
2014 Medina hotel fire
The 2014 Medina hotel fire was a hotel fire that occurred in a hotel in Medina, Saudi Arabia. The fire killed at least 15 people and another 130 were injured.
A hotel fire in Medina, Saudi Arabia kills 15 Egyptian pilgrims with 130 others injured.

The 2014 Medina hotel fire was a hotel fire that occurred in a hotel in Medina, Saudi Arabia. The fire killed at least 15 people and another 130 were injured.

Medina, officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah, is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the Medina Province of Saudi Arabia. As of 2020, the estimated population of the city is 1,488,782, making it the fourth-most populous city in the country. Located at the core of the Medina Province in the western reaches of the country, the city is distributed over 589 km2 (227 sq mi), of which 293 km2 (113 sq mi) constitutes the city's urban area, while the rest is occupied by the Hejaz Mountains, empty valleys, agricultural spaces and older dormant volcanoes.

Egypt, officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world.
A blizzard disrupts transportation and leaves hundreds of thousands of people without electricity in the Northeastern United States and parts of Canada.

The February 2013 North American blizzard, also known as Winter Storm Nemo and the Blizzard of 2013, was a powerful blizzard that developed from the combination of two areas of low pressure, primarily affecting the Northeastern United States and parts of Canada, causing heavy snowfall and hurricane-force winds. The storm crossed the Atlantic Ocean, affecting Ireland and the United Kingdom. The nor'easter's effects in the United States received a Category 3 rank on the Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale, classifying it as a "Major" Winter Storm.
A freak storm triggered a series of avalanches that buried more than 3.5 km (2.2 mi) of road near the Salang Tunnel in Afghanistan, killing 175 people and trapping more than 2,500 travellers.

The 2010 Salang avalanches consisted of a series of at least 36 avalanches that struck the southern approach to the Salang Tunnel, north of Kabul. They were caused by a freak storm in the Hindu Kush mountains.

The Salang Tunnel is a 2.67-kilometre-long (1.66 mi) tunnel located at the Salang Pass in the Hindu Kush mountains, between the Parwan and Baghlan provinces of Afghanistan, about 90 kilometers north of the city of Kabul. Nearly 3,200 m (10,500 ft) above sea level, it was completed by the Soviet Union in 1964 and connects northern Afghanistan with the capital, Kabul, and southern parts of the country. The Salang Tunnel is of strategic importance and is the only pass going in a north–south direction to remain in use throughout the year, although it is often closed during the cold winters by heavy snowfall.
A freak storm in the Hindu Kush mountains of Afghanistan triggers a series of at least 36 avalanches, burying over two miles of road, killing at least 172 people and trapping over 2,000 travelers.

The Hindu Kush is an 800-kilometre-long (500 mi) mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan into northwestern Pakistan and far southeastern Tajikistan. The range forms the western section of the Hindu Kush Himalayan Region (HKH); to the north, near its northeastern end, the Hindu Kush buttresses the Pamir Mountains near the point where the borders of China, Pakistan and Afghanistan meet, after which it runs southwest through Pakistan and into Afghanistan near their border. The eastern end of the Hindu Kush in the north merges with the Karakoram Range. Towards its southern end, it connects with the Spin Ghar Range near the Kabul River. It divides the valley of the Amu Darya to the north from the Indus River valley to the south. The range has numerous high snow-capped peaks, with the highest point being Tirich Mir or Terichmir at 7,708 metres (25,289 ft) in the Chitral District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.

Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east. Occupying 652,864 square kilometers (252,072 sq mi) of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains in the north and the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. As of 2021, its population is 40.2 million, composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and serves as its capital.

The 2010 Salang avalanches consisted of a series of at least 36 avalanches that struck the southern approach to the Salang Tunnel, north of Kabul. They were caused by a freak storm in the Hindu Kush mountains.
Sri Lankan Civil War: Sri Lankan Tamil politician and former MP A. Chandranehru dies of injuries sustained in an ambush the previous day.

The Sri Lankan Civil War was a civil war fought in Sri Lanka from 1983 to 2009. Beginning on 23 July 1983, there was an intermittent insurgency against the government by the Velupillai Prabhakaran-led Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. The LTTE fought to create an independent Tamil state called Tamil Eelam in the north-east of the island, due to the continuous discrimination and violent persecution against Sri Lankan Tamils by the Sinhalese dominated Sri Lankan Government.

Ariyanayagam Chandranehru was a Sri Lankan Tamil merchant seaman, politician and Member of Parliament.
The U.S. Congress passes the Communications Decency Act.

The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The vice president of the United States has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members.
The Communications Decency Act of 1996 (CDA) was the United States Congress's first notable attempt to regulate pornographic material on the Internet. In the 1997 landmark case Reno v. ACLU, the United States Supreme Court unanimously struck the act's anti-indecency provisions.
General Motors sues NBC after Dateline NBC allegedly rigs two crashes intended to demonstrate that some GM pickups can easily catch fire if hit in certain places. NBC settles the lawsuit the next day.

The General Motors Company (GM) is an American multinational automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and was the largest in the world for 77 years before losing the top spot to Toyota in 2008.

The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American English-language commercial broadcast television and radio network. The flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, its headquarters are located at Comcast Building in New York City. The company also has offices in Los Angeles at 10 Universal City Plaza and Chicago at the NBC Tower. NBC is the oldest of the traditional "Big Three" American television networks, having been formed in 1926 by the Radio Corporation of America. NBC is sometimes referred to as the "Peacock Network," in reference to its stylized peacock logo, introduced in 1956 to promote the company's innovations in early color broadcasting.
Dateline NBC is a weekly American television news magazine/reality legal show that is broadcast on NBC. It was previously the network's flagship general interest news magazine, but now focuses mainly on true crime stories with only occasional editions that focus on other topics. The program airs Fridays at 10:00 p.m. Eastern Time. Special Saturday encore editions also air at 9:00 p.m.. Two-hour feature-length editions sometimes air on any given scheduled evening, often to fill vacancies in the primetime schedule on the program's respective nights due to program cancellations. In February 2021, the program aired its first ever docuseries, "The Widower," a five-hour true crime saga about a man who married six women, four of whom died.
An Iran Air Tours Tupolev Tu-154 and an Iranian Air Force Sukhoi Su-24 collide in mid-air near Qods, Iran, killing all 133 people on board both aircraft.
Iran Airtour is an airline based in Tehran, Iran. Iran Airtour's hubs are at Mehrabad International Airport and Mashhad International Airport. In total, the group has 11 aircraft in service. It operates scheduled domestic and international passenger service, Iran Airtours is one of IATA members in Iran and has IATA Operational Safety Audit (IOSA) certificate.

The Tupolev Tu-154 is a three-engined, medium-range, narrow-body airliner designed in the mid-1960s and manufactured by Tupolev. A workhorse of Soviet and (subsequently) Russian airlines for several decades, it carried half of all passengers flown by Aeroflot and its subsidiaries, remaining the standard domestic-route airliner of Russia and former Soviet states until the mid-2000s. It was exported to 17 non-Russian airlines and used as a head-of-state transport by the air forces of several countries.

The Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force (IRIAF); Persian: نیروی هوایی ارتش جمهوری اسلامی ایران, Nirvi-ye Hevayi-ye Artesh-e Jimhuri-ye Eslâmi-ye Iran) is the aviation branch of the Islamic Republic of Iran Army. The present air force came into being when the Imperial Iranian Air Force was renamed in 1979 following the Iranian Revolution. The IRIAF was heavily involved in the Iran–Iraq War, carrying out major operations like Operation Kaman 99, Operation Sultan 10, the H-3 airstrike, and the first attack on a nuclear reactor in history, Operation Scorch Sword. As a result of eight years of aerial combat in that conflict, the IRIAF has the second highest claimed number of fighter aces in the region, exceeded only by the Israeli Air Force; as many as seven IRIAF pilots claimed more than six kills, mostly achieved in the F-14 Tomcat. Veterans of the Iran–Iraq War would go on to form the core of the IRIAF command.

The Sukhoi Su-24 is a supersonic, all-weather attack aircraft developed in the Soviet Union. The aircraft has a variable-sweep wing, twin-engines and a side-by-side seating arrangement for its crew of two. It was the first of the USSR's aircraft to carry an integrated digital navigation/attack system. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force, Syrian Air Force, Ukrainian Air Force, Algerian Air Force and various other air forces to which it was exported.

On 8 February 1993, Iran Air Tours Flight 962, a Tupolev Tu-154, collided in mid-air with an Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force (IRIAF) Sukhoi Su-24 attack aircraft near the Iranian capital of Tehran, killing all 133 people aboard both aircraft. It is the deadliest aviation incident in 1993.
Qods is a city and capital of Qods County, Tehran Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 229,354, in 60,331 families. Before Qods officially became a municipality in 1989 it was named Qal‘eh Hasan. The city is named after Jerusalem, in Arabic spelling.
Independent Air Flight 1851 strikes Pico Alto mountain while on approach to Santa Maria Airport (Azores) killing all 144 passengers on board.

On 8 February 1989, Independent Air Flight 1851, a Boeing 707 on an American charter flight from Bergamo, Italy to Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, struck Pico Alto while on approach to Santa Maria Airport in the Azores for a scheduled stopover. The aircraft was destroyed, with the loss of all 144 people on board, resulting in the deadliest plane crash in Portugal's history. All of the passengers on board were Italian and all of the crew were Americans. The crash is also known as "The disaster of the Azores".

Pico Alto is a mountain which is the highest point, 586.84 metres (1,925.3 ft), on the island of Santa Maria, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores.

Santa Maria Airport is an international airport located 5 km (3.1 mi) west northwest of the urbanized area of Vila do Porto on the island of Santa Maria, in the Portuguese autonomous region of the Azores. A principal hub in transatlantic travel until the end of the 20th century, it was constructed at the start of the Second World War to protect convoys by American troops who were ceded authority until its end. From this period on, the airfield took on a commercial role, reinforced by inter-island travel and connections to Europe, resulting in its obtaining the communication duties for the North Atlantic sector of the airspace corridor.
Hinton train collision: Twenty-three people are killed when a VIA Rail passenger train collides with a 118-car Canadian National freight train near the town of Hinton, Alberta, west of Edmonton. It is the worst rail accident in Canada until the Lac-Mégantic, Quebec derailment in 2013 which killed forty-seven people.
The Hinton train collision was a rail transport accident that occurred in Canada on 8 February 1986. Twenty-three people were killed in a collision between a Canadian National Railway freight train and a Via Rail passenger train called the Super Continental, including the engine crews of both trains. It was the deadliest rail disaster in Canada since the Dugald accident of 1947, which had thirty-one fatalities, and was not surpassed until the Lac-Mégantic rail disaster in 2013, which resulted in 47 deaths.
The Melbourne dust storm hits Australia's second largest city. The result of the worst drought on record and a day of severe weather conditions, a 320 metres (1,050 ft) deep dust cloud envelops the city, turning day to night.
The 1983 Melbourne dust storm was a meteorological phenomenon that occurred during the afternoon of 8 February 1983, throughout much of Victoria, Australia and affected the capital, Melbourne. Red soil, dust and sand from Central and Southeastern Australia was swept up in high winds and carried southeast through Victoria. The dust storm was one of the most dramatic consequences of the 1982/83 drought, at the time the worst in Australian history and is, in hindsight, viewed as a precursor to the Ash Wednesday bushfires which were to occur eight days later.
Irish race horse Shergar is stolen by gunmen.

Shergar was an Irish-bred, British-trained Thoroughbred racehorse. After a very successful season in 1981 he was retired to the Ballymany Stud in County Kildare, Ireland. In 1983 he was stolen from the stud, and a ransom of £2 million was demanded; it was not paid, and negotiations were soon broken off by the thieves. In 1999 a supergrass, formerly in the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA), stated they stole the horse. The IRA has never admitted any role in the theft.
Twenty-one association football spectators are trampled to death at Karaiskakis Stadium in Neo Faliro, Greece, after a football match between Olympiacos F.C. and AEK Athens F.C.

Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is to score more goals than the opposition by moving the ball beyond the goal line into a rectangular framed goal defended by the opposing side. Traditionally, the game has been played over two 45 minute halves, for a total match time of 90 minutes. With an estimated 250 million players active in over 200 countries, it is considered the world's most popular sport.
The Karaiskakis Stadium disaster was an incident that occurred on 8 February 1981 in the Karaiskakis Stadium in Neo Faliro, Piraeus, Greece, after the conclusion of a football match between Olympiacos and AEK Athens. It is the biggest football tragedy in Greece's history,.

The Georgios Karaiskakis Stadium, commonly referred to as the Karaiskakis Stadium, is a football stadium in Piraeus, Attica, Greece, and the home ground of the Piraeus football club Olympiacos. With a capacity of 32,115, it is the second largest only football stadium and the third largest football stadium overall in Greece. It is named after Georgios Karaiskakis, a military commander of the Greek War of Independence, who is considered a national hero and was mortally wounded in the area.

Phalerum or Phaleron was a port of Ancient Athens, 5 km southwest of the Acropolis of Athens, on a bay of the Saronic Gulf. The bay is also referred to as "Bay of Phalerum".

Olympiacos Club of Fans of Piraeus, known simply as Olympiacos or Olympiacos Piraeus, is a Greek professional football club based in Piraeus, Attica. Part of the major multi-sport club Olympiacos CFP, their name was inspired from the ancient Olympic Games and along with the club's emblem, the laurel-crowned Olympic athlete, symbolize the Olympic ideals of ancient Greece. Their home ground is the Karaiskakis Stadium, a 32,115-capacity stadium in Piraeus.

AEK FC is a Greek professional football club based in Nea Filadelfeia, a suburb of Attica, Greece.
Proceedings of the United States Senate are broadcast on radio for the first time.

The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
After 84 days in space, the crew of Skylab 4, the last crew to visit American space station Skylab, returns to Earth.

Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust, and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvins. The plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxies. Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Observations suggest that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable universe is dark energy, a type of vacuum energy that is poorly understood. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.

Skylab 4 was the third crewed Skylab mission and placed the third and final crew aboard the first American space station.

A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station is an artificial satellite. Stations must have docking ports to allow other spacecraft to dock to transfer crew and supplies. The purpose of maintaining an orbital outpost varies depending on the program. Space stations have most often been launched for scientific purposes, but military launches have also occurred.

Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation, and hundreds of experiments.
The NASDAQ stock market index opens for the first time.
The Nasdaq Stock Market is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is ranked second on the list of stock exchanges by market capitalization of shares traded, behind the New York Stock Exchange. The exchange platform is owned by Nasdaq, Inc., which also owns the Nasdaq Nordic stock market network and several U.S.-based stock and options exchanges.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures a stock market, or a subset of the stock market, that helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
South Vietnamese ground troops launch an incursion into Laos to try to cut off the Ho Chi Minh trail and stop communist infiltration.

The Army of the Republic of Vietnam composed the ground forces of the South Vietnamese military from its inception in 1955 to the Fall of Saigon in April 1975. It is estimated to have suffered 1,394,000 casualties during the Vietnam War.

Operation Lam Son 719 or 9th Route – Southern Laos Campaign was a limited-objective offensive campaign conducted in the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos. The campaign was carried out by the armed forces of South Vietnam between 8 February and 25 March 1971, during the Vietnam War. The United States provided logistical, aerial and artillery support for the operation, but its ground forces were prohibited by law from entering Laotian territory. The objective of the campaign was the disruption of a possible future offensive by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), whose logistical system within Laos was known as the Ho Chi Minh Trail.

Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a socialist state and the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. At the heart of the Indochinese Peninsula, Laos is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. Its capital and largest city is Vientiane.

The Ho Chi Minh Trail, also called Annamite Range Trail was a logistical network of roads and trails that ran from North Vietnam to South Vietnam through the kingdoms of Laos and Cambodia. The system provided support, in the form of manpower and materiel, to the Viet Cong and the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), during the Vietnam War. Construction for the network began following the North Vietnamese invasion of Laos in July 1959.

The People's Army of Vietnam, also recognized as the Vietnam People's Army (VPA) or the Vietnamese Army, is the military force of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and the armed wing of the ruling Communist Party of Vietnam. The PAVN is a part of the Vietnam People's Armed Forces and includes: Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, Border Guard and Coast Guard. However, Vietnam does not have a separate Ground Force or Army branch. All ground troops, army corps, military districts and specialised arms belong to the Ministry of Defence, directly under the command of the Central Military Commission, the Minister of Defence, and the General Staff of the Vietnam People's Army. The military flag of the PAVN is the flag of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, with the words Quyết thắng added in yellow at the top left.
American civil rights movement: The Orangeburg massacre: An attack on black students from South Carolina State University who are protesting racial segregation at the town's only bowling alley, leaves three or four dead in Orangeburg, South Carolina.

The civil rights movement was a political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish institutional racial segregation, discrimination, and disenfranchisement throughout the United States. The movement had its origins in the Reconstruction era during the late 19th century, although it made its largest legislative gains in the 1960s after years of direct actions and grassroots protests. The social movement's major nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience campaigns eventually secured new protections in federal law for the civil rights of all Americans.
The Orangeburg massacre refers to the shooting of protesters by South Carolina Highway Patrol officers in Orangeburg, South Carolina, on the South Carolina State University campus on the evening of February 8, 1968. About 200 protesters had previously demonstrated against racial segregation at a local bowling alley. Three of the protesters, African-American males, were killed and 28 other protesters were injured.

South Carolina State University is a public, historically black, land-grant university in Orangeburg, South Carolina, United States. It is the only public, historically black land-grant institution in South Carolina, is a member-school of the Thurgood Marshall College Fund, and is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS).

Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into racial or other ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crime against humanity under the Statute of the International Criminal Court. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, such as schools and hospitals by people of different races. Specifically, it may be applied to activities such as eating in restaurants, drinking from water fountains, using public toilets, attending schools, going to films, riding buses, renting or purchasing homes or renting hotel rooms. In addition, segregation often allows close contact between members of different racial or ethnic groups in hierarchical situations, such as allowing a person of one race to work as a servant for a member of another race.

Orangeburg, also known as The Garden City, is the principal city in and the county seat of Orangeburg County, South Carolina, United States. The population of the city was 13,964 according to the 2010 United States Census and declined to 12,704 in the 2020 census. The city is located 37 miles southeast of Columbia, on the north fork of the Edisto River.
After taking evasive action to avoid a mid-air collision just after taking off from New York's John F. Kennedy International Airport, Eastern Air Lines Flight 663 crashed into the Atlantic Ocean, killing all 84 people on board.

John F. Kennedy International Airport is the main international airport serving New York City. The airport is the busiest of the seven airports in the New York airport system, the 13th-busiest airport in the United States, and the busiest international air passenger gateway into North America. Over 90 airlines operate from the airport, with nonstop or direct flights to destinations in all six inhabited continents.

Eastern Air Lines Flight 663 was a domestic passenger flight from Boston, Massachusetts, to Atlanta, Georgia, with scheduled stopovers at John F. Kennedy International Airport, New York; Richmond, Virginia; Charlotte, North Carolina; and Greenville, South Carolina. On the night of February 8, 1965, the aircraft serving the flight, a Douglas DC-7, crashed near Jones Beach State Park, New York, just after taking off from JFK Airport. All 79 passengers and five crew aboard perished.
Eastern Air Lines Flight 663 crashes into the Atlantic Ocean and explodes, killing everyone aboard.

Eastern Air Lines Flight 663 was a domestic passenger flight from Boston, Massachusetts, to Atlanta, Georgia, with scheduled stopovers at John F. Kennedy International Airport, New York; Richmond, Virginia; Charlotte, North Carolina; and Greenville, South Carolina. On the night of February 8, 1965, the aircraft serving the flight, a Douglas DC-7, crashed near Jones Beach State Park, New York, just after taking off from JFK Airport. All 79 passengers and five crew aboard perished.
The regime of Prime Minister of Iraq, Brigadier General Abd al-Karim Qasim is overthrown by the Ba'ath Party.

The prime minister of Iraq is the head of government of Iraq. On 27 October 2022, Mohammed Shia' Al Sudani became the incumbent prime minister.

Abd al-Karim Qasim Muhammad Bakr al-Fadhli al-Zubaidi was an Iraqi Army brigadier and nationalist who came to power when the Iraqi monarchy was overthrown during the 14 July Revolution. He ruled the country as the prime minister until his downfall and execution during the 1963 Ramadan Revolution.

The Ramadan Revolution, also referred to as the 8 February Revolution and the February 1963 coup d'état in Iraq, was a military coup by the Ba'ath Party's Iraqi-wing which overthrew the Prime Minister of Iraq, Abd al-Karim Qasim in 1963. It took place between 8 and 10 February 1963. Qasim's former deputy, Abdul Salam Arif, who was not a Ba'athist, was given the largely ceremonial title of President, while prominent Ba'athist general Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was named Prime Minister. The most powerful leader of the new government was the secretary general of the Iraqi Ba'ath Party, Ali Salih al-Sa'di, who controlled the National Guard militia and organized a massacre of hundreds—if not thousands—of suspected communists and other dissidents following the coup.

The Arab Socialist Baʿath Party was a political party founded in Syria by Mishel ʿAflaq, Ṣalāḥ al-Dīn al-Bītār, and associates of Zaki al-ʾArsūzī. The party espoused Baʿathism, which is an ideology mixing Arab nationalist, pan-Arabism, Arab socialist, and anti-imperialist interests. Baʿathism calls for unification of the Arab world into a single state. Its motto, "Unity, Liberty, Socialism", refers to Arab unity, and freedom from non-Arab control and interference.
Charonne massacre: Nine trade unionists are killed by French police at the instigation of Nazi collaborator Maurice Papon, then chief of the Paris Prefecture of Police.

The Paris massacre of 1961 occurred on 17 October 1961, during the Algerian War (1954–62). Under orders from the head of the Parisian police, Maurice Papon, the French National Police attacked a demonstration by 30,000 pro-National Liberation Front (FLN) Algerians. After 37 years of denial and censorship of the press, in 1998 the French government finally acknowledged 40 deaths, while some historians estimate that between 200 and 300 Algerians died. Death was due to heavy-handed beating by the police, as well as mass drownings, as police officers threw demonstrators into the river Seine.
Nazism, the common name in English for National Socialism, is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism. The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War.

Maurice Papon was a French civil servant who led the police in major prefectures from the 1930s to the 1960s, before he became a Gaullist politician. When he was secretary general for the police in Bordeaux during World War II, he participated in the deportation of more than 1,600 Jews. He is also known for his activities in the Algerian War (1954–1962), during which he tortured insurgent prisoners as prefect of the Constantinois department, and ordered, as prefect of the Paris police, the deadly repression of a pro-National Liberation Front (FLN) demonstration against a curfew that he had "advised."
In France, a Prefecture of Police , headed by the Prefect of Police, is an agency of the Government of France under the administration of the Ministry of the Interior. Part of the National Police, it provides a police force for an area limited by department borders. As of 2012, two such prefectures exist:The Paris Police Prefecture, created in 1800. The Bouches-du-Rhône Police Prefecture, created in 2012.
The official groundbreaking of the Walk of Fame took place in Hollywood, California.

Groundbreaking, also known as cutting, sod-cutting, turning the first sod, or a sod-turning ceremony, is a traditional ceremony in many cultures that celebrates the first day of construction for a building or other project. Such ceremonies are often attended by dignitaries such as politicians and businesspeople.

The Hollywood Walk of Fame is a historic landmark which consists of more than 2,700 five-pointed terrazzo and brass stars embedded in the sidewalks along 15 blocks of Hollywood Boulevard and three blocks of Vine Street in Hollywood, California. The stars are permanent public monuments to achievement in the entertainment industry, bearing the names of a mix of actors, directors, producers, musicians, theatrical/musical groups, fictional characters, and others.
Hollywood usually refers to:Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California Hollywood, a metonym for the major studio system of American cinema
Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom issues an Order-in-Council, stating that she and her family would be known as the House of Windsor, and that her descendants will take the name Mountbatten-Windsor.
An Order-in-Council is a type of legislation in many countries, especially the Commonwealth realms. In the United Kingdom this legislation is formally made in the name of the monarch by and with the advice and consent of the Privy Council (King-in-Council), but in other countries the terminology may vary. The term should not be confused with Order of Council, which is made in the name of the Council without royal assent.

The House of Windsor is the reigning royal house of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms. In 1901, a line of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha succeeded the House of Hanover to the British monarchy with the accession of King Edward VII, son of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. In 1917, the name of the British royal house was changed from the German Saxe-Coburg and Gotha to the English Windsor because of anti-German sentiment in the United Kingdom during the First World War. There have been five British monarchs of the House of Windsor since then: George V, Edward VIII, George VI, Elizabeth II, and Charles III. The children and male-line descendants of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip also genealogically belong to the House of Oldenburg since Philip belonged to the Glücksburg branch of that house.

Mountbatten-Windsor is the personal surname used by some of the male-line descendants of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. Under a declaration made in Privy Council in 1960, the name Mountbatten-Windsor applies to male-line descendants of Queen Elizabeth II without royal styles and titles. Individuals with royal styles do not usually use a surname, but some descendants of the Queen with royal styles have used Mountbatten-Windsor when a surname was required.
The Hollywood Walk of Fame is established.

The Hollywood Walk of Fame is a historic landmark which consists of more than 2,700 five-pointed terrazzo and brass stars embedded in the sidewalks along 15 blocks of Hollywood Boulevard and three blocks of Vine Street in Hollywood, California. The stars are permanent public monuments to achievement in the entertainment industry, bearing the names of a mix of actors, directors, producers, musicians, theatrical/musical groups, fictional characters, and others.
The Government of Sindh, Pakistan, abolishes the Jagirdari system in the province. One million acres (4000 km2) of land thus acquired is to be distributed among the landless peasants.

Sindh is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province by population after Punjab. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan to the east and north-east and Punjab to the north. It shares International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of the province.
Feudalism in contemporary Pakistan usually refers to the power and influence of large landowning families, particularly through very large estates and in more remote areas. The adjective "feudal" in the context of Pakistan has been used to mean "a relatively small group of politically active and powerful landowners". "Feudal attitude" refers to "a combination of arrogance and entitlement". According to the Pakistan Institute of Labor Education and Research (PILER), five percent of agricultural households in Pakistan own nearly two-thirds of Pakistan's farmland.

A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasants existed: slave, serf, and free tenant. Peasants might hold title to land either in fee simple or by any of several forms of land tenure, among them socage, quit-rent, leasehold, and copyhold.
Cold War: The Stasi, the secret police of East Germany, is established.

The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. Historians do not fully agree on its starting and ending points, but the period is generally considered to span from the announcement of the Truman Doctrine on 12 March 1947 to the dissolution of the Soviet Union on 26 December 1991. The term cold war is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race.

The Ministry for State Security, commonly known as the Stasi, was the state security service of the East Germany from 1950 to 1990.

East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic, was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship.
The first portion of the Revised Standard Version of the Bible, the first serious challenge to the popularity of the Authorized King James Version, is published.

The Revised Standard Version (RSV) is an English translation of the Bible published in 1952 by the Division of Christian Education of the National Council of the Churches of Christ in the USA. This translation itself is a revision of the American Standard Version (ASV) of 1901, and was intended to be a readable and literally accurate modern English translation which aimed to "preserve all that is best in the English Bible as it has been known and used through the centuries" and "to put the message of the Bible in simple, enduring words that are worthy to stand in the great Tyndale-King James tradition."

The Bible is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthology – a compilation of texts of a variety of forms – originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary.

The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of King James VI and I. The 80 books of the King James Version include 39 books of the Old Testament, an intertestamental section containing 14 books of what Protestants consider the Apocrypha, and the 27 books of the New Testament. Noted for its "majesty of style", the King James Version has been described as one of the most important books in English culture and a driving force in the shaping of the English-speaking world.
The People's Republic of Korea is dissolved in the North, establishing the communist-controlled Provisional People's Committee of North Korea.

The People's Republic of Korea (PRK) was a short-lived provisional government that was organized at the time of the surrender of the Empire of Japan at the end of World War II. It was proclaimed on 6 September 1945, as Korea was being divided into two occupation zones, with the Soviet Union occupying the north and the United States occupying the south. Based on a network of people's committees, it presented a program of radical social change.

North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and Tumen rivers, and South Korea to the south at the Korean Demilitarized Zone. North Korea's border with South Korea is a disputed border as both countries claim the entirety of the Korean Peninsula. The country's western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. North Korea, like its southern counterpart, claims to be the legitimate government of the entire peninsula and adjacent islands. Pyongyang is the capital and largest city.

The Communist Party of Korea was a communist party in Korea. It was founded during a secret meeting in Seoul in 1925. The Governor-General of Korea had banned communist and socialist parties under the Peace Preservation Law, so the party had to operate in a clandestine manner. The leaders of the party were Kim Yong-bom and Pak Hon-yong.

The Provisional People's Committee of North Korea was the provisional government of North Korea.
World War II: The United Kingdom and Canada commence Operation Veritable to occupy the west bank of the Rhine.

Operation Veritable was the northern part of an Allied pincer movement that took place between 8 February and 11 March 1945 during the final stages of the Second World War. The operation was conducted by Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery's Anglo-Canadian 21st Army Group, primarily consisting of the First Canadian Army under Lieutenant-General Harry Crerar and the British XXX Corps under Lieutenant-general Brian Horrocks.

The Rhine is one of the major European rivers. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein, Swiss-Austrian, Swiss-German borders. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border, after which it flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally in Germany the Rhine turns into a predominantly westerly direction and flows into the Netherlands where it eventually empties into the North Sea. It digs an area of 9,973 sq km and its name derives from the Celtic Rēnos. There are also two German states named after the river, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate.
World War II: Mikhail Devyataev escapes with nine other Soviet inmates from a Nazi concentration camp in Peenemünde on the island of Usedom by hijacking the camp commandant's Heinkel He 111.

Mikhail Petrovich Devyataev was a Soviet fighter pilot known for his incredible escape from a Nazi concentration camp on the island of Usedom, in the Baltic Sea.

The Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad, Kiev, Minsk, Tashkent, Alma-Ata, and Novosibirsk. It was the largest country in the world, covering over 22,402,200 square kilometres (8,649,500 sq mi) and spanning eleven time zones.

From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps on its own territory and in parts of German-occupied Europe.

Peenemünde is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is part of the Amt of Usedom-Nord. The community is known for the Peenemünde Army Research Center, where the world's first functional large-scale liquid-propellant rocket, the V-2, was developed.

Usedom is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
Aircraft hijacking is the unlawful seizure of an aircraft by an individual or a group. Dating from the earliest of hijackings, most cases involve the pilot being forced to fly according to the hijacker's demands. There have also been incidents where the hijackers have overpowered the flight crew, made unauthorized entry into cockpit and flown them into buildings – most notably in the September 11 attacks – and in several cases, planes have been hijacked by the official pilot or co-pilot; e.g., Germanwings Flight 9525.

The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a "wolf in sheep's clothing". Due to restrictions placed on Germany after the First World War prohibiting bombers, it was presented solely as a civil airliner, although from conception the design was intended to provide the nascent Luftwaffe with a heavy bomber.
World War II: Japan invades Singapore.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories.

The Fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore, took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire of Japan captured the British stronghold of Singapore, with fighting lasting from 8 to 15 February 1942. Singapore was the foremost British military base and economic port in South–East Asia and had been of great importance to British interwar defence strategy. The capture of Singapore resulted in the largest British surrender in its history.

Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Strait of Malacca to the west, the Singapore Strait to the south, the South China Sea to the east, and the Straits of Johor to the north. The country's territory is composed of one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet; the combined area of these has increased by 25% since the country's independence as a result of extensive land reclamation projects. It has the third highest population density in the world. With a multicultural population and recognising the need to respect cultural identities of the major ethnic groups within the nation, Singapore has four official languages: English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. English is the lingua franca and numerous public services are available only in English. Multiracialism is enshrined in the constitution and continues to shape national policies in education, housing, and politics.
World War II: Dutch Colonial Army General Destruction Unit (AVC, Algemene Vernielings Corps) burns Banjarmasin, South Borneo to avoid Japanese capture.

The Royal Netherlands East Indies Army was the military force maintained by the Kingdom of the Netherlands in its colony of the Dutch East Indies, in areas that are now part of Indonesia. The KNIL's air arm was the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force. Elements of the Royal Netherlands Navy and Government Navy were also stationed in the Netherlands East Indies.

Banjarmasin is a city in South Kalimantan, Indonesia. It was the capital of the province until 15 February 2022. The city is located on a delta island near the junction of the Barito and Martapura rivers. Historically the centre of the Banjarese culture, and the capital of the Sultanate of Banjar, it is the biggest city in South Kalimantan and one of main cities of Kalimantan. The city covers an area of 98.46 km2 (38.02 sq mi) and had population of 657,663 in 2020. Greater Banjarmasin, also known as Banjarbakula, is an urban agglomeration of around two million people covering an area of 8,136 km2 (3,141 sq mi), which includes Banjarbaru, parts of Banjar Regency, Barito Kuala Regency, and Tanah Laut Regency and accounts for almost half of the province's population. It is the third most populous city on the island of Borneo.

South Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is the smallest province in Kalimantan, the Indonesian territory of Borneo. The provincial capital was Banjarmasin until 15 February 2022 when it was legally moved to Banjarbaru. The population of South Kalimantan was recorded at just over 3.625 million people at the 2010 Census, and at 4.07 million at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 4,112,576. One of the five Indonesian provinces in Kalimantan, it is bordered by the Makassar Strait in the east, Central Kalimantan in the west and north, the Java Sea in the south, and East Kalimantan in the north. The province also includes the island of Laut, located off the eastern coast of Kalimantan. The province is divided into 11 regencies and 2 cities. South Kalimantan is the traditional homeland of the Banjar people, although some parts of East Kalimantan and Central Kalimantan are also included in this criteria. Nevertheless, South Kalimantan, especially the former capital city Banjarmasin has always been the cultural capital of Banjarese culture. Many Banjarese have migrated to other parts of Indonesia, as well as neighbouring countries such as Singapore and Malaysia. In addition, other ethnic groups also inhabit the province, such as several groups of the Dayaks, who mostly live in the interior part of the province, as well as the Javanese, who mostly migrated from Java due to the Transmigration program which dated from the Dutch colonial era.
Spanish Civil War: Republicans establish the Interprovincial Council of Santander, Palencia and Burgos in Cantabria.

The Spanish Civil War was a civil war in Spain fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republicans and the Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the left-leaning Popular Front government of the Second Spanish Republic, and consisted of various socialist, communist, separatist, anarchist, and republican parties, some of which had opposed the government in the pre-war period. The opposing Nationalists were an alliance of Falangists, monarchists, conservatives, and traditionalists led by a military junta among whom General Francisco Franco quickly achieved a preponderant role. Due to the international political climate at the time, the war had many facets and was variously viewed as class struggle, a religious struggle, a struggle between dictatorship and republican democracy, between revolution and counterrevolution, and between fascism and communism. According to Claude Bowers, U.S. ambassador to Spain during the war, it was the "dress rehearsal" for World War II. The Nationalists won the war, which ended in early 1939, and ruled Spain until Franco's death in November 1975.

The Interprovincial Council of Santander, Palencia and Burgos was a governing body established on 8 February 1937 to coordinate the Republican areas in Cantabria, Palencia and Burgos during the Spanish Civil War. The council was dissolved in August 1937 after the occupation of the region by Nationalist forces.

Cantabria is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a comunidad histórica, a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the east by the Basque autonomous community, on the south by Castile and León, on the west by the Principality of Asturias, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea.
Capital punishment: The first state execution in the United States by gas chamber takes place in Nevada.
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is a state-sanctioned practice of killing a person as a punishment for a crime. The sentence ordering that an offender is to be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is condemned and is commonly referred to as being "on death row".

A gas chamber is an apparatus for killing humans or other animals with gas, consisting of a sealed chamber into which a poisonous or asphyxiant gas is introduced. Poisonous agents used include hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide.

Gee Jon was a Chinese national who was the first person in the United States to be executed by lethal gas. A member of the Hip Sing Tong criminal society from San Francisco, California, Gee was sentenced to death for the murder of an elderly member from another gang in Nevada. An unsuccessful attempt to pump poison gas directly into his cell at Nevada State Prison led to the development of the gas chamber.

Nevada is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the 9th-least densely populated of the U.S. states. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's people live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities. Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state.
United States President Warren G. Harding introduces the first radio set in the White House.

Warren Gamaliel Harding was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party, he was one of the most popular sitting U.S. presidents. After his death, a number of scandals were exposed, including Teapot Dome, as well as an extramarital affair with Nan Britton, which diminished his reputation.

An antique radio is a radio receiving set that is collectible because of its age and rarity.

The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. The term "White House" is often used as a metonym for the president and his advisers.
D. W. Griffith's controversial film The Birth of a Nation premieres in Los Angeles.

David Wark Griffith was an American film director. Considered one of the most influential figures in the history of the motion picture, he pioneered many aspects of film editing and expanded the art of the narrative film.

The Birth of a Nation, originally called The Clansman, is a 1915 American silent epic drama film directed by D. W. Griffith and starring Lillian Gish. The screenplay is adapted from Thomas Dixon Jr.'s 1905 novel and play The Clansman. Griffith co-wrote the screenplay with Frank E. Woods and produced the film with Harry Aitken.

Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world's most populous megacities. Los Angeles is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Southern California. With a population of roughly 3.9 million as of 2020, Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic and cultural diversity, Hollywood film industry, and sprawling metropolitan area. The city of Los Angeles lies in a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean extending through the Santa Monica Mountains and into the San Fernando Valley. It covers about 469 square miles (1,210 km2), and is the seat of Los Angeles County, which is the most populous county in the United States with an estimated 9.86 million as of 2022.
William D. Boyce (pictured) established the Boy Scouts of America, expanding the Scout Movement into the United States.

William Dickson Boyce was an American newspaper man, entrepreneur, magazine publisher, and explorer. He was the founder of the Boy Scouts of America (BSA) and the short-lived Lone Scouts of America (LSA). Born in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, he acquired a love for the outdoors early in his life. After working as a schoolteacher and a coal miner, Boyce attended Wooster Academy in Ohio before moving to the Midwest and Canada. An astute businessman, Boyce successfully established several newspapers, such as The Commercial in Winnipeg, Manitoba and the Lisbon Clipper in Lisbon, North Dakota. With his first wife, Mary Jane Beacom, he moved to Chicago to pursue his entrepreneurial ambitions. There he established the Mutual Newspaper Publishing Company and the weekly Saturday Blade, which catered to a rural audience and was distributed by thousands of newspaper boys. With his novel employment of newsboys to boost newspaper sales, Boyce's namesake publishing company maintained a circulation of 500,000 copies per week by 1894. Boyce strongly supported worker rights, as demonstrated by his businesses' support of labor unions and his concern for his newsboys' well-being.

The Boy Scouts of America is one of the largest scouting organizations and one of the largest youth organizations in the United States, with about 1.2 million youth participants. The BSA was founded in 1910, and since then, about 110 million Americans have participated in BSA programs. BSA is part of the international Scout Movement and became a founding member organization of the World Organization of the Scout Movement in 1922.

Scouting, also known as the Scout Movement, is a worldwide youth movement employing the Scout method, a program of informal education with an emphasis on practical outdoor activities, including camping, woodcraft, aquatics, hiking, backpacking, and sports. Another widely recognized movement characteristic is the Scout uniform, by intent hiding all differences of social standing in a country and encouraging equality, with neckerchief and campaign hat or comparable headwear. Distinctive uniform insignia include the fleur-de-lis and the trefoil, as well as merit badges and other patches.
The Boy Scouts of America is incorporated by William D. Boyce.

The Boy Scouts of America is one of the largest scouting organizations and one of the largest youth organizations in the United States, with about 1.2 million youth participants. The BSA was founded in 1910, and since then, about 110 million Americans have participated in BSA programs. BSA is part of the international Scout Movement and became a founding member organization of the World Organization of the Scout Movement in 1922.

William Dickson Boyce was an American newspaper man, entrepreneur, magazine publisher, and explorer. He was the founder of the Boy Scouts of America (BSA) and the short-lived Lone Scouts of America (LSA). Born in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, he acquired a love for the outdoors early in his life. After working as a schoolteacher and a coal miner, Boyce attended Wooster Academy in Ohio before moving to the Midwest and Canada. An astute businessman, Boyce successfully established several newspapers, such as The Commercial in Winnipeg, Manitoba and the Lisbon Clipper in Lisbon, North Dakota. With his first wife, Mary Jane Beacom, he moved to Chicago to pursue his entrepreneurial ambitions. There he established the Mutual Newspaper Publishing Company and the weekly Saturday Blade, which catered to a rural audience and was distributed by thousands of newspaper boys. With his novel employment of newsboys to boost newspaper sales, Boyce's namesake publishing company maintained a circulation of 500,000 copies per week by 1894. Boyce strongly supported worker rights, as demonstrated by his businesses' support of labor unions and his concern for his newsboys' well-being.
Battle of Port Arthur: A surprise torpedo attack by the Japanese at Port Arthur, Japan starts the Russo-Japanese War.

The Battle of Port Arthur of 8–9 February 1904 marked the commencement of the Russo-Japanese War. It began with a surprise night attack by a squadron of Japanese destroyers on the neutral Russian fleet anchored at Port Arthur, Manchuria, and continued with an engagement the following morning; further skirmishing off Port Arthur would continue until May 1904. The attack ended inconclusively, though the war resulted in a decisive Japanese victory.

A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially a fish. The term torpedo originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, torpedo has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device.

Lüshunkou District is a district of Dalian, Liaoning province, China. Also formerly called Lüshun City or literally Lüshun Port, it was formerly known as both Port Arthur and Ryojun. The district's area is 512.15 square kilometres (197.74 sq mi) and its permanent population as of 2010 is 324,773.

The Russo-Japanese War was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1905 over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major theatres of military operations were located in Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden in Southern Manchuria, and the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia sought a warm-water port on the Pacific Ocean both for its navy and for maritime trade. Vladivostok remained ice-free and operational only during the summer; Port Arthur, a naval base in Liaodong Province leased to Russia by the Qing dynasty of China from 1897, was operational year round. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy east of the Urals, in Siberia and the Far East, since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. Since the end of the First Sino-Japanese War in 1895, Japan had feared Russian encroachment would interfere with its plans to establish a sphere of influence in Korea and Manchuria.
Aceh War: Dutch Colonial Army's Marechaussee regiment led by General G.C.E. van Daalen launch military campaign to capture Gayo Highland, Alas Highland, and Batak Highland in Dutch East Indies' Northern Sumatra region, which ends with genocide to Acehnese and Bataks people.

The Aceh War, also known as the Dutch War or the Infidel War (1873–1913), was an armed military conflict between the Sultanate of Aceh and the Kingdom of the Netherlands which was triggered by discussions between representatives of Aceh and the United States in Singapore during early 1873. The war was part of a series of conflicts in the late 19th century that consolidated Dutch rule over modern-day Indonesia.

The Royal Netherlands East Indies Army was the military force maintained by the Kingdom of the Netherlands in its colony of the Dutch East Indies, in areas that are now part of Indonesia. The KNIL's air arm was the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force. Elements of the Royal Netherlands Navy and Government Navy were also stationed in the Netherlands East Indies.

The Korps Marechaussee te voet were a colonial gendarmerie of the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army (KNIL), principally used for counter-insurgency in the Dutch East Indies.
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.

Gotfried Coenraad Ernst "Frits" van Daalen was an Indo (Eurasian) Lieutenant General of the Royal Dutch East Indies Army who served in the Dutch East Indies. He was also the appointed Governor of Aceh from 1905 until 1908.

Gayo Lues Regency is a regency in the Aceh Special Region of Indonesia. It is located on the island of Sumatra. The regency was created in 2002 under Statute UU 4/2002 from the northern part of Aceh Tenggara. Its capital is Blangkejeren. The regency covers an area of 5,549.91 square kilometres and had a population of 79,560 at the 2010 Census and 99,532 at the 2020 Census. Along with the Central Aceh Regency and the Bener Meriah Regency, it is home to the Gayo people.

Batak is a collective term used to identify a number of closely related Austronesian ethnic groups predominantly found in North Sumatra, Indonesia, who speak Batak languages. The term is used to include the Karo, Pakpak, Simalungun, Toba, Angkola, and Mandailing which are related groups with distinct languages and traditional customs (adat).

The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800.
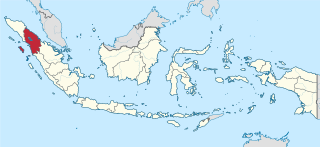
North Sumatra is a province of Indonesia located on the northern part of the island of Sumatra. Its capital and largest city is Medan. North Sumatra is Indonesia's fourth most populous province after West Java, East Java and Central Java, and also the most populous in the island of Sumatra. It covers an area of 72,981 km2. According to the 2020 census, the province's population in that year was 14,799,361. The mid-2021 official estimate is 14,936,148.

Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word γένος with the Latin suffix -caedo.

The Acehnese are an ethnic group from Aceh, Indonesia on the northernmost tip of the island of Sumatra. The area has a history of political struggle against the Dutch. The vast majority of the Acehnese people are Muslims. The Acehnese people are also referred to by other names such as Lam Muri, Lambri, Akhir, Achin, Asji, A-tse and Atse. Their language, Acehnese, belongs to the Aceh–Chamic group of Malayo-Polynesian of the Austronesian language family.
The Dawes Act authorizes the President of the United States to survey Native American tribal land and divide it into individual allotments.

The Dawes Act of 1887 regulated land rights on tribal territories within the United States. Named after Senator Henry L. Dawes of Massachusetts, it authorized the President of the United States to subdivide Native American tribal communal landholdings into allotments for Native American heads of families and individuals. This would convert traditional systems of land tenure into a government-imposed system of private property by forcing Native Americans to "assume a capitalist and proprietary relationship with property" that did not previously exist in their cultures. The act allowed tribes the option to sell the lands that remained after allotment to the federal government. Before private property could be dispensed, the government had to determine "which Indians were eligible" for allotments, which propelled an "official search for a federal definition of Indian-ness."

The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces.

Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States.. There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as "Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders".
The first government-approved Japanese immigrants arrive in Hawaii.

The Japanese in Hawaii are the second largest ethnic group in Hawaii. At their height in 1920, they constituted 43% of Hawaii's population. They now number about 16.7% of the islands' population, according to the 2000 U.S. Census. The U.S. Census categorizes mixed-race individuals separately, so the proportion of people with some Japanese ancestry is likely much larger.
At a meeting of the Royal Canadian Institute, engineer and inventor Sandford Fleming proposed the idea of standard time zones based on a single universal world time.
The Royal Canadian Institute for Science (RCIScience), known also as the Royal Canadian Institute, is a Canadian nonprofit organization dedicated to connecting the public with Canadian science.

Sir Sandford Fleming was a Scottish Canadian engineer and inventor. Born and raised in Scotland, he emigrated to colonial Canada at the age of 18. He promoted worldwide standard time zones, a prime meridian, and use of the 24-hour clock as key elements to communicating the accurate time, all of which influenced the creation of Coordinated Universal Time. He designed Canada's first postage stamp, produced a great deal of work in the fields of land surveying and map making, engineered much of the Intercolonial Railway and the first several hundred kilometers of the Canadian Pacific Railway, and was a founding member of the Royal Society of Canada and founder of the Canadian Institute.

Standard time is the synchronisation of clocks within a geographical region to a single time standard, rather than a local mean time standard. Generally, standard time agrees with the local mean time at some meridian that passes through the region, often near the centre of the region. Historically, standard time was established during the 19th century to aid weather forecasting and train travel. Applied globally in the 20th century, the geographical regions became time zones. The standard time in each time zone has come to be defined as an offset from Universal Time. A further offset is applied for part of the year in regions with daylight saving time.
Universal Time is a time standard based on Earth's rotation. While originally it was mean solar time at 0° longitude, precise measurements of the Sun are difficult. Therefore, UT1 is computed from a measure of the Earth's angle with respect to the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF), called the Earth Rotation Angle. UT1 is the same everywhere on Earth. UT1 is required to follow the relationshipERA = 2π(0.7790572732640 + 1.00273781191135448 · Tu) radians
Angered by a controversial umpiring decision, cricket spectators rioted and attacked the England team during a match in Sydney, Australia.
In cricket, an umpire is a person who has the authority to make decisions about events on the cricket field according to the Laws of Cricket. Besides making decisions about legality of delivery, appeals for wickets and general conduct of the Game in a legal manner, the umpire also keeps a record of the deliveries and announces the completion of an over.

Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a 22-yard (20-metre) pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striking the ball bowled at one of the wickets with the bat and then running between the wickets, while the bowling and fielding side tries to prevent this and dismiss each batter. Means of dismissal include being bowled, when the ball hits the stumps and dislodges the bails, and by the fielding side either catching the ball after it is hit by the bat, but before it hits the ground, or hitting a wicket with the ball before a batter can cross the crease in front of the wicket. When ten batters have been dismissed, the innings ends and the teams swap roles. The game is adjudicated by two umpires, aided by a third umpire and match referee in international matches. They communicate with two off-field scorers who record the match's statistical information.

The Sydney Riot of 1879 was an instance of civil disorder that occurred at an early international cricket match. It took place on 8 February 1879 at what is now the Sydney Cricket Ground, during a match between New South Wales, captained by Dave Gregory, and a touring English team, captained by Lord Harris.
The England cricket team represents England and Wales in international cricket. Since 1997, it has been governed by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), having been previously governed by Marylebone Cricket Club since 1903. England, as a founding nation, is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) with Test, One Day International (ODI) and Twenty20 International (T20I) status. Until the 1990s, Scottish and Irish players also played for England as those countries were not yet ICC members in their own right.
Sydney is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about 70 km (43.5 mi) towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, the Royal National Park to the south and Macarthur to the south-west. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, spread across 33 local government areas. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". The 2021 census recorded the population of Greater Sydney as 5,231,150, meaning the city is home to approximately 66% of the state's population. Nicknames of the city include the 'Emerald City' and the 'Harbour City'.
Sandford Fleming first proposes adoption of Universal Standard Time at a meeting of the Royal Canadian Institute.

Sir Sandford Fleming was a Scottish Canadian engineer and inventor. Born and raised in Scotland, he emigrated to colonial Canada at the age of 18. He promoted worldwide standard time zones, a prime meridian, and use of the 24-hour clock as key elements to communicating the accurate time, all of which influenced the creation of Coordinated Universal Time. He designed Canada's first postage stamp, produced a great deal of work in the fields of land surveying and map making, engineered much of the Intercolonial Railway and the first several hundred kilometers of the Canadian Pacific Railway, and was a founding member of the Royal Society of Canada and founder of the Canadian Institute.
Universal Time is a time standard based on Earth's rotation. While originally it was mean solar time at 0° longitude, precise measurements of the Sun are difficult. Therefore, UT1 is computed from a measure of the Earth's angle with respect to the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF), called the Earth Rotation Angle. UT1 is the same everywhere on Earth. UT1 is required to follow the relationshipERA = 2π(0.7790572732640 + 1.00273781191135448 · Tu) radians
The Royal Canadian Institute for Science (RCIScience), known also as the Royal Canadian Institute, is a Canadian nonprofit organization dedicated to connecting the public with Canadian science.
The England cricket team led by Lord Harris is attacked in a riot during a match in Sydney.
The England cricket team represents England and Wales in international cricket. Since 1997, it has been governed by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), having been previously governed by Marylebone Cricket Club since 1903. England, as a founding nation, is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) with Test, One Day International (ODI) and Twenty20 International (T20I) status. Until the 1990s, Scottish and Irish players also played for England as those countries were not yet ICC members in their own right.

Colonel George Robert Canning Harris, 4th Baron Harris,, generally known as Lord Harris, was a British colonial administrator and Governor of Bombay. He was also an English amateur cricketer, mainly active from 1870 to 1889, who played for Kent and England as captain of both teams. He had a political career from 1885 to 1900 and was for much of his life a highly influential figure in cricket administration through the offices he held with Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC). He was President of the Kent County Football Association between 1881 and 1908.

The Sydney Riot of 1879 was an instance of civil disorder that occurred at an early international cricket match. It took place on 8 February 1879 at what is now the Sydney Cricket Ground, during a match between New South Wales, captained by Dave Gregory, and a touring English team, captained by Lord Harris.
Delaware refuses to ratify the Thirteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. Slavery was outlawed in the United States, including Delaware, when the Amendment was ratified by the requisite number of states on December 6, 1865. Delaware ratified the Thirteenth Amendment on February 12, 1901, which was the ninety-second anniversary of the birth of Abraham Lincoln.

Delaware is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Delaware Bay, in turn named after Thomas West, 3rd Baron De La Warr, an English nobleman and Virginia's first colonial governor.

The Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution abolished slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. The amendment was passed by the Senate on April 8, 1864, by the House of Representatives on January 31, 1865, and ratified by the required 27 of the then 36 states on December 6, 1865, and proclaimed on December 18. It was the first of the three Reconstruction Amendments adopted following the American Civil War.

Abraham Lincoln was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation through the American Civil War and succeeded in preserving the Union, abolishing slavery, bolstering the federal government, and modernizing the U.S. economy.
Richard Mentor Johnson became the only person ever to be elected Vice President of the United States by the Senate.

Richard Mentor Johnson was an American lawyer, military officer and politician who served as the ninth vice president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841 under President Martin Van Buren. He is the only vice president elected by the United States Senate under the provisions of the Twelfth Amendment. Johnson also represented Kentucky in the U.S. House of Representatives and Senate. He began and ended his political career in the Kentucky House of Representatives.

The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice president is also an officer in the legislative branch, as the president of the Senate. In this capacity, the vice president is empowered to preside over Senate deliberations at any time, but may not vote except to cast a tie-breaking vote. The vice president is indirectly elected together with the president to a four-year term of office by the people of the United States through the Electoral College.

The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
Richard Johnson becomes the first Vice President of the United States chosen by the United States Senate.

Richard Mentor Johnson was an American lawyer, military officer and politician who served as the ninth vice president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841 under President Martin Van Buren. He is the only vice president elected by the United States Senate under the provisions of the Twelfth Amendment. Johnson also represented Kentucky in the U.S. House of Representatives and Senate. He began and ended his political career in the Kentucky House of Representatives.

The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice president is also an officer in the legislative branch, as the president of the Senate. In this capacity, the vice president is empowered to preside over Senate deliberations at any time, but may not vote except to cast a tie-breaking vote. The vice president is indirectly elected together with the president to a four-year term of office by the people of the United States through the Electoral College.

The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
Las Heras completes his crossing of the Andes with an army to join San Martín and liberate Chile from Spain.

Grand Marshal Juan Gregorio de las Heras was an Argentine soldier who took part in the Spanish American wars of independence and was also a governor of the province of Buenos Aires.

The Crossing of the Andes was one of the most important feats in the Argentine and Chilean wars of independence, in which a combined army of Argentine soldiers and Chilean exiles invaded Chile crossing the Andes range separating Argentina from Chile, leading to Chile's liberation from Spanish rule.

José Francisco de San Martín y Matorras, known simply as José de San Martín or the Liberator of Argentina, Chile and Peru, was an Argentine general and the primary leader of the southern and central parts of South America's successful struggle for independence from the Spanish Empire who served as the Protector of Peru. Born in Yapeyú, Corrientes, in modern-day Argentina, he left the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata at the early age of seven to study in Málaga, Spain.

Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of 756,096 square kilometers (291,930 sq mi), with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about 1,250,000 square kilometers (480,000 sq mi) of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish.
After two days of bitter fighting, the Russians under Bennigsen and the Prussians under L'Estocq concede the Battle of Eylau to Napoleon.

Levin August Gottlieb Theophil Graf von Bennigsen was a German general in the service of the Russian Empire.

Prussia was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was de facto dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and de jure by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany.

Anton Wilhelm von L'Estocq was a Prussian cavalry general best known for his command of the Prussian troops at the Battle of Eylau.

The Battle of Eylau, or Battle of Preussisch-Eylau, was a bloody and strategically inconclusive battle on 7 and 8 February 1807 between Napoléon's Grande Armée and the Imperial Russian Army under the command of Levin August von Bennigsen near the town of Preussisch Eylau in East Prussia. Late in the battle, the Russians received timely reinforcements from a Prussian division of von L'Estocq. After 1945, the town was renamed Bagrationovsk as part of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia. The engagement was fought during the War of the Fourth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.
The College of William & Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia, America, is granted a charter by King William III and Queen Mary II.

The College of William & Mary is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William III and Queen Mary II, it is the second-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and the ninth-oldest in the English-speaking world. Institutional rankings have placed it among the best public universities in the United States.

Williamsburg is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. At the 2020 U.S. census, it had a population of 15,425. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. It is bordered by James City County on the west and south and York County on the east.

The United States of America, commonly known as the United States or informally America, is a country in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. It is the third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. It has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 331 million, it is the third most populous country in the world. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City.

William III, also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from the 1670s, and King of England, Ireland, and Scotland from 1689 until his death in 1702. As King of Scotland, he is known as William II. He is sometimes informally known as "King Billy" in Ireland and Scotland. His victory at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 is commemorated by Unionists, who display orange colours in his honour. He ruled Britain alongside his wife and cousin, Queen Mary II, and popular histories usually refer to their reign as that of "William and Mary".

Mary II was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland, co-reigning with her husband, William III & II, from 1689 until her death in 1694.
Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, led a failed rebellion against Queen Elizabeth I of England.

Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, KG, PC was an English nobleman and a favourite of Queen Elizabeth I. Politically ambitious, and a committed general, he was placed under house arrest following a poor campaign in Ireland during the Nine Years' War in 1599. In 1601, he led an abortive coup d'état against the government of Elizabeth I and was executed for treason.

Essex's Rebellion was an unsuccessful rebellion led by Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, in 1601 against Queen Elizabeth I of England and the court faction led by Sir Robert Cecil to gain further influence at court.

Elizabeth I was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, rebels against Queen Elizabeth I and the revolt is quickly crushed.

Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, KG, PC was an English nobleman and a favourite of Queen Elizabeth I. Politically ambitious, and a committed general, he was placed under house arrest following a poor campaign in Ireland during the Nine Years' War in 1599. In 1601, he led an abortive coup d'état against the government of Elizabeth I and was executed for treason.

Essex's Rebellion was an unsuccessful rebellion led by Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, in 1601 against Queen Elizabeth I of England and the court faction led by Sir Robert Cecil to gain further influence at court.
Luis de Carvajal y de la Cueva is tortured by the Inquisition in Mexico, charged with concealing the practice of Judaism of his sister and her children.

Luis de Carvajal was governor of the Spanish province of Nuevo León in present-day Mexico, slave trader, and the first Spanish subject known to have entered Texas from Mexico across the lower Rio Grande.
Mary, Queen of Scots, was executed at Fotheringhay Castle for her involvement in the Babington Plot to murder her cousin, Elizabeth I of England.

Mary, Queen of Scots, also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.

Fotheringhay Castle, also known as Fotheringay Castle, was a High Middle Age Norman Motte-and-bailey castle in the village of Fotheringhay 3+1⁄2 miles (5.6 km) to the north of the market town of Oundle, Northamptonshire, England. It was probably founded around 1100 by Simon de Senlis, Earl of Northampton. In 1113, possession passed to Prince David of Scotland when he married Simon's widow. The castle then descended with the Scottish princes until the early 13th century, when it was confiscated by King John of England.

The Babington Plot was a plan in 1586 to assassinate Queen Elizabeth I, a Protestant, and put Mary, Queen of Scots, her Catholic cousin, on the English throne. It led to Mary's execution, a result of a letter sent by Mary in which she consented to the assassination of Elizabeth.

Elizabeth I was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Mary, Queen of Scots, is executed on suspicion of having been involved in the Babington Plot to murder her cousin, Queen Elizabeth I.

Mary, Queen of Scots, also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.

The Babington Plot was a plan in 1586 to assassinate Queen Elizabeth I, a Protestant, and put Mary, Queen of Scots, her Catholic cousin, on the English throne. It led to Mary's execution, a result of a letter sent by Mary in which she consented to the assassination of Elizabeth.

Elizabeth I was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Leiden University is founded, and given the motto Praesidium Libertatis.

Leiden University is a public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of Leiden for its defence against Spanish attacks during the Eighty Years' War. As the oldest institution of higher education in the Netherlands, it enjoys a reputation across Europe and the world.
The Byzantine civil war of 1341–47 ends with a power-sharing agreement between John VI Kantakouzenos and John V Palaiologos.
The Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, sometimes referred to as the Second Palaiologan Civil War, was a conflict that broke out in the Byzantine Empire after the death of Andronikos III Palaiologos over the guardianship of his nine-year-old son and heir, John V Palaiologos. It pitted on the one hand Andronikos III's chief minister, John VI Kantakouzenos, and on the other a regency headed by the Empress-Dowager Anna of Savoy, the Patriarch of Constantinople John XIV Kalekas, and the megas doux Alexios Apokaukos. The war polarized Byzantine society along class lines, with the aristocracy backing Kantakouzenos and the lower and middle classes supporting the regency. To a lesser extent, the conflict acquired religious overtones; Byzantium was embroiled in the Hesychast controversy, and adherence to the mystical doctrine of Hesychasm was often equated with support for Kantakouzenos.

John VI Kantakouzenos or Cantacuzene was a Byzantine Greek nobleman, statesman, and general. He served as grand domestic under Andronikos III Palaiologos and regent for John V Palaiologos before reigning as Byzantine emperor in his own right from 1347 to 1354. Deposed by his former ward, he was forced to retire to a monastery under the name Joasaph Christodoulos and spent the remainder of his life as a monk and historian. At age 90 or 91 at his death, he was the longest-lived of the Roman emperors.

John V Palaiologos or Palaeologus was Byzantine emperor from 1341 to 1391.
Seventh Crusade: Crusaders engage Ayyubid forces in the Battle of Al Mansurah.

The Seventh Crusade (1248–1254) was the first of the two Crusades led by Louis IX of France. Also known as the Crusade of Louis IX to the Holy Land, it aimed to reclaim the Holy Land by attacking Egypt, the main seat of Muslim power in the Near East. The Crusade initially met with success but ended in defeat, with most of the army – including the king – captured by the Muslims.

The Ayyubid dynasty was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladin had originally served Nur ad-Din of Syria, leading Nur ad-Din's army in battle against the Crusaders in Fatimid Egypt, where he was made Vizier. Following Nur ad-Din's death, Saladin was proclaimed as the first Sultan of Egypt, and rapidly expanded the new sultanate beyond the frontiers of Egypt to encompass most of the Levant, in addition to Hijaz, Yemen, northern Nubia, Tarabulus, Cyrenaica, southern Anatolia, and northern Iraq, the homeland of his Kurdish family. By virtue of his sultanate including Hijaz, the location of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina, he was the first ruler to be hailed as the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques, a title that would be held by all subsequent Sultans of Egypt until the Ottoman conquest of 1517. Saladin's military campaigns in the first decade of his rule, aimed at uniting the various Arab and Muslim states in the region against the Crusaders, set the general borders and sphere of influence of the Sultanate of Egypt for the almost three and a half centuries of its existence. Most of the Crusader states, including the Kingdom of Jerusalem, fell to Saladin after his victory at the Battle of Hattin in 1187. However, the Crusaders reconquered the coast of Palestine in the 1190s.

The Battle of Mansurah was fought from 8 to 11 February 1250, between Crusaders led by Louis IX, King of France, and Ayyubid forces led by Sultana Shajar al-Durr, vizier Fakhr ad-Din ibn as-Shaikh, Faris ad-Din Aktai and Baibars al-Bunduqdari. It was fought in present-day Mansoura, Egypt.
The Mongols burn the Russian city of Vladimir.
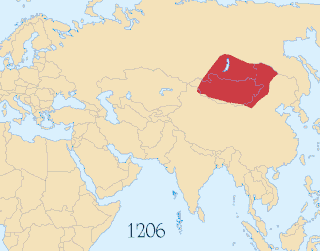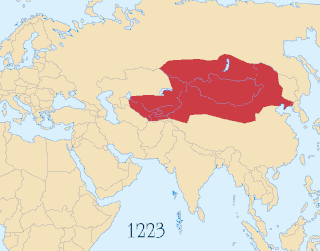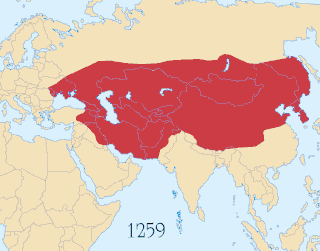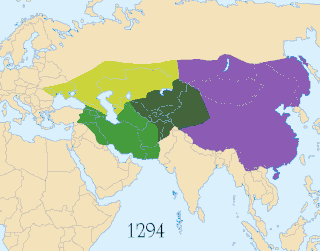
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, attempted invasions of Southeast Asia and conquered the Iranian Plateau; and westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains.

Vladimir is a city and the administrative center of Vladimir Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River, 200 kilometers (120 mi) east of Moscow. It is served by a railway and the M7 motorway. Population: 349,951 (2021 Census); 345,373 (2010 Census); 315,954 (2002 Census); 349,702 (1989 Census).
Constantius III becomes co-Emperor of the Western Roman Empire.

Constantius III was briefly Western Roman emperor of the West in 421. He earned his position as Emperor due to his capability as a general under Honorius, achieving the rank of magister militum by 411. That same year, he suppressed the revolt of Constantine III, a Roman general who had declared himself emperor. Constantius then went on to lead campaigns against various barbarian groups in Hispania and Gaul, recovering much of both for the Western Roman Empire. Constantius married Honorius's sister Galla Placidia in 417, a sign of his ascendant status, and was proclaimed co-emperor by Honorius on 8 February 421. He reigned for seven months before dying on 2 September 421.

The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 395 to 476, where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern provinces, with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were de facto independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts as an administrative expediency. The Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna was formally dissolved by Justinian in 554. The Eastern imperial court survived until 1453.
Marty Schottenheimer, American football player and coach (b. 1943) deaths

Martin Edward Schottenheimer was an American football linebacker and coach who served as a head coach in the National Football League (NFL) from 1984 to 2006. He was the head coach of the Kansas City Chiefs for 10 seasons, the Cleveland Browns and the San Diego Chargers for five each, and the Washington Redskins for one. Eighth in career wins at 205 and seventh in regular season wins at 200, Schottenheimer has the most wins of an NFL head coach to not win a championship. After coaching in the NFL, he won a 2011 championship in his one season with the Virginia Destroyers of the United Football League (UFL). He was inducted to the Kansas City Chiefs Hall of Fame in 2010.
Mary Wilson, American singer (b. 1944) deaths

Mary Wilson was an American singer. She gained worldwide recognition as a founding member of The Supremes, the most successful Motown act of the 1960s and the best-charting female group in U.S. chart history, as well as one of the best-selling girl groups of all-time. The trio reached number one on Billboard's Hot 100 with 12 of their singles, ten of which feature Wilson on backing vocals.
Robert Conrad, American actor (b. 1935) deaths

Robert Conrad was an American film and television actor, singer, and stuntman. He is best known for his role in the 1965–1969 television series The Wild Wild West, playing the sophisticated Secret Service agent James T. West. He portrayed World War II ace Pappy Boyington in the television series Baa Baa Black Sheep. In addition to acting, he was a singer and recorded several pop/rock songs in the late 1950s and early 1960s as Bob Conrad. He hosted a weekly two-hour national radio show on CRN Digital Talk Radio beginning in 2008.
Peter Mansfield, English physicist, Nobel laureate (b. 1933) deaths

Sir Peter Mansfield was an English physicist who was awarded the 2003 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, shared with Paul Lauterbur, for discoveries concerning Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Mansfield was a professor at the University of Nottingham.

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
Rina Matsuno, Japanese idol singer (b. 1998) deaths

Rina Matsuno was a Japanese singer, model, actress and tarento who was a member of girl idol group Shiritsu Ebisu Chugaku.
Alan Simpson, English scriptwriter (b. 1929) deaths

Alan Francis Simpson was an English scriptwriter, best known for the Galton and Simpson comedy writing partnership with Ray Galton. Together they devised and wrote the BBC sitcom Hancock's Half Hour (1954–1961), the first two series of Comedy Playhouse (1961–1963), and Steptoe and Son (1962–1974).
Amelia Bence, Argentine actress (b. 1914) deaths

Amelia Bence was an Argentine film actress and one of the divas of the Golden Age of Argentine Cinema (1940–60).
Nida Fazli, Indian poet and songwriter (b. 1938) deaths

Muqtida Hasan Nida Fazli, known as Nida Fazli, was a prominent Indian Hindi and Urdu poet, lyricist and dialogue writer. He was awarded the Padma Shri in 2013 by the government of India for his contribution to literature.
Margaret Forster, English historian, author, and critic (b. 1938) deaths

Margaret Forster was an English novelist, biographer, memoirist, historian and critic, best known for the 1965 novel Georgy Girl, made into a successful film of the same name, which inspired a hit song by The Seekers. Other successes were a 2003 novel, Diary of an Ordinary Woman, biographies of Daphne du Maurier and Elizabeth Barrett Browning, and her memoirs Hidden Lives and Precious Lives.
Violette Verdy, French ballerina (b. 1933) deaths

Violette Verdy was a French ballerina, choreographer, teacher, and writer who worked as a dance company director with the Paris Opera Ballet in France and the Boston Ballet in the United States. From 1958 to 1977 she was a principal dancer with the New York City Ballet where she performed in the world premieres of several works created specifically for her by choreographers George Balanchine and Jerome Robbins. She was Distinguished Professor of Music (Ballet) at the Jacobs School of Music, Indiana University, in Bloomington, and the recipient of two medals from the French government.
Rauni-Leena Luukanen-Kilde, Finnish physician and parapsychologist (b. 1939) deaths

Rauni-Leena Tellervo Luukanen-Kilde née Valve was a Finnish physician who wrote and lectured on parapsychology, ufology and mind control.
Els Borst, Dutch physician and politician, Deputy Prime Minister of the Netherlands (b. 1932) deaths

Else "Els" Borst-Eilers was a Dutch politician of the Democrats 66 (D66) party and physician. She was granted the honorary title of Minister of State on 21 December 2012.

The deputy prime minister of the Netherlands is the official deputy of the head of government of the Netherlands. In the absence of the prime minister of the Netherlands the deputy prime minister takes over his functions, such as chairing the Cabinet of the Netherlands and the Council of Ministers of the Netherlands. Conventionally, all of the junior partners in the coalition get one deputy, and the deputies are ranked according to the size of their respective parties. The incumbent deputy prime ministers are Sigrid Kaag of the Democrats 66 serving as Minister of Finance, Wopke Hoekstra of the Christian Democratic Appeal serving as Minister of Foreign Affairs and Carola Schouten of the Christian Union serving as Minister for Welfare and Civic Engagement.
Maicon Pereira de Oliveira, Brazilian footballer (b. 1988) deaths
Maicon Pereira de Oliveira commonly known as Maicon, was a Brazilian footballer who played in the Ukrainian Premier League for most of his professional career. He performed as a striker.
Nancy Holt, American sculptor and painter (b. 1938) deaths

Nancy Holt was an American artist most known for her public sculpture, installation art, concrete poetry, and land art. Throughout her career, Holt also produced works in other media, including film and photography, and wrote books and articles about art.
Giovanni Cheli, Italian cardinal (b. 1918) deaths

Giovanni Cheli was an Italian prelate of the Catholic Church, who had a career in the diplomatic service of the Holy See and then in the senior ranks of the Roman Curia. He was made a cardinal in 1998.
James DePreist, American conductor and educator (b. 1936) deaths

James Anderson DePreist was an American conductor. DePreist was one of the first African-American conductors on the world stage. He was the director emeritus of conducting and orchestral studies at The Juilliard School and laureate music director of the Oregon Symphony at the time of his death.
Maureen Dragone, American journalist and author (b. 1920) deaths

Maureen Dragone was an American journalist and author. She was one of the longest-standing members of the Hollywood Foreign Press Association which presents the annual Golden Globe Awards. In 1978 she founded the Young Artist Association, which presents the annual Young Artist Awards.
Nevin Scrimshaw, American scientist (b. 1918) deaths
Nevin Stewart Scrimshaw was an American food scientist and Institute Professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Scrimshaw was born in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. During the course of his long career he developed nutritional supplements for alleviating protein, iodine, and iron deficiencies in the developing world. His pioneering and extensive publications in the area of human nutrition and food science include over 20 books and monographs and hundreds of scholarly articles. Scrimshaw also founded the Department of Nutrition and Food Science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the Institute of Nutrition of Central America and Panama, and the Nevin Scrimshaw International Nutrition Foundation. He was awarded the Bolton L. Corson Medal in 1976 and the World Food Prize in 1991. Scrimshaw spent the last years of his life on a farm in Thornton, New Hampshire, where he died at 95.
Wando, Brazilian singer-songwriter (b. 1945) deaths

Wanderley Alves dos Reis, better known as Wando, was a Brazilian singer-songwriter.
Luis Alberto Spinetta, Argentinian singer-songwriter (b. 1950) deaths

Luis Alberto Spinetta, nicknamed "El Flaco", was an Argentine singer, guitarist, composer and poet. One of the most influential rock musicians of Argentina, he is regarded as one of the founders of Argentine rock, considered the first incarnation of Spanish-language rock. Born in Buenos Aires in the residential neighbourhood of Belgrano, he was the founder of iconic rock bands including Almendra, Pescado Rabioso, Invisible, Spinetta Jade, and Spinetta y Los Socios del Desierto. In Argentina January 23rd is celebrated as "Día Nacional del Músico" in honor of Spinetta's birth
Tony Malinosky, American baseball player and soldier (b. 1909) deaths

Anthony Francis Malinosky was an American baseball player. He played third baseman and shortstop in Major League baseball in 35 games for the Brooklyn Dodgers in the 1937 season. Listed at 5' 10", Weight: 165 lb., he batted and threw right-handed.
John Murtha, American colonel and politician (b. 1932) deaths

John Patrick Murtha Jr. was an American politician from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. Murtha, a Democrat, represented Pennsylvania's 12th congressional district in the United States House of Representatives from 1974 until his death in 2010. He is the longest-serving member ever of the United States House of Representatives from the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.
Ruby Garrard Woodson, American educator and cultural historian (b. 1931) deaths

Ruby Garrard Woodson was an educator and chemistry teacher who founded Cromwell Academy in Washington, D. C. and Florida Academy of African American Culture in Sarasota, Florida.
Anna Nicole Smith, American model and actress (b. 1967) deaths

Anna Nicole Smith was an American model, actress, and television personality. Smith started her career as a Playboy magazine centerfold in May 1992 and won the title of 1993 Playmate of the Year. She later modeled for fashion companies, including Guess, H&M, and Heatherette.
Ian Stevenson, Canadian-American psychiatrist and academic (b. 1918) deaths

Ian Pretyman Stevenson was a Canadian-born American psychiatrist, the founder and director of the Division of Perceptual Studies at the University of Virginia School of Medicine.
Elton Dean, English saxophonist, songwriter, and producer (b. 1945) deaths

Elton Dean was an English jazz musician who performed on alto saxophone, saxello and occasionally keyboards. Part of the Canterbury scene, he featured in, among others, Soft Machine.
Thierry Fortineau, French actor (b. 1953) deaths
Thierry Fortineau was a French actor.
Akira Ifukube, Japanese composer (b. 1914) deaths

Akira Ifukube was a Japanese classical and film music composer, best known for his works on the Godzilla franchise.
A. Chandranehru, Sri Lankan sailor and politician (b. 1944) deaths

Ariyanayagam Chandranehru was a Sri Lankan Tamil merchant seaman, politician and Member of Parliament.
Julius Schwartz, American journalist and author (b. 1915) deaths

Julius "Julie" Schwartz was a comic book editor, and a science fiction agent and prominent fan. He was born in The Bronx, New York. He is best known as a longtime editor at DC Comics, where at various times he was primary editor over the company's flagship superheroes, Superman and Batman.
Ong Teng Cheong, Singaporean architect and politician, 5th President of Singapore (b. 1936) deaths

Ong Teng Cheong was a Singaporean politician who served as the fifth president of Singapore between 1993 and 1999. He was also the first elected president in Singapore's history.

The president of Singapore is the head of state of the Republic of Singapore. The role of the president is to safeguard the reserves and the integrity of the public service. The presidency is largely ceremonial, with the Cabinet led by the prime minister, having the general direction and control of the government. The incumbent president is Halimah Yacob, who took office on 14 September 2017. She is also the first female president in the country's history.
Ivo Caprino, Norwegian director and screenwriter (b. 1920) deaths

Ivo Caprino was a Norwegian film director and writer, best known for his puppet films. His most noted film, Flåklypa Grand Prix, was made in 1975.
Sid Abel, Canadian-American ice hockey player, coach, and sportscaster (b. 1918) deaths

Sidney Gerald Abel was a Canadian Hall of Fame hockey player, coach and general manager in the National Hockey League, most notably for the Detroit Red Wings, and was a member of three Stanley Cup-winning teams in 1943, 1950, and 1952. In 2017 Abel was named one of the '100 Greatest NHL Players' in history.
Derrick Thomas, American football player (b. 1967) deaths

Derrick Vincent Thomas, nicknamed D.T., was an American football outside linebacker for the Kansas City Chiefs of the National Football League (NFL). Considered one of the greatest pass rushers of all time, he played 11 seasons with the Chiefs until his death in 2000. Thomas played college football at Alabama, where he earned consensus All-American honors, and was selected fourth overall by Kansas City in the 1989 NFL Draft. During his career, he received nine Pro Bowl and three first-team All-Pro selections, along with setting the single-game sacks record.
Iris Murdoch, Irish-born British novelist and philosopher (b. 1919) deaths

Dame Jean Iris Murdoch was an Irish and British novelist and philosopher. Murdoch is best known for her novels about good and evil, sexual relationships, morality, and the power of the unconscious. Her first published novel, Under the Net (1954), was selected in 1998 as one of Modern Library's 100 best English-language novels of the 20th century. Her 1978 novel The Sea, the Sea won the Booker Prize. In 1987, she was made a Dame by Queen Elizabeth II for services to literature. In 2008, The Times ranked Murdoch twelfth on a list of "The 50 greatest British writers since 1945".
Halldór Laxness, Icelandic author, poet, and playwright, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1902) deaths

Halldór Kiljan Laxness was an Icelandic writer and winner of the 1955 Nobel Prize in Literature. He wrote novels, poetry, newspaper articles, essays, plays, travelogues and short stories. Writers who influenced Laxness included August Strindberg, Sigmund Freud, Knut Hamsun, Sinclair Lewis, Upton Sinclair, Bertolt Brecht and Ernest Hemingway.

The Nobel Prize in Literature is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in the field of literature, produced the most outstanding work in an idealistic direction". Though individual works are sometimes cited as being particularly noteworthy, the award is based on an author's body of work as a whole. The Swedish Academy decides who, if anyone, will receive the prize. The academy announces the name of the laureate in early October. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895. Literature is traditionally the final award presented at the Nobel Prize ceremony. On some occasions the award has been postponed to the following year, most recently in 2018 as of May 2022.
Enoch Powell, English soldier and politician, Secretary of State for Health (b. 1912) deaths

John Enoch Powell, was a strongly conservative British politician, classical scholar, author, linguist, soldier, philologist, and poet. He served as a Conservative Member of Parliament (1950–1974) and was Minister of Health (1960–1963) then Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) MP (1974–1987).

The secretary of state for health and social care, also referred to as the health secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, responsible for the work of the Department of Health and Social Care. The incumbent is a member of the Cabinet of the United Kingdom, eighth in the ministerial ranking.
Julian Simon, American economist and author (b. 1932) deaths

Julian Lincoln Simon was an American professor of business administration at the University of Maryland and a Senior Fellow at the Cato Institute at the time of his death, after previously serving as a longtime economics and business professor at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Corey Scott, American motorcycle stunt rider (b. 1968) deaths

Corey L. Scott was an American stunt performer and professional motorcycle stunt rider. Scott died during a live stunt in front of a crowd of around 30,000 spectators at the Orange Bowl stadium in Miami, Florida, while attempting to perform a dangerous step-up jump on a motorcycle. The fatal accident was captured on camera.
Kenedy, Brazilian footballer births

Robert Kenedy Nunes do Nascimento, known as Kenedy, is a Brazilian professional footballer who plays as a winger for La Liga club Real Valladolid.
Del Ennis, American baseball player (b. 1925) deaths

Delmer Ennis was an American professional baseball outfielder, who played in Major League Baseball (MLB) from 1946 to 1959 for the Philadelphia Phillies, St. Louis Cardinals, Cincinnati Reds, and Chicago White Sox. From 1949 to 1957, he accumulated more runs batted in (RBI) than anyone besides Stan Musial and was eighth in the National League (NL) in home runs. In 1950, Ennis led the NL with 126 RBI as the Phillies won their first pennant in 35 years. He held the Phillies career record of 259 home runs from 1956 to 1980, and ranked 10th in National League history with 1,824 games in the outfield, when his career ended.
Joshua Kimmich, German footballer births

Joshua Walter Kimmich is a German professional footballer who plays as a defensive midfielder or right-back for Bundesliga club Bayern Munich and the Germany national team. He is known for his complete playstyle, versatility, aggression, and playmaking ability and is considered one of the best and most complete midfielders in the world. He is often compared with former Bayern Munich captain Philipp Lahm and is considered his successor.
Hakan Çalhanoğlu, Turkish footballer births

Hakan Çalhanoğlu is a Turkish professional footballer who plays as an attacking midfielder for Serie A club Inter Milan and the Turkey national team, which he captains. He is well renowned as a free kick specialist, known for being effective from a multitude of angles and distances.
Nikki Yanofsky, Canadian singer-songwriter births

Nicole Rachel "Nikki" Yanofsky is a Canadian jazz-pop singer from Montreal, Quebec. She sang the CTV Olympic broadcast theme song, "I Believe", which was also the theme song of the 2010 Winter Olympic Games. She also performed at the opening and closing ceremonies for the Olympics and at the opening ceremony of the 2010 Winter Paralympic Games. She has released three studio albums to date, including Nikki in 2010, Little Secret in 2014, and Turn Down the Sound in 2020.
Raymond Scott, American pianist and composer (b. 1908) deaths

Raymond Scott was an American composer, band leader, pianist, record producer, and inventor of electronic instruments.
Bruno Martins Indi, Portuguese-Dutch footballer births

Rolando Maximiliano "Bruno" Martins Indi is a Dutch professional footballer who plays as a defender for Eredivisie club AZ Alkmaar and the Netherlands national team.
Stanley Armour Dunham, American sergeant (b. 1918) deaths
Stanley Armour Dunham was the maternal grandfather of Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United States. He and his wife Madelyn Payne Dunham raised Obama from the age of 10 in Honolulu, Hawaii.
Nam Woo-hyun, South Korean singer births

Nam Woo-hyun, also known mononymously as Woohyun, is a South Korean singer, songwriter and actor. He is well known as a member of South Korean boy group Infinite.
Klay Thompson, American professional basketball player births

Klay Alexander Thompson is an American professional basketball player for the Golden State Warriors of the National Basketball Association (NBA). A four-time NBA champion with the Warriors, he is a five-time NBA All-Star, a two-time All-NBA Third Team honoree and was once named to the NBA All-Defensive Second Team. He has also won gold medals with the United States national team on their 2014 World Cup team and 2016 Olympic team.
Del Shannon, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (b. 1934) deaths

Charles Weedon Westover, better known by his stage name Del Shannon, was an American musician, singer and songwriter, best known for his 1961 number-one Billboard hit "Runaway". In 1999, he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. In addition, he also had minor acting roles.
Ernest Titterton, British Australian nuclear physicist (b. 1916) deaths

Sir Ernest William Titterton was a British nuclear physicist.
Zac Guildford, New Zealand rugby player births

Zachary Robert Guildford is a New Zealand rugby union player of English and Māori descent who plays for Waikato in the Mitre 10 Cup. A wing, he has won 11 caps for the New Zealand national team, the All Blacks, including during their victorious 2011 Rugby World Cup campaign.
Julio Jones, American football player births

Quintorris Lopez "Julio" Jones Jr. is an American football wide receiver for the Tampa Bay Buccaneers of the National Football League (NFL). He played college football at Alabama, and was drafted by the Atlanta Falcons in the first round of the 2011 NFL Draft. He is regarded as one of the best receivers of the 2010s.
Keegan Meth, Zimbabwean cricketer births
Keegan Orry Meth is a Zimbabwean cricketer. He plays domestically for the Matabeleland Tuskers and has represented Zimbabwe in One Day Internationals (ODIs). An all-rounder, he bowls right-arm medium-fast and generally bats in the lower middle order.
Javi García, Spanish footballer births

Francisco Javier "Javi" García Fernández is a Spanish former professional footballer who is an assistant manager for Benfica. A defensive midfielder by nature, he could also appear as a central defender.
Carolina Kostner, Italian figure skater births

Carolina Kostner is an Italian figure skater. She is the 2014 Olympic bronze medalist, the 2012 World champion, a five-time European champion, and the 2011 Grand Prix Final champion. She is also a medalist at five other World Championships, six other European Championships, and three other Grand Prix Finals, the 2003 World Junior bronze medalist, and a nine-time Italian national champion. Kostner has won 11 medals at the European championships, most recently in 2018, and is the most decorated singles skater in the history of the competition.
Harriet E. MacGibbon, American actress (b. 1905) deaths

Harriet MacGibbon was an American film, stage and television actress best known for her role as the insufferably snobbish, "blue-blooded Bostonian" Mrs. Margaret Drysdale in the CBS sitcom The Beverly Hillbillies.
Anderson Paak, American singer, songwriter, rapper, record producer, and multi-instrumentalist births

Brandon Paak Anderson, better known by his stage name Anderson .Paak, is an American rapper, singer, songwriter, record producer, and drummer. He released his debut mixtape, O.B.E. Vol. 1, in 2012 and went on to release Venice in 2014. In 2016 he followed up with Malibu, which received a nomination for Best Urban Contemporary Album at the Grammy Awards, followed by Oxnard, in 2018. At the 61st Grammy Awards, Paak won his first Grammy award for Best Rap Performance with the song "Bubblin". He won two more Grammy awards in 2020 for Best R&B Album with Ventura and for Best R&B Performance for "Come Home".
Petra Cetkovská, Czech tennis player births

Petra Cetkovská is a retired Czech tennis player. Having turned professional in 2000, she reached a career-high singles ranking of world No. 25, on 18 June 2012. Over her career, Cetkovská defeated top-ten players Marion Bartoli, Elena Dementieva, Angelique Kerber, Li Na, Agnieszka Radwańska, Caroline Wozniacki, and Vera Zvonareva.
Jeremy Davis, American bass player and songwriter births

Jeremiah Clayton "Jeremy" Davis, also known as Jerm, is an American musician, songwriter, and rapper. He was the bassist for the rock band Paramore until his departure in December 2015.
Brian Randle, American basketball player and coach births

Brian Charles Randle is an American assistant coach for the Phoenix Suns of the NBA. He played college basketball at the University of Illinois. He is a former professional basketball player. He was a three-time Israeli Basketball Premier League Defensive Player of the Year, and was the 2010 Israeli Basketball Premier League Finals MVP.
William Lyons, English businessman, co-founded Swallow Sidecar Company (b. 1901) deaths

Sir William Lyons, known as "Mr. Jaguar", was with fellow motorcycle enthusiast William Walmsley, the co-founder in 1922 of the Swallow Sidecar Company, which became Jaguar Cars Limited after the Second World War.

Swallow Sidecar Company, Swallow Sidecar and Coachbuilding Company, and Swallow Coachbuilding Company were trading names used by Walmsley & Lyons, partners and joint owners of a British manufacturer of motorcycle sidecars and automobile bodies in Blackpool, Lancashire, before incorporating a company in 1930 to own their business, which they named Swallow Coachbuilding Company Limited.
Cecily Strong, American actress births

Cecily Legler Strong is an American actress and comedian who has been a cast member of Saturday Night Live since 2012, making her the longest-tenured female cast member in the show's history. She was hired for SNL while doing improv at The Second City in Chicago, where she moved after graduating from CalArts. She was the co-anchor of the Weekend Update segment during her second year, which was also her first as a full cast member.
Panagiotis Vasilopoulos, Greek basketball player births

Panagiotis Vasilopoulos, commonly known as Panos Vasilopoulos is a Greek former professional basketball player who currently serves as an assistant coach for Peristeri of the Greek Basket League and the Basketball Champions League, under head coach Vassilis Spanoulis. He is 2.05 m tall. He played at both the small forward and power forward positions.
Jermaine Anderson, Canadian basketball player births
Jermaine Anderson is a Canadian retired professional basketball player. He is a veteran member of the Canadian national basketball team.
Cory Jane, New Zealand rugby player births

Cory Steven Jane is a New Zealand international rugby union player.
John Hay Whitney, American financier and diplomat, United States Ambassador to the United Kingdom (b. 1904) deaths

John Hay Whitney was U.S. Ambassador to the United Kingdom, publisher of the New York Herald Tribune, and president of the Museum of Modern Art. He was a member of the Whitney family.

The United States ambassador to the United Kingdom is the official representative of the president of the United States and the American government to the monarch and government of the United Kingdom. The position is held by Jane D. Hartley, who presented her credentials to Queen Elizabeth II on July 19, 2022.
Steve Gohouri, Ivorian footballer (d. 2015) births

Lohoré Steve Ulrich Gohouri was an Ivorian professional footballer who played as a defender.
Myriam Montemayor Cruz, Mexican singer births

Myriam Montemayor Cruz, better known mononymously as Myriam, is a Mexican recording artist, known for winning the first season of Mexican talent show La Academia.
William Jackson Harper, American actor births

William Fitzgerald Harper, known professionally as William Jackson Harper, is an American actor and playwright. He is best known for his role as Chidi Anagonye on the NBC comedy The Good Place (2016–2020), for which he was nominated for the Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Comedy Series. In 2022, he starred in a lead role in the comedy mystery series The Resort.
Nikos Xilouris, Greek singer-songwriter (b. 1936) deaths

Nikos Xylouris, Cretan nickname: Psaronikos, was a Greek singer, Cretan Lyra player and composer, who was and remains to this day among the most renowned and beloved Greek folk musicians of all time. Xylouris' outstanding vocal ability and diverse discographic repertoire managed to capture the essence of the Greek psyche, ethos and demeanor, rendering him extremely popular among the youth of his day, and making his work an essential part of the Great Greek Songbook. This fact, along with his appealing physical features and enormous personal affability earned him the honorific moniker Archangel of Crete which is still in use, especially in Athens. His songs continue to be played regularly on Greek radio stations, and his legacy is held in the highest regard throughout the Greek Nation and the Greek Diaspora alike.
Aaron Cook, American baseball player births

Aaron Lane Cook is an American former professional baseball pitcher. He played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Colorado Rockies and Boston Red Sox.
Dennis Gabor, Hungarian-English physicist and engineer, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1900) deaths

Dennis Gabor was a Hungarian-British electrical engineer and physicist, most notable for inventing holography, for which he later received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physics. He obtained British citizenship in 1934, and spent most of his life in England.

The Nobel Prize in Physics is a yearly award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901, the others being the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Physics is traditionally the first award presented in the Nobel Prize ceremony.
Mick de Brenni, Australian politician births

Michael Christopher de Brenni is an Australian politician currently serving as the Minister for Energy, Renewables and Hydrogen and Minister for Public Works and Procurement of Queensland. He previously served as the Minister for Housing and Public Works, Minister for Sport and Minister for Digital Technology. He has been the Labor member for Springwood in the Queensland Legislative Assembly since 2015.
Roman Kostomarov, Russian ice dancer births

Roman Sergeyevich Kostomarov is a Russian ice dancer. With partner Tatiana Navka, he is the 2006 Olympic champion, two-time World champion (2004–05), three-time Grand Prix Final champion (2003–05), and three-time European champion (2004–06).
Eivind Groven, Norwegian composer and theorist (b. 1901) deaths

Eivind Groven was a Norwegian composer and music-theorist. He was from traditional region of Vest-Telemark and had a background in the folk music of the area.
Khaled Mashud, Bangladeshi cricketer births
Khaled Mashud, popularly known as Khaled Mashud Pilot is a former Bangladeshi cricketer and a captain in Tests and ODIs. A wicketkeeper and middle order batsman, he was a regular member of the national team between 1995 and 2007. Bangladeshi coach Dav Whatmore claimed Mashud as the "best wicketkeeper in Asia." He contributed to Bangladesh's first ever ODI hat-trick by taking two catches off Shahadat Hossain's bowling. After the international retirement in 2008, he continued to play domestic cricket in Bangladesh as captain of the Rajshahi Division team. Mashud announced his retirement from domestic cricket after captaining his team to win the title in 2011.
Nicolas Vouilloz, French rally driver and mountain biker births

Nicolas Vouilloz is a French professional mountain biker and former professional rally driver.
Robert Robinson, English chemist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1886) deaths

Sir Robert Robinson was a British organic chemist and Nobel laureate recognised in 1947 for his research on plant dyestuffs (anthocyanins) and alkaloids. In 1947, he also received the Medal of Freedom with Silver Palm.

The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation, and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences on proposal of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry which consists of five members elected by the Academy. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death.
Seth Green, American actor, voice artist, comedian, producer, writer, and director births

Seth Benjamin Green is an American actor, producer, and writer. Green's film debut came with a role in the comedy-drama film The Hotel New Hampshire (1984), and he went on to have supporting roles in comedy films throughout the 1980s, including Can't Buy Me Love (1987) and My Stepmother Is an Alien (1988).
Big Show, American wrestler and actor births

Paul Donald Wight II is an American professional wrestler and actor. He is signed to All Elite Wrestling (AEW) as an in-ring performer, and as a commentator for its web television show, AEW Dark: Elevation, under his real name of Paul Wight. He is best known for his tenure with World Championship Wrestling (WCW) from 1995 to 1999 as The Giant and with the World Wrestling Federation from 1999 to 2021 under the ring name (The) Big Show.
Markos Vamvakaris, Greek singer-songwriter and bouzouki player (b. 1905) deaths

Márkos Vamvakáris, was a rebetiko musician. He is universally referred to by rebetiko writers and fans simply by his first name, Márkos. The great significance of Vamvakaris for the rebetiko is also reflected by his nickname: the "patriarch of the rebetiko".

The bouzouki, also spelled buzuki or buzuci, is a musical instrument popular in Greece. It is a member of the long-necked lute family, with a round body with a flat top and a long neck with a fretted fingerboard. It has steel strings and is played with a plectrum producing a sharp metallic sound, reminiscent of a mandolin but pitched lower. There are two main types of bouzouki: the trichordo (three-course) has three pairs of strings and the tetrachordo (four-course) has four pairs of strings. The instrument was brought to Greece in the early 1900s by Greek refugees from Anatolia, and quickly became the central instrument to the rebetiko genre and its music branches. It is now an important element of modern Laïko pop Greek music.
Aidy Boothroyd, English footballer and manager births

Adrian Neil Boothroyd is an English former footballer who is currently the manager of Indian Super League club Jamshedpur.
Mika Karppinen, Swedish-Finnish drummer and songwriter births

Mika Kristian Karppinen, better known as Gas Lipstick, is a Swedish-Finnish musician, best known as the previous drummer of the Finnish gothic rock band HIM. He is also a drummer for other bands currently on hiatus, such as deathgrind group To Separate the Flesh from the Bones, heavy metal group Bendover, punk group Valvontakomissio, and punk group Ääritila.
Kanaiyalal Munshi, Indian independence movement activist, politician, writer and educationist (b. 1887) deaths

Kanhaiyalal Maneklal Munshi, popularly known by his pen name Ghanshyam Vyas, was an Indian independence movement activist, politician, writer and educationist from Gujarat state. A lawyer by profession, he later turned to author and politician. He is a well-known name in Gujarati literature. He founded Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, an educational trust, in 1938.
Stephanie Courtney, American actress and comedian births
Stephanie Courtney is an American actress and comedian, best known for playing the advertising character Flo in television and radio commercials for Progressive Corporation beginning in 2008.
John Filan, Australian footballer and coach births
John Richard Filan is an Australian football coach and former professional player.
Alonzo Mourning, American basketball player and executive births

Alonzo Harding Mourning Jr. is an American former professional basketball player who has served as vice president of player programs and development for the Miami Heat since June 2009. Mourning played most of his 15-year National Basketball Association (NBA) career for the Heat.
Pauly Fuemana, New Zealand-Australian singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 2010) births

Paul Lawrence Fuemana was a Niuean-New Zealand singer, songwriter and musician from Auckland. One of the first globally successful pioneers of his country's unique style of hip-hop, Fuemana was one of New Zealand's greatest popular music icons of the 1990s.
Mary Robinette Kowal, American puppeteer and author births

Mary Robinette Kowal is an American author and puppeteer. Originally a puppeteer by primary trade after receiving a bachelor's degree in art education, she became art director for science fiction magazines and by 2010 was also authoring her first full-length published novels. The majority of her work is characterized by science fiction themes, such as interplanetary travel; a common element present in many of her novels is historical or alternate history fantasy, such as in her Glamourist Histories and Lady Astronaut books.
Mary McCormack, American actress and producer births

Mary Catherine McCormack is an American actress. She has had leading roles as Justine Appleton in the series Murder One (1995–97), as Deputy National Security Adviser Kate Harper in The West Wing (2004–06), as Deputy U.S. Marshal Mary Shannon in In Plain Sight (2008–12), and as Peggy in the comedy series The Kids Are Alright (2018–19).
Gary Coleman, American actor (d. 2010) births

Gary Wayne Coleman was an American actor and comedian. Coleman was the highest-paid child actor on television throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. He was rated first on a list of VH1's "100 Greatest Kid Stars".
Kirk Muller, Canadian ice hockey player and coach births

Kirk Christopher Muller is a Canadian former professional ice hockey winger who played in the National Hockey League for 19 seasons from 1984–85 until 2002–03. He was also the head coach of the National Hockey League's Carolina Hurricanes from 2011 to 2014. He was an associate coach with the Montreal Canadiens from 2016 to 2021, where he previously served as assistant coach from 2006 to 2011.
Hristo Stoichkov, Bulgarian footballer and manager births

Hristo Stoichkov Stoichkov is a Bulgarian former professional footballer who is a football commentator for TUDN. A prolific forward, he is regarded as one of the best players of his generation and is regarded as the greatest Bulgarian footballer of all time. He was runner-up for the FIFA World Player of the Year award in 1992 and 1994, and received the Ballon d'Or in 1994. In 2004, Stoichkov was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players.
Arlie Petters, Belizean-American mathematical physicist and academic births

Arlie Oswald Petters, MBE is a Belizean-American mathematical physicist, who is the Benjamin Powell Professor of Mathematics and a Professor of Physics and Economics at Duke University. Petters will become the Provost at New York University Abu Dhabi effective September 1, 2020. Petters is a founder of mathematical astronomy, focusing on problems connected to the interplay of gravity and light and employing tools from astrophysics, cosmology, general relativity, high energy physics, differential geometry, singularities, and probability theory. His monograph "Singularity Theory and Gravitational Lensing" developed a mathematical theory of gravitational lensing. Petters was also the dean of academic affairs for Trinity College of Arts and Sciences and associate vice provost for undergraduate education at Duke University (2016-2019).
Santosh Sivan, Indian director, cinematographer, producer, and actor births

Santosh Sivan is an Indian cinematographer, film director, producer and actor known for his works in Malayalam, Tamil and Hindi cinema. Santosh graduated from the Film and Television Institute of India and has to date completed 55 feature films and 50 documentaries.
Trinny Woodall, English fashion designer and author births

Sarah-Jane Duncanson "Trinny" Woodall is an English fashion and makeover expert, television presenter and author. In 1994, after ten years working in marketing, Woodall met Susannah Constantine, whom she teamed up with to write a weekly fashion column for The Daily Telegraph. This led to the launch of their own internet fashion-advice business and the release of their first fashion-advice book.
Ernst Kretschmer, German psychiatrist and author (b. 1888) deaths

Ernst Kretschmer was a German psychiatrist who researched the human constitution and established a typology.
Mohammad Azharuddin, Indian cricketer and politician births

Mohammad Azharuddin is an Indian politician and a former international cricketer and former captain of India national cricket team. He is the working president of the Telangana Pradesh Congress Committee and was the member of parliament for Moradabad. He played 99 Test matches and 334 One Day Internationals for the Indian national cricket team before his international career came to an end after he was found to have been involved in a match fixing scandal in 2000 and subsequently banned by the Board of Control for Cricket in India for life. In 2012, the Andhra Pradesh High Court lifted the life ban.
George Dolenz, Italian-American actor (b. 1908) deaths

George Dolenz was an American film actor born in Trieste, in the city's Slovene community.
Vince Neil, American singer-songwriter and actor births

Vincent Neil Wharton, best known by the stage name Vince Neil, is an American musician. He is the lead vocalist and occasional rhythm guitarist of heavy metal band Mötley Crüe, which he fronted from their 1981 formation until his departure in 1992. Neil reunited with the band in 1996 and continued with them until the band's 2015 retirement, and again from the band's 2018 reunion onwards. Outside of Mötley Crüe, Neil has also released three studio albums as a solo artist – the most recent of which, Tattoos & Tequila, was released in 2010.
Benigno Aquino III, Filipino politician, 15th President of the Philippines (d. 2021) births

Benigno Simeon Cojuangco Aquino III, also known as Noynoy Aquino and colloquially as PNoy, was a Filipino politician who served as the 15th president of the Philippines from 2010 to 2016. The son of assassinated politician Benigno Aquino Jr. and 11th president Corazon Aquino, he was a fourth-generation politician as part of the Aquino family of Tarlac.

The president of the Philippines is the head of state, head of government and chief executive of the Philippines. The president leads the executive branch of the Philippine government and is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of the Philippines.
Dino Ciccarelli, Canadian ice hockey player births

Dino Ciccarelli is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player who played 19 seasons in the National Hockey League, primarily with the Minnesota North Stars, but also notably with the Detroit Red Wings, with whom he had his third-highest scoring season. He scored 1,200 points in his NHL career. His 608 career NHL goals are also the most goals scored by a draft-eligible player who was not drafted by an NHL team. Ciccarelli was elected to the Hockey Hall of Fame in 2010.
J. L. Austin, English philosopher and academic (b. 1911) deaths

John Langshaw Austin was a British philosopher of language and leading proponent of ordinary language philosophy, perhaps best known for developing the theory of speech acts.
Giles Gilbert Scott, English architect and engineer, designed the Red telephone box and Liverpool Cathedral (b. 1880) deaths

Sir Giles Gilbert Scott was a British architect known for his work on the New Bodleian Library, Cambridge University Library, Lady Margaret Hall, Oxford, Battersea Power Station, Liverpool Cathedral, and designing the iconic red telephone box. Scott came from a family of architects. He was noted for his blending of Gothic tradition with modernism, making what might otherwise have been functionally designed buildings into popular landmarks.

The red telephone box, a telephone kiosk for a public telephone designed by Sir Giles Gilbert Scott, is a familiar sight on the streets of the United Kingdom, Malta, Bermuda and Gibraltar.

Liverpool Cathedral is the Cathedral of the Anglican Diocese of Liverpool, built on St James's Mount in Liverpool, and the seat of the Bishop of Liverpool. It may be referred to as the Cathedral Church of Christ in Liverpool or the Cathedral Church of the Risen Christ, Liverpool, being dedicated to Christ 'in especial remembrance of His most glorious Resurrection'. Liverpool Cathedral is the largest cathedral and religious building in Britain, and the eighth largest church in the world.
Heinz Gunthardt, Swiss tennis player births

Heinz Peter Günthardt is a retired tennis player from Switzerland.
Andrew Hoy, Australian equestrian rider births

Andrew James Hoy, OAM is an Australian equestrian rider. He has won six Olympic medals: three gold, two silvers and one bronze. He has competed in eight Olympic games, from 1984 to 2020 with the exception of 2008,[] which is an Australian record; and at the 2020 Summer Olympics he was 62 years old, making him Australia's oldest ever male Olympian. After winning two medals in Tokyo, he did not rule out trying for future Olympic teams.
Mauricio Macri, Argentinian businessman and politician, President of Argentina births

Mauricio Macri is an Argentine businessman and politician who served as the President of Argentina from 2015 to 2019. He has been the leader of the Republican Proposal (PRO) party since its founding in 2005. He previously served as 5th Chief of Government of Buenos Aires from 2007 to 2015, and was a member of the Chamber of Deputies representing Buenos Aires from 2005 to 2007. Ideologically, he identifies himself as a liberal and conservative on the Argentine centre-right.

The president of Argentina, officially known as the president of the Argentine Nation, is both head of state and head of government of Argentina. Under the national constitution, the president is also the chief executive of the federal government and commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
William J. Donovan, American head of the Office of Strategic Services (OSS) (b. 1883) deaths

William Joseph "Wild Bill" Donovan was an American soldier, lawyer, intelligence officer and diplomat, best known for serving as the head of the Office of Strategic Services (OSS), the precursor to the Bureau of Intelligence and Research and the Central Intelligence Agency, during World War II. He is regarded as the founding father of the CIA, and a statue of him stands in the lobby of the CIA headquarters building in Langley, Virginia.
Sherri Martel, American wrestler and manager (d. 2007) births

Sherry Schrull was an American professional wrestler and manager, better known by her ring names, Sherri Martel and Sensational Sherri.
Marina Silva, Brazilian environmentalist and politician births

Maria Osmarina da Silva Vaz de Lima is a Brazilian politician and environmentalist. She is the founder and former spokeswoman for the Sustainability Network Party (REDE). During her political career, Silva served as a senator of the state of Acre between 1995 and 2011 and Minister of the Environment from 2003 to 2008. She ran for president in 2010, 2014 and 2018.
Karine Chemla, French historian of mathematics and sinologist births

Karine Chemla is a French historian of mathematics and sinologist who works as a director of research at the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS). She is also a senior fellow at the New York University Institute for the Study of the Ancient World. She was elected a Member of the American Philosophical Society in 2019.
Walther Bothe, German physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1891) deaths

Walther Wilhelm Georg Bothe was a German nuclear physicist, who shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1954 with Max Born.

The Nobel Prize in Physics is a yearly award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions for humankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901, the others being the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Physics is traditionally the first award presented in the Nobel Prize ceremony.
John von Neumann, Hungarian-American mathematician and physicist (b. 1903) deaths

John von Neumann was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time and was said to have been "the last representative of the great mathematicians who were equally at home in both pure and applied mathematics". He integrated pure and applied sciences.
Marques Johnson, American basketball player and sportscaster births
Marques Kevin Johnson is an American former professional basketball player who is a basketball analyst for the Milwaukee Bucks on Bally Sports Wisconsin. He played as a small forward in the National Basketball Association (NBA) from 1977 to 1989, where he was a five-time All-Star. He played the majority of his career with the Bucks.
Connie Mack, American baseball player and manager (b. 1862) deaths

Cornelius McGillicuddy, better known as Connie Mack, was an American professional baseball catcher, manager, and team owner. The longest-serving manager in Major League Baseball history, he holds untouchable records for wins (3,731), losses (3,948), and games managed (7,755). Mack's victory total is 829 more than the second highest total, 2,902 wins by Tony La Russa. Mack's lead in career losses is even greater, 1,433 higher than the second highest total, La Russa's 2,515.
John Grisham, American lawyer and author births

John Ray Grisham Jr. is an American novelist, lawyer and former member of the 7th district of the Mississippi House of Representatives, known for his popular legal thrillers. According to the American Academy of Achievement, Grisham has written 28 consecutive number-one fiction bestsellers, and his books have sold 300 million copies worldwide. Along with Tom Clancy and J. K. Rowling, Grisham is one of only three authors to have sold two million copies on a first printing.
Jim Neidhart, American wrestler (d. 2018) births

James Henry Neidhart was an American professional wrestler known for his appearances in the 1980s and 1990s in the World Wrestling Federation as Jim "The Anvil" Neidhart, where he was a two-time WWF Tag Team Champion with his real-life brother-in-law Bret Hart in The Hart Foundation. He also won titles in Stampede Wrestling, Championship Wrestling from Florida, Mid-South Wrestling, Memphis Championship Wrestling and the Mid-Eastern Wrestling Federation. He was part of the Hart wrestling family through marriage to his wife Ellie Hart, teaming with various members throughout his career, and appearing with his daughter Natalya Neidhart on the reality television show Total Divas.
Mary Steenburgen, American actress births

Mary Nell Steenburgen is an American actress, comedian, singer, and songwriter. After studying at New York's Neighborhood Playhouse in the 1970s, she made her professional acting debut in 1978 Western comedy film Goin' South. Steenburgen went on to earn critical acclaim for her role in Jonathan Demme's 1980 comedy-drama film Melvin and Howard, for which she received the Golden Globe Award for Best Supporting Actress – Motion Picture and the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actress.
Marinho Chagas, Brazilian footballer and coach (d. 2014) births

Francisco das Chagas Marinho, generally known as Marinho Chagas or Francisco Marinho, was a Brazilian professional footballer. One of the best left-backs of his era, he is best known for his flowing curly blond hair and his performance at the 1974 FIFA World Cup, in which Brazil finished fourth. At club level he is mostly associated with Botafogo FR of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo FC, but he played for numerous other teams, as well as in the North American Soccer League, in a career which spanned from 1969 to 1987.
Brooke Adams, American actress, producer, and screenwriter births

Brooke Adams is an American actress. She is best known for her film roles in Days of Heaven (1978), Invasion of the Body Snatchers (1978) and The Dead Zone (1983).
Niels Arestrup, French actor, director, and screenwriter births

Niels Arestrup is a French-Danish actor, film director and screenwriter. He has won three César Awards.
Dan Seals, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 2009) births

Danny Wayland Seals was an American musician. The younger brother of Seals and Crofts member Jim Seals, he first gained fame as one half of the soft rock duo England Dan & John Ford Coley, who charted nine singles between 1976 and 1980, including the No. 2 Billboard Hot 100 hit "I'd Really Love to See You Tonight".
Italo Santelli, Italian fencer and coach (b. 1866) deaths

Italo Santelli was an Italian fencer who is considered to be the "father of modern sabre fencing".
Roger Lloyd-Pack, English actor (d. 2014) births

Roger Lloyd-Pack was an English actor. He is best known for playing Trigger in Only Fools and Horses from 1981 to 2003, and Owen Newitt in The Vicar of Dibley from 1994 to 2007. He later starred as Tom in The Old Guys with Clive Swift. He is also well known for the role of Barty Crouch Sr. in Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire and for his appearances in Doctor Who as John Lumic in the episodes "Rise of the Cybermen" and "The Age of Steel". He was sometimes credited without the hyphen in his surname. He died in 2014 from pancreatic cancer.
Sebastião Salgado, Brazilian photographer and journalist births

Sebastião Ribeiro Salgado Júnior is a Brazilian social documentary photographer and photojournalist.
Valerie Thomas, American scientist and inventor births

Valerie L. Thomas is an American scientist and inventor. She invented the illusion transmitter, for which she received a patent in 1980. She was responsible for developing the digital media formats image processing systems used in the early years of NASA's Landsat program.
Robert Klein, American comedian, actor, and singer births

Robert Klein is an American stand-up comedian, singer, and actor. He is known for his appearances on stage and screen. He has released four standup comedy specials: A Child of the 50s (1973), Mind Over Matter (1974), New Teeth (1975), and Let's Not Make Love (1990). The first two albums received Grammy Award for Best Comedy Album nominations. Klein hosted Saturday Night Live in its first season in 1975 and again in 1978. Klein made his Broadway debut in the 1966 production of The Apple Tree opposite Alan Alda. He earned a Tony Award for Best Actor in a Musical nomination for his performance in Neil Simon's musical comedy They're Playing Our Song (1979).
Terry Melcher, American singer-songwriter and producer (d. 2004) births

Terrence Paul Melcher was an American record producer, singer, and songwriter who was instrumental in shaping the mid-to-late 1960s California Sound and folk rock movements. His best-known contributions were producing the Byrds' first two albums Mr. Tambourine Man (1965) and Turn! Turn! Turn! (1965), as well as most of the hit recordings of Paul Revere & the Raiders and Gentle Soul. He is also known for his collaborations with Bruce Johnston and for his association with the Manson Family.
Nick Nolte, American actor and producer births

Nicholas King Nolte is an American actor. He won the Golden Globe Award for Best Actor – Motion Picture Drama and was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actor for the 1991 film The Prince of Tides. He received Academy Award nominations for Affliction (1998) and Warrior (2011), and was nominated for a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Lead Actor in a Limited or Anthology Series or Movie for the 1976 miniseries Rich Man, Poor Man.
Tom Rush, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and producer births

Thomas Walker Rush is an American folk and blues singer and songwriter.
Jagjit Singh, Indian singer-songwriter (d. 2011) births

Jagjit Singh was an Indian composer, singer and musician. He composed and sang in numerous languages and is credited for the revival and popularity of ghazal, an Indian classical art form, by choosing poetry that was relevant to the masses and composing them in a way that laid more emphasis on the meaning of words and melody evoked by them. In terms of Indian classical music, his style of composing and gayaki (singing) is considered as Bol-pradhan, one that lays emphasis on words. He highlighted this in his music for films such as Prem Geet (1981), Arth (1982), and Saath Saath (1982), and TV serials Mirza Ghalib (1988) and Kahkashan (1991). Singh is considered to be the most successful ghazal singer and composer of all time in terms of critical acclaim and commercial success. With a career spanning five decades and many albums, the range and breadth of his work has been regarded as genre-defining.
Sophie Lihau-Kanza, Congolese politician (d. 1999) births

Sophie Lihau-Kanza or Zala Lusibu N'Kanza was a Congolese politician and sociologist. She was the first woman of her country to receive a secondary education, the first to graduate from a university, and the first to hold a government office in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, serving as Minister of Social Affairs from 31 October 1966 to 6 December 1970. In her later life she held positions within the United Nations.
Ted Koppel, English-American journalist births

Edward James Martin Koppel is a British-born American broadcast journalist, best known as the anchor for Nightline, from the program's inception in 1980 until 2005.
Jose Maria Sison, Filipino activist and theorist births

Jose Maria Canlas Sison, also known by his nickname Joma, is a Filipino writer and activist who founded the Communist Party of the Philippines and added elements of Maoism to its philosophy — which would be known as national democracy. He applied the theory of Marxism-Leninism-Maoism to the history and current circumstances of the Philippines.
Joe Raposo, American pianist and composer (d. 1989) births

Joseph Guilherme Raposo, OIH was an American composer, songwriter, pianist, singer and lyricist, best known for his work on the children's television series Sesame Street, for which he wrote the theme song, as well as classic songs such as "Bein' Green", "C Is For Cookie" and "Sing". He also wrote music for television shows such as The Electric Company, Shining Time Station and the sitcoms Three's Company and The Ropers, including their theme songs. In addition to these works, Raposo also composed extensively for three Dr. Seuss TV specials in collaboration with the DePatie-Freleng Enterprises: Halloween Is Grinch Night (1977), Pontoffel Pock, Where Are You? (1980), and The Grinch Grinches the Cat in the Hat (1982).
Harry Wu, Chinese human rights activist (d. 2016) births

Harry Wu was a Chinese-American human rights activist. Wu spent 19 years in Chinese labor camps, and he became a resident and citizen of the United States. In 1992, he founded the Laogai Research Foundation.
Charles Curtis, American lawyer and politician, 31st Vice President of the United States (b. 1860) deaths

Charles Curtis was an American attorney and Republican politician from Kansas who served as the 31st vice president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 under Herbert Hoover. He had served as the Senate Majority Leader from 1924 to 1929. A member of the Kaw Nation born in the Kansas Territory, Curtis was the first Native American and first person with acknowledged non-European ancestry to reach either of the highest offices in the federal executive branch.

The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice president is also an officer in the legislative branch, as the president of the Senate. In this capacity, the vice president is empowered to preside over Senate deliberations at any time, but may not vote except to cast a tie-breaking vote. The vice president is indirectly elected together with the president to a four-year term of office by the people of the United States through the Electoral College.
Eemil Nestor Setälä, Finnish linguist and politician, Finnish Minister for Foreign Affairs (b. 1864) deaths

Eemil Nestor Setälä was a Finnish politician and once the Chairman of the Senate of Finland, from September 1917 to November 1917, when he was author of the Finnish Declaration of Independence.
The minister for foreign affairs handles the Finnish Government's foreign policy and relations, and is in charge of the Ministry for Foreign Affairs. The minister for foreign trade and development is also associated with this ministry.
Elly Ameling, Dutch soprano births

Elisabeth Sara "Elly" Ameling is a retired Dutch soprano, who was particularly known for lieder recitals and for performing works by Johann Sebastian Bach. Performing with distinguished pianists and ensembles around the globe, she was awarded various honours and recording prizes.
Cliff Allison, English racing driver and businessman (d. 2005) births

Henry Clifford "Cliff" Allison was a British racing driver from England, who participated in Formula One during seasons 1958 to 1961 for the Lotus, Scuderia Centro Sud, Ferrari and UDT Laystall teams. He was born and died in Brough, Westmorland.
John Williams, American pianist, composer, and conductor births

John Towner Williams is an American composer, conductor and pianist. In a career that has spanned seven decades, he has composed some of the most popular, recognizable and critically acclaimed film scores in cinematic history. Williams has won 25 Grammy Awards, seven British Academy Film Awards, five Academy Awards and four Golden Globe Awards. With 52 Academy Award nominations, he is the second most-nominated individual, after Walt Disney. His compositions are considered the epitome of film music and he is considered among the greatest composers in the history of cinema.
Yordan Milanov, Bulgarian architect, designed the Sveti Sedmochislenitsi Church (b. 1867) deaths

Yordan Milanov was a Bulgarian architect.

The Sveti Sedmochislenitsi Church and formerly The Black Mosque is a Bulgarian Orthodox church in Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria. It was created between 1901 and 1902 as an Ottoman mosque later converted into orthodox Church, and was inaugurated on 27 July 1903. The church is named after Cyril and Methodius and their five disciples, known in the Orthodox Church collectively as the Sedmochislenitsi.
James Dean, American actor (d. 1955) births

James Byron Dean was an American actor. He is remembered as a cultural icon of teenage disillusionment and social estrangement, as expressed in the title of his most celebrated film, Rebel Without a Cause (1955), in which he starred as troubled teenager Jim Stark. The other two roles that defined his stardom were loner Cal Trask in East of Eden (1955) and surly ranch hand Jett Rink in Giant (1956).
Alejandro Rey, Argentinian-American actor and director (d. 1987) births

Alejandro Rey was an Argentine-American actor and television director.
Theodor Curtius, German chemist (b. 1857) deaths

Geheimrat Julius Wilhelm Theodor Curtius was professor of Chemistry at Heidelberg University and elsewhere. He published the Curtius rearrangement in 1890/1894 and also discovered diazoacetic acid, hydrazine and hydrazoic acid.
Neal Cassady, American author and poet (d. 1968) births

Neal Leon Cassady was a major figure of the Beat Generation of the 1950s and the psychedelic and counterculture movements of the 1960s.
Birgitte Reimer, Danish film actress (d. 2021) births

Birgitte Reimer was a Danish film actress. She appeared in 17 films between 1947 and 1964. Reimer died in April 2021 at the age of 95.
Jack Lemmon, American actor (d. 2001) births

John Uhler Lemmon III was an American actor. Considered equally proficient in both dramatic and comic roles, Lemmon was known for his anxious, middle-class everyman screen persona in dramedy pictures, leading The Guardian to coin him "the most successful tragi-comedian of his age."
Audrey Meadows, American actress and banker (d. 1996) births

Audrey Meadows was an American actress best known for her role as the deadpan housewife Alice Kramden on the 1950s American television comedy The Honeymooners. She was the younger sister of Hollywood leading lady Jayne Meadows.
Barney Danson, Canadian colonel and politician, 21st Canadian Minister of National Defence (d. 2011) births
Barnett Jerome "Barney" Danson, was a Canadian politician and Cabinet minister.

The minister of national defence is a minister of the Crown in the Cabinet of Canada responsible for the management and direction of all matters relating to the national defence of Canada.
Nexhmije Hoxha, Albanian politician (d. 2020) births

Nexhmije Hoxha was an Albanian communist politician. For many years she was the wife of Enver Hoxha, the first leader of the Socialist People's Republic of Albania and the First Secretary of the Party of Labour of Albania. Very close to her husband, she attempted to remain politically influential after his death in 1985. She was one of the few spouses of a ruling communist party leader with a high political profile of her own.
Balram Singh Rai, Guyanese politician, 1st Minister of Home Affairs (d. 2022) births
Balram Singh Rai was a Guyanese politician. He served as Minister of Community Development and Education from 1959 to 1961, then the first Minister of Home Affairs from 1961 to 1962.
Lana Turner, American actress (d. 1995) births

Lana Turner was an American actress. Over the course of her nearly 50-year career, she achieved fame as both a pin-up model and a film actress, as well as for her highly publicized personal life. In the mid-1940s, she was one of the highest-paid actresses in the United States, and one of Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer's (MGM) biggest stars, with her films earning more than $50 million for the studio during her 18-year contract with them. Turner is frequently cited as a popular culture icon of Hollywood glamour and a screen legend of classical Hollywood cinema.
George Formby Sr, English actor and singer (b. 1876) deaths

George Formby was an English comedian and singer in musical theatre, known as one of the greatest music hall performers of the early 20th century. His comedy played upon Lancashire stereotypes, and he was popular around Britain. His nickname, "The Wigan Nightingale", was coined because of the way he would use his bronchial cough as a comedic device in his act.
Peter Kropotkin, Russian zoologist, geographer, and philologist (b. 1842) deaths

Pyotr Alexeyevich Kropotkin was a Russian anarchist, socialist, revolutionary, historian, scientist, philosopher, and activist who advocated anarcho-communism.
Freddie Blassie, American wrestler and manager (d. 2003) births

Frederick Kenneth Blassman was an American professional wrestler and manager, known by the ring name "Classy" Freddie Blassie. Renowned as "The Hollywood Fashion Plate", he was a one-time NWA World Junior Heavyweight Champion, and was inducted into the WWF Hall of Fame in 1994. He is regarded as one of the greatest wrestling heels, or villains, of all time.
Georges Guétary, Egyptian-French singer, dancer, and actor (d. 1997) births

Georges Guétary, born Lambros Vorloou was a French singer, dancer, cabaret performer and film actor, best known for his role in the 1951 musical An American in Paris.
François Langelier, Canadian journalist, lawyer, and politician, 10th Lieutenant Governor of Quebec (b. 1838) deaths

Sir François Langelier, was a Canadian lawyer, professor, journalist, politician, the tenth Lieutenant Governor of Quebec, and author. He was born in Sainte-Rosalie, Lower Canada and died in Spencer Wood, Sillery, Quebec.

The lieutenant governor of Quebec is the viceregal representative in Quebec of the Canadian monarch, King Charles III, who operates distinctly within the province but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada, as well as the other Commonwealth realms and any subdivisions thereof, and resides predominantly in his oldest realm, the United Kingdom. The lieutenant governor of Quebec is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties. The present and 29th lieutenant governor of Quebec is J. Michel Doyon, who has served in the role since September 24, 2015.
Bill Finger, American author and screenwriter, co-created Batman (d. 1974) births

Milton "Bill" Finger was an American comic strip, comic book, film and television writer who was the co-creator of the DC Comics character Batman. Despite making major contributions as an innovative writer, visionary mythos/world builder and illustration architect, Finger was often relegated to ghostwriter status on many comics—including Batman, and the original Green Lantern, Alan Scott.

Batman is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by artist Bob Kane and writer Bill Finger, and debuted in the 27th issue of the comic book Detective Comics on March 30, 1939. In the DC Universe continuity, Batman is the alias of Bruce Wayne, a wealthy American playboy, philanthropist, and industrialist who resides in Gotham City. Batman's origin story features him swearing vengeance against criminals after witnessing the murder of his parents Thomas and Martha as a child, a vendetta tempered with the ideal of justice. He trains himself physically and intellectually, crafts a bat-inspired persona, and monitors the Gotham streets at night. Kane, Finger, and other creators accompanied Batman with supporting characters, including his sidekicks Robin and Batgirl; allies Alfred Pennyworth, James Gordon, and Catwoman; and foes such as the Penguin, the Riddler, Two-Face, and his archenemy the Joker.
Dayrolles Eveleigh-de-Moleyns, 4th Baron Ventry, Irish hereditary peer (b. 1828) deaths
Dayrolles Blakeney Eveleigh-de-Moleyns, 4th Baron Ventry, DL, JP, was an Irish hereditary peer, elected as a representative peer in 1871.
Betty Field, American actress (d. 1973) births

Betty Field was an American film and stage actress.
Danai Stratigopoulou, Greek singer-songwriter (d. 2009) births

Danai Stratigopoulou was a Greek singer, writer, and university academic. She acquired recognition in the literary world for translating the works of the Chilean nobel laureate Pablo Neruda into the Greek language.
Elizabeth Bishop, American poet and author (d. 1979) births

Elizabeth Bishop was an American poet and short-story writer. She was Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress from 1949 to 1950, the Pulitzer Prize winner for Poetry in 1956, the National Book Award winner in 1970, and the recipient of the Neustadt International Prize for Literature in 1976. Dwight Garner argued that she was perhaps "the most purely gifted poet of the 20th century".
Hans Jæger, Norwegian philosopher and activist (b. 1854) deaths

Hans Henrik Jæger was a Norwegian writer, philosopher and anarchist political activist who was part of the Oslo -based bohemian group known as the Kristiania Bohemians. In 1886 he was prosecuted for his book Fra Kristiania-bohêmen, then convicted and sentenced to 60 days' imprisonment and a fine of 80 kr for infringement of modesty and public morals, and for blasphemy. He also lost his position as a stenographer at the Parliament of Norway. Jæger was defended in court by barrister Ludvig Meyer. He and other bohemians tried to live by the nine commandments he had formulated in Fra Kristiania-bohêmen.
Elisabeth Murdoch, Australian philanthropist (d. 2012) births

Dame Elisabeth Joy Murdoch, Lady Murdoch, also known as Elisabeth, Lady Murdoch, was an Australian philanthropist and matriarch of the Murdoch family. She was the widow of Australian newspaper publisher Sir Keith Murdoch and the mother of international media proprietor Rupert Murdoch. She was appointed a Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire (DBE) in 1963 for her charity work in Australia and overseas.
Hendrik Willem Bakhuis Roozeboom, Dutch chemist and academic (b. 1854) deaths

H. W. Bakhuis Roozeboom was a Dutch chemist who studied phase behaviour in physical chemistry.
Chester Carlson, American physicist and lawyer, invented Xerography (d. 1968) births
Chester Floyd Carlson was an American physicist, inventor, and patent attorney born in Seattle, Washington.

Xerography is a dry photocopying technique. Originally called electrophotography, it was renamed xerography—from the Greek: [n] roots ξηρός xeros, meaning "dry" and -γραφία -graphia, meaning "writing"—to emphasize that unlike reproduction techniques then in use such as cyanotype, the process of xerography used no liquid chemicals.
Greta Keller, Austrian-American singer and actress (d. 1977) births

Margaretha "Greta" Keller was an Austrian and American cabaret singer and actress, who worked in some Hollywood movies and Television dramas.
Tunku Abdul Rahman, 1st Prime Minister of Malaysia (d. 1990) births

Tunku Abdul Rahman Putra Al-Haj ibni Almarhum Sultan Abdul Hamid Halim Shah was a Malaysian statesman and lawyer who served as the 1st Prime Minister of Malaysia and the head of government of its predecessor states from 1955 to 1970. He was the first chief minister of the Federation of Malaya from 1955 to 1957. He supervised the independence process that culminated on 31 August 1957. As Malaya's first prime minister he dominated politics there for the next 13 years. In 1963, he successfully incorporated the Federation of Malaya, British North Borneo, Sarawak, and Singapore into the state of Malaysia. However, tensions between the Malay and Chinese communities resulted in Singapore's expulsion in 1965. His poor performance during race riots in Kuala Lumpur in 1969 led to his resignation in 1970. Commonly known simply as "Tunku", Tunku Abdul Rahman is widely regarded, even by his critics, as Malaysia's "founding father", the architect of Malayan independence and of the formation of Malaysia. As such, he is often referred to as Father of Independence or Father of Malaysia.
Demchugdongrub, Mongol prince and politician, head of state of Mengjiang (d. 1966) births

Demchugdongrub, also known as Prince De, courtesy name Xixian, was a Qing dynasty Mongol prince descended from the Borjigin imperial clan who lived during the 20th century and became the leader of an independence movement in Inner Mongolia. He was most notable for being the chairman of the pro-Japanese Mongol Military Government (1938–39) and later of the puppet state of Mengjiang (1939–45), during the Second Sino-Japanese War. In modern day, some see Demchugdongrub as a Mongol nationalist promoting Pan-Mongolism while others view him as a traitor and as the pawn of the Japanese during World War II.

Mengjiang, also known as Mengkiang or the Mongol Border Land, and governed as the Mengjiang United Autonomous Government, was an autonomous area in Inner Mongolia, formed in 1939 as a puppet state of the Empire of Japan, then from 1940 being under the nominal sovereignty of the Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China. It consisted of the previously Chinese provinces of Chahar and Suiyuan, corresponding to the central part of modern Inner Mongolia. It has also been called Mongukuo or Mengguguo. The capital was Kalgan, from where it was under the nominal rule of Mongol nobleman Demchugdongrub. The territory returned to Chinese control after the defeat of the Japanese Empire in 1945.
Lonnie Johnson, American singer-songwriter and guitarist (d. 1970) births

Alonzo "Lonnie" Johnson was an American blues and jazz singer, guitarist, violinist and songwriter. He was a pioneer of jazz guitar and jazz violin and is recognized as the first to play an electrically amplified violin.
Zakir Hussain, Indian academic and politician, 3rd president of India (d. 1969) births

Zakir Husain Khan known as Dr. Zakir Husain, was an Indian educationist and politician who served as President of India from 13 May 1967 until his death on 3 May 1969.

The president of India is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murmu is the 15th and current president, having taken office from 25 July 2022.
King Vidor, American director, producer, and screenwriter (d. 1982) births

King Wallis Vidor was an American film director, film producer, and screenwriter whose 67-year film-making career successfully spanned the silent and sound eras. His works are distinguished by a vivid, humane, and sympathetic depiction of contemporary social issues. Considered an auteur director, Vidor approached multiple genres and allowed the subject matter to determine the style, often pressing the limits of film-making conventions.
Ba Maw, Burmese lawyer and politician, Prime Minister of Burma (d. 1977) births

Ba Maw was a Burmese lawyer and political leader, active during the interwar and World War II periods. Dr. Ba Maw is a descendant of the Mon Dynasty. He was the first Burma Premier (1937–1939) and head of State of Burma from 1942 to 1945.

The prime minister of Myanmar is the head of government of Myanmar. The post was re-established in 2021 by the State Administration Council, the country's ruling military junta, to lead its nominally-civilian provisional government. The provisional government is subject to the decision-making of the SAC; additionally, there is a significant overlap in the membership of both bodies. There is no provision for a prime minister in the 2008 Constitution of Myanmar, with the president being the constitutional head of government. The current prime minister is Min Aung Hlaing, who is also the leader of the junta and the commander-in-chief of defence services. The post had been used by previous military governments, as recently as 2011.
Claro M. Recto, Filipino lawyer, jurist, and politician (d. 1960) births

Claro Mayo Recto Jr. was a Filipino politician, jurist, and poet. He is remembered for his nationalism, for "the impact of his patriotic convictions on modern political thought", and has been seen in the same class as Dr. Jose Rizal, Sen. Jose W. Diokno, and Sen. Lorenzo Tañada.
Edith Evans, English actress (d. 1976) births

Dame Edith Mary Evans, was an English actress. She was best known for her work on the stage, but also appeared in films at the beginning and towards the end of her career. Between 1964 and 1968, she was nominated for three Academy Awards.
Giuseppe Ungaretti, Egyptian-Italian soldier, journalist, and poet (d. 1970) births

Giuseppe Ungaretti was an Italian modernist poet, journalist, essayist, critic, academic, and recipient of the inaugural 1970 Neustadt International Prize for Literature. A leading representative of the experimental trend known as Ermetismo ("Hermeticism"), he was one of the most prominent contributors to 20th century Italian literature. Influenced by symbolism, he was briefly aligned with futurism. Like many futurists, he took an irredentist position during World War I. Ungaretti debuted as a poet while fighting in the trenches, publishing one of his best-known pieces, L'allegria.
Charlie Ruggles, American actor (d. 1970) births

Charles Sherman Ruggles was an American comic character actor. In a career spanning six decades, Ruggles appeared in close to 100 feature films, often in mild-mannered and comic roles. He was also the elder brother of director, producer, and silent film actor Wesley Ruggles (1889–1972).
Snowy Baker, Australian boxer, rugby player, and actor (d. 1953) births

Reginald Leslie "Snowy" Baker was an Australian athlete, sports promoter, and actor. Born in Surry Hills, an inner-city suburb of Sydney, New South Wales, Baker excelled at a number of sports, winning New South Wales swimming and boxing championships while still a teenager. Playing rugby union for Eastern Suburbs, he played several games for New South Wales against Queensland, and in 1904 represented Australia in two Test matches against Great Britain. At the 1908 London Olympics, Baker represented Australasia in swimming and diving, as well as taking part in the middleweight boxing event, in which he won a silver medal. He also excelled in horsemanship, water polo, running, rowing and cricket. However, "His stature as an athlete depends largely upon the enormous range rather than the outstanding excellence of his activities; it was as an entrepreneur-showman, publicist and businessman that he seems in retrospect to have been most important."
Joseph Schumpeter, Czech-American economist and political scientist (d. 1950) births
Joseph Alois Schumpeter was an Austrian-born political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of German-Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at Harvard University, where he remained until the end of his career, and in 1939 obtained American citizenship.
Thomas Selfridge, American lieutenant and pilot (d. 1908) births

Thomas Etholen Selfridge was a first lieutenant in the U.S. Army and the first person to die in an airplane crash. He was also the first active-duty member of the U.S. military to die in a crash while on duty. He was killed while seated as a passenger in a Wright Flyer, on a demonstration flight piloted by Orville Wright.
Franz Marc, German soldier and painter (d. 1916) births

Franz Moritz Wilhelm Marc was a German painter and printmaker, one of the key figures of German Expressionism. He was a founding member of Der Blaue Reiter, a journal whose name later became synonymous with the circle of artists collaborating in it.
Viktor Schwanneke, German actor and director (d. 1931) births
Viktor Schwanneke was a German stage director and actor, writer, and film actor whose acting career began at the turn of the 20th century.
Martin Buber, Austrian-Israeli philosopher and academic (d. 1965) births

Martin Buber was an Austrian Jewish and Israeli philosopher best known for his philosophy of dialogue, a form of existentialism centered on the distinction between the I–Thou relationship and the I–It relationship. Born in Vienna, Buber came from a family of observant Jews, but broke with Jewish custom to pursue secular studies in philosophy. In 1902, he became the editor of the weekly Die Welt, the central organ of the Zionist movement, although he later withdrew from organizational work in Zionism. In 1923, Buber wrote his famous essay on existence, Ich und Du, and in 1925, he began translating the Hebrew Bible into the German language reflecting the patterns of the Hebrew language.
Paula Modersohn-Becker, German painter (d. 1907) births

Paula Modersohn-Becker was a German Expressionist painter of the late 19th and early 20th century. Her work is noted for its intensity and its blunt, unapologetic humanity, and for the many self-portraits the artist produced, including nude self-portraits. She is considered one of the most important representatives of early expressionism, producing more than 700 paintings and over 1000 drawings during her active painting life. She is recognized both as the first known woman painter to paint nude self-portraits, and the first woman to have a museum devoted exclusively to her art. Additionally, she is considered to be the first woman artist to depict herself both pregnant and nude and pregnant.
Moses Gomberg, Ukrainian-American chemist and academic (d. 1947) births

Moses Gomberg was a chemistry professor at the University of Michigan. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences and served as president of the American Chemical Society.
Adella Brown Bailey, American politician and suffragist (d. 1937) births

Adella Brown Bailey (1860-1937) was an American politician and suffragist.
Agostino Bassi, Italian entomologist and academic (b. 1773) deaths

Agostino Bassi, sometimes called de Lodi, was an Italian entomologist. He preceded Louis Pasteur in the discovery that microorganisms can be the cause of disease. He discovered that the muscardine disease of silkworms was caused by a living, very small, parasitic organism, a fungus that would be named eventually Beauveria bassiana in his honor. In 1844, he stated the idea that not only animal (insect), but also human diseases are caused by other living microorganisms; for example, measles, syphilis, and the plague.
Kate Chopin, American author (d. 1904) births
Kate Chopin was an American author of short stories and novels based in Louisiana. She is considered by scholars to have been a forerunner of American 20th-century feminist authors of Southern or Catholic background, such as Zelda Fitzgerald, and she is one of the more frequently read and recognized writers of Louisiana Creole heritage. She is best known today for her 1899 novel The Awakening.
François Habeneck, French violinist and conductor (b. 1781) deaths

François Antoine Habeneck was a French classical violinist and conductor.
France Prešeren, Slovenian poet and lawyer (b. 1800) deaths

France Prešeren was a 19th-century Romantic Slovene poet whose poems have been translated into many languages.
Dmitri Mendeleev, Russian chemist and academic (d. 1907) births

Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev was a Russian chemist and inventor. He is best known for formulating the Periodic Law and creating a version of the periodic table of elements. He used the Periodic Law not only to correct the then-accepted properties of some known elements, such as the valence and atomic weight of uranium, but also to predict the properties of three elements that were yet to be discovered.
Abdülaziz of the Ottoman Empire (d. 1876) births

Abdulaziz was the 32nd Sultan of the Ottoman Empire and reigned from 25 June 1861 up until 30 May 1876, where he was overthrown via a government coup. He was the son of Sultan Mahmud II and succeeded his brother Abdulmejid I in 1861.
Vital-Justin Grandin, French-Canadian bishop and missionary (d. 1902) births

Vital-Justin Grandin was a Roman Catholic priest and bishop known as a key architect of the Canadian Indian residential school system, which has been labeled an instrument of cultural genocide. In June 2021, this led to governments and private businesses to begin removing his name from institutions and infrastructure previously named for him. He served the Church in the western parts of what is now Canada both before and after Confederation. He is also the namesake or co-founder of various small communities and neighbourhoods in what is now Alberta, Canada, especially those of francophone residents.
Jules Verne, French author, poet, and playwright (d. 1905) births

Jules Gabriel Verne was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the Voyages extraordinaires, a series of bestselling adventure novels including Journey to the Center of the Earth (1864), Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas (1870), and Around the World in Eighty Days (1872). His novels, always well documented, are generally set in the second half of the 19th century, taking into account the technological advances of the time.
Henry Walter Bates, English geographer, biologist, and explorer (d. 1892) births

Henry Walter Bates was an English naturalist and explorer who gave the first scientific account of mimicry in animals. He was most famous for his expedition to the rainforests of the Amazon with Alfred Russel Wallace, starting in 1848. Wallace returned in 1852, but lost his collection on the return voyage when his ship caught fire. When Bates arrived home in 1859 after a full eleven years, he had sent back over 14,712 species of which 8,000 were new to science. Bates wrote up his findings in his best-known work, The Naturalist on the River Amazons.
Maxime Du Camp, French photographer and journalist (d. 1894) births

Maxime Du Camp was a French writer and photographer.
William Tecumseh Sherman, American general (d. 1891) births

William Tecumseh Sherman was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his command of military strategy as well as criticism for the harshness of the scorched-earth policies that he implemented against the Confederate States. British military theorist and historian B. H. Liddell Hart declared that Sherman was "the first modern general".
John Ruskin, English author, critic, and academic (d. 1900) births

John Ruskin was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and political economy.
Richard S. Ewell, American general (d. 1872) births

Richard Stoddert Ewell was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general during the American Civil War. He achieved fame as a senior commander under Stonewall Jackson and Robert E. Lee and fought effectively through much of the war, but his legacy has been clouded by controversies over his actions at the Battle of Gettysburg and at the Battle of Spotsylvania Court House.
Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins, English sculptor and zoologist (d. 1889) births

Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins was an English sculptor and natural history artist renowned for his work on the life-size models of dinosaurs in the Crystal Palace Park in south London. The models, accurately made using the latest scientific knowledge, created a sensation at the time. Hawkins was also a noted lecturer on zoological topics.
Grand Duke Michael Pavlovich of Russia (d. 1849) births

Grand Duke Mikhail Pavlovich of Russia was a Russian grand duke, the tenth child and fourth son of Paul I of Russia and his second wife, Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg, who took the name Maria Feodorovna. He was the younger brother of two Tsars, Alexander I and Nicholas I, and the disputed Tsar Konstantin I.
Caroline Augusta of Bavaria (d. 1873) births

Princess Caroline Augusta of Bavaria was Empress of Austria by marriage to Francis I of Austria. She was a daughter of King Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria and Princess Augusta Wilhelmine of Hesse-Darmstadt. She married Crown Prince William of Württemberg, whom she divorced, and Emperor Francis I of Austria.
Princess Augusta of Saxe-Gotha (b. 1719) deaths

Princess Augusta of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg was Princess of Wales by marriage to Frederick, Prince of Wales, eldest son and heir apparent of King George II. She never became queen consort, as Frederick predeceased his father in 1751. Augusta's eldest son succeeded her father-in-law as King George III in 1760. After her spouse died, Augusta was presumptive regent of Great Britain in the event of a regency until her son reached majority in 1756.
George Dance the Elder, English architect, designed St Leonard's and St Botolph's Aldgate (b. 1695) deaths
George Dance the Elder was a British architect of the 18th century. He was the City of London surveyor and architect from 1735 until his death.

St Leonard's, Shoreditch, is the ancient parish church of Shoreditch, often known simply as Shoreditch Church. It is located at the intersection of Shoreditch High Street with Hackney Road, within the London Borough of Hackney in East London. The current building dates from about 1740 and is Grade I listed. The church is mentioned in the line ""When I grow rich", say the bells of Shoreditch" from the nursery rhyme Oranges and Lemons.

St Botolph's Aldgate is a Church of England parish church in the City of London and also, as it lies outside the line of the city's former eastern walls, a part of the East End of London.
Joseph Leopold Eybler, Austrian composer and conductor (d. 1846) births

Joseph Leopold Eybler was an Austrian composer and contemporary of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.
Gia Long, Vietnamese emperor (d. 1820) births

Gia Long, born Nguyễn Phúc Ánh (阮福暎) or Nguyễn Ánh, was the founding emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last dynasty of Vietnam. His dynasty would rule the unified territories that constitute modern-day Vietnam until 1945.
Aaron Hill, English playwright and poet (b. 1685) deaths
Aaron Hill was an English dramatist and miscellany writer.
Jan van Huysum, Dutch painter (b. 1682) deaths
Jan van Huysum is the most notable member of the Van Huysum family of artists working in Dutch Golden Age of the 17th and 18th centuries; “by common consent, Jan van Huysum has been held to be the best painter of flowers.” Trained in decoration from a young age, he “gradually developed an execution of details of the utmost beauty and finish” creating “wonderful flower pieces whereon drops of water and crawling ants could be seen without a magnifying glass.”
André Grétry, Belgian-French organist and composer (d. 1813) births

André Ernest Modeste Grétry was a composer from the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, who worked from 1767 onwards in France and took French nationality. He is most famous for his opéras comiques.
Peter the Great, Russian emperor (b. 1672) deaths

Peter I, most commonly known as Peter the Great, was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from 7 May [O.S. 27 April] 1682 to 1721 and subsequently the Russian Empire until his death in 1725, jointly ruling with his elder half-brother, Ivan V until 1696. He is primarily credited with the modernisation of the country, transforming it into a European power.
Emperor Sakuramachi of Japan (d. 1750) births

Emperor Sakuramachi was the 115th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. Sakuramachi's birth name was Teruhito before he became enthroned as Emperor in 1735, a reign that would last until 1747 with his retirement. As with previous Emperors during the Edo period, the Tokugawa shogunate had control over Japan. The Emperor's role was a religious figure who performed limited duties. This changed when Sakuramachi was granted permission from the Shōgun to restore some Imperial rites. Ceremonies such as the Harvest Festival that had previously been absent for over 250 years were now allowed. Sakuramachi had one wife and a concubine with whom he fathered 4 children. His first son would go on to become Emperor Momozono, while his second daughter would later be Empress Go-Sakuramachi. Sakuramachi died on 28 May 1750, which was almost three years after his abdication.
Giuseppe Torelli, Italian violinist and composer (b. 1658) deaths

Giuseppe Torelli was an Italian violist, violinist, teacher, and composer of the middle Baroque era.
Daniel Bernoulli, Dutch-Swiss mathematician and physicist (d. 1782) births

Daniel Bernoulli FRS was a Swiss mathematician and physicist and was one of the many prominent mathematicians in the Bernoulli family from Basel. He is particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechanics, especially fluid mechanics, and for his pioneering work in probability and statistics. His name is commemorated in the Bernoulli's principle, a particular example of the conservation of energy, which describes the mathematics of the mechanism underlying the operation of two important technologies of the 20th century: the carburetor and the airplane wing.
Ivan V of Russia (b. 1666) deaths

Ivan V Alekseyevich was a joint Tsar of Russia with his younger half-brother Peter the Great, who co-reigned between 1682 and 1696. Ivan was the youngest son of Alexis I of Russia by his first wife, Maria Miloslavskaya, while Peter was the only son of Alexis by his second wife, Natalya Naryshkina. Ivan's reign was solely titular because he had serious physical and mental issues.
Charles-Jean-François Hénault, French historian and author (d. 1770) births

Charles-Jean-François Hénault was a French writer and historian.
Alexis of Russia (b. 1629) deaths

Aleksey Mikhaylovich was the Tsar of Russia from 1645 until his death in 1676. While finding success in foreign affairs, his reign saw several wars with Iran, Poland and Sweden, as well as internal instabilities such as the Salt Riot in Moscow and the Cossack revolt of Stenka Razin in southern Russia. In religious matters, he sided closely with Patriarch Nikon during the schism in the Russian Orthodox Church which saw unpopular liturgical reforms. He was the first tsar to sign laws on his own authority and his council passed the Sobornoye Ulozheniye of 1649 which strengthened the bonds between autocracy and the lower nobility, at the time of his death Russia spanned almost two billion acres (8.1 million km2).
Thomas Cecil, 1st Earl of Exeter, English soldier and politician, Lord Lieutenant of Northamptonshire (b. 1546) deaths

Thomas Cecil, 1st Earl of Exeter, KG, known as Lord Burghley from 1598 to 1605, was an English politician, courtier and soldier.
Below is a list of people who have served as Lord Lieutenant of Northamptonshire. Since 1735, all Lords Lieutenant have also been Custos Rotulorum of Northamptonshire. The lieutenancy included the Soke of Peterborough until 1965, when the Lord Lieutenant of Huntingdonshire became Lord Lieutenant of Huntingdon and Peterborough. This merged with the lieutenancy of Cambridgeshire and Isle of Ely in 1974, forming the jurisdiction of the present Lord Lieutenant of Cambridgeshire.
Robert Rollock, Scottish theologian and academic (b. 1555) deaths

Robert Rollock was Scottish academic and minister in the Church of Scotland, and the first regent and first principal of the University of Edinburgh. Born into a noble family, he distinguished himself during his education at the University of St Andrews, which led to him being appointed regent of the newly created college in Edinburgh in 1583, and its first principal in 1586.
Guercino, Italian painter (d. 1666) births

Giovanni Francesco Barbieri, better known as Guercino, or il Guercino [ɡwerˈtʃiːno], was an Italian Baroque painter and draftsman from Cento in the Emilia region, who was active in Rome and Bologna. The vigorous naturalism of his early manner contrasts with the classical equilibrium of his later works. His many drawings are noted for their luminosity and lively style.
Mary, Queen of Scots (b. 1542) deaths

Mary, Queen of Scots, also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
Robert Burton, English priest, physician, and scholar (d. 1640) births

Robert Burton was an English author and fellow of Oxford University, who wrote the encyclopedic tome The Anatomy of Melancholy.
Agrippa d'Aubigné, French poet and soldier (d. 1630) births

Théodore-Agrippa d'Aubigné was a French poet, soldier, propagandist and chronicler. His epic poem Les Tragiques (1616) is widely regarded as his masterpiece. In a book about his Catholic contemporary Jean de La Ceppède, English poet Keith Bosley has called d'Aubigné, "the epic poet of the Protestant cause," during the French Wars of Religion. Bosley added, however, that after d'Aubigné's death, he, "was forgotten until the Romantics rediscovered him."
Saint Gerolamo Emiliani, Italian humanitarian (b. 1481) deaths

Gerolamo Emiliani was an Italian humanitarian, founder of the Somaschi Fathers, and is considered a saint by the Catholic Church.
Daniele Barbaro, Venetian churchman, diplomat and scholar (d. 1570) births

Daniele Matteo Alvise Barbaro was an Italian cleric and diplomat. He was also an architect, writer on architecture, and translator of, and commentator on, Vitruvius.
Ulrich, Duke of Württemberg (d. 1550) births

Duke Ulrich of Württemberg succeeded his kinsman Eberhard II as Duke of Württemberg in 1498. He was declared of age in 1503. His volatile personality made him infamous, being called the "Swabian Henry VIII" by historians.
Constantine XI Palaiologos, Byzantine emperor (d. 1453) births

Constantine XI Dragases Palaiologos or Dragaš Palaeologus was the last Roman emperor, reigning from 1449 until his death in battle at the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. Constantine's death marked the definitive end of the Eastern Roman Empire, which traced its origin to Constantine the Great's foundation of Constantinople as the Roman Empire's new capital in 330. Given that the Eastern Roman Empire was the Roman Empire's medieval continuation, with its citizens continuing to refer to themselves as Romans, Constantine XI's death and Constantinople's fall also marked the definitive end of the Roman Empire, founded by Augustus almost 1,500 years earlier.
Blanche of France, Duchess of Orléans (b. 1328) deaths

Blanche of France was the posthumous daughter of King Charles IV of France and his third wife, Joan of Évreux. She was the last direct Capetian and the last-surviving member of her family, and her marriage to her second-cousin, Philip, Duke of Orléans, proved childless. With Blanche's death in 1393, the House of Capet continued to exist only via its numerous cadet branches.
Helen of Anjou, queen of Serbia (b. 1236) deaths

Helen of Anjou was the queen consort of the Serbian Kingdom, as the spouse of King Stefan Uroš I, who ruled from 1243 to 1276. Their sons were later Serbian kings Stefan Dragutin (1276–1282) and Stefan Milutin (1282–1321). As a dowager-queen, she held the provincial governorship in the regions of Zeta and Travunija. She built Gradac monastery and was known for her religious tolerance. She is revered as a saint by the Serbian Orthodox Church.Her relics, however, are now lost.
Przemysł II of Poland (b. 1257) deaths

Przemysł II was the Duke of Poznań from 1257–1279, of Greater Poland from 1279 to 1296, of Kraków from 1290 to 1291, and Gdańsk Pomerania (Pomerelia) from 1294 to 1296, and then King of Poland from 1295 until his death. After a long period of Polish high dukes and two nominal kings, he was the first to obtain the hereditary title of king, and thus to return Poland to the rank of kingdom. A member of the Greater Poland branch of the House of Piast as the only son of Duke Przemysł I and the Silesian princess Elisabeth, he was born posthumously; for this reason he was brought up at the court of his uncle Bolesław the Pious and received his own district to rule, the Duchy of Poznań in 1273. Six years later, after the death of his uncle, he also obtained the Duchy of Kalisz.
Afonso IV of Portugal (d. 1357) births

Afonso IV, called the Brave, was King of Portugal from 1325 until his death in 1357. He was the only legitimate son of King Denis of Portugal and Elizabeth of Aragon.
Theodoric of Landsberg (b. 1242) deaths
Theodoric of Landsberg, a member of the House of Wettin was Margrave of Landsberg from 1265 until his death.
Hulagu Khan, Mongol ruler (b. 1217) deaths

Hulagu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulegu, was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Western Asia. Son of Tolui and the Keraite princess Sorghaghtani Beki, he was a grandson of Genghis Khan and brother of Ariq Böke, Möngke Khan, and Kublai Khan.
Robert I, Count of Artois (b. 1216) deaths

Robert I, called the Good, was the first Count of Artois. He was the fifth son of King Louis VIII of France and Blanche of Castile.
William II Longespée, English martyr (b. 1212) deaths

Sir William Longespée was an English knight and crusader, the son of William Longespée and Ela, Countess of Salisbury. His death became of significant importance to the English psyche, having died at the Battle of Mansurah, near Al-Mansurah in Egypt.
Ali ibn Hanzala, sixth Dāʿī al-Muṭlaq of Tayyibi Isma'ilism deaths

Ali ibn Hanzala ibn Abi Salim al-Mahfuzi al-Wadi'i al-Hamdani was the sixth Tayyibi Isma'ili Dāʿī al-Muṭlaq in Yemen, from 1215 to his death in 1229.

The term Da'i al-Mutlaq literally meaning 'the absolute, or unrestricted, missionary', is the most senior spiritual rank and office in Tayyibi Isma'ilism. The Da'i al-Mutlaq has headed the Tayyibi community since the seclusion of the 21st Tayyibi Imam, at-Tayyib Abu'l-Qasim, traditionally placed in 528 AH/1134 AD.

Tayyibi Isma'ilism is the only surviving sect of the Musta'li branch of Isma'ilism, the other being the extinct Hafizi branch. Followers of Tayyibi Isma'ilism are found in various Bohra communities: Dawoodi, Sulaymani, and Alavi.
Alexios IV Angelos, Byzantine emperor (b. 1182) deaths

Alexios IV Angelos or Alexius IV Angelus was Byzantine Emperor from August 1203 to January 1204. He was the son of Emperor Isaac II Angelos and his first wife, an unknown Palaiologina, who became a nun with the name Irene. His paternal uncle was his predecessor Emperor Alexios III Angelos.
Yaroslav II of Vladimir (d. 1246) births

Yaroslav II, Christian name Theodor (Феодо́р) was the Grand Prince of Vladimir (1238–1246) who helped to restore his country and capital after the Mongol invasion of Rus'.
Elvira of Castile, Queen of Sicily (b.c. 1100) deaths
Elvira of Castile was a member of the House of Jiménez and the first Queen of Sicily as the wife of Roger II of Sicily.
Muhammad ibn Tughj al-Ikhshid, Egyptian commander and politician, Abbasid Governor of Egypt (d. 946) births
Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Ṭughj ibn Juff ibn Yiltakīn ibn Fūrān ibn Fūrī ibn Khāqān, better known by the title al-Ikhshīd after 939, was an Abbasid commander and governor who became the autonomous ruler of Egypt and parts of Syria (Levant) from 935 until his death in 946. He was the founder of the Ikhshidid dynasty, which ruled the region until the Fatimid conquest of 969.
Governors of Arab Egypt (640–1250) and Mamluk Egypt (1250–1517). For other periods, see the list of rulers of Egypt.
Severus of Antioch, patriarch of Antioch deaths

Severus the Great of Antioch, also known as Severus of Gaza or Crown of Syrians, was the Patriarch of Antioch, and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church, from 512 until his death in 538. He is venerated as a saint in the Oriental Orthodox Church, and his feast day is 8 February.
Patriarch of Antioch is a traditional title held by the bishop of Antioch. As the traditional "overseer" of the first gentile Christian community, the position has been of prime importance in Pauline Christianity from its earliest period. This diocese is one of the few for which the names of its bishops from the apostolic beginnings have been preserved. Today five churches use the title of patriarch of Antioch: one Oriental Orthodox ; three Eastern Catholic ; and one Eastern Orthodox.
Proclus, Greek mathematician and philosopher (probable; d. 485) births

Proclus Lycius, called Proclus the Successor, was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers of late antiquity. He set forth one of the most elaborate and fully developed systems of Neoplatonism and, through later interpreters and translators, exerted an influence on Byzantine philosophy, Early Islamic philosophy, and Scholastic philosophy.
Vettius Valens, Greek astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer (probable; d. 175) births
Year 120 (CXX) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Fulvus. The denomination 120 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Vettius Valens was a 2nd-century Hellenistic astrologer, a somewhat younger contemporary of Claudius Ptolemy.
Christian feast day: Cuthmann of Steyning

Saint Cuthmann of Steyning, also spelt Cuthman, was an Anglo-Saxon hermit and church-builder.
Christian feast day: Elffled of Whitby

Saint Ælfflæd (654–714) was the daughter of King Oswiu of Northumbria and Eanflæd. She was abbess of Whitby Abbey, an abbey of nuns that were known for their skills in medicine, from the death of her kinswoman Hilda in 680, first jointly with her mother, then alone. Ælfflæd was particularly known for her skills in surgery and her personal attention to patients, as was Hilda, who was known for her personalized medical care.
Christian feast day: Gerolamo Emiliani

Gerolamo Emiliani was an Italian humanitarian, founder of the Somaschi Fathers, and is considered a saint by the Catholic Church.
Christian feast day: Josephine Bakhita

Josephine Margaret Bakhita,, was a Sudanese-Italian Canossian religious sister who lived in Italy for 45 years, after having been a slave in Sudan. In 2000, she was declared a saint, the first Black woman to receive the honor in the modern era.
Christian feast day: Juventius of Pavia
Saint Iuventius was a bishop of Pavia during the 1st century. Together with Syrus of Pavia he was sent there by Saint Hermagoras. Both Iuventius and Syrus are reported to have been the first bishop of Pavia.
Christian feast day: Meingold of Huy
Saint Meingold is said to have been count of Huy, who was murdered by his opponents in 892. It is possible that the holy Meingold was a different person confused with the count, with both having been killed in the same year.
Christian feast day: Stephen of Muret

Stephen of Muret was the founder of the Abbey of Grandmont and the Order of Grandmont.
Christian feast day: February 8 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)

February 7 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar - February 9
Earliest day on which Feast of Orthodoxy can fall, while March 14 is the latest; celebrated 42 days before Easter; the first Sunday of Lent. (Orthodoxy)
The Feast of Orthodoxy is celebrated on the first Sunday of Great Lent in the Eastern Orthodox Church and other churches using the Byzantine Rite to commemorate, originally, only the final defeat of iconoclasm on the first Sunday of Lent in 843, and later also opposition to all heterodoxy.
Orthodoxy is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Parinirvana Day (some Mahayana Buddhism traditions, most celebrate on February 15)
Parinirvana Day, or Nirvana Day is a Mahayana Buddhist holiday celebrated in East Asia, Vietnam and the Philippines. By some it is celebrated on 8 February, but by most on the 15 February. In Bhutan, it is celebrated on the fifteenth day of the fourth month of the Bhutanese calendar. It celebrates the day when the Buddha is said to have achieved Parinirvana, or complete Nirvana, upon the death of his physical body.

Mahāyāna is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices. Mahāyāna Buddhism developed in India and is considered one of the two main existing branches of Buddhism. Mahāyāna accepts the main scriptures and teachings of early Buddhism, but also recognizes various doctrines and texts which are not accepted by Theravada Buddhism as original. These include the Mahāyāna Sūtras and its emphasis on the bodhisattva path and Prajñāpāramitā. Vajrayāna or Mantra traditions are a subset of Mahāyāna, which make use of numerous tantric methods considered to be faster and more powerful at achieving Buddhahood by Vajrayānists.
Prešeren Day (Slovenia)

Prešeren Day, full name Prešeren Day, the Slovene Cultural Holiday, is a public holiday celebrated in Slovenia on 8 February. It is marking the anniversary of the death of the Slovene national poet France Prešeren on 8 February 1849 and is the celebration of the Slovenian culture. It was established in 1945 to raise the cultural consciousness and the self-confidence of the Slovene nation, and declared a work-free day in 1991. On February 7, the eve of the holiday, the Prešeren Awards and the Prešeren Fund Awards, the highest Slovenian recognitions for cultural achievements, are conferred. Prešeren Day continues to be one of the most widely celebrated Slovene holidays. During the holiday all state and municipal museums and galleries offer free entry, and various other cultural events are held. The holiday is celebrated not only in Slovenia, but also by Slovene communities all around the world.

Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers 20,271 square kilometres (7,827 sq mi), and has a population of 2.1 million. Slovenes constitute over 80% of the country's population. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geographically situated near the centre of the country.
Propose Day

Propose Day is celebrated in India on 8 February as a day to propose to one's significant other. A large number of young people give roses to propose to their prospective girlfriend or boyfriend. It is the second day in Valentines Week. Although Valentine's day is celebrated across whole world, Valentine week is something celebrated in India only. This week marks various festivities across India including Rose Day on the 7th.