.
Jaap Stam, Dutch footballer and manager births

Jakob Stam is a Dutch professional football coach and former player. As a player, he played as a centre-back and is regarded as one of the best defenders of his generation.
Eric Williams, American basketball player births
Eric C. Williams is an American former professional basketball player who played in the National Basketball Association (NBA) from 1995 to 2007. He played for seven teams during his career, including two stints with the Boston Celtics.
Calbert Cheaney, American basketball player and coach births

Calbert Nathaniel Cheaney is an American basketball coach and former player who serves as assistant coach for the Indiana Pacers of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He starred as a player for the Indiana Hoosiers from 1989–93 under coach Bob Knight. Cheaney ended his career as a three-time All-American and remains the Big Ten's all-time leading scorer with 2,613 career points. He led Indiana to a 105–27 record and the NCAA Tournament all four years, including a Final Four appearance in 1992.
Cory Doctorow, Canadian author and activist births

Cory Efram Doctorow is a Canadian-British blogger, journalist, and science fiction author who served as co-editor of the blog Boing Boing. He is an activist in favour of liberalising copyright laws and a proponent of the Creative Commons organization, using some of their licences for his books. Some common themes of his work include digital rights management, file sharing, and post-scarcity economics.
Nico Mattan, Belgian cyclist births

Nico Mattan is a Belgian former road racing cyclist. His greatest achievement in cycling was winning the Gent–Wevelgem classic in 2005.
Scott Johnson, American cartoonist births

Scott Blaine Johnson is an American cartoonist, illustrator, game designer, and podcaster. He lives in South Jordan, Utah, with his wife and three children. In 2008, Johnson launched Frog Pants Studios, LLC, an illustration and audio production company.
Jaan Kirsipuu, Estonian cyclist births

Jaan Kirsipuu is an Estonian former road bicycle racer, who currently works as a directeur sportif for UCI Continental team Team Ampler–Tartu2024.
John Coltrane, American saxophonist and composer (b. 1926) deaths

John William Coltrane was an American jazz saxophonist, bandleader and composer. He is among the most influential and acclaimed figures in the history of jazz and 20th-century music.
Lou Barlow, American guitarist and songwriter births

Louis Knox Barlow is an American alternative rock musician and songwriter. A founding member of the groups Dinosaur Jr., Sebadoh and The Folk Implosion, Barlow is credited with helping to pioneer the lo-fi style of rock music in the late 1980s and early 1990s. His first band, which was formed in Amherst, Massachusetts, was Deep Wound. Barlow was born in Dayton, Ohio, and raised in Jackson, Michigan, and Westfield, Massachusetts.
Sten Tolgfors, Swedish lawyer and politician, 30th Swedish Minister of Defence births

Sten Sture Tolgfors is a Swedish former politician, public affairs executive and government official who is serving as Governor of Västra Götaland County since 1 September 2022, having been appointed to the position on 9 June 2022.

The Minister for Defence of Sweden is a member of the Government of Sweden. The Minister heads the Ministry for Defence and is appointed and dismissed at the sole discretion of the prime minister of Sweden.
Craig Morgan, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Craig Morgan Greer is an American country music artist. A veteran of the United States Army as a forward observer, Morgan began his musical career in 2000 on Atlantic Records, releasing his self-titled debut album for that label before the closure of its Nashville division in 2000. In 2002, Morgan signed to the independent Broken Bow Records, on which he released three studio albums: 2003's I Love It, 2005's My Kind of Livin', and 2006's Little Bit of Life. These produced several chart hits, including "That's What I Love About Sunday", which spent four weeks at the top of the Billboard country charts while also holding the No. 1 position on that year's Billboard Year-End chart for the country format. A greatest hits package followed in mid-2008 before Morgan signed to BNA Records and released That's Why later that same year. After exiting BNA, Morgan signed with Black River Entertainment and released This Ole Boy in 2012, followed by A Whole Lot More to Me in 2016.
Alex Winter, English-American actor, film director and screenwriter births

Alexander Ross Winter is a British-American actor and filmmaker. He played the slacker Bill in the 1989 film Bill & Ted's Excellent Adventure and its sequels Bill & Ted's Bogus Journey (1991) and Bill & Ted Face the Music (2020). He is also known for his role as Marko in the 1987 vampire film The Lost Boys; for co-writing, co-directing, and starring in the 1993 film Freaked; and for directing documentaries in the 2010s.
Heather Langenkamp, American actress and producer births

Heather Elizabeth Langenkamp is an American actress. She is considered an influential figure in horror films and in popular culture, noted for her acting in several works of the genre and her behind-the-scenes work coordinating prosthetic makeup. She is established as a scream queen, and was inducted into the Fangoria Chainsaw Hall of Fame in 1995.
Regina Belle, American singer-songwriter, producer, and actress births

Regina Elaine Belle is an American singer-songwriter who started her career in the mid-1980s. Known for her singles "Baby Come to Me" (1989) and "Make It Like It Was" (1990), Belle's most notable for two hit duets, both with Peabo Bryson: "Without You", the love theme from the comedy film Leonard Part 6, recorded in 1987 and "A Whole New World", the main theme of the Disney's animated feature film Aladdin, recorded in 1992, with which Belle and Bryson won the Grammy award. The theme song "Far Longer than Forever" from the animated movie The Swan Princess, performed with Jeffrey Osborne, was nominated for a Golden Globe in 1995 for Best Original Song.
Letsie III of Lesotho births

Letsie III is King of Lesotho. He succeeded his father, Moshoeshoe II, who was forced into exile in 1990. His father was briefly restored in 1995 but died in a car crash in early 1996, and Letsie became king again. As a constitutional monarch, most of King Letsie's duties as monarch of Lesotho are ceremonial. In 2000, he declared HIV/AIDS in Lesotho to be a natural disaster, prompting immediate national and international response to the epidemic.
Matti Nykänen, Finnish ski jumper and singer (d. 2019) births

Matti Ensio Nykänen was a Finnish ski jumper who competed from 1981 to 1991. Widely considered to be the greatest male ski jumper of all time, he won five Winter Olympic medals, nine World Championship medals, and 22 Finnish Championship medals. Most notably, he won three gold medals at the 1988 Winter Olympics, becoming, along with Yvonne van Gennip of the Netherlands, the most medaled athlete that winter.
António Costa, Portuguese politician, 119th Prime Minister of Portugal births

António Luís Santos da Costa GCIH is a Portuguese lawyer and politician serving as the 119th and current prime minister of Portugal since 26 November 2015, presiding over the XXI (2015–2019), XXII (2019–2022) and XXIII Constitutional Governments (2022–present). Previously, he was the secretary of state for parliamentary affairs from 1995 to 1997, minister of parliamentary affairs from 1997 to 1999, minister of justice from 1999 to 2002, minister of internal administration from 2005 to 2007, and mayor of Lisbon from 2007 to 2015. He was elected as secretary general of the Socialist Party in September 2014.

The prime minister of Portugal is the head of government of Portugal. As head of government, the prime minister coordinates the actions of ministers, represents the Government of Portugal to the other bodies of state, is accountable to parliament and keeps the president informed. The prime minister can hold the role of head of government with the portfolio of one or more ministries.
Jeremy Hardy, English comedian and actor (d. 2019) births

Jeremy James Hardy was an English comedian. Born and raised in Hampshire, Hardy studied at the University of Southampton and began his stand-up career in the 1980s, going on to win the Perrier Comedy Award at the Edinburgh Festival Fringe in 1988. He is best known for his appearances on radio panel shows such as the News Quiz and I'm Sorry I Haven't a Clue.
Ty Cobb, American baseball player and manager (b. 1886) deaths

Tyrus Raymond Cobb, nicknamed "the Georgia Peach", was an American Major League Baseball (MLB) center fielder. He was born in rural Narrows, Georgia. Cobb spent 22 seasons with the Detroit Tigers, the last six as the team's player-manager, and finished his career with the Philadelphia Athletics. In 1936, Cobb received the most votes of any player on the inaugural ballot for the National Baseball Hall of Fame, receiving 222 out of a possible 226 votes (98.2%); no other player received a higher percentage of votes until Tom Seaver in 1992. In 1999, the Sporting News ranked Cobb third on its list of "Baseball's 100 Greatest Players."
Emin Halid Onat, Turkish architect and academic (b. 1908) deaths
Emin Halid Onat was a Turkish architect and former rector of Istanbul Technical University.
Kim Barnett, English cricketer and coach births
Kim John Barnett is a former English cricketer. Barnett was a batsman who played internationally for England between 1988 and 1989.
Mark Burnett, English-American screenwriter and producer births

Mark Burnett is a television producer who is the former Chairman of MGM Worldwide Television Group. He is best known for creating and producing the reality shows The Apprentice, Survivor, The Voice, and Shark Tank.
Nancy Giles, American journalist and actress births

Nancy Giles is an American actress and commentator, perhaps best known for her appearances in the series China Beach and on CBS News Sunday Morning.
Robin Shou, Hong Kong martial artist and actor births

Shou Wan-por, known professionally as Robin Shou, is a Hong Kong-American actor, martial artist and stuntman. He is known for roles such as Liu Kang in the Mortal Kombat film series, Gobei in Beverly Hills Ninja (1997), Gen in Street Fighter: The Legend of Chun-Li (2009), and 14K in the Death Race films (2008-2013). Shou was also a Hong Kong action star in the late 1980s and early 1990s and has appeared in about 40 movies during his Hong Kong career before he entered Hollywood in 1994.
Dawn Upshaw, American soprano births
Dawn Upshaw is an American soprano. She is the recipient of several Grammy Awards and has released a number of Edison Award-winning discs; she performs both opera and art song, and her repertoire spans Baroque to contemporary. Many composers, including Henri Dutilleux, Osvaldo Golijov, John Harbison, Esa-Pekka Salonen, John Adams, and Kaija Saariaho, have written for her. In 2007, she was awarded a MacArthur Fellowship.
Jan Wouters, Dutch footballer and manager births

Jan Jacobus Wouters is a Dutch professional football coach and former player. He played as a defensive midfielder and was Dutch Footballer of the Year in 1990.
Maud Menten, Canadian physician and biochemist (b. 1879) deaths

Maud Leonora Menten was a Canadian physician and chemist. As a bio-medical and medical researcher, she made significant contributions to enzyme kinetics and histochemistry and invented a procedure that remains in use. She is primarily known for her work with Leonor Michaelis on enzyme kinetics in 1913. The paper has been translated from its original German into English.
Pola Uddin, Baroness Uddin, Bangladeshi-English politician births

Manzila Pola Khan Uddin, Baroness Uddin, is a British non-affiliated life peer and community activist of Bangladeshi descent. In 2009 she was included on The Guardian's Muslim Women Power List for Britain. She previously sat for Labour when, in 2012, Uddin was required to repay £125,349, the largest amount in the United Kingdom parliamentary expenses scandal.
Billie Holiday, American singer (b. 1915) deaths

Billie Holiday was an American jazz and swing music singer. Nicknamed "Lady Day" by her friend and music partner, Lester Young, Holiday had an innovative influence on jazz music and pop singing. Her vocal style, strongly inspired by jazz instrumentalists, pioneered a new way of manipulating phrasing and tempo. She was known for her vocal delivery and improvisational skills.
Eugene Meyer, American businessman and publisher (b. 1875) deaths

Eugene Isaac Meyer was an American financier and newspaper publisher. Through his public career, he served as the 5th chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1930 to 1933 and was the first president of the World Bank Group from June to December 1946. Meyer published The Washington Post from 1933 to 1946, and the paper stayed in his family throughout the rest of the 20th century.
Wong Kar-wai, Chinese director, producer, and screenwriter births

Wong Kar-wai is a Hong Kong film director, screenwriter, and producer. His films are characterised by nonlinear narratives, atmospheric music, and vivid cinematography involving bold, saturated colours. A pivotal figure of Hong Kong cinema, Wong is considered a contemporary auteur, and ranks third on Sight & Sound's 2002 poll of the greatest filmmakers of the previous 25 years. His films frequently appear on best-of lists domestically and internationally.
Suzanne Moore, English journalist births

Suzanne Lynn Moore is an English journalist.
Susan Silver, American music manager births
Susan Jean Silver is an American music manager, best known for managing Seattle rock bands such as Soundgarden, Alice in Chains and Screaming Trees. Silver also owns the company Susan Silver Management, and co-owns the club The Crocodile in Seattle. Silver was named "the most powerful figure in local rock management" by The Seattle Times in 1991.
Thérèse Rein, Australian businesswoman, founded Ingeus births

Thérèse Virginia Rein is an Australian entrepreneur who is the founder of Ingeus, an international employment and business psychology services company.

Ingeus Limited is a British-based, Australian provider of employment and health programmes, services for young people, training and skills support, Labour hire and probation services.
Bruce Crump, American drummer and songwriter (d. 2015) births

Bruce Hull Crump, Jr. was the drummer with the rock band Molly Hatchet from 1976 to 1982 and 1984 to 1991. He also played as a member of the Canadian band Streetheart in the early 1980s, appearing on their Live After Dark recording, and joined several of his former Molly Hatchet bandmates in the band Gator Country in the mid-2000s. At his death, Crump was in the Jacksonville, Florida-based band White Rhino and the newly reformed China Sky.
Wendy Freedman, Canadian-American cosmologist and astronomer births

Wendy Laurel Freedman is a Canadian-American astronomer, best known for her measurement of the Hubble constant, and as director of the Carnegie Observatories in Pasadena, California, and Las Campanas, Chile. She is now the John & Marion Sullivan University Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago. Her principal research interests are in observational cosmology, focusing on measuring both the current and past expansion rates of the universe, and on characterizing the nature of dark energy.
Julie Bishop, Australian lawyer and politician, 38th Australian Minister for Foreign Affairs births

Julie Isabel Bishop is an Australian former politician who served as Minister for Foreign Affairs from 2013 to 2018 and deputy leader of the Liberal Party from 2007 to 2018. She was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Curtin from 1998 to 2019. She has been the chancellor of the Australian National University since January 2020.

The Minister for Foreign Affairs is the minister in the Government of Australia who is responsible for overseeing the international diplomacy section of the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Senator Penny Wong was appointed as Foreign Minister in the ministry led by Prime Minister Anthony Albanese in May 2022 following the 2022 Australian federal election. As the first female foreign minister from the Australian Labor Party, Wong also became the third female foreign minister in a row, following Julie Bishop and Marise Payne. The Foreign Minister is one of two cabinet-level portfolio ministers under the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, the other being the Minister for Trade and Tourism Senator Don Farrell.
Bryan Trottier, Canadian-American ice hockey player and coach births

Bryan John Trottier is a Canadian-American former professional ice hockey centre who played 18 seasons in the National Hockey League (NHL) for the New York Islanders and Pittsburgh Penguins. He won four Stanley Cups with the Islanders, two with the Penguins and one as an assistant coach with the Colorado Avalanche. He shares the NHL record for points in a single period with six in the second period against the Rangers on December 23, 1978. He is also one of only eight NHL players with multiple five-goal games. On August 4, 2014, Trottier was announced as an assistant coach for the Buffalo Sabres. In 2017 Trottier was named one of the "100 Greatest NHL Players" in history.
Sylvie Léonard, Canadian actress and screenwriter births

Sylvie Léonard is a French-Canadian actress. She has acted in theater, film and television for over 40 years. Her most notable roles include Mimi Jarry in Rue des Pignons, Annick Jacquemin in Terre Humaine, Julie Galarneau in L'Héritage, Sylvie in Un gars, une fille and most recently Madeleine in Lâcher prise.
Paul Stamets, American mycologist and author births

Paul Edward Stamets is an American mycologist and entrepreneur who sells various mushroom products through his company. He is an author and advocate of medicinal fungi and mycoremediation.
Angela Merkel, German chemist and politician, Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. births

Angela Dorothea Merkel is a German former politician and scientist who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), she previously served as Leader of the Opposition from 2002 to 2005 and as Leader of the Christian Democratic Union from 2000 to 2018. Merkel was the first female chancellor of Germany. During her tenure as Chancellor, Merkel was frequently referred to as the de facto leader of the European Union (EU), the most powerful woman in the world, and since 2016 the leader of the free world.

The chancellor of Germany, officially the federal chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany, is the head of the federal government of Germany and the commander in chief of the German Armed Forces during wartime. The chancellor is the chief executive of the Federal Cabinet and heads the executive branch. The chancellor is elected by the Bundestag on the proposal of the federal president and without debate.
Edward Natapei, Vanuatuan politician, 6th Prime Minister of Vanuatu (d. 2015) births

Edward Nipake Natapei Tuta Fanua`araki was a Vanuatuan politician. He was the prime minister of Vanuatu on two occasions, and was previously the minister of Foreign Affairs briefly in 1991, the acting president of Vanuatu from 2 March 1999 to 24 March 1999 and the deputy prime minister. He was the president of the Vanua'aku Pati, a socialist, Anglophone political party.

The prime minister of Vanuatu is the head of government of the Republic of Vanuatu.
J. Michael Straczynski, American author, screenwriter, and producer births

Joseph Michael Straczynski is an American filmmaker and comic book writer. He is the founder of Synthetic Worlds Ltd. and Studio JMS and is best known as the creator of the science fiction television series Babylon 5 (1993–1998) and its spinoff Crusade (1999), as well as the series Jeremiah (2002–2004) and Sense8 (2015–2018). He is also the executor of the estate of Harlan Ellison.
David Hasselhoff, American actor, singer, and producer births

David Michael Hasselhoff, nicknamed "The Hoff", is an American actor, singer, and television personality. He has set a Guinness World Record as the most watched man on TV. Hasselhoff first gained recognition on The Young and The Restless (1975–1982), playing the role of Dr. Snapper Foster. His career continued with his leading role as Michael Knight on Knight Rider (1982–1986) and as L.A. County Lifeguard Mitch Buchannon in Baywatch (1989–2000). He also produced Baywatch from the 1990s until 2001 when the series ended with Baywatch Hawaii.
Nicolette Larson, American singer-songwriter (d. 1997) births

Nicolette Larson was an American singer. She is perhaps best known for her work in the late 1970s with Neil Young and her 1978 hit single of Young's "Lotta Love", which hit No. 1 on the Hot Adult Contemporary Tracks chart and No. 8 on the pop singles chart. It was followed by four more adult contemporary hits, two of which were also minor pop hits.
Thé Lau, Dutch singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 2015) births

Matheus J. "Thé" Lau was a Dutch musician and writer. Besides his solo career, he was the lead singer of the Dutch band The Scene. He was born in Bergen, North Holland.
Robert R. McCammon, American author births
Robert Rick McCammon is an American novelist from Birmingham, Alabama. One of the influential names in the late 1970s–early 1990s American horror literature boom, by 1991 McCammon had three New York Times bestsellers and around 5 million books in print. Since 2002 he’s written several books in a historical mystery series featuring a 17th-century magistrate’s clerk, Matthew Corbett, as he unravels mysteries in colonial America.
Lucie Arnaz, American actress and singer births

Lucie Désirée Arnaz is an American actress and singer. She is the daughter of actors Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz.
Mark Bowden, American journalist and author births

Mark Robert Bowden is an American journalist and writer. He is a national correspondent for The Atlantic. He is best known for his book Black Hawk Down: A Story of Modern War (1999) about the 1993 U.S. military raid in Mogadishu, Somalia. It was adapted as a motion picture of the same name that received two Academy Awards.
Andrew Robathan, English soldier and politician, Minister of State for the Armed Forces births

Andrew Robert George Robathan, Baron Robathan, is a British Conservative politician, who served as Member of Parliament (MP) for South Leicestershire in Leicestershire as well as a government minister.

The minister of state for the armed forces, is a junior ministerial position at the Ministry of Defence in the Government of the United Kingdom.
Phoebe Snow, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 2011) births

Phoebe Snow was an American roots music singer-songwriter and guitarist, known for her 1974 and 1975 songs "San Francisco Bay Blues", "Poetry Man"(hit song), "Harpo's Blues", and her credited guest vocals backing Paul Simon on "Gone at Last". She recorded "San Francisco Bay Blues" also. She was described by The New York Times as a "contralto grounded in a bluesy growl and capable of sweeping over four octaves." Snow also sang numerous commercial jingles for many U.S. products during the 1980s and 1990s, including General Foods International Coffees, Salon Selectives, and Stouffer's. Snow experienced success in Australia in the late 1970s and early 1980s with five top 100 albums in that territory. In 1995 she recorded a gospel album with Sisters of Glory.
Tengku Sulaiman Shah, Malaysian corporate figure births

Tengku Sulaiman Shah Al-Haj ibni Almarhum Sultan Salahuddin Abdul Aziz Shah Al-Haj is a Malaysian corporate figure and a member of the Selangor Royal Family. He is the second son of eighth Sultan, Sultan Salahuddin Abdul Aziz Shah and the brother of the current Sultan, Sultan Sharafuddin Idris Shah.
Sadhan Chandra Majumder, Bangladeshi politician births

Sadhan Chandra Majumder is a Bangladeshi politician serving as the Minister of Food since 2019 and Member of Jatiya Sangsad since 2008 for Naogaon-1 constituency. He is the first ever cabinet minister from Niamatpur Upazila.
Evangeline Booth, English 4th General of The Salvation Army (b. 1865) deaths

Evangeline Cory Booth, OF was a British evangelist and the 4th General of The Salvation Army from 1934 to 1939. She was the first woman to hold the post.

General is the title of the international leader and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the Salvation Army, a Christian denomination with extensive charitable social services that gives quasi-military rank to its ministers. The General is elected by the High Council of The Salvation Army and serves a term of five years, which may be extended to seven years. Brian Peddle, the current general, assumed the position in August 2018 upon the retirement of Andre Cox. The organisation's founder, William Booth, was the first and longest-serving general. There have been 21 generals as of 2018.
Antonie Nedošinská, Czech actress (b. 1885) deaths

Antonie Nedošinská was a Czechoslovak film actress. She appeared in 89 films between 1916 and 1947.
Geezer Butler, English bass player and songwriter births

Terence Michael Joseph "Geezer" Butler is a British musician and songwriter. He is best known as the bassist and primary lyricist of the heavy metal band Black Sabbath. He has also recorded and performed with Heaven & Hell, GZR, and Ozzy Osbourne. Butler was the bassist of Deadland Ritual, which has since disbanded.
Charley Steiner, American journalist and sportscaster births

Charley Steiner is an American sportscaster and broadcast journalist. He is currently the radio play-by-play announcer for the Major League Baseball's Los Angeles Dodgers, paired with Rick Monday.
Ron Asheton, American guitarist and songwriter (d. 2009) births

Ronald Franklin Asheton was an American musician, who was best known as the guitarist, bassist, and co-songwriter for the rock band the Stooges. He formed the Stooges along with Iggy Pop and his brother, drummer Scott Asheton, and bassist Dave Alexander. Asheton, once ranked as number 29 on Rolling Stone's list of 100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time is currently ranked at number 60.
Luc Bondy, Swiss director and producer (d. 2015) births

Luc Bondy was a Swiss theatre and film director.
Joyce Anelay, Baroness Anelay of St John's, English educator and politician births

Joyce Anne Anelay, Baroness Anelay of St Johns,, is a British Conservative Party politician, previously serving as Minister of State of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office from August 2014 to June 2017. Anelay was appointed as Minister of State at the Department for Exiting the European Union in the Second May ministry, after the 2017 reshuffle.
Robert Begerau, German footballer and manager births
Robert Begerau is a former German footballer.
Camilla, Queen consort of the United Kingdom births

Camilla is Queen of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms as the wife of King Charles III. Camilla became queen consort on 8 September 2022, upon the accession of her husband following the death of his mother, Queen Elizabeth II.
Wolfgang Flür, German musician (Kraftwerk) births

Wolfgang Flür is a German musician, best known for playing percussion in the electronic group Kraftwerk from 1973 to 1987. Flür claims that he invented the electric drums the group used throughout the 1970s. However, patent records dispute this, citing Florian Schneider and Ralf Hütter as the creators.

Kraftwerk is a German band formed in Düsseldorf in 1970 by Ralf Hütter and Florian Schneider. Widely considered innovators and pioneers of electronic music, Kraftwerk were among the first successful acts to popularize the genre. The group began as part of West Germany's experimental krautrock scene in the early 1970s before fully embracing electronic instrumentation, including synthesizers, drum machines, and vocoders. Wolfgang Flür joined the band in 1974 and Karl Bartos in 1975, expanding the band to a quartet.
Mick Tucker, English rock drummer (Sweet) (d. 2002) births
Michael Thomas Tucker was an English musician, best known as the drummer and backing vocalist of the glam rock and hard rock band Sweet.

The Sweet, are a British glam rock band that rose to prominence in the 1970s. Their best known line-up consisted of lead vocalist Brian Connolly, bass player Steve Priest, guitarist Andy Scott, and drummer Mick Tucker. The group were originally called The Sweetshop.
Chris Crutcher, American novelist and short story writer births

Chris Crutcher is an American novelist and a family therapist. He received the Margaret A. Edwards Award from the American Library Association in 2000 for his lifetime contribution in writing for teens.
Ted Sampley, American POW/MIA activist (d. 2009) births

Theodore Lane Sampley was an American Vietnam War veteran and activist. He primarily advocated for those servicemembers still considered missing in action or prisoners of war (POW-MIA) as of the end of hostilities in 1975. A staunch political conservative, he also ran for local political office several times. He is credited with the research that identified Air Force Lt. Michael Blassie as the Vietnam fatality buried at the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, and for his role in organizing the annual Rolling Thunder motorcycle event in Washington. In Kinston, North Carolina, where he lived for much of his adult life, he was known for his local civic activism, most notably his effort to build a replica of the Confederate ironclad CSS Neuse, the only full-size replica of a Confederate ironclad, in the city's downtown.
Florence Fuller, South African-born Australian artist (b. 1867) deaths

Florence Ada Fuller was a South African-born Australian artist. Originally from Port Elizabeth, Fuller migrated as a child to Melbourne with her family. There she trained with her uncle Robert Hawker Dowling and teacher Jane Sutherland and took classes at the National Gallery of Victoria Art School, becoming a professional artist in the late 1880s. In 1892 she left Australia, travelling first to South Africa, where she met and painted for Cecil Rhodes, and then on to Europe. She lived and studied there for the subsequent decade, except for a return to South Africa in 1899 to paint a portrait of Rhodes. Between 1895 and 1904 her works were exhibited at the Paris Salon and London's Royal Academy.
Draža Mihailović, Serbian general (b. 1893) deaths

Dragoljub "Draža" Mihailović was a Yugoslav Serb general during World War II. He was the leader of the Chetnik Detachments of the Yugoslav Army (Chetniks), a royalist and nationalist movement and guerrilla force established following the German invasion of Yugoslavia in 1941.
Alexander, Crown Prince of Yugoslavia births

Alexander, Crown Prince of Yugoslavia, is the head of the House of Karađorđević, the former royal house of the defunct Kingdom of Yugoslavia and its predecessor the Kingdom of Serbia. Alexander is the only child of King Peter II and his wife, Princess Alexandra of Greece and Denmark. He held the position of crown prince in the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia for the first four-and-a-half months of his life, from his birth until the declaration of the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia later in 1945. In public he is also claiming the crowned royal title of "Alexander II Karađorđević" although the kingdom was abolished.
John Patten, Baron Patten, English politician, Secretary of State for Education births
John Haggitt Charles Patten, Baron Patten, is a former Conservative Member of Parliament for Oxford West and Abingdon.

The secretary of state for education, also referred to as the education secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, responsible for the work of the Department for Education. The incumbent is a member of the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, 14th in the ministerial ranking.
Ernst Busch, German field marshal (b. 1885) deaths

Ernst Bernhard Wilhelm Busch was a German Generalfeldmarschall during World War II who commanded the 16th Army and later the massive Army Group Centre.
Mark Burgess, New Zealand cricketer and footballer births
Mark Gordon Burgess is a New Zealand former cricketer who captained the New Zealand cricket team from 1978 to 1980. He was a right-handed batsman, and bowled right-arm off-breaks. He played in New Zealand's first One Day International (ODI).
Catherine Schell, Hungarian-English actress births

Catherine Schell is a Hungarian-born actress who came to prominence in British film and television productions from the 1960s. Her notable roles include the Bond girl Nancy in On Her Majesty's Secret Service (1969), Lady Claudine Litton in The Return of the Pink Panther (1975), Countess Scarlioni in the Doctor Who serial City of Death (1979), and a regular role as Maya in Series Two of the television series Space: 1999 (1975).
Carlos Alberto Torres, Brazilian footballer and manager (d. 2016) births

Carlos Alberto "Capita" Torres, also known as "O Capitão do Tri", was a Brazilian football player and manager who played as an attacking right-sided full-back or wing-back. A technically gifted defender with good ball skills and defensive capabilities, he is widely regarded as one of the best defenders of all time. He also stood out for his leadership, and was an excellent penalty taker. Nicknamed O Capitão, he captained the Brazil national team to victory in the 1970 World Cup, scoring the fourth goal in the final, considered one of the greatest goals in the history of the tournament.
William James Sidis, American mathematician and anthropologist (b. 1898) deaths

William James Sidis was an American child prodigy with exceptional mathematical and linguistic skills. He is notable for his 1920 book The Animate and the Inanimate, in which he speculates about the origin of life in the context of thermodynamics.
LaVyrle Spencer, American author and educator births
LaVyrle Spencer is an American best-selling author of contemporary and historical romance novels. She has successfully published a number of books, with several of them made into movies. Twelve of her books have been New York Times bestsellers, and Spencer was inducted into the Romance Writers of America Hall of Fame in 1988. She retired from writing in 1997.
Don Kessinger, American baseball player and manager births

Donald Eulon Kessinger is an American former professional baseball player and manager. He played in Major League Baseball as a shortstop from 1964 to 1979, most prominently as a member of the Chicago Cubs where, he was a six-time All-Star player and a two-time Gold Glove Award winner. He ended his career playing for the St. Louis Cardinals and the Chicago White Sox.
Gale Garnett, New Zealand–born Canadian singer births

Gale Zoë Garnett is a New Zealand–born Canadian singer best known in the United States for her self-penned, Grammy-winning folk hit "We'll Sing in the Sunshine". Garnett has since carved out a career as an author and actress.
Connie Hawkins, American basketball player (d. 2017) births

Cornelius Lance "Connie" Hawkins was an American professional basketball player. A New York City playground legend, "the Hawk" was inducted into the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame in 1992.
Zoot Money, English singer-songwriter and keyboard player births
George Bruno Money is an English vocalist, keyboardist and bandleader. He is best known for his playing of the Hammond organ and association with his Big Roll Band. Inspired by Jerry Lee Lewis and Ray Charles, he was drawn to rock and roll music and became a leading light in the vibrant music scene of Bournemouth and Soho during the 1960s. He took his stage name 'Zoot' from Zoot Sims after seeing him in concert.
Robina Nicol, New Zealand photographer and suffragist (b. 1861) deaths

Robina Nicol was a New Zealand photographer and suffragist.
Daryle Lamonica, American football player (d. 2022) births
Daryle Pasquale Lamonica was an American football quarterback who played in the American Football League (AFL) and the National Football League (NFL) for 12 seasons, primarily with the Oakland Raiders. He spent his first four seasons mostly as a backup for the Buffalo Bills, who selected him in the 24th round of the 1963 AFL Draft. Lamonica played his next eight seasons as the primary starter of the Raiders, including after they joined the NFL through the AFL–NFL merger.
Bob Taylor, English cricketer births

Robert William Taylor is an English former cricketer who played as wicket-keeper for Derbyshire between 1961 and 1984 and for England between 1971 and 1984. He made 57 Test, and 639 first-class cricket appearances in total, taking 1,473 catches. The 2,069 victims across his entire career is the most of any wicket-keeper in first-class history. He is considered one of the world's most accomplished wicket-keepers. He made his first-class debut for Minor Counties against South Africa in 1960, having made his Staffordshire debut in 1958. He became Derbyshire's first choice wicket-keeper when George Dawkes sustained a career-ending injury. His final First Class appearance was at the Scarborough Festival in 1988. He remained first choice until his retirement except for a short period in 1964 when Laurie Johnson was tried as a batsman-wicketkeeper.
Achim Warmbold, German race car driver and manager births
Achim Warmbold is a German former rally driver. He won the West German Rally Championship in 1971 and 1980, and scored two outright victories during the inaugural World Rally Championship season in 1973 at the Rally of Poland and Austrian Alpine Rally events.
Tim Brooke-Taylor, English actor and screenwriter (d. 2020) births

Timothy Julian Brooke-Taylor OBE was an English actor and comedian best known as a member of The Goodies.
Andrée Champagne, Canadian actress and politician (d. 2020) births
Andrée Champagne was a Canadian actress, pianist and politician.
Spencer Davis, Welsh singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 2020) births

Spencer Davis was a Welsh singer and musician. He founded The Spencer Davis Group, a band that had several hits in the 1960s including "Keep On Running", "Gimme Some Lovin'", and "I'm a Man", all sung by Steve Winwood. Davis subsequently enjoyed success as an A&R executive with Island Records.
Hermann Huppen, Belgian author and illustrator births

Hermann Huppen is a Belgian comic book artist. He is better known under his pen-name Hermann. He is most famous for his post-apocalyptic comic Jeremiah which was made into a television series.
Diahann Carroll, American actress and singer (d. 2019) births

Diahann Carroll was an American actress, singer, model, and activist. She rose to prominence in some of the earliest major studio films to feature black casts, including Carmen Jones (1954) and Porgy and Bess (1959). In 1962, Carroll won a Tony Award for Best Actress in a Musical, a first for an African-American woman, for her role in the Broadway musical No Strings. In 1974 she starred in Claudine alongside James Earl Jones for which she was nominated for an Academy Award for Best Actress.
Peter Schickele, American composer and educator births

"Professor" Peter Schickele is an American composer, musical educator, and parodist, best known for comedy albums featuring his music, but which he presents as being composed by the fictional P. D. Q. Bach. He also hosted a long-running weekly radio program called Schickele Mix.
Donald Sutherland, Canadian actor and producer births

Donald McNichol Sutherland is a Canadian actor whose film career spans over six decades. He has been nominated for nine Golden Globe Awards, winning two for his performances in the television films Citizen X (1995) and Path to War (2002); the former also earned him a Primetime Emmy Award. An inductee of the Hollywood Walk of Fame and Canadian Walk of Fame, he also received a Canadian Academy Award for the drama film Threshold (1981). Multiple film critics and media outlets have cited him as one of the best actors never to have received an Academy Award nomination. In 2017, he received an Academy Honorary Award for his contributions to cinema. In 2021, he won the Critics' Choice Television Award for Best Supporting Actor in a Movie/Miniseries for his work in the HBO miniseries The Undoing (2020).
George William Russell, Irish poet and painter (b. 1867) deaths

George William Russell, who wrote with the pseudonym Æ, was an Irish writer, editor, critic, poet, painter and Irish nationalist. He was also a writer on mysticism, and a central figure in the group of devotees of theosophy which met in Dublin for many years.
Lucio Tan, Chinese-Filipino billionaire businessman and educator births

Lucio Chua Tan Sr. is a Filipino business magnate, investor, and philanthropist. He presides over the Filipino conglomerate company LT Group, Inc., a company with extensive business interests in sports, banking, airline, liquor, tobacco, real estate, beverages, and education. As of September 2021, his net worth is estimated at US$1.9 billion.
Keiko Awaji, Japanese actress (d. 2014) births

Keiko Awaji was a Japanese film actress.
Karmenu Mifsud Bonnici, Maltese politician, 9th Prime Minister of Malta (d. 2022) births
Karmenu Mifsud Bonnici, was a Maltese politician who served as Prime Minister of Malta from December 1984 to May 1987.

The prime minister of Malta is the head of government, which is the highest official of Malta. The Prime Minister chairs Cabinet meetings, and selects its ministers to serve in their respective portfolios. The Prime Minister holds office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the Parliament, as such they sit as Members of Parliament.
Tony Pithey, Zimbabwean-South African cricketer (d. 2006) births

Anthony John Pithey was a Rhodesian cricketer who played in seventeen Test matches for South Africa between 1957 and 1965. He also made 65 appearances for Rhodesia, captaining them 34 times. He was a technically correct top-order batsmen who developed a reputation for being a stayer rather than a strokemaker. His early promise saw him represent South Africa as a young player, but he only secured his place in the team toward the end of his career. He toured Australia with Trevor Goddard's Springboks in 1963–64, during which, with his brother David and the Pollocks he formed part of the first pair of brothers to represent a country in a Test match.
Niccolò Castiglioni, Italian composer (d. 1996) births
Niccolò Castiglioni was an Italian composer, pianist, and writer on music.
Red Kerr, American basketball player and coach (d. 2009) births

John Graham "Red" Kerr was an American basketball player, coach, and color commentator. He played in the NBA from 1954 to 1966, mainly as a member of the Syracuse Nationals. He later held several coaching and administrative positions before embarking on a thirty-three-year career as a television color commentator for the Chicago Bulls.
Wojciech Kilar, Polish pianist and composer (d. 2013) births

Wojciech Kilar was a Polish classical and film music composer. One of his greatest successes came with his score to Francis Ford Coppola's Bram Stoker's Dracula in 1992, which received the ASCAP Award and the nomination for the Saturn Award for Best Music. In 2003, he won the César Award for Best Film Music written for The Pianist, for which he also received a BAFTA nomination.
Karla Kuskin, American author and illustrator (d. 2009) births
Karla Kuskin was a prolific American author, poet, illustrator, and reviewer of children's literature. Kuskin was known for her poetic, alliterative style.
Slick Leonard, American basketball player and coach (d. 2021) births

William Robert "Slick" Leonard was an American professional basketball player, coach and color commentator. He played college basketball for the Indiana Hoosiers, where he was a two-time All-American and a member of their national championship squad in 1953. After playing professionally in the National Basketball Association (NBA), Leonard coached the Indiana Pacers to three American Basketball Association (ABA) championships. He was inducted into the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame as a coach in 2014.
Ian Moir, Australian rugby league player (d. 1990) births

Ian James Moir (1932–1990) was an Australian professional rugby league footballer, a champion wing three-quarter who played in the 1950s and 1960s for South Sydney and Western Suburbs. He made eight Test appearances for the Australian national representative side and represented in four World Cup matches in two World Cups and in 14 Kangaroo tour matches.
Quino, Spanish-Argentinian cartoonist (d. 2020) births

Joaquín Salvador Lavado Tejón, better known by his pen name Quino, was an Argentinian cartoonist. His comic strip Mafalda is popular in many parts of the Americas and Europe and has been praised for its use of social satire as a commentary on real-life issues.
Hal Riney, American businessman, founded Publicis & Hal Riney (d. 2008) births
Hal Patrick Riney was an American advertising executive.
Publicis & Hal Riney is an American advertising agency, founded in San Francisco in 1977 by Hal Riney as Hal Riney & Partners. He had previously led the west coast office of Ogilvy & Mather since 1976.
Rasmus Rasmussen, Norwegian actor, singer, and director (b. 1862) deaths

Rasmus Rasmussen was a Norwegian actor, folk singer and theatre director.
Sergei K. Godunov, Russian mathematician and academic births

Sergei Konstantinovich Godunov is a Soviet and Russian professor at the Sobolev Institute of Mathematics of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Novosibirsk, Russia.
Vince Guaraldi, American singer-songwriter and pianist (d. 1976) births

Vincent Anthony Guaraldi was an American jazz pianist noted for his innovative compositions and arrangements, and for composing music for animated television adaptations of the Peanuts comic strip. His compositions for this series included their signature melody "Linus and Lucy" and the holiday standard "Christmas Time Is Here". He is also known for his performances on piano as a member of Cal Tjader's 1950s ensembles and for his own solo career. His 1962 composition "Cast Your Fate to the Wind" became a radio hit and won a Grammy Award in 1963 for Best Original Jazz Composition. He died of a sudden heart attack in February 1976 at age 47, moments after concluding a nightclub performance in Menlo Park, California.
Giovanni Giolitti, Italian politician, 13th Prime Minister of Italy (b. 1842) deaths

Giovanni Giolitti was an Italian statesman. He was the Prime Minister of Italy five times between 1892 and 1921. After Benito Mussolini, he is the second-longest serving Prime Minister in Italian history. A prominent leader of the Historical Left and the Liberal Union, he is widely considered one of the most powerful and important politicians in Italian history; due to his dominant position in Italian politics, Giolitti was accused by critics of being an authoritarian leader and a parliamentary dictator.

The prime minister, officially the president of the Council of Ministers, of Italy is the head of government of the Italian Republic. The office of president of the Council of Ministers is established by articles 92–96 of the Constitution of Italy; the president of the Council of Ministers is appointed by the president of the Republic and must have the confidence of the Parliament to stay in office.
Álvaro Obregón, Mexican general and politician, 39th President of Mexico (b. 1880) deaths

Álvaro Obregón Salido better known as Álvaro Obregón was a Sonoran-born general in the Mexican Revolution. A pragmatic centrist, natural soldier, and able politician, he became the 46th President of Mexico from 1920 to 1924 and was assassinated in 1928 as President-elect. In the popular image of the Revolution, "Alvaro Obregón stood out as the organizer, the peacemaker, the unifier."

The president of Mexico, officially the president of the United Mexican States, is the head of state and head of government of Mexico. Under the Constitution of Mexico, the president heads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the Mexican Armed Forces. The current president is Andrés Manuel López Obrador, who took office on 1 December 2018.
Édouard Carpentier, French-Canadian wrestler (d. 2010) births

Édouard Ignacz Weiczorkiewicz was a French-born Canadian professional wrestler, better known by his ring name, Édouard Carpentier. Over the course of his career, Carpentier held multiple world heavyweight championships, including the NWA World Heavyweight Championship and the WWA World Heavyweight Championship. Nicknamed "The Flying Frenchman", Carpentier was known for his athletic manoeuvres including "back flips, cartwheels and somersaults".
Willis Carto, American activist and theorist (d. 2015) births

Willis Allison Carto was an American far-right political activist. He described himself as a Jeffersonian and a populist, but was primarily known for his promotion of antisemitic conspiracy theories and Holocaust denial.
Jimmy Scott, American singer and actor (d. 2014) births

James Victor Scott, known professionally as Little Jimmy Scott or Jimmy Scott, was an American jazz vocalist known for his high natural contralto voice and his sensitivity on ballads and love songs.
Mohammad Hasan Sharq, Afghan politician births

Mohammad Hasan Sharq is an Afghan former politician who was active in the communist government of Afghanistan. Sharq became Chairman of the Council of Ministers – the government of the Soviet-backed Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. He was selected as a compromise candidate after a loya jirga ratified a new constitution in 1987. However, the power of his office was relatively slight compared with the powers held by the Presidency.
Lovis Corinth, German painter (b. 1858) deaths

Lovis Corinth was a German artist and writer whose mature work as a painter and printmaker realized a synthesis of impressionism and expressionism.
Garde Gardom, Canadian lawyer and politician, 26th Lieutenant Governor of British Columbia (d. 2013) births

Garde Basil Gardom, was a Canadian politician, lawyer, and the 26th Lieutenant Governor of British Columbia.

The lieutenant governor of British Columbia is the viceregal representative of the Canadian monarch, King Charles III, in the province of British Columbia, Canada. The office of lieutenant governor is an office of the Crown and serves as a representative of the monarchy in the province, rather than the governor general of Canada. The office was created in 1871 when the Colony of British Columbia joined the Confederation. Since then the lieutenant governor has been the representative of the monarchy in British Columbia. Previously, between 1858 and 1863 under colonial administration the title of lieutenant governor of British Columbia was given to Richard Clement Moody as commander of the Royal Engineers, Columbia Detachment. This position coexisted with the office of governor of British Columbia served by James Douglas during that time.
Jeanne Block, American psychologist (d. 1981) births
Jeanne Lavonne Humphrey Block was an American psychologist and expert on child development. She conducted research into sex-role socialization and, with her husband Jack Block, created a person-centered personality framework. Block was a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and conducted her research with the National Institute of Mental Health and the University of California, Berkeley. She was an active researcher when she was diagnosed with cancer in 1981.
John Cooper, English car designer, co-founded the Cooper Car Company (d. 2000) births
John Newton Cooper CBE was a co-founder, with his father Charles Cooper, of the Cooper Car Company. Born in Surbiton, Surrey, United Kingdom, he became an auto racing legend with his rear-engined chassis design that would eventually change the face of the sport at its highest levels, from Formula One to the Indianapolis 500.

The Cooper Car Company is a British car manufacturer founded in December 1947 by Charles Cooper and his son John Cooper. Together with John's boyhood friend, Eric Brandon, they began by building racing cars in Charles's small garage in Surbiton, Surrey, England, in 1946. Through the 1950s and early 1960s they reached motor racing's highest levels as their mid-engined, single-seat cars competed in both Formula One and the Indianapolis 500, and their Mini Cooper dominated rally racing. The Cooper name lives on in the Cooper versions of the Mini production cars that are built in England, but is now owned and marketed by BMW.
George Barnes, American guitarist, producer, and songwriter (d. 1977) births
George Warren Barnes was an American swing jazz guitarist. He was also a conductor and arranger of music, and became the youngest ever for NBC when he was hired by them in that role at the age of seventeen. At this age he was considered a great player by many musicians including Tommy Dorsey, and Jimmy McPartland. Barnes also later became a recording engineer. During his career Barnes recorded with singers Mel Tormé, Ella Fitzgerald, Frank Sinatra, Bing Crosby, Patti Page, Dinah Washington, Lena Horne, Billy Eckstine and Johnny Mathis among many others. He was an inspiration and influence to the musician Roy Clark and guitarists Herb Ellis and Merle Travis, among others.
Louis Lachenal, French mountaineer (d. 1955) births
Louis Lachenal, a French climber born in Annecy, Haute-Savoie, was one of the first two mountaineers to climb a summit of more than 8,000 meters. On 3 June 1950 on the 1950 French Annapurna expedition, along with Maurice Herzog, he reached the summit of Annapurna I in Nepal at a height of 8,091 m (26,545 ft). Previously he had made the second ascent of the North Face of the Eiger in 1947, with Lionel Terray. He died falling into a snow-covered crevasse while skiing the Vallee Blanche in Chamonix. The mountain Pointe Lachenal in the Mont Blanc massif was named after him.
Mary Osborne, American guitarist (d. 1992) births

Mary Osborne was an American jazz guitarist and guitar manufacturer. She began performing at a young age and was featured on a radio program in North Dakota, where she grew up. In New York City during the 1940s, she played with jazz musicians such as Dizzy Gillespie, Art Tatum, Coleman Hawkins, and Thelonious Monk. After moving to California in 1968, she and her husband founded the Osborne Guitar Company.
Toni Stone, American baseball player (d. 1996) births

Toni Stone, born as Marcenia Lyle Stone in West Virginia, was the first of three women to play professional baseball full-time for the Indianapolis Clowns, in the previously all-male Negro leagues. This also made her the first woman to play as a regular on an American big-league professional baseball team. A baseball player from her early childhood, she went on to play for the San Francisco Sea Lions, the New Orleans Creoles, the Indianapolis Clowns, and the Kansas City Monarchs before retiring from baseball in 1954. Stone was taunted at times by teammates, once being told, “Go home and fix your husband some biscuits,” but she was undeterred. It has been widely reported that during an exhibition game in 1953, she hit a single off a fastball pitch delivered by legendary player Satchel Paige, although this is also disputed.
František Zvarík, Slovak actor (d. 2008) births
František Zvarík was an accomplished theater actor and movie character actor. He has appeared in about two dozen Slovak films since the 1940s. Among his accomplishments is the key supporting role of the town commander Markuš Kolkotský in The Shop on Main Street, a film which won the 1965 Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film.
Gordon Gould, American physicist and academic, invented the laser (d. 2005) births

Gordon Gould was an American physicist who is sometimes credited with the invention of the laser and the optical amplifier.. Gould is best known for his thirty-year fight with the United States Patent and Trademark Office to obtain patents for the laser and related technologies. He also fought with laser manufacturers in court battles to enforce the patents he subsequently did obtain.

A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow.
Juan Antonio Samaranch, Spanish businessman, 7th President of the International Olympic Committee (d. 2010) births

Juan Antonio Samaranch y Torelló, 1st Marquess of Samaranch was a Spanish sports administrator under the Franco regime (1973–1977) who served as the seventh President of the International Olympic Committee (IOC) from 1980 to 2001.

The president of the International Olympic Committee is head of the executive board that assumes the general overall responsibility for the administration of the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and the management of its affairs. The IOC Executive Board consists of the president, four vice-presidents and ten other IOC members; all of the board members are elected by the IOC Session, using a secret ballot, by a majority vote.
Albert Stubbins, English footballer (d. 2002) births
Albert Stubbins was an English footballer. He played in the position of centre forward, although his career was limited by the onset of World War II. While playing for Liverpool, he won the League Championship in 1947. He was later included on the front cover of The Beatles' Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band album.
Carlos Manuel Arana Osorio, Guatemalan soldier and politician, President of Guatemala (d. 2003) births

Carlos Manuel Arana Osorio was President of Guatemala from 1970 to 1974. His government enforced torture, disappearances and killings against political and military adversaries, as well as common criminals.

The president of Guatemala, officially known as the President of the Republic of Guatemala, is the head of state and head of government of Guatemala, elected to a single four-year term. The position of President was created in 1839.
Red Sovine, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 1980) births
Woodrow Wilson "Red" Sovine was an American country music singer and songwriter associated with truck driving songs, particularly those recited as narratives but set to music. His most noted examples are "Giddyup Go" (1965) and "Teddy Bear" (1976), both of which topped the Billboard Hot Country Songs chart.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov, known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer, was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland, ruling from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. During his reign, Nicholas gave support to the economic and political reforms promoted by his prime ministers, Sergei Witte and Pyotr Stolypin. He advocated modernization based on foreign loans and close ties with France, but resisted giving the new parliament major roles. Ultimately, progress was undermined by Nicholas's commitment to autocratic rule, strong aristocratic opposition and defeats sustained by the Russian military in the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. By March 1917, public support for Nicholas had collapsed and he was forced to abdicate the throne, thereby ending the Romanov dynasty's 304-year rule of Russia (1613–1917).
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Alexandra Feodorovna, Princess Alix of Hesse and by Rhine at birth, was the last Empress of Russia as the consort of Emperor Nicholas II from their marriage on 26 November [O.S. 14 November] 1894 until his forced abdication on 15 March [O.S. 2 March] 1917. A favourite granddaughter of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom, she was, like her grandmother, one of the most famous royal carriers of haemophilia and bore a haemophiliac heir, Alexei Nikolaevich, Tsarevich of Russia. Her reputation for encouraging her husband's resistance to the surrender of autocratic authority and her known faith in the Russian mystic Grigori Rasputin severely damaged her popularity and that of the Romanov monarchy in its final years. She and her immediate family were all killed while in Bolshevik captivity in 1918, during the Russian Revolution. In 2000, the Russian Orthodox Church canonized her as Saint Alexandra the Passion Bearer.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Grand Duchess Olga Nikolaevna of Russia was the eldest child of the last Tsar of the Russian Empire, Emperor Nicholas II, and of Empress Alexandra of Russia.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Grand Duchess Tatiana Nikolaevna of Russia was the second daughter of Tsar Nicholas II, the last monarch of Russia, and of Tsarina Alexandra. She was born at Peterhof Palace, near Saint Petersburg.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Grand Duchess Maria Nikolaevna of Russia was the third daughter of Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and Tsarina Alexandra Feodorovna. Her murder following the Russian Revolution of 1917 resulted in her canonization as a passion bearer by the Russian Orthodox Church.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Grand Duchess Anastasia Nikolaevna of Russia was the youngest daughter of Tsar Nicholas II, the last sovereign of Imperial Russia, and his wife, Tsarina Alexandra Feodorovna.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Alexei Nikolaevich was the last Tsesarevich. He was the youngest child and only son of Emperor Nicholas II and Empress Alexandra Feodorovna. He was born with haemophilia, which his parents tried treating with the methods of a peasant faith healer named Grigori Rasputin.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Anna Stepanovna Demidova was a lady-in-waiting in the service of Empress Alexandra of Russia. She stayed with the Romanov family when they were arrested, and was executed together with Alexandra and the Romanov family on 17 July 1918.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Ivan Mikhailovich Kharitonov was the Head Cook at the court of Tsar Nicholas II of Russia. He followed the Romanov family into internal exile following the Russian Revolution of 1917 and was executed with them by the Bolsheviks on 17 July 1918 at Ekaterinburg.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Aloise "Alexei" Yegorovich Trupp was the Latvian head footman in the household of Tsar Nicholas II of Russia.
Victims of the Shooting of the Romanov family deaths

Yevgeny Sergeyevich Botkin, commonly known as Eugene Botkin, was the court physician since 1908 for Tsar Nicholas II and Tsarina Alexandra. He sometimes treated the Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich of Russia for haemophilia-related complications, like in Spala in 1912.
Lou Boudreau, American baseball player and manager (d. 2001) births

Louis Boudreau, nicknamed "Old Shufflefoot", "Handsome Lou", and "The Good Kid", was an American professional baseball player and manager. He played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for 15 seasons, primarily as a shortstop on the Cleveland Indians, and managed four teams for 15 seasons including 10 seasons as a player-manager. He was also a radio announcer for the Chicago Cubs and in college was a dual sport athlete in both baseball and earning All-American honors in basketball for the University of Illinois.
Phyllis Diller, American actress, comedian, and voice artist (d. 2012) births

Phyllis Ada Diller was an American stand-up comedian, actress, author, musician, and visual artist, best known for her eccentric stage persona, self-deprecating humor, wild hair and clothes, and exaggerated, cackling laugh.
Kenan Evren, Turkish general and politician, 7th President of Turkey (d. 2015) births

Ahmet Kenan Evren was a Turkish politician and military officer, who served as the seventh President of Turkey from 1980 to 1989. He assumed the post by leading the 1980 military coup.

The president of Turkey, officially the president of the Republic of Türkiye, is the head of state and head of government of Turkey. The president directs the executive branch of the national government and is the commander-in-chief of the Turkish military. The president also heads the National Security Council.
Christiane Rochefort, French author (d. 1998) births

Christiane Rochefort was a French feminist writer. She was born into a left-wing working class Parisian family; her father joined the International Brigades during the Spanish Civil War. Rochefort worked as a journalist and spent fifteen years as a press attaché to the Cannes Film Festival before publishing her first novel, Le Repos du guerrier, in 1958. Like several of her later novels, Le Repos du guerrier was a bestseller; in 1962 it was adapted into a popular film directed by Roger Vadim and starring Brigitte Bardot. Her novels are divided between social realist satires set in present-day France and utopian or dystopian fantasies. She won the Prix Médicis in 1988. Rochefort's novels also have strong sexual elements.
Eleanor Hadley, American economist and policymaker (d. 2007) births

Eleanor Martha Hadley was an American economist and policymaker. Because of her relatively rare research specialization in Japanese economics, during World War II Hadley was recruited first into OSS and then the State Department to support the United States' war effort while she was a doctoral candidate in economics at Radcliffe College. Hadley helped draft the United States' plans for dissolving zaibatsu business conglomerates as part of a planned effort to democratize Japan after the war, and she participated in implementing this economic deconcentration program when the postwar occupation brought her to Japan to work for SCAP as an economist.
Bijon Bhattacharya, Indian actor, singer, and screenwriter (d. 1978) births

Bijon Bhattacharya was an Indian theatre and film actor from West Bengal. He was an eminent playwright and dramatist.
Arthur Rothstein, American photographer and educator (d. 1985) births

Arthur Rothstein was an American photographer. Rothstein is recognized as one of America's premier photojournalists. During a career that spanned five decades, he provoked, entertained and informed the American people. His photographs ranged from a hometown baseball game to the drama of war, from struggling rural farmers to US Presidents.
Eleanor Steber, American soprano and educator (d. 1990) births

Eleanor Steber was an American operatic soprano. Steber is noted as one of the first major opera stars to have achieved the highest success with training and a career based in the United States.
Bertrand Goldberg, American architect, designed the Marina City Building (d. 1997) births

Bertrand Goldberg was an American architect and industrial designer, best known for the Marina City complex in Chicago, Illinois, the tallest reinforced concrete building in the world at the time of completion.

Marina City is a mixed-use residential-commercial building complex in Chicago, Illinois, United States, North America, designed by architect Bertrand Goldberg. The multi-building complex opened between 1963 and 1967 and occupies almost an entire city block on State Street on the north bank of the Chicago River on the Near North Side, directly across from the Loop. Portions of the complex were designated a Chicago Landmark in 2016.
Erwin Bauer, German race car driver (d. 1958) births
Erwin Erich Bauer was a German Formula One driver who raced a privately entered Veritas in his one World Championship Grand Prix.
Art Linkletter, Canadian-American radio and television host (d. 2010) births
Arthur Gordon Linkletter was a Canadian-born American radio and television personality. He was the host of House Party, which ran on CBS radio and television for 25 years, and People Are Funny, which aired on NBC radio and television for 19 years. He became a naturalized United States citizen in 1942.
Henri Poincaré, French mathematician, physicist, and engineer (b. 1854) deaths

Jules Henri Poincaré was a French mathematician, theoretical physicist, engineer, and philosopher of science. He is often described as a polymath, and in mathematics as "The Last Universalist", since he excelled in all fields of the discipline as it existed during his lifetime.
Lionel Ferbos, American trumpet player (d. 2014) births

Lionel Charles Ferbos was an American jazz trumpeter. He was from New Orleans, Louisiana.
Heinz Lehmann, German-Canadian psychiatrist and academic (d. 1999) births
Heinz Edgar Lehmann was a German-born Canadian psychiatrist best known for his use of chlorpromazine for the treatment of schizophrenia in 1950s and "truly the father of modern psychopharmacology."
James Coyne, Canadian lawyer and banker, 2nd Governor of the Bank of Canada (d. 2012) births

James Elliott Coyne, was the second Governor of the Bank of Canada, from 1955 to 1961, succeeding Graham Towers. During his time in office, he had a much-publicized debate with Prime Minister John Diefenbaker, a debate often referred to as the "Coyne Affair", which led to his resignation and, eventually, to greater central-bank independence in Canada.

The governor of the Bank of Canada is the chief executive officer of the Bank of Canada and acts as chair of its board of directors. The Bank of Canada Act, 1985, S. 6(1), provides that the governor and deputy governor shall be appointed by the directors with the approval of the Governor in Council.
Frank Olson, American chemist and microbiologist (d. 1953) births

Frank Rudolph Emmanuel Olson was an American bacteriologist, biological warfare scientist, and an employee of the United States Army Biological Warfare Laboratories (USBWL) who worked at Camp Detrick in Maryland. At a meeting in rural Maryland, he was covertly dosed with LSD by his colleague Sidney Gottlieb and, nine days later, plunged to his death from the window of the Hotel Statler in New York. The U.S. government first described his death as a suicide, and then as misadventure, while others allege murder. The Rockefeller Commission report on the CIA in 1975 acknowledged their having conducted covert drug studies on fellow agents. Olson's death is one of the most mysterious outcomes of the CIA mind control project MKUltra.
Hector Malot, French author and critic (b. 1830) deaths

Hector-Henri Malot was a French writer born in La Bouille, Seine-Maritime. He studied law in Rouen and Paris, but eventually literature became his passion. He worked as a dramatic critic for Lloyd Francais and as a literary critic for L'Opinion Nationale.
William Gargan, American actor (d. 1979) births

William Dennis Gargan was an American film, television and radio actor. He was the 5th recipient of the Screen Actors Guild Life Achievement Award in 1967, and in 1941, was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for his role as Joe in They Knew What They Wanted. He acted in decades of movies including parts in Follow the Leader, Rain, Night Flight, Three Sons, Isle of Destiny and many others. The role he was best known for was that of a private detective Martin Kane in the 1949–1952 radio-television series Martin Kane, Private Eye. In television, he was also in 39 episodes of The New Adventures of Martin Kane.
Christina Stead, Australian author and academic (d. 1983) births

Christina Stead was an Australian novelist and short-story writer acclaimed for her satirical wit and penetrating psychological characterisations. Christina Stead was a committed Marxist, although she was never a member of the Communist Party. She spent much of her life outside Australia, although she returned before her death.
Luigi Chinetti, Italian-American race car driver (d. 1994) births

Luigi Chinetti was an Italian-born racecar driver, who emigrated to the United States during World War II. He drove in 12 consecutive 24 Hours of Le Mans races, taking three outright wins there and taking two more at the Spa 24 Hours race. Chinetti owned the North American Racing Team, which successfully ran privateer Ferraris in sports car and Formula One races. For many years he was the exclusive American importer of Ferrari automobiles to the United States.
Bruno Jasieński, Polish poet and author (d. 1938) births

Bruno Jasieński pronounced [ˈbrunɔ jaˈɕeɲskʲi], born Wiktor Bruno Zysman, was a Polish poet, novelist, playwright, Catastrophist, and leader of the Polish Futurist movement in the interwar period. Jasieński was also a communist activist in Poland, France and the Soviet Union, where he was executed during the Great Purge. He is acclaimed by members of the various modernist art groups as their patron. An annual literary festival Brunonalia is held in Klimontów, Poland, his birthplace, where one of the streets is also named after him.
Patrick Smith, Irish farmer and politician, Minister for Agriculture, Food and the Marine (d. 1982) births
Patrick Smith was an Irish Fianna Fáil politician, who served as a Teachta Dála from 1923 until 1977; a tenure of 53 years, the longest in the state. He held a number of ministerial positions within the governments of Éamon de Valera and Seán Lemass.

The Minister for Agriculture, Food and the Marine is a senior minister in the Government of Ireland and leads the Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine. Historically, the agriculture portfolio has gone under a number of different names; the holder has often borne the title of simply Minister for Agriculture.
Thomas McIlwraith, Scottish-Australian politician, 8th Premier of Queensland (b. 1835) deaths

Sir Thomas McIlwraith was for many years the dominant figure of colonial politics in Queensland. He was Premier of Queensland from 1879 to 1883, again in 1888, and for a third time in 1893. In common with most politicians of his era, McIlwraith was an influential businessman, who combined his parliamentary career with a prosperous involvement in the pastoral industry.

The premier of Queensland is the head of government in the Australian state of Queensland.
James Cagney, American actor and dancer (d. 1986) births

James Francis Cagney Jr. was an American actor, dancer and film director. On stage and in film, Cagney was known for his consistently energetic performances, distinctive vocal style, and deadpan comic timing. He won acclaim and major awards for a wide variety of performances. He is remembered for playing multifaceted tough guys in films such as The Public Enemy (1931), Taxi! (1932), Angels with Dirty Faces (1938), The Roaring Twenties (1939), City for Conquest (1940) and White Heat (1949), finding himself typecast or limited by this reputation earlier in his career. He was able to negotiate dancing opportunities in his films and ended up winning the Academy Award for his role in the musical Yankee Doodle Dandy (1942). In 1999 the American Film Institute ranked him eighth among its list of greatest male stars of the Golden Age of Hollywood. Orson Welles described Cagney as "maybe the greatest actor who ever appeared in front of a camera".
Berenice Abbott, American photographer (d. 1991) births

Berenice Alice Abbott was an American photographer best known for her portraits of between-the-wars 20th century cultural figures, New York City photographs of architecture and urban design of the 1930s, and science interpretation in the 1940s to 1960s.
Osmond Borradaile, Canadian soldier and cinematographer (d. 1999) births

Osmond Hudson Borradaile was a Canadian cameraman, cinematographer, and veteran of World War I and World War II.
Rupert Atkinson, English RAF officer (d. 1919) births
Captain Rupert Norman Gould Atkinson was a British World War I flying ace credited with five aerial victories.
Georges Lemaître, Belgian priest, astronomer, and cosmologist (d. 1966) births

Georges Henri Joseph Édouard Lemaître was a Belgian Catholic priest, theoretical physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and professor of physics at the Catholic University of Louvain. He was the first to theorize that the recession of nearby galaxies can be explained by an expanding universe, which was observationally confirmed soon afterwards by Edwin Hubble. He first derived "Hubble's law", now called the Hubble–Lemaître law by the IAU, and published the first estimation of the Hubble constant in 1927, two years before Hubble's article. Lemaître also proposed the "Big Bang theory" of the origin of the universe, calling it the "hypothesis of the primeval atom", and later calling it "the beginning of the world".
Leconte de Lisle, French poet and translator (b. 1818) deaths

Charles Marie René Leconte de Lisle was a French poet of the Parnassian movement. He is traditionally known by his surname only, Leconte de Lisle.
Josef Hyrtl, Austrian anatomist and biologist (b. 1810) deaths

Josef Hyrtl was an Austrian anatomist.
Frederick A. Johnson, American banker and politician (b. 1833) deaths
Frederick Avery Johnson was an American politician and banker who served a U.S. Representative from New York from 1883 to 1887. He was a member of the Republican Party and a resident of Glens Falls, New York.
Erle Stanley Gardner, American lawyer and author (d. 1970) births

Erle Stanley Gardner was an American lawyer and author. He is best known for the Perry Mason series of detective stories, but he wrote numerous other novels and shorter pieces and also a series of nonfiction books, mostly narrations of his travels through Baja California and other regions in Mexico.
Shmuel Yosef Agnon, Ukrainian-Israeli novelist, short story writer and poet, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1970) births

Shmuel Yosef Agnon was one of the central figures of modern Hebrew literature. In Hebrew, he is known by the acronym Shai Agnon. In English, his works are published under the name S. Y. Agnon.

The Nobel Prize in Literature is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in the field of literature, produced the most outstanding work in an idealistic direction". Though individual works are sometimes cited as being particularly noteworthy, the award is based on an author's body of work as a whole. The Swedish Academy decides who, if anyone, will receive the prize. The academy announces the name of the laureate in early October. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895. Literature is traditionally the final award presented at the Nobel Prize ceremony. On some occasions the award has been postponed to the following year, most recently in 2018 as of May 2022.
Jean-Charles Chapais, Canadian farmer and politician, 1st Canadian Minister of Agriculture (b. 1811) deaths

Jean-Charles Chapais, was a Canadian Conservative politician, and considered a Father of Canadian Confederation for his participation in the Quebec Conference to determine the form of Canada's government.

The minister of agriculture and agri-food is a minister of the Crown in the Cabinet of Canada, who is responsible for overseeing several organizations including Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, the Canadian Dairy Commission, Farm Credit Canada, the Canadian Food Inspection Agency, the National Farm Products Council and the Canadian Grain Commission.
Tự Đức, Vietnamese emperor (b. 1829) deaths

Tự Đức was the fourth emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty of Vietnam; he ruled from 1847 to 1883.
James Somerville, English admiral and politician, Lord Lieutenant of Somerset (d. 1949) births

Admiral of the Fleet Sir James Fownes Somerville, was a Royal Navy officer. He served in the First World War as fleet wireless officer for the Mediterranean Fleet where he was involved in providing naval support for the Gallipoli Campaign. He also served in the Second World War as commander of the newly formed Force H: after the French armistice with Germany, Winston Churchill gave Somerville and Force H the task of neutralizing the main element of the French battle fleet, then at Mers El Kébir in Algeria. After he had destroyed the French Battle fleet, Somerville played an important role in the pursuit and sinking of the German battleship Bismarck.
This is an incomplete list of people who have served as Lord Lieutenant of Somerset. Since 1714, all Lord Lieutenants have also been Custos Rotulorum of Somerset.
Jim Bridger, American scout and explorer (b. 1804) deaths

James Felix "Jim" Bridger was an American mountain man, trapper, Army scout, and wilderness guide who explored and trapped in the Western United States in the first half of the 19th century. He was known as Old Gabe in his later years. He was from the Bridger family of Virginia, English immigrants who had been in North America since the early colonial period.
Jack Laviolette, Canadian ice hockey player, coach, and manager (d. 1960) births

Jean-Baptiste "Jack" Laviolette was a Canadian professional ice hockey player. Laviolette played nine seasons for the Montreal Canadiens hockey club and was their first captain, coach, and general manager.
Maurycy Gottlieb, Ukrainian-Polish painter (b. 1856) deaths

Maurycy Gottlieb (Polish pronunciation ; 21/28 February 1856 – 17 July 1879) was a Polish realist painter of the Romantic period. Considered one of the most talented students of Jan Matejko, Gottllieb died at the age of 23.
Aleardo Aleardi, Italian poet and politician (b. 1812) deaths
Aleardo Aleardi, born Gaetano Maria, was an Italian poet who belonged to the so-called Neo-romanticists.
Lyonel Feininger, German-American painter and illustrator (d. 1956) births

Lyonel Charles Feininger was a German-American painter, and a leading exponent of Expressionism. He also worked as a caricaturist and comic strip artist. He was born and grew up in New York City, traveling to Germany at 16 to study and perfect his art. He started his career as a cartoonist in 1894 and met with much success in this area. He was also a commercial caricaturist for 20 years for magazines and newspapers in the USA and Germany. At the age of 36, he started to work as a fine artist. He also produced a large body of photographic works between 1928 and the mid 1950s, but he kept these primarily within his circle of friends. He was also a pianist and composer, with several piano compositions and fugues for organ extant.
Karl Tausig, Polish virtuoso pianist, arranger and composer (b. 1841) deaths

Karl Tausig was a Polish virtuoso pianist, arranger and composer. He is generally regarded as Franz Liszt's most esteemed pupil, and one of the greatest pianists of all time.
Charles Davidson Dunbar, Scottish soldier and bagpipe player (d. 1939) births
Charles Davidson Dunbar, DCM was the first pipe major in Britain and the British Empire to be commissioned as a pipe officer. He emigrated from Scotland to Canada, where he came to be called "Canada's greatest military piper".

Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, Northern Africa, Western Asia, around the Persian Gulf and northern parts of South Asia.
Henri Nathansen, Danish director and playwright (d. 1944) births

Henri Nathansen was a Danish writer and stage director, today best known for the play Inside the Walls.
Alexius Meinong, Ukrainian-Austrian philosopher and academic (d. 1920) births

Alexius Meinong Ritter von Handschuchsheim was an Austrian philosopher, a realist known for his unique ontology. He also made contributions to philosophy of mind and theory of value.
Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey, English politician, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (b. 1764) deaths

Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey, known as Viscount Howick between 1806 and 1807, was a British Whig politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1830 to 1834. He was a member of the noble House of Grey.

The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern prime ministers hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons, they sit as members of Parliament.
Ephraim Shay, American engineer, invented the Shay locomotive (d. 1916) births

Ephraim Shay was an American merchant, entrepreneur and self-taught railroad engineer who worked in the state of Michigan. He designed the first Shay locomotive and patented the type. He licensed it for manufacture through what became known as Lima Locomotive Works in Ohio; from 1882 to 1892 some 300 locomotives of this type were sold.

The Shay locomotive is a geared steam locomotive that originated and was primarily used in North America. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a geared steam locomotive. Although the design of Ephraim Shay's early locomotives differed from later ones, there is a clear line of development that joins all Shays. Shay locomotives were especially suited to logging, mining and industrial operations and could operate successfully on steep or poor quality track.
Joseph-Alfred Mousseau, Canadian lawyer, judge, and politician, 7th Secretary of State for Canada (d. 1886) births

Joseph-Alfred Mousseau, was a French Canadian politician, who served in the federal Cabinet and also as the sixth premier of Quebec.

The Secretary of State for Canada, established in 1867 with a corresponding department, was a Canadian Cabinet position that served as the official channel of communication between the Dominion of Canada and the Imperial government in London.
Xianfeng Emperor of China (d. 1861) births

The Xianfeng Emperor, or by temple name Emperor Wenzong of Qing (清文宗), given name Yizhu (奕詝), was the eighth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the seventh Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigned from 1850 to 1861. During his reign, the Qing dynasty experienced several wars and rebellions including the Taiping Rebellion, Nian Rebellion, and Second Opium War. He was the last Chinese emperor to have authoritarian and total executive ruling power. After his death, the Qing government was controlled by Empress Dowager Cixi.
Leander Clark, American businessman, judge, and politician (d. 1910) births

Leander Clark was an American businessman, Iowa state legislator, Union Army officer during the Civil War, and Indian agent who was the namesake for Leander Clark College.
Paul Delaroche, French painter and academic (d. 1856) births

Hippolyte-Paul Delaroche was a French painter who achieved his greater successes painting historical scenes. He became famous in Europe for his melodramatic depictions that often portrayed subjects from English and French history. The emotions emphasised in Delaroche's paintings appeal to Romanticism while the detail of his work along with the deglorified portrayal of historic figures follow the trends of Academicism and Neoclassicism. Delaroche aimed to depict his subjects and history with pragmatic realism. He did not consider popular ideals and norms in his creations, but rather painted all his subjects in the same light whether they were historical figures like Marie-Antoinette, figures of Christianity, or people of his time like Napoleon Bonaparte. Delaroche was a leading pupil of Antoine-Jean Gros and later mentored a number of notable artists such as Thomas Couture, Jean-Léon Gérôme, and Jean-François Millet.
John Roebuck, English chemist and businessman (b. 1718) deaths
John Roebuck of Kinneil FRS FRSE was an English inventor and industrialist who played an important role in the Industrial Revolution and who is known for developing the industrial-scale manufacture of sulphuric acid.
Charlotte Corday, French murderer (b. 1768) deaths

Marie-Anne Charlotte de Corday d'Armont, known as Charlotte Corday, was a figure of the French Revolution. In 1793, she was executed by guillotine for the assassination of Jacobin leader Jean-Paul Marat, who was in part responsible for the more radical course the Revolution had taken through his role as a politician and journalist. Marat had played a substantial role in the political purge of the Girondins, with whom Corday sympathized. His murder was depicted in the painting The Death of Marat by Jacques-Louis David, which shows Marat's dead body after Corday had stabbed him in his medicinal bath. In 1847, writer Alphonse de Lamartine gave Corday the posthumous nickname l'ange de l'assassinat.
Martin Dobrizhoffer, Austrian missionary and author (b. 1717) deaths
Martin Dobrizhoffer was an Austrian Roman Catholic missionary and writer.
Adam Smith, Scottish economist and philosopher (b. 1723) deaths

Adam Smith was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics" or "The Father of Capitalism", he wrote two classic works, The Theory of Moral Sentiments (1759) and An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (1776). The latter, often abbreviated as The Wealth of Nations, is considered his magnum opus and the first modern work that treats economics as a comprehensive system and as an academic discipline. Smith refuses to explain the distribution of wealth and power in terms of God’s will and instead appeals to natural, political, social, economic and technological factors and the interactions between them. Among other economic theories, the work introduced Smith's idea of absolute advantage.
John Wilbur, American minister and theologian (d. 1856) births
John Wilbur was a prominent American Quaker minister and religious thinker who was at the forefront of a controversy that led to "the second split" in the Religious Society of Friends in the United States.
John Jacob Astor, German-American businessman and philanthropist (d. 1848) births

John Jacob Astor was a German-American businessman, merchant, real estate mogul, and investor who made his fortune mainly in a fur trade monopoly, by smuggling opium into China, and by investing in real estate in or around New York City. He was the first prominent member of the Astor family and the first multi-millionaire in the United States.
Peter III of Russia (b. 1728) deaths

Peter III was an emperor of Russia who was overthrown by his wife, Catherine the Great. He was born in Kiel as Charles Peter Ulrich of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp, the only child of Charles Frederick, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp, and Anna Petrovna.
Elbridge Gerry, American merchant and politician, 5th Vice President of the United States (d. 1814) births

Elbridge Gerry was an American Founding Father, merchant, politician, and diplomat who served as the fifth vice president of the United States under President James Madison from 1813 until his death in 1814. The political practice of gerrymandering is named after him. He was the second vice president to die in office.

The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice president is also an officer in the legislative branch, as the president of the Senate. In this capacity, the vice president is empowered to preside over Senate deliberations at any time, but may not vote except to cast a tie-breaking vote. The vice president is indirectly elected together with the president to a four-year term of office by the people of the United States through the Electoral College.
Thomas King, English and British soldier, MP for Queenborough, lieutenant-governor of Sheerness (b. before 1660?). deaths
Thomas King was an English professional soldier, lieutenant governor of Sheerness, Kent, and Member of Parliament for Queenborough, in Kent.
Alexander Gottlieb Baumgarten, German philosopher and academic (d. 1762) births
Alexander Gottlieb Baumgarten was a German philosopher. He was a brother to theologian Siegmund Jakob Baumgarten (1706–1757).
Robert Bolling, English planter and merchant (b. 1646) deaths

Colonel Robert Bolling, sometimes called Robert Bolling, Sr., after he gave a son his own name, was a wealthy early American settler planter and merchant.
Frederick Christian, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (d. 1769) births

Frederick Christian of Brandenburg-Bayreuth, was a member of the House of Hohenzollern and Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth.
Pierre-Charles Le Sueur, French fur trader and explorer (b. 1657) deaths
Pierre-Charles Le Sueur was a French fur trader and explorer in North America, recognized as the first known European to explore the Minnesota River valley.
Pierre Louis Maupertuis, French mathematician and philosopher (d. 1759) births

Pierre Louis Moreau de Maupertuis was a French mathematician, philosopher and man of letters. He became the Director of the Académie des Sciences, and the first President of the Prussian Academy of Science, at the invitation of Frederick the Great.
Christian Karl Reinhard of Leiningen-Dachsburg-Falkenburg-Heidesheim (d. 1766) births

Count Christian Karl Reinhard of Leiningen-Dagsburg-Falkenburg was a German nobleman.
Isaac Watts, English hymnwriter and theologian (d. 1748) births

Isaac Watts was an English Congregational minister, hymn writer, theologian, and logician. He was a prolific and popular hymn writer and is credited with some 750 hymns. His works include "When I Survey the Wondrous Cross", "Joy to the World", and "Our God, Our Help in Ages Past". He is recognized as the "Godfather of English Hymnody"; many of his hymns remain in use today and have been translated into numerous languages.
Robert Carr, 1st Earl of Somerset, English-Scottish politician, Lord Chamberlain of the United Kingdom (b. 1587) deaths

Robert Carr, 1st Earl of Somerset, was a politician, and favourite of King James VI and I.

The Lord Chamberlain of the Household is the most senior officer of the Royal Household of the United Kingdom, supervising the departments which support and provide advice to the Sovereign of the United Kingdom while also acting as the main channel of communication between the Sovereign and the House of Lords. The office organises all ceremonial activity such as garden parties, state visits, royal weddings, and the State Opening of Parliament. They also handle the Royal Mews and Royal Travel, as well as the ceremony around the awarding of honours.
William, Count of Nassau-Siegen, German count, field marshal of the Dutch State Army (b. 1592) deaths

William, Count of Nassau-Siegen, German: Wilhelm Graf von Nassau-Siegen, official titles: Graf zu Nassau, Katzenelnbogen, Vianden und Diez, Herr zu Beilstein, was Count of Nassau-Siegen, a part of the County of Nassau from 1624 to 1642. A member of the House of Nassau-Siegen, a cadet branch of the Ottonian Line of the House of Nassau, he was a professional soldier who served in the armies of the Hanseatic League and the Republic of Venice, then with the Dutch States Army during the Eighty Years War. Promoted field marshal in 1633, he was successively governor of Emmerich, Heusden and Sluis.
Mózes Székely, Hungarian noble (b. 1553) deaths
Moses Székely was Prince of Transylvania in 1603.
Mimar Sinan, Ottoman architect and engineer, designed the Sokollu Mehmet Pasha Mosque and Süleymaniye Mosque (b. 1489) deaths

Mimar Sinan also known as Koca Mi'mâr Sinân Âğâ, was the chief Ottoman architect and civil engineer for sultans Suleiman the Magnificent, Selim II and Murad III. He was responsible for the construction of more than 300 major structures and other more modest projects, such as schools. His apprentices would later design the Sultan Ahmed Mosque in Istanbul and Stari Most in Mostar.

The Sokollu Mehmed Pasha Mosque is a 16th-century Ottoman mosque located in Istanbul, Turkey.

The Süleymaniye Mosque is an Ottoman imperial mosque located on the Third Hill of Istanbul, Turkey. The mosque was commissioned by Suleiman the Magnificent and designed by the imperial architect Mimar Sinan. An inscription specifies the foundation date as 1550 and the inauguration date as 1557. Behind the qibla wall of the mosque is an enclosure containing the separate octagonal mausoleums of Suleiman the Magnificent and his wife Hurrem Sultan (Roxelana). For 462 years, the Süleymaniye Mosque was the largest mosque in the city, until it was surpassed by the Çamlıca Mosque in 2019. The Süleymaniye Mosque is one of the best-known sights of Istanbul, and from its location on the Third Hill, it commands an extensive view of the city around the Golden Horn.
Georg Fabricius, German poet and historian (b. 1516) deaths

Georg Fabricius, born Georg Goldschmidt, was a Protestant German poet, historian and archaeologist who wrote in Latin during the German Renaissance.
Antoine de Créqui Canaples, Roman Catholic cardinal (d. 1574) births

Antoine de Créqui Canaples (1531–1574) was a French Roman Catholic bishop and cardinal.
Hosokawa Takakuni, Japanese commander (b. 1484) deaths

Hosokawa Takakuni was the most powerful military commander in the Muromachi period under Ashikaga Yoshiharu, the twelfth shōgun. His father was Hosokawa Masaharu, a member of the branch of the Hosokawa clan. His childhood name was Rokuro (六郎).
Maria Salviati, Italian noblewoman (d. 1543) births

Maria Salviati was a Florentine noblewoman, the daughter of Lucrezia di Lorenzo de' Medici and Jacopo Salviati. She married Giovanni delle Bande Nere and was the mother of Cosimo I de Medici. Her husband died 30 November 1526, leaving her a widow at the age of 27. Salviati never remarried; after her husband's death she adopted the somber garb of a novice, which is how she is remembered today as numerous late portraits show her attired in black and white.
Ismail I of Iran (d. 1524) births

Ismail I, also known as Shah Ismail, was the founder of the Safavid dynasty of Iran, ruling as its King of Kings (Shahanshah) from 1501 to 1524. His reign is often considered the beginning of modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires.
Dmitry Shemyaka, Grand Prince of Moscow deaths

Dmitriy Yurievich Shemyaka was the second son of Yury of Zvenigorod by Anastasia of Smolensk and grandson of Dmitri Donskoi. His hereditary patrimony was the rich Northern town Galich-Mersky. Shemyaka was twice Grand Prince of Moscow.

Moscow is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 20 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of 2,511 square kilometers (970 sq mi), while the urban area covers 5,891 square kilometers (2,275 sq mi), and the metropolitan area covers over 26,000 square kilometers (10,000 sq mi). Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent.
John Talbot, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury, English commander and politician (b. 1387) deaths

John Talbot, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury, 1st Earl of Waterford, 7th Baron Talbot, KG, known as "Old Talbot", was an English nobleman and a noted military commander during the Hundred Years' War. He was the most renowned in England and most feared in France of the English captains in the last stages of the conflict. Known as a tough, cruel, and quarrelsome man, Talbot distinguished himself militarily in a time of decline for the English. Called the "English Achilles" and the "Terror of the French", he is lavishly praised in the plays of Shakespeare. The manner of his death, leading an ill-advised charge against field artillery, has come to symbolize the passing of the age of chivalry. He also held the subsidiary titles of 10th Baron Strange of Blackmere and 6th Baron Furnivall jure uxoris.
Jadwiga, queen of Poland (b. 1374) deaths

Jadwiga, also known as Hedwig, was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland, and his wife, Elizabeth of Bosnia. Jadwiga was a member of the Capetian House of Anjou, but she had more close forebears among the Polish Piasts than among the Angevins.

Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi). Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin.
Edmund Mortimer, 2nd Baron Mortimer (b. 1251) deaths

Edmund Mortimer, 2nd Baron Mortimer of Wigmore was the second son and eventual heir of Roger Mortimer, 1st Baron Mortimer of Wigmore. His mother was Maud de Braose.
Sverker II, king of Sweden (b. 1210) deaths
Sverker II or Sverker the Younger was King of Sweden from 1195 or 1196 to 1208 when he was defeated in the Battle of Lena by Prince Eric. Sverker died in the 1210 Battle of Gestilren where his forces battled those of King Eric X.

Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic country in Scandinavia. It borders Norway to the west and north, Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridge–tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the largest Nordic country, the third-largest country in the European Union, and the fifth-largest country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a total population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of 25.5 inhabitants per square kilometre (66/sq mi), with around 87% of Swedes residing in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country.
Baldwin VII, count of Flanders (b. 1093) deaths
Baldwin VII of Flanders was Count of Flanders from 1111 to 1119.
Robert Guiscard, Norman adventurer deaths

Robert Guiscard was a Norman adventurer remembered for the conquest of southern Italy and Sicily. Robert was born into the Hauteville family in Normandy, went on to become count and then duke of Apulia and Calabria (1057–1059), Duke of Sicily (1059–1085), and briefly prince of Benevento (1078–1081) before returning the title to the papacy.
Baldwin VI, count of Flanders (b. 1030) deaths
Baldwin VI, also known as Baldwin the Good, was Count of Hainaut from 1051 to 1070 and Count of Flanders from 1067 to 1070.

The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
Du, empress dowager of the Song Dynasty deaths

Empress Dowager Du was an empress dowager of imperial China's Song Dynasty. She was the wife of general Zhao Hongyin and the mother of Emperor Taizu of Song, who founded the Song Dynasty.

The Song dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty.
Wu Hanyue, Chinese noblewoman (b. 913) deaths
Lady Wu Hanyue (吳漢月), formally the Lady Dowager Gongyi of Wuyue (吳越國恭懿太夫人), was the mother of Qian Chu, the fifth and final king of the Chinese state Wuyue of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period.
Leo IV, pope of the Catholic Church (b. 790) deaths

Pope Leo IV was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 10 April 847 to his death. He is remembered for repairing Roman churches that had been damaged during the Arab raid against Rome, and for building the Leonine Wall around Vatican Hill to protect the city. Pope Leo organized a league of Italian cities who fought and won the sea Battle of Ostia against the Saracens.

The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2019. As the world's oldest and largest continuously functioning international institution, it has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. The church consists of 24 sui iuris churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state.
Magnus Felix Ennodius, Gallo-Roman bishop deaths
Magnus Felix Ennodius was Bishop of Pavia in 514, and a Latin rhetorician and poet.
Christian feast day: Alexius of Rome (Western Church)

Saint Alexius of Rome or Alexius of Edessa, also Alexis, was a fourth-century Greek monk who lived in anonymity and is known for his dedication to Christ. There are two versions of his life that are known, a Syriac one and a Greek one.

The Latin Church is the largest autonomous particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Christians in communion with the Pope in Rome. The Latin Church is one of 24 churches sui iuris in communion with the pope; the other 23 are referred to as the Eastern Catholic Churches, and have approximately 18 million members combined. The Latin Church traditionally employs the Latin liturgical rites, which since the mid-twentieth century are very often translated into the vernacular language. The predominant liturgical rite is the Roman Rite, elements of which have been practiced since the fourth century.
Christian feast day: Andrew Zorard
Andrew Zorard was a Benedictine monk originating from Poland but active in Slovakia, who is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church and the Orthodox Churches
Christian feast day: Cynehelm

Saint Kenelm was an Anglo-Saxon saint, venerated throughout medieval England, and mentioned in the Canterbury Tales. William of Malmesbury, writing in the 12th century, recounted that "there was no place in England to which more pilgrims travelled than to Winchcombe on Kenelm's feast day".
Christian feast day: Cynllo

Saint Cynllo is a British saint, who lived in the late 5th and early 6th centuries, generally described as a brother of Saint Teilo. Cynllo was known for "...the sanctity of his life and the austerity of his manners."
Christian feast day: Inácio de Azevedo

Inácio de Azevedo (1526–1570) was a Portuguese Jesuit missionary. He is one of the Forty Martyrs of Brazil, beatified by Pope Pius IX in 1854.
Christian feast day: Jadwiga of Poland

Jadwiga, also known as Hedwig, was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland, and his wife, Elizabeth of Bosnia. Jadwiga was a member of the Capetian House of Anjou, but she had more close forebears among the Polish Piasts than among the Angevins.
Christian feast day: Magnus Felix Ennodius
Magnus Felix Ennodius was Bishop of Pavia in 514, and a Latin rhetorician and poet.
Christian feast day: Marcellina

Marcellina was born in Trier, Gaul the daughter of the Praetorian prefect of Gaul, and was the elder sister of Ambrose of Milan and Satyrus of Milan. Marcellina devoted her life as a consecrated virgin to the practice of prayer and asceticism. Her feast is on 17 July.
Christian feast day: Martyrs of Compiègne

The Martyrs of Compiègne were the 16 members of the Carmel of Compiègne, France: 11 Discalced Carmelite nuns, three lay sisters, and two externs. They were executed by the guillotine towards the end of the Reign of Terror, at what is now the Place de la Nation in Paris on 17 July 1794, and are venerated as beatified martyrs of the Catholic Church. Ten days after their execution, Maximilien Robespierre himself was executed, ending the Reign of Terror. Their story has inspired a novella, a motion picture, a television movie, and an opera, Dialogues of the Carmelites, written by French composer Francis Poulenc.
Christian feast day: Blessed Pavel Peter Gojdič (Greek Catholic Church)

Pavel Peter Gojdič, was a Rusyn Basilian monk and the eparch of the Slovak Catholic Eparchy of Prešov. He was imprisoned by the communist regime in Czechoslovakia. He was beatified by Pope John Paul II in 2001 and recognised as Righteous Among the Nations by Yad Vashem in 2007.
The term Greek Catholic Church can refer to a number of Eastern Catholic Churches following the Byzantine (Greek) liturgy, considered collectively or individually.
Christian feast day: Pope Leo IV

Pope Leo IV was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 10 April 847 to his death. He is remembered for repairing Roman churches that had been damaged during the Arab raid against Rome, and for building the Leonine Wall around Vatican Hill to protect the city. Pope Leo organized a league of Italian cities who fought and won the sea Battle of Ostia against the Saracens.
Christian feast day: Romanov sainthood (Russian Orthodox Church)

The canonization of the Romanovs was the elevation to sainthood of the last Imperial Family of Russia – Tsar Nicholas II, his wife Tsarina Alexandra, and their five children Olga, Tatiana, Maria, Anastasia, and Alexei – by the Russian Orthodox Church.

The Russian Orthodox Church, alternatively legally known as the Moscow Patriarchate, is the largest autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The primate of the ROC is the Patriarch of Moscow and all Rus'. The ROC, as well as its primate, officially ranks fifth in the Eastern Orthodox order of precedence, immediately below the four ancient patriarchates of the Greek Orthodox Church: Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, and Jerusalem.
Christian feast day: Speratus and companions
The Scillitan Martyrs were a company of twelve North African Christians who were executed for their beliefs on 17 July 180 AD. The martyrs take their name from Scilla, a town in Numidia. The Acts of the Scillitan Martyrs are considered to be the earliest documents of the church of Africa and also the earliest specimen of Christian Latin.
Christian feast day: William White (Episcopal Church))

William White was the first and fourth Presiding Bishop of the Episcopal Church of the United States, the first bishop of the Diocese of Pennsylvania (1787–1836), and the second United States Senate Chaplain. He also served as the first and fourth President of the House of Deputies for the General Convention of the Episcopal Church.
The veneration of saints in the Episcopal Church is a continuation of an ancient tradition from the early Church which honors important and influential people of the Christian faith. The usage of the term saint is similar to Roman Catholic and Orthodox traditions. Episcopalians believe in the communion of saints in prayer and as such the Episcopal liturgical calendar accommodates feasts for saints.
Christian feast day: July 17 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)

July 16 - Eastern Orthodox Church calendar - July 18
Constitution Day (South Korea)

Constitution Day or Jeheonjeol in South Korea is observed on 17 July, the day that the South Korean constitution was proclaimed in 1948. The date was deliberately chosen to match the founding date of 17 July of the Joseon dynasty.
Gion Matsuri (Yasaka Shrine, Kyoto)

The Gion Festival is one of the largest and most famous festivals in Japan, taking place annually during the month of July in Kyoto. Many events take place in central Kyoto and at the Yasaka Shrine, the festival's patron shrine, located in Kyoto's famous Gion district, which gives the festival its name. It is formally a Shinto festival, and its original purposes were purification and pacification of disease-causing entities. There are many ceremonies held during the festival, but it is best known for its two Yamaboko Junkō (山鉾巡行) processions of floats, which take place on July 17 and 24.

Yasaka Shrine , once called Gion Shrine , is a Shinto shrine in the Gion District of Kyoto, Japan. Situated at the east end of Shijō-dōri, the shrine includes several buildings, including gates, a main hall and a stage. The Yasaka shrine is dedicated to Susanoo as its chief kami, with his consort Kushinadahime on the east, and eight offspring deities on the west. The yahashira no mikogami include Yashimajinumi no kami, Itakeru no kami, Ōyatsuhime no kami, Tsumatsuhime no kami, Ōtoshi no kami, Ukanomitama no kami, Ōyatsuhiko no kami, and Suseribime no mikoto.

Kyoto, officially Kyoto City , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. As of 2020, the city had a population of 1.46 million. The city is the cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Kyoto, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 3.8 million people.
Independence Day (Slovakia)
Remembrance Days in Slovakia are working days.
International Firgun Day (international)
Firgun is an informal modern Hebrew term and concept in Israeli culture, which compliments someone or describes genuine, unselfish delight or pride in the accomplishment of the other person. Another definition describes firgun as a generosity of spirit, an unselfish, empathetic joy that something good has happened, or might happen, to another person. The concept does not have a one-word equivalent in English. The infinitive form of the word, lefargen, means to make someone feel good without any ulterior motives. This absence of negativity is an integral part of the concept of firgun.
King's Birthday (Lesotho)
This is a list of holidays in Lesotho.January 1: New Year's Day March 11: Moshoeshoe's Day March 29: Good Friday April 1: Easter Monday May 1: Workers' Day May 10: Ascension Day May 25: Africa Day July 17: King's Birthday October 4: Independence Day December 25: Christmas Day December 26: Boxing Day
U Tirot Sing Day (Meghalaya, India)
Tirot Sing, also known as U Tirot Sing Syiem born in the year 1802 and died in the year 1835, was one of the chiefs of the Khasi people in the early 19th century. He drew his lineage from the Syiemlieh clan. He was Syiem (chief) of Nongkhlaw, part of the Khasi Hills. His surname was Syiemlieh. He was a constitutional head sharing corporate authority with his Council, general representatives of the leading clans within his territory. Tirot Sing declared war and fought against British for attempts to take over control of the Khasi Hills.

Meghalaya is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: (a) the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills and (b) the Garo Hills on 21 January 1972. Meghalaya was previously part of Assam, but on 21 January 1972, the districts of Khasi, Garo and Jaintia Hills became the new state of Meghalaya. The population of Meghalaya as of 2014 is estimated to be 3,211,474. Meghalaya covers an area of approximately 22,430 square kilometres, with a length-to-breadth ratio of about 3:1.

India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia.
World Day for International Justice (International)
World Day for International Justice, also referred to as Day of International Criminal Justice or International Justice Day, is an international day celebrated throughout the world on July 17 as part of an effort to recognize the emerging system of international criminal justice. July 17 is the date of the adoption of the treaty that created the International Criminal Court. On 1 June 2010, at the Review Conference of the Rome Statute held in Kampala (Uganda), the Assembly of State Parties decided to celebrate 17 July as the Day of International Criminal Justice.
Lists of holidays by various categorizations.
World Emoji Day (International)

World Emoji Day is an annual unofficial holiday occurring on 17 July, intended to celebrate emoji; in the years since the earliest observance, it has become a popular date to make product or other announcements and releases relating to emoji.
Lists of holidays by various categorizations.