COVID-19 vaccine
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
The World Health Organization issues its first emergency use validation for a COVID-19 vaccine.

A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
The World Health Organization is informed of cases of pneumonia with an unknown cause, detected in Wuhan. This later turned out to be COVID-19, the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic.

The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide.

Wuhan is the capital of Hubei Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the ninth-most populous Chinese city and one of the nine National Central Cities of China.

Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.

The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified from an outbreak in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019. Attempts to contain it there failed, allowing the virus to spread to other areas of Asia and later worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on 30 January 2020 and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. As of 9 December 2022, the pandemic had caused more than 648 million cases and 6.65 million confirmed deaths, making it one of the deadliest in history.
Thirty-nine people are killed after a ten-story building collapses in the industrial city of Magnitogorsk, Russia.

On 31 December 2018, at approximately 6:02 a.m. local time, an apartment block in Magnitogorsk, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, partially collapsed. The collapse killed 39 people and injured 17 more. The cause of the collapse is believed to have been a gas explosion.

Magnitogorsk is an industrial city in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located on the eastern side of the extreme southern extent of the Ural Mountains by the Ural River. Its population is 407,775 (2010 Census).
A fire breaks out at the Downtown Address Hotel in Downtown Dubai, United Arab Emirates, located near the Burj Khalifa, two hours before the fireworks display is due to commence. Sixteen injuries were reported; one had a heart attack, another suffered a major injury, and fourteen others with minor injuries.

Downtown Dubai or The Dubai Downtown, is a large-scale, mixed-use complex in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. The Dubai Downtown was created by the Emaar Real Estate Development Company. Before 2000, the place was called Umm Al Tarif. It is home to some of the city's largest landmarks including Burj Khalifa, The Dubai Mall, and The Dubai Fountain. It covers an area of 2 square kilometres (0.77 sq mi), at an estimated cost of US$20 billion upon completion and as of 2017, had a population of 13,201.

The United Arab Emirates, or simply the Emirates, is a country in Western Asia. It is located at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula and shares borders with Oman and Saudi Arabia, while having maritime borders in the Persian Gulf with Qatar and Iran. Abu Dhabi is the nation's capital, while Dubai, the most populous city, is an international hub.

The Burj Khalifa, known as the Burj Dubai prior to its inauguration in 2010, is a skyscraper in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It is known for being the world’s tallest building. With a total height of 829.8 m and a roof height of 828 m (2,717 ft), the Burj Khalifa has been the tallest structure and building in the world since its topping out in 2009, supplanting Taipei 101, the previous holder of that status.

Fireworks are a class of low explosive pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays, combining a large number of devices in an outdoor setting. Such displays are the focal point of many cultural and religious celebrations.
A New Year's Eve celebration stampede in Shanghai kills at least 36 people and injures 49 others.

On 31 December 2014, a deadly crush occurred in Shanghai, near Chen Yi Square on the Bund, where around 300,000 people had gathered for the new year celebration. 36 people were killed and another 49 were injured, 13 seriously.

Shanghai is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. With a population of 24.89 million as of 2021, Shanghai is the most populous urban area in China with 39,300,000 inhabitants living in the Shanghai metropolitan area, the second most populous city proper in the world and the only city in East Asia with a GDP greater than its corresponding capital. Shanghai ranks second among the administrative divisions of Mainland China in human development index. As of 2018, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (nominal) of nearly 9.1 trillion RMB, exceeding that of Mexico with GDP of $1.22 trillion, the 15th largest in the world. Shanghai is one of the world's major centers for finance, business and economics, research, education, science and technology, manufacturing, tourism, culture, dining, art, fashion, sports, and transportation, and the Port of Shanghai is the world's busiest container port. In 2019, the Shanghai Pudong International Airport was one of the world's 10 busiest airports by passenger traffic, and one of the two international airports serving the Shanghai metropolitan area, the other one being the Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport.
Samoa and Tokelau skip the day of December 30, 2011 as they jump to the other side of the International Date Line, changing their time zones.

Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ; two smaller, inhabited islands ; and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands. Samoa is located 64 km (40 mi) west of American Samoa, 889 km (552 mi) northeast of Tonga, 1,152 km (716 mi) northeast of Fiji, 483 km (300 mi) east of Wallis and Futuna, 1,151 km (715 mi) southeast of Tuvalu, 519 km (322 mi) south of Tokelau, 4,190 km (2,600 mi) southwest of Hawaii, and 610 km (380 mi) northwest of Niue. The capital city is Apia. The Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan cultural identity.

Tokelau is a dependent territory of New Zealand in the southern Pacific Ocean. It consists of three tropical coral atolls: Atafu, Nukunonu, and Fakaofo. They have a combined land area of 10 km2 (4 sq mi). The capital rotates yearly among the three atolls. In addition to these three, Swains Island, which forms part of the same archipelago, is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute; it is currently administered by the United States as part of American Samoa. Tokelau lies north of the Samoan Islands, east of Tuvalu, south of the Phoenix Islands, southwest of the more distant Line Islands, and northwest of the Cook Islands.

The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South Pole and North Pole and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Crossing the date line eastbound decreases the date by one day, while crossing the date line westbound increases the date.
NASA succeeds in putting the first of two Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory satellites in orbit around the Moon.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.

The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) was an American lunar science mission in NASA's Discovery Program which used high-quality gravitational field mapping of the Moon to determine its interior structure. The two small spacecraft GRAIL A (Ebb) and GRAIL B (Flow) were launched on 10 September 2011 aboard a single launch vehicle: the most-powerful configuration of a Delta II, the 7920H-10. GRAIL A separated from the rocket about nine minutes after launch, GRAIL B followed about eight minutes later. They arrived at their orbits around the Moon 25 hours apart. The first probe entered orbit on 31 December 2011 and the second followed on 1 January 2012. The two spacecraft impacted the Lunar surface on December 17, 2012.

A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz.

The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth. The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at 0.1654 g, with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density.
Tornadoes touch down in midwestern and southern United States, including Washington County, Arkansas; Greater St. Louis, Sunset Hills, Missouri, Illinois, and Oklahoma, with a few tornadoes in the early hours. A total of 36 tornadoes touched down, resulting in the deaths of nine people and $113 million in damages.

The 2010 New Year's Eve tornado outbreak was a three-day-long tornado outbreak that impacted the central and lower Mississippi Valley from December 30, 2010 to January 1, 2011. Associated with a low pressure system and a strong cold front, 37 tornadoes tracked across five states over the length of the severe event, killing nine and injuring several others. Activity was centered in the states of Missouri and later Mississippi on December 31. Seven tornadoes were rated EF3 on the Enhanced Fujita Scale; these were the strongest during the outbreak. Non-tornadic winds were recorded to have reached as high as 80 mph (130 km/h) at eight locations on December 31, while hail as large as 2.75 in (7.0 cm) was documented north-northeast of Mansfield, Missouri. Overall, damage from the outbreak totaled US$123.3 million, most of which was related to tornadoes.

The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It was officially named the North Central Region by the Census Bureau until 1984. It is between the Northeastern United States and the Western United States, with Canada to the north and the Southern United States to the south.

The Southern United States is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the Western United States, with the Midwestern and Northeastern United States to its north and the Gulf of Mexico and Mexico to its south.

Washington County is a regional economic, educational, and cultural hub in the Northwest Arkansas region. Created as Arkansas's 17th county on November 30, 1848, Washington County has 13 incorporated municipalities, including Fayetteville, the county seat, and Springdale. The county is also the site of small towns, bedroom communities, and unincorporated places. The county is named for George Washington, the first President of the United States.

Greater St. Louis is a bi-state metropolitan area that completely surrounds and includes the independent city of St. Louis, the principal city. It includes parts of both Missouri and Illinois. The city core is on the Mississippi Riverfront on the border with Illinois in the geographic center of the metro area. The Mississippi River bisects the metro area geographically between Illinois and Missouri; however, the Missouri portion is much more populous. St. Louis is the focus of the largest metro area in Missouri and the Illinois portion known as Metro East is the second largest metropolitan area in that state. St. Louis County is independent of the City of St. Louis and their two populations are generally tabulated separately.

Sunset Hills is a city in south St. Louis County, Missouri, United States. The population was 8,496 at the 2010 census.

Illinois is a state in the Midwestern United States. It’s largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockford, as well Springfield it’s capital. Of the fifty U.S. states, Illinois has the fifth-largest gross domestic product (GDP), the sixth-largest population, and the 25th-largest land area.

Oklahoma is a state in the South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the 20th-most extensive and the 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans, and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City.
Both a blue moon and a lunar eclipse occur.

A blue moon is an additional full moon that appears in a subdivision of a year: the third of four full moons in a season.

A partial lunar eclipse was visible on 31 December 2009. It was the last and largest of four minor lunar eclipses in 2009. This lunar eclipse is also notable, because it occurred during a blue moon. The next eclipse on New Year's Eve and blue moon will occur on 31 December 2028.
The official opening of Taipei 101, the tallest skyscraper at that time in the world, standing at a height of 509 metres (1,670 ft).

Taipei 101, formerly known as the Taipei World Financial Center, is a supertall skyscraper in Taipei, Taiwan. This building was officially classified as the world's tallest from its opening in 2004 until the 2009 completion of the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, UAE. Upon completion, it became the world's first skyscraper to exceed a height of half a kilometer. Taipei 101 is the tallest building of Taiwan.

The world's tallest human-made structure is the 828-metre-tall (2,717 ft) Burj Khalifa in Dubai. The building gained the official title of "tallest building in the world" and the tallest self-supported structure at its opening on January 9, 2010. Burj Khalifa was developed by Emaar properties, designed by Skidmore, Owings and Merrill and built by BESIX, Samsung Construction and Arabtec. The second-tallest self-supporting structure and the tallest tower in the world is the Tokyo Skytree. The tallest guyed structure is the KVLY-TV mast at 1987 feet.

A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least 100 metres (330 ft) or 150 metres (490 ft) in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-rise buildings. Historically, the term first referred to buildings with between 10 and 20 stories when these types of buildings began to be constructed in the 1880s. Skyscrapers may host offices, hotels, residential spaces, and retail spaces.
The last day of the 20th Century and 2nd Millennium.

The 20th (twentieth) century began on January 1, 1901 (MCMI), and ended on December 31, 2000 (MM). The 20th century was dominated by significant events that defined the modern era: Spanish flu pandemic, World War I and World War II, nuclear weapons, nuclear power and space exploration, nationalism and decolonization, technological advances, and the Cold War and post-Cold War conflicts. These reshaped the political and social structure of the globe.

The second millennium of the Anno Domini or Common Era was a millennium spanning the years 1001 to 2000.
Russian prime minister Vladimir Putin became acting president upon President Boris Yeltsin's unexpected resignation.

Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has held office as president of Russia since 2012, having previously done so between 2000 and 2008. He was the Prime Minister of Russia from 1999 to 2000 and again from 2008 to 2012, thus having served continuously as either president or prime minister from 1999 onwards.
That of acting president of the Russian Federation is a temporary post provided by the Constitution of Russia. The acting president is a person who fulfills the duties of the president of the Russian Federation when cases of incapacity and vacancy occur. This post is held by the prime minister of Russia.

Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the first president of the Russian Federation from 1991 to 1999. He was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1961 to 1990. He later stood as a political independent, during which time he was viewed as being ideologically aligned with liberalism and Russian nationalism.
The first President of Russia, Boris Yeltsin, resigns from office, leaving Prime Minister Vladimir Putin as the acting President and successor.

The president of the Russian Federation is the supreme head of state of the Russian Federation. The president is the head of the executive branch of the federal government of Russia as well as the commander-in-chief of the Russian Armed Forces. It is the highest office in Russia.

Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the first president of the Russian Federation from 1991 to 1999. He was a member of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1961 to 1990. He later stood as a political independent, during which time he was viewed as being ideologically aligned with liberalism and Russian nationalism.

The chairman of the government of the Russian Federation, also informally known as the prime minister, is the nominal head of government of Russia. Although the post dates back to 1905, its current form was established on 12 December 1993 following the introduction of a new constitution.

Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has held office as president of Russia since 2012, having previously done so between 2000 and 2008. He was the Prime Minister of Russia from 1999 to 2000 and again from 2008 to 2012, thus having served continuously as either president or prime minister from 1999 onwards.
That of acting president of the Russian Federation is a temporary post provided by the Constitution of Russia. The acting president is a person who fulfills the duties of the president of the Russian Federation when cases of incapacity and vacancy occur. This post is held by the prime minister of Russia.
The U.S. government hands control of the Panama Canal (as well all the adjacent land to the canal known as the Panama Canal Zone) to Panama. This act complied with the signing of the 1977 Torrijos–Carter Treaties.

The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. One of the largest and most difficult engineering projects ever undertaken, the Panama Canal shortcut greatly reduces the time for ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, enabling them to avoid the lengthy, hazardous Cape Horn route around the southernmost tip of South America via the Drake Passage or Strait of Magellan and the even less popular route through the Arctic Archipelago and the Bering Strait.

The Panama Canal Zone, also simply known as the Canal Zone, was an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the Isthmus of Panama, that existed from 1903 to 1979. It was located within the territory of Panama, consisting of the Panama Canal and an area generally extending five miles (8 km) on each side of the centerline, but excluding Panama City and Colón. Its capital was Balboa.

Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Its capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's 4 million people.

The Torrijos–Carter Treaties are two treaties signed by the United States and Panama in Washington, D.C. on September 7, 1977, which superseded the Hay–Bunau-Varilla Treaty of 1903. The treaties guaranteed that Panama would gain control of the Panama Canal after 1999, ending the control of the canal that the U.S. had exercised since 1903. The treaties are named after the two signatories, U.S. president Jimmy Carter and the Commander of Panama's National Guard, General Omar Torrijos.
Indian Airlines Flight 814 hijacking ends after seven days with the release of 190 survivors at Kandahar Airport, Afghanistan.

Indian Airlines Flight 814, commonly known as IC 814, was an Indian Airlines Airbus A300 en route from Tribhuvan International Airport in Kathmandu, Nepal, to Indira Gandhi International Airport in Delhi, India, on Friday, 24 December 1999, when it was hijacked and flown to several locations before landing in Kandahar, Afghanistan.

Ahmad Shah Baba International Airport, also referred to as Kandahar International Airport and by some military officials as Kandahar Airfield, KAF), is located about 9 nautical miles south-east of the city Kandahar in Afghanistan. It serves as the nation's second main international airport and as one of the largest main operating bases, capable of housing up to 250 aircraft of different sizes. The current head of the airport is Maulvi Fathullah Mansour.

Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east. Occupying 652,864 square kilometers (252,072 sq mi) of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains in the north and the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. As of 2021, its population is 40.2 million, composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and serves as its capital.
The European Exchange Rate Mechanism froze the exchange rates of the legacy currencies in the eurozone, establishing the value of the euro.

The European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM II) is a system introduced by the European Economic Community on 1 January 1999 alongside the introduction of a single currency, the euro as part of the European Monetary System (EMS), to reduce exchange rate variability and achieve monetary stability in Europe.

In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of the euro.

The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies.

The euro is the official currency of 19 out of the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens as of 2019. The euro is divided into 100 cents.
The European Exchange Rate Mechanism freezes the values of the legacy currencies in the Eurozone, and establishes the value of the euro currency.

The European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM II) is a system introduced by the European Economic Community on 1 January 1999 alongside the introduction of a single currency, the euro as part of the European Monetary System (EMS), to reduce exchange rate variability and achieve monetary stability in Europe.

The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies.

The euro is the official currency of 19 out of the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens as of 2019. The euro is divided into 100 cents.
This date is skipped altogether in Kiribati as the Phoenix Islands and Line Islands change time zones from UTC−11:00 to UTC+13:00 and UTC−10:00 to UTC+14:00, respectively.

Kiribati, officially the Republic of Kiribati, is an island country in Oceania in the central Pacific Ocean. The permanent population is over 119,000 (2020), more than half of whom live on Tarawa atoll. The state comprises 32 atolls and one remote raised coral island, Banaba. There is a total land area of 811 square kilometres dispersed over 3.5 million km2 (1.4 million sq mi) of ocean.
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Republic of Kiribati. Their combined land area is 28 square kilometres (11 sq mi). The only island of any commercial importance is Canton Island. The other islands are Enderbury, Rawaki, Manra, Birnie, McKean, Nikumaroro, and Orona.

The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands are a chain of 11 atolls and coral islands in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands. The island chain stretches northwest to southeast across 2,350 km (1,460 mi), making it one of the longest island chains in the world. It lies at the geographic center of the Pacific Ocean, near Starbuck Island. One of the atolls in the group, Kiritimati, has the largest land area of any atoll in the world. Of the 11 atolls, all of which were formed by volcanic activity, only the Kiritimati and Tabuaeran atolls and Teraina island have a permanent population. Eight of the atolls are parts of Kiribati. The remaining three—Jarvis Island, Kingman Reef, and Palmyra Atoll—are territories of the United States grouped with the United States Minor Outlying Islands.

UTC−11:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −11:00. This time is used in Niue, American Samoa, Swains Island, and parts of the United States Minor Outlying Islands. This is the latest inhabited time zone, meaning this is the last inhabited time zone to celebrate the New Year, as the world's latest time zone (UTC-12:00) is completely uninhabited.
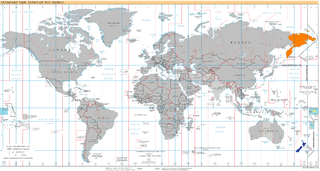
UTC+13:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +13:00. Because it does not contain any land in the Northern Hemisphere, this time zone is exclusive to the Southern Hemisphere.
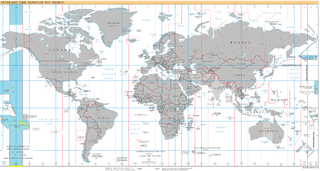
UTC−10:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −10:00. This time is used in Hawaii, Alaska, French Polynesia, and the Cook Islands.
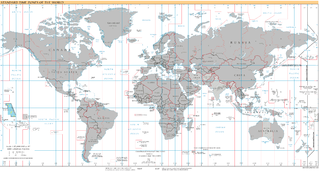
UTC+14:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +14:00. This is the earliest time zone on Earth, meaning that areas in this zone are the first to see a new day, and therefore the first to celebrate a New Year. It is also referred to as the "latest time zone" on Earth, as clocks in it always show the 'latest' time of all time zones.
The First Chechen War: The Russian Ground Forces begin a New Year's storming of Grozny.

The First Chechen War, also known as the First Chechen Campaign, or the First Russian-Chechen war, was a war of independence which the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria waged against the Russian Federation from December 1994 to August 1996. The first war was preceded by the Russian Intervention in Ichkeria, in which Russia tried to covertly overthrow the Ichkerian government. After the initial campaign of 1994–1995, culminating in the devastating Battle of Grozny, Russian federal forces attempted to seize control of the mountainous area of Chechnya, but they faced heavy resistance from Chechen guerrillas and raids on the flatlands. Despite Russia's overwhelming advantages in firepower, manpower, weaponry, artillery, combat vehicles, airstrikes and air support, the resulting widespread demoralization of federal forces and the almost universal opposition to the conflict by the Russian public led Boris Yeltsin's government to declare a ceasefire with the Chechens in 1996, and finally, it signed a peace treaty in 1997.

The Russian Ground Forces, also known as the Russian Army, are the land forces of the Russian Armed Forces.

The First Battle of Grozny was the Russian Army's invasion and subsequent conquest of the Chechen capital, Grozny, during the early months of the First Chechen War. The attack lasted from December 1994 to March 1995, which resulted in the military occupation of the city by the Russian Army and rallied most of the Chechen nation around the government of Dzhokhar Dudayev.

Grozny, also spelled Groznyy, is the capital city of Chechnya, Russia.
Brandon Teena, an American trans man, was raped and murdered in Humboldt, Nebraska; his death led to increased lobbying for hate crime laws in the United States.

Brandon Teena was an American trans man who was raped and later, along with Phillip DeVine and Lisa Lambert, murdered in Humboldt, Nebraska by John Lotter and Tom Nissen. His life and death were the subject of the films The Brandon Teena Story and Boys Don't Cry.

A trans man is a man who was assigned female at birth. The label of transgender man is not always interchangeable with that of transsexual man, although the two labels are often used in this way. Transgender is an umbrella term that includes different types of gender variant people. Trans men have a male gender identity, and many trans men choose to undergo surgical or hormonal transition, or both, to alter their appearance in a way that aligns with their gender identity or alleviates gender dysphoria.

Humboldt is a city in Richardson County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 877 at the 2010 census.
Hate crime laws in the United States are state and federal laws intended to protect against hate crimes. Although state laws vary, current statutes permit federal prosecution of hate crimes committed on the basis of a person's characteristics of race, religion, ethnicity, nationality, gender, sexual orientation, and/or gender identity. The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ), Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and campus police departments are required to collect and publish hate crime statistics.
Czechoslovakia is peacefully dissolved in what is dubbed by media as the Velvet Divorce, resulting in the creation of the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic.

Czechoslovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland became part of Germany, while the country lost further territories to Hungary and Poland. Between 1939 and 1945 the state ceased to exist, as Slovakia proclaimed its independence and the remaining territories in the east became part of Hungary, while in the remainder of the Czech Lands the German Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia was proclaimed. In 1939, after the outbreak of World War II, former Czechoslovak President Edvard Beneš formed a government-in-exile and sought recognition from the Allies.
The dissolution of Czechoslovakia took effect on December 31, 1992, and was the self-determined split of the federal republic of Czechoslovakia into the independent countries of the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Both mirrored the Czech Socialist Republic and the Slovak Socialist Republic, which had been created in 1969 as the constituent states of the Czechoslovak Federal Republic.

The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of 78,871 square kilometers (30,452 sq mi) with a mostly temperate continental and oceanic climate. The capital and largest city is Prague; other major cities and urban areas include Brno, Ostrava, Plzeň and Liberec.

Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice.
All official Soviet Union institutions have ceased operations by this date, five days after the Soviet Union is officially dissolved.

The Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad, Kiev, Minsk, Tashkent, Alma-Ata, and Novosibirsk. It was the largest country in the world, covering over 22,402,200 square kilometres (8,649,500 sq mi) and spanning eleven time zones.

The dissolution of the Soviet Union was the process of internal disintegration within the Soviet Union (USSR) which resulted in the end of the country's and its federal government's existence as a sovereign state, thereby resulting in its constituent republics gaining full sovereignty on 26 December 1991. It brought an end to General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev's effort to reform the Soviet political and economic system in an attempt to stop a period of political stalemate and economic backslide. The Soviet Union had experienced internal stagnation and ethnic separatism. Although highly centralized until its final years, the country was made up of fifteen top-level republics that served as homelands for different ethnicities. By late 1991, amid a catastrophic political crisis, with several republics already departing the Union and the waning of centralized power, the leaders of three of its founding members declared that the Soviet Union no longer existed. Eight more republics joined their declaration shortly thereafter. Gorbachev resigned in December 1991 and what was left of the Soviet parliament voted to end itself.
Three disgruntled employees set fire to the Dupont Plaza Hotel in San Juan, Puerto Rico, killing more than 90 people and injuring 140 others (rescue efforts depicted), making it the second-deadliest hotel fire in United States history.

The Dupont Plaza Hotel arson was a fire that occurred on New Year's Eve, December 31, 1986, at the Hotel Dupont Plaza in San Juan, the capital of the U.S. territory of Puerto Rico.

San Juan is the capital city and most populous municipality in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States. As of the 2020 census, it is the 57th-largest city under the jurisdiction of the United States, with a population of 342,259. San Juan was founded by Spanish colonists in 1521, who called it Ciudad de Puerto Rico.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has documented several dozen hotel fires in the United States since the 1930s that have killed more than ten people each, deeming these incidents to be fires of historical note. The Winecoff Hotel fire of December 7, 1946, in Atlanta, Georgia, which claimed 119 lives, is the deadliest hotel fire disaster in the history of the United States.
The AT&T Bell System is broken up by the United States Government.

AT&T Corporation, originally the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is the subsidiary of AT&T Inc. that provides voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional services to businesses, consumers, and government agencies.

The Bell System was a system of telecommunication companies, led by the Bell Telephone Company and later by the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), that dominated the telephone services industry in North America for over one hundred years from its creation in 1877 until its antitrust breakup in 1983. The system of companies was often colloquially called Ma Bell, as it held a vertical monopoly over telecommunication products and services in most areas of the United States and Canada. At the time of the breakup of the Bell System in the early 1980s, it had assets of $150 billion and employed over one million people.

The federal government of the United States is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a federal district, five major self-governing territories and several island possessions. The federal government, sometimes simply referred to as Washington, is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the president and the federal courts, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of Congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court.
Benjamin Ward is appointed New York City Police Department's first ever African American police commissioner.
Benjamin Ward was the first African American New York City Police Commissioner.

The New York City Police Department (NYPD), officially the City of New York Police Department, established on May 23, 1845, is the primary municipal law enforcement agency within the City of New York, and the largest and one of the oldest in the United States.

African Americans are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of enslaved Africans who are from the United States. While some Black immigrants or their children may also come to identify as African-American, the majority of first generation immigrants do not, preferring to identify with their nation of origin.

The New York City Police Commissioner is the head of the New York City Police Department and presiding member of the Board of Commissioners. The commissioner is appointed by and serves at the pleasure of the mayor. The commissioner is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the department as well as the appointment of deputies including the Chief of Department and subordinate officers. Commissioners are civilian administrators, and they and their subordinate deputies are civilians under an oath of office, not sworn members of the force. This is a separate position from the Chief of Department, who is the senior sworn uniformed member of the force. The First Deputy Commissioner is the Commissioner and department's second-in-command. The office of the Police Commissioner is located at the NYPD Headquarters, One Police Plaza. Both the commissioner and first deputy commissioner outrank all uniformed officers, including the chief of department.
In Nigeria, a coup d'état led by Major General Muhammadu Buhari ends the Second Nigerian Republic.

Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea to the south in the Atlantic Ocean. It covers an area of 923,769 square kilometres (356,669 sq mi), and with a population of over 225 million, it is the most populous country in Africa, and the world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in the north, Chad in the northeast, Cameroon in the east, and Benin in the west. Nigeria is a federal republic comprising 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory, where the capital, Abuja, is located. The largest city in Nigeria is Lagos, one of the largest metropolitan areas in the world and the second-largest in Africa.

The Nigerian military coup of 1983 took place on 31 December that year. It was coordinated by key officers of the Nigerian military and led to the ousting of the democratically elected government of President Shehu Shagari and the installation of Major General Muhammadu Buhari as head of state.

Muhammadu Buhari (listen) is a Nigerian politician, who has served as the president of Nigeria since 2015.

The Second Nigerian Republic was a brief formation of the Nigerian state which succeeded the military governments formed after the overthrow of the first republic.
A coup d'état in Ghana removes President Hilla Limann's PNP government and replaces it with the Provisional National Defence Council led by Flight lieutenant Jerry Rawlings.

A coup d'état, also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, military, or a dictator. Many scholars consider a coup successful when the usurpers seize and hold power for at least seven days.

Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Togo in the east. Ghana covers an area of 238,535 km2 (92,099 sq mi), spanning diverse biomes that range from coastal savannas to tropical rainforests. With nearly 31 million inhabitants, Ghana is the second-most populous country in West Africa, after Nigeria. The capital and largest city is Accra; other major cities are Kumasi, Tamale, and Sekondi-Takoradi.

This is a list of the heads of state of Ghana, from the independence of Ghana in 1957 to the present day.

Hilla Limann, was a Ghanaian diplomat and politician who served the President of Ghana from 24 September 1979 to 31 December 1981. He served as a diplomat in Lome, Togo and Geneva, Switzerland.
The People's National Party (PNP) was the ruling party in Ghana during the Third Republic (1979-1981).

This is a listing of the ministers who served in Limann's People's National Party government during the Third Republic of Ghana. The Third Republic was inaugurated on 24 September 1979. It ended with the coup on 31 December 1981, which brought the Provisional National Defence Council of Jerry Rawlings to power.

The Provisional National Defence Council (PNDC) was the name of the Ghanaian government after the People's National Party's elected government was overthrown by Jerry Rawlings, the former head of the Armed Forces Revolutionary Council, in a coup d'état on 31 December 1981. He remained in power until 7 January 1993. In a statement, Rawlings said that a "holy war" was necessary due to the PNP's failure to provide effective leadership and the collapse of the national economy and state services.
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in air forces that use the Royal Air Force (RAF) system of ranks, especially in Commonwealth countries. It has a NATO rank code of OF-2. Flight lieutenant is abbreviated as Flt Lt in the Indian Air Force (IAF) and RAF, and as FLTLT in the Pakistan Air Force (PAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) and Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) and has sometimes also been abbreviated as F/L in many services; it has never been correctly abbreviated as "lieutenant". A flight lieutenant ranks above flying officer and below a squadron leader and is sometimes used as an English language translation of a similar rank in non-English-speaking countries.

Jerry John Rawlings was a Ghanaian military officer and politician who led the country for a brief period in 1979, and then from 1981 to 2001. He led a military junta until 1992, and then served two terms as the democratically elected President of Ghana.
Puerto Rican baseball player Roberto Clemente died in a plane crash en route to deliver aid to victims of that year's Nicaragua earthquake.

Roberto Enrique Clemente Walker was a Puerto Rican professional baseball right fielder who played 18 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Pittsburgh Pirates. After his early death, he was posthumously inducted into the National Baseball Hall of Fame in 1973, becoming both the first Caribbean and the first Latin-American player to be enshrined. Because he died at a young age and had such a historic career, the Hall of Fame changed its rules of eligibility. As an alternative to a player having to be retired for five years before eligibility, a player who has been deceased for at least six months is eligible for entry.

The 1972 Puerto Rico DC-7 crash was an aviation accident that occurred on December 31, 1972, in Carolina, Puerto Rico. As a result of inadequate maintenance, the aircraft's No. 2 engine failed after takeoff. After initiating a turn to return to the airport, the aircraft eventually descended into, or attempted to ditch into, the ocean a mile offshore. All five people on board died, including baseball legend Roberto Clemente. The crash site was listed on the US National Register of Historic Places in 2022.
The 1972 Nicaragua earthquake occurred at 12:29:44 a.m. local time on December 23 near Managua, the capital of Nicaragua. It had a moment magnitude of 6.3 and a maximum MSK intensity of IX (Destructive). The epicenter was 28 km (17 mi) northeast of the city centre and a depth of about 10 km (6.2 mi). The earthquake caused widespread casualties among Managua's residents: 4,000–11,000 were killed, 20,000 were injured and over 300,000 were left homeless.
The first flight of the Tupolev Tu-144, the first civilian supersonic transport in the world.

The Tupolev Tu-144 is a Soviet supersonic passenger airliner designed by Tupolev in operation from 1968 to 1999.
MacRobertson Miller Airlines Flight 1750 crashes near Port Hedland, Western Australia, killing all 26 people on board.

On 31 December 1968 a Vickers Viscount aircraft departed from Perth, Western Australia for a flight of 724 nautical miles (1 341 km) to Port Hedland. The aircraft crashed 28 nautical miles (52 km) short of its destination with the loss of all twenty-six people on board. More than half of the right wing, from outboard of the inner engine to the wingtip, including the outer engine and its propeller, broke away from the rest of the aircraft in flight and struck the ground a significant distance from the main wreckage. Investigation by the Australian Department of Civil Aviation and British Aircraft Corporation concluded that a mysterious action during maintenance led to extensive fatigue cracking in the right wing spar. This accident remains the third worst in Australia's civil aviation history.

Port Hedland is the second largest town in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, with an urban population of 14,320 at June 2018 including the satellite town of South Hedland, 18 kilometres (11 mi) away. It is also the site of the highest tonnage port in Australia.
Central African military officers led by Jean-Bédel Bokassa began a coup d'état against the government of President David Dacko.

Jean-Bédel Bokassa, also known as Bokassa I, was a Central African political and military leader who served as the second president of the Central African Republic (CAR) and as the emperor of its successor state, the Central African Empire (CAE), from the Saint-Sylvestre coup d'état on 1 January 1966 until his overthrow in a subsequent coup in 1979.
The Saint-Sylvestre coup d'état was a coup d'état staged by Jean-Bédel Bokassa, commander-in-chief of the Central African Republic (CAR) army, and his officers against the government of President David Dacko on 31 December 1965 and 1 January 1966. Dacko, Bokassa's cousin, took over the country in 1960, and Bokassa, an officer in the French army, joined the CAR army in 1962. By 1965, the country was in turmoil—plagued by corruption and slow economic growth, while its borders were breached by rebels from neighboring countries. Dacko obtained financial aid from the People's Republic of China, but despite this support, the country's problems persisted. Bokassa made plans to take over the government; Dacko was made aware of this, and attempted to counter by forming the gendarmerie headed by Jean Izamo, who quickly became Dacko's closest adviser.

David Dacko was a Central African politician who served as the first president of the Central African Republic from 14 August 1960 to 1 January 1966, and 3rd President from 21 September 1979 to 1 September 1981. After his second removal from power in a coup d'état led by General André Kolingba, he pursued an active career as an opposition politician and presidential candidate with many loyal supporters; Dacko was an important political figure in the country for over 50 years.
Jean-Bédel Bokassa, leader of the Central African Republic army, and his military officers begin a coup d'état against the government of President David Dacko.

Jean-Bédel Bokassa, also known as Bokassa I, was a Central African political and military leader who served as the second president of the Central African Republic (CAR) and as the emperor of its successor state, the Central African Empire (CAE), from the Saint-Sylvestre coup d'état on 1 January 1966 until his overthrow in a subsequent coup in 1979.

The Central African Republic is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to the north, Sudan to the northeast, South Sudan to the southeast, the DR Congo to the south, the Republic of the Congo to the southwest, and Cameroon to the west.

The Saint-Sylvestre coup d'état was a coup d'état staged by Jean-Bédel Bokassa, commander-in-chief of the Central African Republic (CAR) army, and his officers against the government of President David Dacko on 31 December 1965 and 1 January 1966. Dacko, Bokassa's cousin, took over the country in 1960, and Bokassa, an officer in the French army, joined the CAR army in 1962. By 1965, the country was in turmoil—plagued by corruption and slow economic growth, while its borders were breached by rebels from neighboring countries. Dacko obtained financial aid from the People's Republic of China, but despite this support, the country's problems persisted. Bokassa made plans to take over the government; Dacko was made aware of this, and attempted to counter by forming the gendarmerie headed by Jean Izamo, who quickly became Dacko's closest adviser.

This article lists the heads of state of the Central African Republic. There have been seven heads of state of the Central African Republic and the Central African Empire since independence was obtained from the French on 13 August 1960. This list includes not only those persons who were sworn into office as President of the Central African Republic but also those who served as de facto heads of state.

David Dacko was a Central African politician who served as the first president of the Central African Republic from 14 August 1960 to 1 January 1966, and 3rd President from 21 September 1979 to 1 September 1981. After his second removal from power in a coup d'état led by General André Kolingba, he pursued an active career as an opposition politician and presidential candidate with many loyal supporters; Dacko was an important political figure in the country for over 50 years.
The Central African Federation officially collapses, subsequently becoming Zambia, Malawi and Rhodesia.

The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, also known as the Central African Federation or CAF, was a colonial federation that consisted of three southern African territories: the self-governing British colony of Southern Rhodesia and the British protectorates of Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland. It existed between 1953 and 1963.

Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the northeast, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka, located in the south-central part of Zambia. The nation's population of around 19.5 million is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the north, the core economic hubs of the country.

Malawi, officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeast, and Mozambique to the east, south and southwest. Malawi spans over 118,484 km2 (45,747 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 19,431,566. Malawi's capital is Lilongwe. Its second-largest is Blantyre, its third-largest is Mzuzu and its fourth-largest is its former capital, Zomba. The name Malawi comes from the Maravi, an old name for the Chewa people who inhabit the area. The country is nicknamed "The Warm Heart of Africa" because of the friendliness of its people.

Rhodesia, officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was a state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the de facto successor state to the British colony of Southern Rhodesia, which had been self-governing since achieving responsible government in 1923. A landlocked nation, Rhodesia was bordered by South Africa to the south, Bechuanaland to the southwest, Zambia to the northwest, and Mozambique to the east. From 1965 to 1979, Rhodesia was one of two independent states on the African continent governed by a white minority of European descent and culture, the other being South Africa.
RTÉ, Ireland's state broadcaster, launches its first national television service.

Raidió Teilifís Éireann (RTÉ) is the national broadcaster of Ireland headquartered in Dublin. It both produces and broadcasts programmes on television, radio and online. The radio service began on 1 January 1926, while regular television broadcasts began on 31 December 1961, making it one of the oldest continuously operating public service broadcasters in the world. RTÉ also publishes a weekly listings and lifestyle magazine, the RTÉ Guide.
The Romanian Television network begins its first broadcast in Bucharest.

Televiziunea Română, more commonly referred to as TVR [teveˈre], is the short name for Societatea Română de Televiziune, the Romanian public television. It operates six channels: TVR1, TVR2, TVR3, TVR Info, TVR Cultural, TVRi, and TVR Moldova along with six regional studios in Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, Iași, Timișoara, Craiova and Târgu Mureș.

Bucharest is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than 60 km (37.3 mi) north of the Danube River and the Bulgarian border.
General Motors becomes the first U.S. corporation to make over US$1 billion in a year.

The General Motors Company (GM) is an American multinational automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and was the largest in the world for 77 years before losing the top spot to Toyota in 2008.
Cold War: The Marshall Plan expires after distributing more than US$13.3 billion in foreign aid to rebuild Western Europe.

The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term cold war is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race.

The Marshall Plan was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred over $13 billion in economic recovery programs to Western European economies after the end of World War II. Replacing an earlier proposal for a Morgenthau Plan, it operated for four years beginning on April 3, 1948. The goals of the United States were to rebuild war-torn regions, remove trade barriers, modernize industry, improve European prosperity and prevent the spread of communism. The Marshall Plan proposed the reduction of interstate barriers and the economic integration of the European Continent while also encouraging an increase in productivity as well as the adoption of modern business procedures.

Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
President Harry S. Truman officially proclaims the end of hostilities in World War II.

Harry S. Truman was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin Roosevelt and as a United States senator from Missouri from 1935 to January 1945. Assuming the presidency after Roosevelt's death, Truman implemented the Marshall Plan to rebuild the economy of Western Europe and established both the Truman Doctrine and NATO to contain the expansion of Soviet communism. He proposed numerous liberal domestic reforms, but few were enacted by the Conservative Coalition which dominated the Congress.

A ceasefire, also spelled cease fire, is a temporary stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions. Ceasefires may be between state actors or involve non-state actors.
World War II: Operation Nordwind, the last major Wehrmacht offensive on the Western Front, begins.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

Operation Northwind was the last major German offensive of World War II on the Western Front. Northwind was launched to support the German Ardennes offensive campaign in the Battle of the Bulge, which by December of 1944 had decisively turned against the German forces. It began on 31 December 1944 in Rhineland-Palatinate, Alsace and Lorraine in southwestern Germany and northeastern France, and ended on 25 January 1945. The German offensive was an operational failure, with its main objectives not achieved.

The Wehrmacht was the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the Heer (army), the Kriegsmarine (navy) and the Luftwaffe. The designation "Wehrmacht" replaced the previously used term Reichswehr and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted.

The Western Front was a military theatre of World War II encompassing Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Germany. World War II military engagements in Southern Europe and elsewhere are generally considered as separate theatres. The Western Front was marked by two phases of large-scale combat operations. The first phase saw the capitulation of Luxembourg, Netherlands, Belgium, and France during May and June 1940 after their defeat in the Low Countries and the northern half of France, and continued into an air war between Germany and Britain that climaxed with the Battle of Britain. The second phase consisted of large-scale ground combat, which began in June 1944 with the Allied landings in Normandy and continued until the defeat of Germany in May 1945.
USS Essex, first aircraft carrier of a 24-ship class, is commissioned.

USS Essex (CV/CVA/CVS-9) was an aircraft carrier and the lead ship of the 24-ship Essex class built for the United States Navy during World War II. She was the fourth US Navy ship to bear the name. Commissioned in December 1942, Essex participated in several campaigns in the Pacific Theater of Operations, earning the Presidential Unit Citation and 13 battle stars. Decommissioned shortly after the end of the war, she was modernized and recommissioned in the early 1950s as an attack carrier (CVA), eventually becoming an antisubmarine aircraft carrier (CVS). In her second career, she served mainly in the Atlantic, playing a role in the Cuban Missile Crisis. She also participated in the Korean War, earning four battle stars and the Navy Unit Commendation. She was the primary recovery carrier for the Apollo 7 space mission.
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition.
World War II: The Royal Navy defeats the Kriegsmarine at the Battle of the Barents Sea. This leads to the resignation of Grand Admiral Erich Raeder a month later

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service.
The Kriegsmarine was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war Reichsmarine (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The Kriegsmarine was one of three official branches, along with the Heer and the Luftwaffe, of the Wehrmacht, the German armed forces from 1935 to 1945.

The Battle of the Barents Sea was a World War II naval engagement on 31 December 1942 between warships of the German Navy (Kriegsmarine) and British ships escorting convoy JW 51B to Kola Inlet in the USSR. The action took place in the Barents Sea north of North Cape, Norway. The German raiders' failure to inflict significant losses on the convoy infuriated Hitler, who ordered that German naval strategy would henceforth concentrate on the U-boat fleet rather than surface ships.
Grand admiral is a historic naval rank, the highest rank in the several European navies that used it. It is best known for its use in Germany as Großadmiral. A comparable rank in modern navies is that of admiral of the fleet.

Erich Johann Albert Raeder was a German admiral who played a major role in the naval history of World War II. Raeder attained the highest possible naval rank, that of grand admiral, in 1939, becoming the first person to hold that rank since Henning von Holtzendorff in 1918. Raeder led the Kriegsmarine for the first half of the war; he resigned in January 1943 and was replaced by Karl Dönitz. At the Nuremberg Trials he was sentenced to life imprisonment but was released early owing to failing health.
The Manhattan Bridge, connecting Lower Manhattan to Downtown Brooklyn and considered to be the forerunner of modern suspension bridges, opened to traffic.

The Manhattan Bridge is a suspension bridge that crosses the East River in New York City, connecting Lower Manhattan at Canal Street with Downtown Brooklyn at the Flatbush Avenue Extension. The main span is 1,480 ft (451 m) long, with the suspension cables being 3,224 ft (983 m) long. The bridge's total length is 6,855 ft (2,089 m). It is one of four toll-free vehicular bridges connecting Manhattan Island to Long Island; the nearby Brooklyn Bridge is just slightly further downtown, while the Queensboro and Williamsburg bridges are to the north.

Lower Manhattan is the southernmost part of Manhattan, the central borough for business, culture, and government in New York City, which is the most populated city in the United States with over 8.8 million residents as of the 2020 census.

Downtown Brooklyn is the third largest central business district in New York City, United States, and is located in the northwestern section of the borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is known for its office and residential buildings, such as the Williamsburgh Savings Bank Tower and the MetroTech Center office complex.

A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck is hung below suspension cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridges, which lack vertical suspenders, have a long history in many mountainous parts of the world.
New York City held its first annual ball drop event in Times Square as part of New Year's Eve celebrations.

The Times Square Ball is a time ball located in New York City's Times Square. Located on the roof of One Times Square, the ball is a prominent part of a New Year's Eve celebration in Times Square commonly referred to as the ball drop, where the ball descends down a specially designed flagpole, beginning at 11:59:00 p.m. ET, and resting at midnight to signal the start of the new year. In recent years, the ball drop has been preceded by live entertainment, including performances by musicians.

Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent Duffy Square, Times Square is a bowtie-shaped space five blocks long between 42nd and 47th Streets.

In the Gregorian calendar, New Year's Eve, also known as Old Year's Day or Saint Sylvester's Day in many countries, is the evening or the entire day of the last day of the year, on 31 December. The last day of the year is commonly referred to as “New Year’s Eve”. In many countries, New Year's Eve is celebrated with dancing, eating, drinking, and watching or lighting fireworks. Some Christians attend a watchnight service. The celebrations generally go on past midnight into New Year's Day, 1 January.
The first New Year's Eve celebration is held in Times Square (then known as Longacre Square) in Manhattan.

In the Gregorian calendar, New Year's Eve, also known as Old Year's Day or Saint Sylvester's Day in many countries, is the evening or the entire day of the last day of the year, on 31 December. The last day of the year is commonly referred to as “New Year’s Eve”. In many countries, New Year's Eve is celebrated with dancing, eating, drinking, and watching or lighting fireworks. Some Christians attend a watchnight service. The celebrations generally go on past midnight into New Year's Day, 1 January.

Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent Duffy Square, Times Square is a bowtie-shaped space five blocks long between 42nd and 47th Streets.

Manhattan, known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state of New York. Located near the southern tip of New York State, Manhattan is based in the Eastern Time Zone and constitutes both the geographical and demographic center of the Northeast megalopolis and the urban core of the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass. Over 58 million people live within 250 miles of Manhattan, which serves as New York City’s economic and administrative center, cultural identifier, and the city’s historical birthplace. Manhattan has been described as the cultural, financial, media, and entertainment capital of the world, is considered a safe haven for global real estate investors, and hosts the United Nations headquarters. New York City is the headquarters of the global art market, centered in Manhattan.
Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar signs the Persian Constitution of 1906.

Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar, was the fifth shah of Qajar Iran, reigning from 1896 until his death in 1907. He is often credited with the creation of the Persian Constitution of 1906, which he approved of as one of his final actions as Shah.

The Persian Constitution of 1906, was the first constitution of the Sublime State of Persia, resulting from the Persian Constitutional Revolution and it was written by Hassan Pirnia, Hossein Pirnia, and Ismail Mumtaz, among others. It divides into five chapters with many articles that developed over several years. The Quran was the foundation of this constitution while the Belgian constitution served as a partial model for the document.
Thomas Edison demonstrates incandescent lighting to the public for the first time, in Menlo Park, New Jersey.

Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, which include the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and early versions of the electric light bulb, have had a widespread impact on the modern industrialized world. He was one of the first inventors to apply the principles of organized science and teamwork to the process of invention, working with many researchers and employees. He established the first industrial research laboratory.

An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections.
Menlo Park is an unincorporated community located within Edison Township in Middlesex County, New Jersey, United States.
Karl Benz, working in Mannheim, Germany, files for a patent on his first reliable two-stroke gas engine. He was granted the patent in 1879.

Carl Friedrich Benz, sometimes also Karl Friedrich Benz, was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent Motorcar from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automobile and first car put into series production. He received a patent for the motorcar in 1886.

Mannheim, officially the University City of Mannheim, is the second-largest city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg after the state capital of Stuttgart, and Germany's 21st-largest city, with a 2020 population of 309,119 inhabitants. The city is the cultural and economic centre of the Rhine-Neckar Metropolitan Region, Germany's seventh-largest metropolitan region with nearly 2.4 million inhabitants and over 900,000 employees.

The German Empire, also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a republic.

A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention. In most countries, patent rights fall under private law and the patent holder must sue someone infringing the patent in order to enforce their rights. In some industries patents are an essential form of competitive advantage; in others they are irrelevant.

A two-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust functions occurring at the same time.
The Battle of Stones River in Murfreesboro, Tennessee, began with an engagement in which both sides would suffer their highest casualty rates in the American Civil War.

The Battle of Stones River, also known as the Second Battle of Murfreesboro, was a battle fought from December 31, 1862, to January 2, 1863, in Middle Tennessee, as the culmination of the Stones River Campaign in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. Of the major battles of the war, Stones River had the highest percentage of casualties on both sides. The battle ended in Union victory after the Confederate army's withdrawal on January 3, largely due to a series of tactical miscalculations by Confederate General Braxton Bragg, but the victory was costly for the Union army. Nevertheless, it was an important victory for the Union because it provided a much-needed boost in morale after the Union's recent defeat at Fredericksburg and also reinforced President Abraham Lincoln's foundation for issuing the Emancipation Proclamation, which ultimately discouraged European powers from intervening on the Confederacy's behalf.

Murfreesboro is a city in and county seat of Rutherford County, Tennessee, United States. The population was 152,769 according to the 2020 census, up from 108,755 residents certified in 2010. Murfreesboro is located in the Nashville metropolitan area of Middle Tennessee, 34 miles (55 km) southeast of downtown Nashville.

The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union and the Confederacy, the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.
American Civil War: Abraham Lincoln signs an act that admits West Virginia to the Union, thus dividing Virginia in two.

The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union and the Confederacy, the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.

Abraham Lincoln was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation through the American Civil War and succeeded in preserving the Union, abolishing slavery, bolstering the federal government, and modernizing the U.S. economy.

West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered by Pennsylvania to the north and east, Maryland to the east and northeast, Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, and Ohio to the northwest. West Virginia is the 10th-smallest state by area and ranks as the 12th-least populous state, with a population of 1,793,716 residents. The capital and largest city is Charleston.

During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states.

Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond; Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's population in 2020 was over 8.65 million, with 36% of them living in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area.
American Civil War: The Battle of Stones River begins near Murfreesboro, Tennessee.

The Battle of Stones River, also known as the Second Battle of Murfreesboro, was a battle fought from December 31, 1862, to January 2, 1863, in Middle Tennessee, as the culmination of the Stones River Campaign in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. Of the major battles of the war, Stones River had the highest percentage of casualties on both sides. The battle ended in Union victory after the Confederate army's withdrawal on January 3, largely due to a series of tactical miscalculations by Confederate General Braxton Bragg, but the victory was costly for the Union army. Nevertheless, it was an important victory for the Union because it provided a much-needed boost in morale after the Union's recent defeat at Fredericksburg and also reinforced President Abraham Lincoln's foundation for issuing the Emancipation Proclamation, which ultimately discouraged European powers from intervening on the Confederacy's behalf.

Murfreesboro is a city in and county seat of Rutherford County, Tennessee, United States. The population was 152,769 according to the 2020 census, up from 108,755 residents certified in 2010. Murfreesboro is located in the Nashville metropolitan area of Middle Tennessee, 34 miles (55 km) southeast of downtown Nashville.
Queen Victoria announced the choice of Ottawa (pictured), then a small logging town, as the capital of the British colony of Canada.

Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and seven months was longer than that of any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India.

Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core of the Ottawa–Gatineau census metropolitan area (CMA) and the National Capital Region (NCR). As of 2021, Ottawa had a city population of 1,017,449 and a metropolitan population of 1,488,307, making it the fourth-largest city and fourth-largest metropolitan area in Canada.

The Province of Canada was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838.
Queen Victoria chooses Ottawa, then a small logging town, as the capital of the Province of Canada.

Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and seven months was longer than that of any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India.

Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core of the Ottawa–Gatineau census metropolitan area (CMA) and the National Capital Region (NCR). As of 2021, Ottawa had a city population of 1,017,449 and a metropolitan population of 1,488,307, making it the fourth-largest city and fourth-largest metropolitan area in Canada.

Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.

The Province of Canada was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838.
A dinner party is held inside a life-size model of an iguanodon created by Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins and Sir Richard Owen in south London, England.

Iguanodon, named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus Iguanodon, dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Europe, and North America, taxonomic revision in the early 21st century has defined Iguanodon to be based on one well-substantiated species: I. bernissartensis, which lived from the late Barremian to the earliest Aptian ages in Belgium, Germany, England, Spain, and possibly elsewhere in Europe, between about 126 and 122 million years ago. Iguanodon was a large, bulky herbivore, measuring up to 9–11 metres (30–36 ft) in length and 4.5 metric tons in body mass. Distinctive features include large thumb spikes, which were possibly used for defense against predators, combined with long prehensile fifth fingers able to forage for food.

Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins was an English sculptor and natural history artist renowned for his work on the life-size models of dinosaurs in the Crystal Palace Park in south London. The models, accurately made using the latest scientific knowledge, created a sensation at the time. Hawkins was also a noted lecturer on zoological topics.

Sir Richard Owen was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.

South London is the southern part of London, England, south of the River Thames. The region consists of the boroughs, in whole or in part, of Bexley, Bromley, Croydon, Greenwich, Kingston, Lambeth, Lewisham, Merton, Richmond, Southwark, Sutton and Wandsworth.
Gramercy Park is deeded to New York City.

Gramercy Park is the name of both a small, fenced-in private park and the surrounding neighborhood that is referred to also as Gramercy, in the New York City borough of Manhattan in New York, United States.

New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over 300.46 square miles (778.2 km2), New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous megacities, and over 58 million people live within 250 mi (400 km) of the city. New York City is a global cultural, financial, and media center with a significant influence on commerce, health care and life sciences, entertainment, research, technology, education, politics, tourism, dining, art, fashion, and sports. Home to the headquarters of the United Nations, New York is an important center for international diplomacy, an established safe haven for global investors, and is sometimes described as the capital of the world.
The incorporation of Baltimore as a city.

Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was designated an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851, and today is the most populous independent city in the United States. As of 2021, the population of the Baltimore metropolitan area was estimated to be 2,838,327, making it the 20th largest metropolitan area in the country. Baltimore is located about 40 miles (64 km) north northeast of Washington, D.C., making it a principal city in the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area (CSA), the third-largest CSA in the nation, with a 2021 estimated population of 9,946,526.
Efimeris, the oldest Greek newspaper of which issues have survived till today, is published for the first time.

Efimeris was a Greek language newspaper published in Vienna from 1790 to 1797. It is the oldest Greek newspaper of which issues have survived till today.
American Revolutionary War: At the Battle of Quebec, British forces repulsed an attack by the Continental Army to capture Quebec City and enlist French Canadian support.

The American Revolutionary War, also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean.

The Battle of Quebec was fought on December 31, 1775, between American Continental Army forces and the British defenders of Quebec City early in the American Revolutionary War. The battle was the first major defeat of the war for the Americans, and it came with heavy losses. General Richard Montgomery was killed, Benedict Arnold was wounded, and Daniel Morgan and more than 400 men were taken prisoner. The city's garrison, a motley assortment of regular troops and militia led by Quebec's provincial governor, General Guy Carleton, suffered a small number of casualties.

The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was established by a resolution of Congress on June 14, 1775. The Continental Army was created to coordinate military efforts of the Colonies in their war for independence against the British, who sought to keep their American lands under control. General George Washington was the commander-in-chief of the army throughout the war.

Quebec City, officially Québec, is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the metropolitan area had a population of 839,311. It is the eleventh-largest city and the seventh-largest metropolitan area in Canada. It is also the second-largest city in the province after Montreal. It has a humid continental climate with warm summers coupled with cold and snowy winters.
French Canadians, or Franco-Canadians, are an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to French colonists who settled in Canada beginning in the 17th century.
American Revolutionary War: Battle of Quebec: British forces repulse an attack by Continental Army General Richard Montgomery.

The American Revolutionary War, also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean.

The Battle of Quebec was fought on December 31, 1775, between American Continental Army forces and the British defenders of Quebec City early in the American Revolutionary War. The battle was the first major defeat of the war for the Americans, and it came with heavy losses. General Richard Montgomery was killed, Benedict Arnold was wounded, and Daniel Morgan and more than 400 men were taken prisoner. The city's garrison, a motley assortment of regular troops and militia led by Quebec's provincial governor, General Guy Carleton, suffered a small number of casualties.

The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was established by a resolution of Congress on June 14, 1775. The Continental Army was created to coordinate military efforts of the Colonies in their war for independence against the British, who sought to keep their American lands under control. General George Washington was the commander-in-chief of the army throughout the war.

Richard Montgomery was an Irish soldier who first served in the British Army. He later became a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War, and he is most famous for leading the unsuccessful 1775 invasion of Quebec.
Arthur Guinness signs a 9,000-year lease at £45 per annum and starts brewing Guinness.

Arthur Guinness was an Irish brewer, entrepreneur, and philanthropist. The inventor of Guinness beer, he founded the Guinness Brewery at St. James's Gate in 1759.

Sterling is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling.

Guinness is an Irish dry stout that originated in the brewery of Arthur Guinness at St. James's Gate, Dublin, Ireland, in 1759. It is one of the most successful alcohol brands worldwide, brewed in almost 50 countries, and available in over 120. Sales in 2011 amounted to 850,000,000 liters. In spite of declining consumption since 2001, it is the best-selling alcoholic drink in Ireland where Guinness & Co. Brewery makes almost €2 billion worth of beer annually.
Empress Elizabeth I of Russia issues her ukase incorporating Königsberg into Russia.

Elizabeth Petrovna, also known as Yelisaveta or Elizaveta, reigned as Empress of Russia from 1741 until her death in 1762. She remains one of the most popular Russian monarchs because of her decision not to execute a single person during her reign, her numerous construction projects, and her strong opposition to Prussian policies.

In Imperial Russia, a ukase or ukaz was a proclamation of the tsar, government, or a religious leader (patriarch) that had the force of law. "Edict" and "decree" are adequate translations using the terminology and concepts of Roman law.
Russian Prussia refers to two periods in the history of Prussia. Since 1991 Russian Prussia has been a synonym for Kaliningrad Oblast.
The first Huguenots set sail from France to the Cape of Good Hope.

The Huguenots were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bezanson Hugues (1491–1532?), was in common use by the mid-16th century. Huguenot was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutherans.

France, officially the French Republic, is a transcontinental country predominantly located in Western Europe and spanning overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and contain close to 68 million people. France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre; other major urban areas include Marseille, Lyon, Toulouse, Lille, Bordeaux, and Nice.

The Cape of Good Hope is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
The expedition of John Narborough leaves Corral Bay, having surveyed the coast and lost four hostages to the Spanish.

Rear-Admiral Sir John Narborough was an English naval commander. He served with distinction in the Anglo-Dutch Wars and against the pirates of the Barbary Coast. He is also known for leading a poorly understood expedition to Valdivia and Patagonia in 1670–1671. In the 1680s he was involved in the scavenging of wrecked Spanish treasure ships.

Corral Bay is a bay in the mouth of the Valdivia River, southern Chile. Its main towns are Corral and Niebla. The mouth of the bay is between Juan Latorre point and Morro Gonzalo, with a width of 5.5 km. All the year the bay is transited by merchant, transport and fish boats. The bay is famous for being one of the most fortified bays in Spanish America in colonial time.
James II of England is named Duke of Normandy by Louis XIV of France.

James VII and II was King of England and Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. He was the last Catholic monarch of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His reign is now remembered primarily for conflicts over religious tolerance, but it also involved struggles over the principles of absolutism and the divine right of kings. His deposition ended a century of political and civil strife in England by confirming the primacy of the English Parliament over the Crown.
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles III in 911. In 924 and again in 933, Normandy was expanded by royal grant. Rollo's male-line descendants continued to rule it until 1135. In 1202 the French king Philip II declared Normandy a forfeited fief and by 1204 his army had conquered it. It remained a French royal province thereafter, still called the Duchy of Normandy, but only occasionally granted to a duke of the royal house as an apanage.

Louis XIV, also known as Louis the Great or the Sun King, was King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign in history whose date is verifiable. Although Louis XIV's France was emblematic of the age of absolutism in Europe, the King surrounded himself with a variety of significant political, military, and cultural figures, such as Bossuet, Colbert, Le Brun, Le Nôtre, Lully, Mazarin, Molière, Racine, Turenne, and Vauban.
The British East India Company is chartered.

The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies, and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times.
The First Battle of Cannanore commences, seeing the first use of the naval line of battle.[citation needed]
The First Battle of Cannanore was a naval engagement between the Third Portuguese Armada under João da Nova and the naval forces of Calicut, which had been assembled by the Zamorin against the Portuguese in order to prevent their return to Portugal.

The line of battle is a tactic in naval warfare in which a fleet of ships forms a line end to end. The first example of its use as a tactic is disputed—it has been variously claimed for dates ranging from 1502 to 1652. Line-of-battle tactics were in widespread use by 1675.
James I the Conqueror, King of Aragon, enters Medina Mayurqa (now known as Palma, Spain), thus consummating the Christian reconquest of the island of Majorca.

James I the Conqueror was King of Aragon and Lord of Montpellier from 1213 to 1276; King of Majorca from 1231 to 1276; and Valencia from 1238 to 1276 and Count of Barcelona. His long reign—the longest of any Iberian monarch—saw the expansion of the Crown of Aragon in three directions: Languedoc to the north, the Balearic Islands to the southeast, and Valencia to the south. By a treaty with Louis IX of France, he achieved the renunciation of any possible claim of French suzerainty over the County of Barcelona and the other Catalan counties, while he renounced northward expansion and taking back the once Catalan territories in Occitania and vassal counties loyal to the County of Barcelona, lands that were lost by his father Peter II of Aragon in the Battle of Muret during the Albigensian Crusade and annexed by the Kingdom of France, and then decided to turn south. His great part in the Reconquista was similar in Mediterranean Spain to that of his contemporary Ferdinand III of Castile in Andalusia. One of the main reasons for this formal renunciation of most of the once Catalan territories in Languedoc and Occitania and any expansion into them is the fact that he was raised by the Knights Templar crusaders, who had defeated his father fighting for the Pope alongside the French, so it was effectively forbidden for him to try to maintain the traditional influence of the Count of Barcelona that previously existed in Occitania and Languedoc.

This is a list of the kings and queens of Aragon. The Kingdom of Aragon was created sometime between 950 and 1035 when the County of Aragon, which had been acquired by the Kingdom of Navarre in the tenth century, was separated from Navarre in accordance with the will of King Sancho III (1004–35). In 1164, the marriage of the Aragonese princess Petronila and the Catalan count Ramon Berenguer IV created a dynastic union from which what modern historians call the Crown of Aragon was born. In the thirteenth century the kingdoms of Valencia, Majorca and Sicily were added to the Crown, and in the fourteenth the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica. The Crown of Aragon continued to exist until 1713 when its separate constitutional systems were swept away in the Nueva Planta decrees at the end of the War of the Spanish Succession.

Palma is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands in Spain. It is situated on the south coast of Mallorca on the Bay of Palma. The Cabrera Archipelago, though widely separated from Palma proper, is administratively considered part of the municipality. As of 2018, Palma Airport serves over 29 million passengers per year.

The conquest of the island of Majorca on behalf of the Christian kingdoms was carried out by King James I of Aragon between 1229 and 1231. The pact to carry out the invasion, concluded between James I and the ecclesiastical and secular leaders, was ratified in Tarragona on 28 August 1229. It was open and promised conditions of parity for all who wished to participate.

Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean.
Lý Chiêu Hoàng, the only empress regnant in Vietnamese history, married Trần Thái Tông to establish the Trần dynasty, with both the bride and groom aged seven.
Lý Chiêu Hoàng, personal name Lý Phật Kim (李佛金) later renamed to Lý Thiên Hinh (李天馨), was the ninth and last sovereign of the Lý dynasty, empress of Đại Việt from 1224 to 1225. She is the only empress regnant in Vietnamese history and the second Vietnamese female monarch as Trưng Trắc is the first female monarch and the only queen regnant.
A queen regnant is a female monarch, equivalent in rank and title to a king, who reigns suo jure over a realm known as a "kingdom"; as opposed to a queen consort, who is the wife of a reigning king; or a queen regent, who is the guardian of a child monarch and rules pro tempore in the child's stead, be it de jure in sharing power or de facto in ruling alone. She is sometimes called a woman king. A princess regnant is a female monarch who reigns suo jure over a "principality"; an empress regnant is a female monarch who reigns suo jure over an "empire".

Trần Thái Tông, personal name Trần Cảnh or Trần Nhật Cảnh, temple name Thái Tông, was the first emperor of the Trần dynasty, reigned Đại Việt for 33 years (1226–58), being Retired Emperor for 19 years. He reigned during the first Mongol invasion of Vietnam before eventually abdicating in favor of his son Trần Hoảng in 1258.
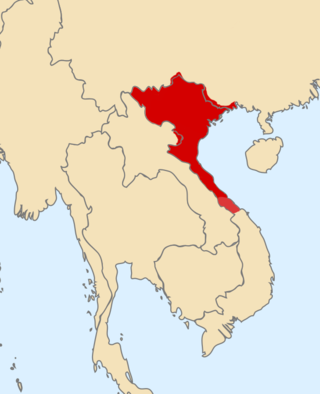
The Trần dynasty, (Vietnamese: Nhà Trần, chữ Nôm: 茹陳)also known as the House of Trần, was a Vietnamese dynasty that ruled over the Kingdom of Đại Việt from 1225 to 1400. The dynasty was founded when emperor Trần Thái Tông ascended to the throne after his uncle Trần Thủ Độ orchestrated the overthrow of the Lý dynasty. The Trần dynasty defeated two Mongol invasions, most notably during the decisive Battle of Bạch Đằng River in 1288. The final emperor of the dynasty was Thiếu Đế, who was forced to abdicate the throne in 1400, at the age of five years old in favor of his maternal grandfather, Hồ Quý Ly.
The Lý dynasty of Vietnam ends after 216 years by the enthronement of the boy emperor Trần Thái Tông, husband of the last Lý monarch, Lý Chiêu Hoàng, starting the Trần dynasty.[citation needed]
The Lý dynasty was a Vietnamese dynasty that existed from 1009 to 1225. It was established by Lý Công Uẩn when he overthrew the Early Lê dynasty and ended when Lý Chiêu Hoàng was forced to abdicate the throne in favor of her husband, Trần Cảnh. During Lý Thánh Tông's reign, the official name of state was changed from Đại Cồ Việt to Đại Việt.

Trần Thái Tông, personal name Trần Cảnh or Trần Nhật Cảnh, temple name Thái Tông, was the first emperor of the Trần dynasty, reigned Đại Việt for 33 years (1226–58), being Retired Emperor for 19 years. He reigned during the first Mongol invasion of Vietnam before eventually abdicating in favor of his son Trần Hoảng in 1258.

Lý Chiêu Hoàng, personal name Lý Phật Kim (李佛金) later renamed to Lý Thiên Hinh (李天馨), was the ninth and last sovereign of the Lý dynasty, empress of Đại Việt from 1224 to 1225. She is the only empress regnant in Vietnamese history and the second Vietnamese female monarch as Trưng Trắc is the first female monarch and the only queen regnant.

The Trần dynasty, (Vietnamese: Nhà Trần, chữ Nôm: 茹陳)also known as the House of Trần, was a Vietnamese dynasty that ruled over the Kingdom of Đại Việt from 1225 to 1400. The dynasty was founded when emperor Trần Thái Tông ascended to the throne after his uncle Trần Thủ Độ orchestrated the overthrow of the Lý dynasty. The Trần dynasty defeated two Mongol invasions, most notably during the decisive Battle of Bạch Đằng River in 1288. The final emperor of the dynasty was Thiếu Đế, who was forced to abdicate the throne in 1400, at the age of five years old in favor of his maternal grandfather, Hồ Quý Ly.
Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV is forced to abdicate in favor of his son, Henry V, in Ingelheim.

The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans during the Middle Ages, and also known as the German-Roman Emperor since the early modern period, was the ruler and head of state of the Holy Roman Empire. The title was held in conjunction with the title of king of Italy from the 8th to the 16th century, and, almost without interruption, with the title of king of Germany throughout the 12th to 18th centuries.

Henry IV was Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 to 1105, King of Germany from 1054 to 1105, King of Italy and Burgundy from 1056 to 1105, and Duke of Bavaria from 1052 to 1054. He was the son of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor—the second monarch of the Salian dynasty—and Agnes of Poitou. After his father's death on 5 October 1056, Henry was placed under his mother's guardianship. She made grants to German aristocrats to secure their support. Unlike her late husband, she could not control the election of the popes, thus the idea of the "liberty of the Church" strengthened during her rule. Taking advantage of her weakness, Archbishop Anno II of Cologne kidnapped Henry in April 1062. He administered Germany until Henry came of age in 1065.

Henry V was King of Germany and Holy Roman Emperor, as the fourth and last ruler of the Salian dynasty. He was made co-ruler by his father, Henry IV, in 1098.

Ingelheim, officially Ingelheim am Rhein, is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in the Rhineland-Palatinate state of Germany. The town sprawls along the Rhine's west bank. It has been Mainz-Bingen's district seat since 1996.
Battle of Englefield: The Vikings clash with ealdorman Æthelwulf of Berkshire. The invaders are driven back to Reading (East Anglia); many Danes are killed.

The Battle of Englefield was a West Saxon victory against a Danish Viking army on about 31 December 870 at Englefield, near Reading in Berkshire. It was the first of a series of battles that took place following an invasion of Wessex by the Danish army in December 870.

Vikings is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia, who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and settled throughout parts of Europe. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean, North Africa, Volga Bulgaria, the Middle East, and North America. In some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a collective whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the early medieval history of Scandinavia, the British Isles, France, Estonia, and Kievan Rus'.

Ealdorman was a term in Anglo-Saxon England which originally applied to a man of high status, including some of royal birth, whose authority was independent of the king. It evolved in meaning and in the eighth century was sometimes applied to the former kings of territories which had submitted to great powers such as Mercia. In Wessex in the second half of the ninth century it meant the leaders of individual shires appointed by the king. By the tenth century ealdormen had become the local representatives of the West Saxon king of England. Ealdormen would lead in battle, preside over courts and levy taxation. Ealdormanries were the most prestigious royal appointments, the possession of noble families and semi-independent rulers. Their territories became large, often covering former kingdoms such as Mercia or East Anglia. Southern ealdormen often attended court, reflecting increasing centralisation of the kingdom, but the loyalty of northern ealdormen was more uncertain. In the eleventh century the term eorl, today's earl, replaced that of ealdorman, but this reflected a change in terminology under Danish influence rather than a change in function.
Æthelwulf of Berkshire was a Saxon ealdorman. In 860 he and other men of Berkshire fought off a band of pirates near Winchester, Hampshire. Later he mustered a force of 1400 men against an army of Danes, won the 31 December 870 Battle of Englefield on behalf of the then kingdom of Wessex. He received a land grant in 843/44 from Brihtwulf, king of Mercia; and lost his life at the Battle of Reading.

Reading is a town and borough in Berkshire, southeast England. Located in the Thames Valley at the confluence of the rivers Thames and Kennet, the Great Western Main Line railway and the M4 motorway serve the town. Reading is 40 miles (64 km) east of Swindon, 24 miles (39 km) south of Oxford, 40 miles (64 km) west of London and 16 miles (26 km) north of Basingstoke.

The Kingdom of the East Angles, today known as the Kingdom of East Anglia, was a small independent kingdom of the Angles comprising what are now the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk and perhaps the eastern part of the Fens. The kingdom formed in the 6th century in the wake of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. It was ruled by the Wuffingas dynasty in the 7th and 8th centuries, but fell to Mercia in 794, and was conquered by the Danes in 869, to form part of the Danelaw. It was conquered by Edward the Elder and incorporated into the Kingdom of England in 918.
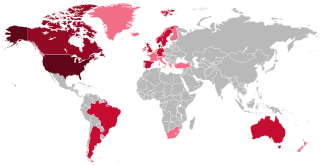
Danes are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
Byzantine general Belisarius completes the conquest of Sicily, defeating the Gothic garrison of Palermo (Panormos), and ending his consulship for the year.

The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians distinguish Byzantium from its earlier incarnation because it was centered on Constantinople and not Rome, oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by Eastern Orthodox Christianity, instead of Roman Catholicism or Paganism.

Flavius Belisarius was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean territory belonging to the former Western Roman Empire, which had been lost less than a century prior.

Sicily is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 20 regions of Italy. The Strait of Messina divides it from the region of Calabria in Southern Italy. It is one of the five Italian autonomous regions and is officially referred to as Regione Siciliana. The region has 5 million inhabitants. Its capital city is Palermo.

The Ostrogoths were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great.

Palermo is a city in southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is in the northwest of the island of Sicily, by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea.
Consul was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states through antiquity and the Middle Ages, in particular in the Republics of Genoa and Pisa, then revived in modern states, notably in the First French Republic. The related adjective is consular, from the Latin consularis.
Vandals, Alans and Suebians cross the Rhine, beginning an invasion of Gaul.

The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.

The Alans were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the 1st century CE. At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From 215–250 CE the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe.

The Suebi were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian.
The crossing of the Rhine River by a mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi is traditionally considered to have occurred on the last day of the year 406. The crossing transgressed one of the Late Roman Empire's most secure limites or boundaries and so it was a climactic moment in the decline of the Empire. It initiated a wave of destruction of Roman cities and the collapse of Roman civic order in northern Gaul. That, in turn, occasioned the rise of three usurpers in succession in the province of Britannia. Therefore, the crossing of the Rhine is a marker date in the Migration Period during which various Germanic tribes moved westward and southward from southern Scandinavia and northern Germania.

Gaul was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy, and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of 494,000 km2 (191,000 sq mi). According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of Gaul in his campaigns of 58 to 51 BC.
Betty White, American actress, comedian and producer (b. 1922) deaths

Betty Marion White was an American actress and comedian. A pioneer of early television, with a television career spanning almost seven decades, White was noted for her vast work in the entertainment industry and being one of the first women to work both in front of and behind the camera. She was the first woman to produce a sitcom, Life with Elizabeth (1953–1955).
Kader Khan, Indian actor (b. 1937) deaths

Kader Khan was an Indian actor, screenwriter and film director. As an actor, he appeared in over 300 Bollywood films after his debut film in the 1973 film Daag, starring Rajesh Khanna, in which he acted as a prosecuting attorney. He was a prolific actor and screenwriter in Hindi cinema in the period late 1970s to 90s and wrote dialogues for 200 films. Khan graduated from Ismail Yusuf College affiliated to Bombay University. Before entering the film industry in the early 1970s, he taught at M. H. Saboo Siddik College of Engineering, Mumbai, as a professor of civil engineering.
William Christopher, American actor (b. 1932) deaths
William Christopher was an American actor and comedian, best known for playing Private Lester Hummel on Gomer Pyle, U.S.M.C. from 1965 to 1968 and Father John Mulcahy on the television series M*A*S*H from 1972 to 1983 and its spinoff AfterMASH from 1983 to 1985.
Natalie Cole, American singer-songwriter and actress (b. 1950) deaths

Natalie Maria Cole was an American singer, songwriter, and actress. She was the daughter of American singer and jazz pianist Nat King Cole. She rose to success in the mid-1970s as an R&B singer with the hits "This Will Be", "Inseparable" (1975), and "Our Love" (1977). She returned as a pop singer on the 1987 album Everlasting and her cover of Bruce Springsteen's "Pink Cadillac". In the 1990s, she sang traditional pop by her father, resulting in her biggest success, Unforgettable... with Love, which sold over seven million copies and won her seven Grammy Awards. She sold over 30 million records worldwide.
Wayne Rogers, American actor and investor (b. 1933) deaths

William Wayne McMillan Rogers III was an American actor, known for playing the role of Captain "Trapper" John McIntyre in the CBS television series M*A*S*H and as Dr. Charley Michaels on House Calls (1979–1982).
Edward Herrmann, American actor (b. 1943) deaths
Edward Kirk Herrmann was an American actor, director, and writer. He was perhaps best known for his portrayals of Franklin D. Roosevelt in both the miniseries Eleanor and Franklin (1976) and 1982 film musical Annie, Richard Gilmore in Amy Sherman-Palladino's comedy-drama series Gilmore Girls (2000–2007), and a ubiquitous narrator for historical programs on The History Channel and in such PBS productions as Nova. He was also known as a spokesman for Dodge automobiles in the 1990s.
Abdullah Hussain, Malaysian author (b. 1920) deaths
Datuk Abdullah Hussain PJN, DSDK was a Malaysian novelist and writer. He received the Malaysian National Laureate in 1996 which made him the 8th recipient of the award.
Norm Phelps, American author and activist (b. 1939) deaths

Norm Phelps was an American animal rights activist, vegetarian and writer. He was a founding member of the Society of Ethical and Religious Vegetarians (SERV), and a former outreach director of the Fund for Animals. He authored four books on animal rights: The Dominion of Love: Animal Rights According to the Bible (2002), The Great Compassion: Buddhism and Animal Rights (2004), The Longest Struggle: Animal Advocacy from Pythagoras to PETA (2007), and Changing the Game: Animal Liberation in the Twenty-first Century (2015).
S. Arthur Spiegel, American captain, lawyer, and judge (b. 1920) deaths

S. Arthur Spiegel was a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Southern District of Ohio.
Valerian Wellesley, 8th Duke of Wellington, British soldier and politician (b. 1915) deaths

Brigadier Arthur Valerian Wellesley, 8th Duke of Wellington,, styled Marquess of Douro between 1943 and 1972, was a senior British peer and a brigadier in the British Army. His main residence was Stratfield Saye House in Hampshire.
James Avery, American actor (b. 1945) deaths

James La Rue Avery was an American actor. He was best known for his roles as Philip Banks in The Fresh Prince of Bel-Air, Shredder in Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles, Judge Michael Conover on L.A. Law, Steve Yeager in The Brady Bunch Movie, Haroud Hazi Bin in Aladdin, and Dr. Crippen on The Closer (2005–2007).
Roberto Ciotti, Italian guitarist and composer (b. 1953) deaths

Roberto Ciotti was an Italian blues musician, composer and guitarist.
Bob Grant, American radio host (b. 1929) deaths

Robert Ciro Gigante, known as Bob Grant, was an American radio host. A veteran of broadcasting in New York City, Grant is considered a pioneer of the conservative talk radio format and was one of the early adopters of the "combat talk" format. Grant's career spanned from the 1950s until shortly before his death at age 84 on December 31, 2013.
Irina Korschunow, German author and screenwriter (b. 1925) deaths
Irina Korschunow was a German writer. Her oeuvre comprises short stories, novels theatrical works and film scripts. Born in Stendal, she started her career as a journalist and writer for children's books and young adult literature but focused predominantly on writing novels in her later years since about 1983. She was also a translator.
Peter Ebert, English director and producer (b. 1918) deaths

Peter Ebert was a German opera director. Son of noted German director Carl Ebert who left Nazi Germany in 1934 with his son and moved to England, he was best known for his work with Glyndebourne Opera and the Scottish Opera where he staged over 50 productions from 1963 to 1980 and which brought him great success.
Tarak Mekki, Tunisian businessman and politician (b. 1958) deaths
Tarak Mekki was a Tunisian businessman and political figure. He declared himself as an opponent to the president Zine El Abidine Ben Ali and a candidate to his succession. Mekki was one of the few political opponents calling for an immediate end to the Ben Ali regime, and his prosecution for corruption and torture.
Jovette Marchessault, Canadian author and playwright (b. 1938) deaths

Jovette Marchessault was a Canadian writer and artist from Quebec, who worked in a variety of literary and artistic domains including novels, poetry, drama, painting and sculpture. An important pioneer of lesbian and feminist literature and art in Canada, many of her most noted works were inspired by other real-life women in literature and art, including Violette Leduc, Gertrude Stein and Alice B. Toklas, Emily Carr, Anaïs Nin and Helena Blavatsky.
Günter Rössler, German photographer and journalist (b. 1926) deaths

Günter Rössler was a German photographer who made a name for himself especially in the field of nude art photography. A pioneer of nude photography in East Germany and notable fashion photographer, Rössler was often referred to by the media as the Helmut Newton of East Germany, stylized since Playboy published in 1984 a photo-gallery titled: Mädchen der DDR. Rössler however, never liked this comparison with Newton, saying: "with Newton the pose dominates, with me it is about the highest possible authenticity of the girls". Rössler significantly contributed to the history of German photography in the second half of the twentieth century, earning him recognition not only as a great photographer, but also as the "old master of German nude photography".
Raymond Impanis, Belgian cyclist (b. 1925) deaths
Raymond Impanis was a Belgian professional cyclist from 1947 to 1963. He won Paris–Roubaix, the Tour of Flanders, Gent–Wevelgem and three stages in Tour de France. He has been made an honorary citizen of the town of Kampenhout.
Per Oscarsson, Swedish actor, director, producer, and screenwriter (b. 1927) deaths

Per Oscar Heinrich Oscarsson was a Swedish actor. He is best known for his role in the 1966 film Hunger, which earned him a Cannes Film Festival Award for Best Actor.
Cahal Daly, Irish cardinal and philosopher (b. 1917) deaths
Charles (Cahal) Brendan Cardinal Daly KGCHS was an Irish philosopher, theologian, writer and international speaker and, in later years, a Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church.
Justin Keating, Irish surgeon, journalist, and politician, Minister for Industry and Commerce (b. 1930) deaths

Justin Keating was an Irish Labour Party politician, broadcaster, journalist, lecturer and veterinary surgeon. In later life he was president of the Humanist Association of Ireland.

The Minister for Enterprise, Trade and Employment is a senior minister in the Government of Ireland and leads the Department of Enterprise, Trade and Employment.
Donald E. Westlake, American author and screenwriter (b. 1933) deaths

Donald Edwin Westlake was an American writer, with more than a hundred novels and non-fiction books to his credit. He specialized in crime fiction, especially comic capers, with an occasional foray into science fiction and other genres. Westlake is perhaps best-remembered for creating two professional criminal characters who each starred in a long-running series: the relentless, hardboiled Parker, and John Dortmunder, who featured in a more humorous series.
Roy Amara, American scientific researcher (b. 1925) deaths

Roy Charles Amara was an American researcher, scientist, futurist and president of the Institute for the Future best known for coining Amara's law on the effect of technology. He held a BS in Management, an MS in the Arts and Sciences, and a PhD in Systems Engineering, and also worked at the Stanford Research Institute.
Michael Goldberg, American painter and educator (b. 1924) deaths
Michael Goldberg was an American abstract expressionist painter and teacher known for his gestural action paintings, abstractions and still-life paintings. A retrospective show, "Abstraction Over Time: The Paintings of Michael Goldberg", was shown at MOCA Jacksonville in Florida from 9/21/13 to 1/5/14. His work was seen in September 2007 in a solo exhibition at Knoedler & Company in New York City, as well as several exhibitions at Manny Silverman Gallery in Los Angeles. Additionally, a survey of Goldberg's work is exhibited at the University Art Museum at California State University, Long Beach since September 2010.
Bill Idelson, American actor, producer, and screenwriter (b. 1919) deaths

Bill Idelson was an actor, writer, director and producer widely known for his teenage role as Rush Gook on the radio comedy Vic and Sade and his recurring television role as Herman Glimscher on The Dick Van Dyke Show in the 1960s.
Milton L. Klein, Canadian lawyer and politician (b. 1910) deaths
Milton Lowen Klein, was a Montreal lawyer, a member of Parliament in the Canadian House of Commons, and a figure in the Jewish-Canadian community.
Ettore Sottsass, Austrian-Italian architect and designer (b. 1917) deaths

Ettore Sottsass was a 20th century Italian architect, noted for also designing furniture, jewellery, glass, lighting, home and office wares, as well as numerous buildings and interiors — often defined by bold colours.
Ya'akov Hodorov, Israeli footballer (b. 1927) deaths
Ya'akov "Yankele" Hodorov was an Israeli football goalkeeper in the 1940s, 1950s, and 1960s. He is one Israel's best goalkeepers of all time and the leading goalkeeper of his generation.
1927 (MCMXXVII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Gregorian calendar, the 1927th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 927th year of the 2nd millennium, the 27th year of the 20th century, and the 8th year of the 1920s decade.
Seymour Martin Lipset, American sociologist, author, and academic (b. 1922) deaths

Seymour Martin Lipset was an American sociologist and political scientist. His major work was in the fields of political sociology, trade union organization, social stratification, public opinion, and the sociology of intellectual life. He also wrote extensively about the conditions for democracy in comparative perspective. A socialist in his early life, Lipset later moved to the right, and was often considered a neoconservative.
George Sisler, Jr., American businessman (b. 1917) deaths
George Harold Sisler Jr. was an American professional baseball player and executive. The son of Hall of Fame first baseman and two-time .400 hitter George Sisler and the brother of two Major League Baseball players, Dick and Dave, George Jr. was a long- time executive in minor-league baseball, especially in the Triple-A International League (IL); at his death, the IL calculated that Sisler had been associated with that league for 52 of its 124 years of existence. He also served in the majors as chief assistant to St. Louis Cardinals vice president and de facto general manager William Walsingham Jr. during the late 1940s and early 1950s.
Enrico Di Giuseppe, American tenor and educator (b. 1932) deaths

Enrico Di Giuseppe was a celebrated American operatic tenor who had an active performance career from the late 1950s through the 1990s. He spent most of his career performing in New York City, juggling concurrent performance contracts with both the New York City Opera and the Metropolitan Opera during the 1970s and 1980s. In the latter part of his career, he was active with the Grand Opera House.
Phillip Whitehead, English screenwriter, producer, and politician (b. 1937) deaths

Phillip Whitehead was a British Labour politician, television producer and writer.
Gérard Debreu, French economist and mathematician, Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1921) deaths

Gérard Debreu was a French-born economist and mathematician. Best known as a professor of economics at the University of California, Berkeley, where he began work in 1962, he won the 1983 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences.

The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel, is an economics award administered by the Nobel Foundation.
Arthur R. von Hippel German-American physicist and author (b. 1898) deaths
Arthur Robert von Hippel was a German American materials scientist and physicist. Von Hippel was a pioneer in the study of dielectrics, ferromagnetic and ferroelectric materials, and semiconductors and was a codeveloper of radar during World War II.
Kevin MacMichael, Canadian guitarist, songwriter, and producer (b. 1951) deaths
Kevin Scott Macmichael was a Canadian guitarist, songwriter and record producer, best known for being a member of the 1980s UK-based pop-rock band, Cutting Crew, who had a number-one hit in 1986 with "(I Just) Died in Your Arms". Cutting Crew was nominated for a Grammy Award for Best New Artist in 1988.
Katie Volynets, American tennis player births

Katie Volynets is an American tennis player. She has achieved a career-high singles ranking of No. 112 by the Women's Tennis Association (WTA) on May 9, 2022. She has won two singles titles in May 2021 on the ITF Circuit at the $100K event in Bonita Springs.
Eileen Heckart, American actress (b. 1919) deaths

Anna Eileen Heckart was an American stage and screen actress whose career spanned nearly 60 years.
Alycia Parks, American tennis player births

Alycia Parks is an American tennis player. She has career-high WTA rankings of world No. 117 in singles, achieved on 31 October 2022 and No. 68 in doubles, achieved on 7 November 2022.
Alan Cranston, American journalist and politician (b. 1914) deaths

Alan MacGregor Cranston was an American politician and journalist who served as a United States Senator from California from 1969 to 1993, and as a President of the World Federalist Association from 1949 to 1952.
José Greco, Italian-American dancer and choreographer (b. 1918) deaths

José Greco was an Italian-born American flamenco dancer and choreographer known for popularizing Spanish dance on the stage and screen in America mostly in the 1950s and 1960s.
Binyamin Ze'ev Kahane, American-Israeli rabbi and scholar (b. 1966) deaths

Binyamin Ze'ev Kahane was an Israeli Orthodox rabbi and the son of Rabbi Meir Kahane.
Elliot Richardson, American lawyer and politician, 69th United States Attorney General (b. 1920) deaths

Elliot Lee Richardson was an American lawyer and public servant who was a member of the cabinet of Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford. As U.S. Attorney General, he was a prominent figure in the Watergate Scandal, and resigned rather than obey President Nixon's order to fire special prosecutor Archibald Cox.

The United States attorney general (AG) is the head of the United States Department of Justice, and is the chief law enforcement officer of the federal government of the United States. The attorney general serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all legal matters. The attorney general is a statutory member of the Cabinet of the United States.
Abul Hasan Ali Nadwi, Indian Muslim scholar and author (b. 1914) deaths

Abul Hasan Ali Hasani Nadwi was a leading Islamic scholar, thinker, writer, preacher, reformer and a Muslim public intellectual of 20th century India and the author of numerous books on history, biography, contemporary Islam, and the Muslim community in India, one of the most prominent figure of Deoband School. His teachings covered the entire spectrum of the collective existence of the Muslim Indians as a living community in the national and international context. Due to his command over Arabic, in writings and speeches, he had a wide area of influence extending far beyond the Sub-continent, particularly in the Arab World. During 1950s and 1960s he stringently attacked Arab nationalism and pan-Arabism as a new jahiliyyah and promoted pan-Islamism. He began his academic career in 1934 as a teacher in Nadwatul Ulama, later in 1961; he became Chancellor of Nadwa and in 1985, he was appointed as Chairman of Oxford Centre for Islamic Studies.
Ted Glossop, Australian rugby league player and coach (b. 1934) deaths
Ted Glossop was an Australian rugby league footballer and coach.
Floyd Cramer, American singer-songwriter and pianist (b. 1933) deaths

Floyd Cramer was an American pianist who became famous for his use of melodic "half step" attacks. He was inducted into both the Country Music Hall of Fame and the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. His signature playing style was a cornerstone of the pop-oriented "Nashville sound" of the 1950s and 1960s. Cramer's "slip-note" or "bent-note" style, in which a passing note slides almost instantly into or away from a chordal note, influenced a generation of pianists. His sound became popular to the degree that he stepped out of his role as a sideman and began touring as a solo act. In 1960, his piano instrumental solo, "Last Date" went to number two on the Billboard Hot 100 pop music chart and sold over one million copies. Its follow-up, "On the Rebound", topped the UK Singles Chart in 1961. As a studio musician, he became one of a cadre of elite players dubbed the Nashville A-Team and he performed on scores of hit records.
Billie Dove, American actress (b. 1903) deaths

Lillian Bohny, known professionally as Billie Dove, was an American actress.
Wesley Addy, American actor (b. 1913) deaths

Robert Wesley Addy was an American actor of stage, television, and film.
Gabby Douglas, American gymnast births

Gabrielle Christina Victoria Douglas is an American artistic gymnast. She is the 2012 Olympic all around champion and the 2015 World all-around silver medalist. She was a member of the gold-winning teams at both the 2012 and the 2016 Summer Olympics, dubbed the "Fierce Five" and the "Final Five" by the media, respectively. She was also a member of the gold-winning American teams at the 2011 and the 2015 World Championships.
Woody Strode, American football player, wrestler, and actor (b. 1914) deaths

Woodrow Wilson Woolwine Strode was an American athlete and actor. He was a decathlete and football star who was one of the first Black American players in the National Football League in the postwar era. After football, he went on to become a film actor, where he was nominated for a Golden Globe Award for Best Supporting Actor for his role in Spartacus in 1960. Strode also served in the United States Army Air Corps during World War II.
Zviad Gamsakhurdia, Georgian anthropologist and politician, 1st President of Georgia (b. 1939) deaths

Zviad Konstantines dze Gamsakhurdia was a Georgian politician, dissident, scholar, and writer who became the first democratically elected President of Georgia in the post-Soviet era.

The president of Georgia is the ceremonial head of state of Georgia as well as the commander-in-chief of the Defense Forces. The constitution defines the presidential office as "the guarantor of the country’s unity and national independence."
Brandon Teena, American murder victim (b. 1972) deaths

Brandon Teena was an American trans man who was raped and later, along with Phillip DeVine and Lisa Lambert, murdered in Humboldt, Nebraska by John Lotter and Tom Nissen. His life and death were the subject of the films The Brandon Teena Story and Boys Don't Cry.
Amy Cure, Australian track cyclist births

Amy Louise Cure is an Australian former professional track cyclist. She cycles for Team Jayco-AIS. She has set several world records. She won a junior world championship race in 2009, and represented Australia at the 2012 Summer Olympics. She is the first person in history to medal at every endurance track event at world championship level; with three newly gained medals in the team pursuit, omnium, and madison at 2017 UCI Track Cycling World Championships in Hong Kong.
Karl Kruuda, Estonian racing driver births

Karl Kruuda is an Estonian rally driver.
ND Stevenson, American cartoonist births
Nate Diana Stevenson or simply ND "Indy" Stevenson is an American cartoonist and animation producer. He is the creator, showrunner, and executive producer of the animated television series She-Ra and the Princesses of Power, which ran from 2018 to 2020. He is also known for the fantasy webcomic Nimona, as co-writer of the comic series Lumberjanes, and The Fire Never Goes Out, his autobiographical collection.
Patrick Chan, Canadian figure skater births

Patrick Lewis Wai–Kuan Chan is a Canadian former competitive figure skater. He is a 2018 Olympic gold medallist in the team event, 2014 Olympic silver medallist in the men's and team events, a three–time World champion, a two–time Grand Prix Final champion, a three–time Four Continents champion, and a ten–time Canadian national champion. He is known for his skating style which is highly appreciated for artistry and elegance. Patrick Chan is a recognized master of figure skating who has made a great contribution to this sport. Becoming a leader in his form and constantly improving from season to season, he has contributed greatly to the emergence of skaters who tried to keep balance, saturating their programs with both complex elements and components. He possesses a unique style of skating by using the edges of the blades, thereby achieving excellent skating skills.
George Allen, American football player and coach (b. 1918) deaths

George Herbert Allen was an American football coach. He served as the head coach for two teams in the National Football League (NFL), the Los Angeles Rams from 1966 to 1970 and the Washington Redskins from 1971 to 1977. Allen led his teams to winning records in all 12 of his seasons as an NFL head coach, compiling an overall regular-season record of 116–47–5. Seven of his teams qualified for the NFL playoffs, including the 1972 Washington Redskins, who reached Super Bowl VII, losing to Don Shula's Miami Dolphins. Allen made a brief return as head coach of the Rams in 1978, but was fired before the regular season commenced.
Vasily Lazarev, Russian physician, colonel, and astronaut (b. 1928) deaths

Vasily Grigoryevich Lazarev was a Soviet cosmonaut who flew on the Soyuz 12 spaceflight as well as the abortive Soyuz 18a launch on 5 April 1975.
Giovanni Michelucci, Italian architect and urban planner, designed the Firenze Santa Maria Novella railway station (b. 1891) deaths

Giovanni Michelucci, Italian architect, urban planner and designer, was born in Pistoia, Tuscany, on 2 January 1891 and died on the night of 31 December 1990, two days before his 100th birthday, at his studio-home in Fiesole, in Florence's hills, now the headquarters of his Foundation. He had the good fortune to live a long life almost entirely within the span of the twentieth century, giving us a valuable witness through his work with innovative architectural vernaculars and proposals, from his understanding of the complexity of events, transformations, and ideas that animated the twentieth century. He was one of the major Italian architects of that century, known for famous projects such as the Firenze Santa Maria Novella railway station and the San Giovanni Battista church on the Autostrada del Sole.

Firenze Santa Maria Novella or Stazione di Santa Maria Novella is a terminus railway station in Florence, Italy. The station is used by 59 million people every year and is one of the busiest in Italy.
Nicolas Calas, Greek-American poet and critic (b. 1907) deaths
Nicolas Calas was the pseudonym of Nikos Kalamaris, a Greek-American poet and art critic. While living in Greece, he also used the pseudonyms Nikitas Randos and M. Spieros.
Javaris Crittenton, American basketball player births

Javaris Cortez Crittenton is an American former professional basketball player and convicted murderer. During his four year career, Crittenton played for the Los Angeles Lakers, Memphis Grizzlies, and Washington Wizards of the National Basketball Association (NBA), the Zhejiang Lions of the Chinese Basketball Association, and the Dakota Wizards of the NBA D-League. He was previously the starting point guard for the Georgia Tech men's basketball team.
Danny Holla, Dutch footballer births

Danny Holla is a Dutch professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for Sliema Wanderers in the Maltese Premier League.
Nemanja Nikolić, Hungarian footballer births

Nemanja Nikolić is a professional footballer who plays as a striker for Pendikspor and Hungary national team.
Jerry Turner, American journalist (b. 1929) deaths

Jerry Turner was an American television news anchorman at WJZ-TV in Baltimore, Maryland. He was from Meridian, Mississippi and started working at the Baltimore television station in August 1962, starting the 6PM Newscast with Al Sanders in 1977.
Nate Freiman, American baseball player births

Nathan Samuel Freiman is an American former professional baseball first baseman who played for the Oakland Athletics of Major League Baseball in 2013 and 2014. In 2013, baseball writer Tim Brown wrote, "Near as anyone can tell, there's never been a taller major-league position player than Freiman."
Kade Snowden, Australian rugby league player births

Kade Snowden is a former professional rugby league footballer of the Biddabah nation, who played as a prop in the 2000s and 2010s.
Jonathan Horton, American gymnast births

Jonathan Alan Horton is a former American artistic gymnast. He is the 2008 Olympic silver medalist on high bar, the 2010 World all-around bronze medalist, a two-time Olympian, a two-time U.S. National All-Around Champion, and a 17-time medalist at the U.S. National Championships. At the 2008 Olympics, he also won a bronze medal with his U.S. teammates in the team competition. He also competed at the 2012 Summer Olympics in London, where he qualified for the high bar event final and finished in sixth place. In 2016, he had surgery on his left rotator cuff and as a result was unable to qualify for the 2016 Olympics in Rio de Janeiro.
Jan Smit, Dutch singer and television host births

Jan Smit is a Dutch singer, television host, and actor. Smit mostly sings songs in the Dutch language, in a genre known as Volendam music. In addition to his solo career, in 2015 Smit joined the schlager trio KLUBBB3, and in 2017 The Toppers. As a TV presenter, he has worked on programs like the Beste Zangers and Sterren Muziekfeest op het Plein Since 1999, Smit has been serving as an ambassador for the SOS Children's Villages, and is a member of the board for the football club FC Volendam.
Ricky Nelson, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and actor (b. 1940) deaths

Eric Hilliard Nelson was an American musician, songwriter and actor. From age eight he starred alongside his family in the radio and television series The Adventures of Ozzie and Harriet. In 1957, he began a long and successful career as a popular recording artist. The expression "teen idol" was first coined to describe Nelson, and his fame as both a recording artist and television star also led to a motion picture role co-starring alongside John Wayne, Dean Martin, Walter Brennan, and Angie Dickinson in Howard Hawks's western feature film Rio Bravo (1959). He placed 54 songs on the Billboard Hot 100, and its predecessors, between 1957 and 1973, including "Poor Little Fool" in 1958, which was the first number one song on Billboard magazine's then-newly created Hot 100 chart. He recorded 19 additional top ten hits and was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame on January 21, 1987. In 1996 Nelson was ranked No. 49 on TV Guide's 50 Greatest TV Stars of All Time.
Ben Hannant, Australian rugby league player births

Benjamin Hannant, also known by the nickname of "Polar Bear", is an Australian rugby league footballer who plays as a prop for the Burleigh Bears in the Intrust Super Cup.
Édgar Lugo, Mexican footballer births

Edgar Gerardo Lugo Aranda is a Mexican former professional footballer.
Calvin Zola, Congolese footballer births

Calvin Zola-Makongo, often known simply as Calvin Zola is a Congolese former professional footballer. Born in Kinshasa, Zaire, he began his career as a youth player at Newcastle United. Zola went on to have spells at Tranmere Rovers, Crewe Alexandra, Burton Albion and Aberdeen. His last club was Stevenage, who released him in May 2015 due to injury setbacks.
Sevim Burak, Turkish author and playwright (b. 1931) deaths
Zeliha Sevim Burak was a Turkish author and playwright.
Julio DePaula, Dominican baseball player births

Julio César DePaula is a Dominican professional baseball pitcher who is a free agent.
Craig Gordon, Scottish footballer births

Craig Sinclair Gordon is a Scottish professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for Scottish Premiership club Heart of Midlothian, where he is club captain, and the Scottish national team.
Luke Schenscher, Australian basketball player births
Luke Dean Schenscher is an Australian former professional basketball player. He played four years of college basketball for Georgia Tech before having stints in the NBA with the Chicago Bulls in 2006 and the Portland Trail Blazers in 2007. In 2010, he won an NBL championship with the Perth Wildcats.
The Rocket Summer, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and producer births

The Rocket Summer is the solo-project of Bryce Avary, a multi-instrumentalist, singer-songwriter, and record producer based in Dallas–Fort Worth, Texas. He writes and produces every song on his records, and plays every instrument on them.
Jason Campbell, American football player births

Jason S. Campbell is a former American football quarterback who played in the National Football League (NFL). He was drafted by the Washington Redskins in the first round of the 2005 NFL Draft. He played college football at Auburn. Campbell also played for the Oakland Raiders, Chicago Bears, Cleveland Browns, and Cincinnati Bengals.
Matthew Pavlich, Australian footballer births

Matthew Pavlich is a former professional Australian rules footballer who played for the Fremantle Football Club in the Australian Football League (AFL).
Margaret Simpson, Ghanaian heptathlete births
Margaret Simpson is a Ghanaian heptathlete. She won a bronze medal at the 2005 World Championships, setting several personal bests in the process. Her personal best is 6423 points, achieved in Götzis in May 2005.
Ricky Whittle, English actor births

Richard George Whittle is a British actor. Whittle first came to prominence as a model for Reebok in the early 2000s. He is known in the United Kingdom for his role as Calvin Valentine in the soap opera Hollyoaks. In 2009, he finished second in the BBC reality competition Strictly Come Dancing. In 2012, Whittle crossed over to American television when he booked a recurring role on VH-1's Single Ladies, followed by a recurring role on ABC's Mistresses in 2014. From 2014 to 2016, Whittle appeared in The CW's post-apocalyptic drama The 100 as Lincoln. Whittle starred in the Starz television series American Gods for three seasons.
Jesse Carlson, American baseball player births

Jesse Craig Carlson is an American former professional baseball pitcher for the Toronto Blue Jays.
Matt Cross, American wrestler births

Matthew Capiccioni is an American professional wrestler, better known by his ring names M-Dogg 20, Matt Cross and Son of Havoc. He currently competes on the independent circuit and Major League Wrestling. Cross has also worked for prominent promotions such as Ring of Honor, Lucha Underground, Chikara and the short-lived Wrestling Society X. His main gimmick is that of an adherent of the straight edge lifestyle, a culture which he follows in real life. In 2011, Capiccioni joined the cast of the fifth season of WWE Tough Enough.
Richie McCaw, New Zealand rugby player births

Richard Hugh McCaw is a retired New Zealand professional rugby union player. He captained the national team, the All Blacks, in 110 out of his 148 test matches, and won two Rugby World Cups. He has won the World Rugby player of the year award a joint record three times and was the most capped test rugby player of all time from August 2015 to October 2020. McCaw was awarded World Rugby player of the decade (2011–2020) in 2021. McCaw is also a winner of the New Zealand sportsman of the decade award, the highest sporting honour a sports individual can achieve in New Zealand.
Carsten Schlangen, German runner births

Carsten Schlangen is a German middle distance runner who specialises in the 1500 metres.
Marshall McLuhan, Canadian philosopher and theorist (b. 1911) deaths

Herbert Marshall McLuhan was a Canadian philosopher whose work is among the cornerstones of the study of media theory. He studied at the University of Manitoba and the University of Cambridge. He began his teaching career as a professor of English at several universities in the United States and Canada before moving to the University of Toronto in 1946, where he remained for the rest of his life.
Raoul Walsh, American actor, director, producer, and screenwriter (b. 1887) deaths

Raoul Walsh was an American film director, actor, founding member of the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS), and the brother of silent screen actor George Walsh. He was known for portraying John Wilkes Booth in the silent film The Birth of a Nation (1915) and for directing such films as the widescreen epic The Big Trail (1930) starring John Wayne in his first leading role, The Roaring Twenties starring James Cagney and Humphrey Bogart, High Sierra (1941) starring Ida Lupino and Humphrey Bogart, and White Heat (1949) starring James Cagney and Edmond O'Brien. He directed his last film in 1964. His work has been noted as influences on director such as Rainer Werner Fassbinder, Jack Hill, and Martin Scorsese.
Paul O'Neill, English racing driver births

Paul O'Neill is a British auto racing driver, and the half-brother of English singer Melanie C.
Jeff Waldstreicher, American lawyer and politician births

Jeffrey D. Waldstreicher is an American politician from Maryland and a member of the Democratic Party. He is currently a member of the Maryland Senate, representing District 18 in Montgomery County after serving two terms in the Maryland House of Delegates.
Basil Wolverton, American illustrator (b. 1909) deaths

Basil Wolverton was an American cartoonist and illustrator known for his intricately detailed grotesques of bizarre or misshapen people. Wolverton was described as "Producer of Preposterous Pictures of Peculiar People who Prowl this Perplexing Planet." His many publishers included Marvel Comics and Mad magazine.
Wardy Alfaro, Costa Rican footballer and coach births
Wardy Alfaro Pizarro is a retired Costa Rican football player, who currently is goalkeeper coach at Alajuelense.
Psy, South Korean musician births

Park Jae-sang, known professionally as Psy, is a South Korean singer, rapper, songwriter, and record producer. Psy is known domestically for his humorous videos and stage performances, and internationally for his hit single "Gangnam Style". The song's refrain was entered into The Yale Book of Quotations as one of the most famous quotations of 2012.
Donald Trump Jr., American businessman and son of U.S. President Donald Trump births

Donald John Trump Jr. is an American political activist, businessman, author, and former television presenter. He is the eldest child of Donald Trump, 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021, and his first wife Ivana Trump.

Donald John Trump is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Luís Carreira, Portuguese motorcycle racer (d. 2012) births
Luis Filipe de Sousa Carreira was a Portuguese motorcycle road racer. He died on 15 November 2012 after an accident during qualifying in the 2012 Macau Motorcycle Grand Prix.
Matthew Hoggard, English cricketer births

Matthew James Hoggard, is a former English cricketer, who played international cricket for England cricket team from 2000 to 2008, playing both Test cricket and One Day Internationals. The 6' 2" Hoggard was a right arm fast-medium bowler and right-handed batsman.
Rami Alanko, Finnish ice hockey player births

Rami Alanko is a Finnish former professional ice hockey player.
Toni Kuivasto, Finnish footballer and coach births

Toni Kuivasto is a retired Finnish footballer who last played for Veikkausliigaside FC Haka.
Rob Penders, Dutch footballer births
Rob Penders is a Dutch football coach and a former player who mainly played for NAC Breda during his career. He is the manager of FC Eindhoven. Penders was a defender who made his debut in professional football, being part of the RBC Roosendaal squad in the 1994–95 season. In the season 1999-2000 he joined NAC Breda. He played there for 10 seasons.
Sander Schutgens, Dutch runner births

Sander Schutgens is a Dutch runner.
Joe Abercrombie, English author births

Joseph Edward Abercrombie is a British fantasy writer and film editor. He is the author of The First Law trilogy, as well as other fantasy books in the same setting and a trilogy of young adult novels. His novel Half a King won the 2015 Locus Award for best young adult book.
Mario Aerts, Belgian cyclist births

Mario Aerts is a former professional road bicycle racer, who competed between 1996 and 2011. He competed for three teams; Vlaanderen 2002, Team Telekom and the Lotto team through various sponsorships, competing with that particular team for twelve seasons during his career. During this time he raced in the Tours de France, the Giro d'Italia, and the Vuelta a España. In the 2007 cycling season, he finished in these three major stage races in cycling. He was only the 25th racer in the history of cycling to achieve this.
Tony Kanaan, Brazilian race car driver births

Antoine Rizkallah "Tony" Kanaan Filho, nicknamed TK, is a Brazilian racing driver. He currently competes full-time in the Brazilian Stock Car Pro Series, driving the No. 6 Toyota Corolla E210 for Full Time Bassani and part time for Chip Ganassi Racing, driving the No. 1 Dallara Honda for the 2022 IndyCar Series season.
Ryan Sakoda, Japanese-American wrestler and trainer births

Ryan Keiji Sakoda was a Japanese American professional wrestler. He was best known for his appearances in WWE and later Ultimate Pro Wrestling as a part-time trainer for the wrestlers, as well as working in the independents as Ryan Sakoda.
Shandon Anderson, American basketball player births
Shandon Rodriguez Anderson is an American former professional basketball player who played in the National Basketball Association (NBA) from 1996 to 2006. Growing up in Atlanta, Anderson attended the University of Georgia and played for four teams during his ten-year NBA career after being drafted by the Utah Jazz in 1996: the Jazz, Houston Rockets, New York Knicks, and Miami Heat. He played the shooting guard and small forward positions.
Malcolm Middleton, Scottish singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Malcolm Bruce Middleton (born 31 December 1973) is a Scottish musician and member of indie band Arab Strap. He has also released seven solo studio albums and three albums performing under the pseudonym Human Don't Be Angry.
Curtis Myden, Canadian swimmer births
Curtis Allen Myden is a former breaststroke and medley swimmer from Canada, who competed at three consecutive Summer Olympics in 1992, 1996 and 2000. He won a total number of three medals at the Olympics, all of them bronze. Myden was one of Canada's leading swimmers in the 1990s. He was coached by Canadian coach Deryk Snelling.
Grégory Coupet, French footballer births

Grégory Coupet is a French former professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper. Throughout his playing career, he represented Saint-Étienne, Lyon, Atlético Madrid and Paris Saint-Germain, as well as the France national team. He holds the record for most Ligue 1 titles won (seven), along with Hervé Revelli and Jean-Michel Larqué of Saint-Étienne, as well as Thiago Silva and Marco Verratti of Paris Saint–Germain, and his own club teammates, Juninho and Sidney Govou, of Lyon.
Joey McIntyre, American singer-songwriter and actor births

Joseph Mulrey McIntyre is an American singer-songwriter and actor. He is best known as the youngest member of the pioneering boy band, New Kids on the Block. He has sold over one million records worldwide as a solo artist. He has worked in film, television, and stage, including performing on Broadway.
Scott Manley, Scottish YouTube personality births

Scott Park Manley is a Scottish YouTube personality, gamer, programmer, astrophysicist and DJ. On his YouTube channel, he makes videos discussing space-related topics and news, mainly concerning up-to-date rocket science developments. He also plays space-themed video games, usually Kerbal Space Program, while he explains much of the science involved. He uses his scientific background to help teach science while playing games.
Roberto Clemente, Puerto Rican-American baseball player and Marine (b. 1934) deaths

Roberto Enrique Clemente Walker was a Puerto Rican professional baseball right fielder who played 18 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Pittsburgh Pirates. After his early death, he was posthumously inducted into the National Baseball Hall of Fame in 1973, becoming both the first Caribbean and the first Latin-American player to be enshrined. Because he died at a young age and had such a historic career, the Hall of Fame changed its rules of eligibility. As an alternative to a player having to be retired for five years before eligibility, a player who has been deceased for at least six months is eligible for entry.
Henry Gerber, German-American activist, founded the Society for Human Rights (b. 1892) deaths
Henry Gerber was an early homosexual rights activist in the United States. Inspired by the work of Germany's Magnus Hirschfeld and his Scientific-Humanitarian Committee and by the organisation Bund für Menschenrecht by Friedrich Radszuweit and Karl Schulz, Gerber founded the Society for Human Rights (SHR) in 1924, the nation's first known homosexual organization, and Friendship and Freedom, the first known American homosexual publication. SHR was short-lived, as police arrested several of its members shortly after it incorporated. Although embittered by his experiences, Gerber maintained contacts within the fledgling homophile movement of the 1950s and continued to agitate for the rights of homosexuals. Gerber has been repeatedly recognized for his contributions to the LGBT movement.
The Society for Human Rights was an American LGBT rights organization established in Chicago in 1924. Society founder Henry Gerber was inspired to create it by the work of German doctor Magnus Hirschfeld and the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee and by the organisation Bund für Menschenrecht by Friedrich Radszuweit and Karl Schulz in Berlin. It was the first recognized gay rights organization in the United States, having received a charter from the state of Illinois, and produced the first American publication for homosexuals, Friendship and Freedom. A few months after being chartered, the group ceased to exist in the wake of the arrest of several of the Society's members. Despite its short existence and small size, the Society has been recognized as a precursor to the modern gay liberation movement.
Brent Barry, American basketball player and sportscaster births

Brent Robert Barry, also known by the nickname "Bones", is an American basketball executive, broadcaster and former player. He is the current vice president of basketball operations for the San Antonio Spurs. The shooting guard played professionally in the National Basketball Association (NBA), winning two league championships with the Spurs in 2005 and 2007, and also won the Slam Dunk Contest in 1996. He is the son of former NBA player Rick Barry.
Esteban Loaiza, Mexican baseball player births

Esteban Antonio Loaiza Veyna [lo-EYE-sa] is a Mexican retired professional baseball pitcher. He played in Major League Baseball for the Pittsburgh Pirates, Texas Rangers, Toronto Blue Jays, Chicago White Sox, New York Yankees, Washington Nationals, Oakland Athletics, and Los Angeles Dodgers. Loaiza was the American League's (AL) starting pitcher in the 2003 All-Star Game. That year, he led the AL in strikeouts.
Jorge Alberto da Costa Silva, Brazilian footballer births
Jorge Alberto da Costa Silva known as Jorjão or sometimes Jorgeao is a former Brazilian footballer.
Danny McNamara, English singer-songwriter births

Daniel Anthony McNamara is an English musician, best known as the lead singer of English band Embrace.
Carlos Morales Quintana, Spanish-Danish architect and sailor births

Princess Alexia of Greece and Denmark is a Greek princess and educator. She is the eldest child of Constantine II and Anne-Marie of Denmark, who were King and Queen of Greece from 1964 until the abolition of the monarchy in 1973. She was heiress presumptive to the Greek throne from her birth in 1965 until the birth of her brother Crown Prince Pavlos in 1967.
Bryon Russell, American basketball player births
Bryon Demetrise Russell is an American former professional basketball player. During a National Basketball Association (NBA) career that spanned from 1993 to 2006, he played for the Denver Nuggets, Washington Wizards and Los Angeles Lakers and was a key member of the Utah Jazz, helping them reach back-to-back NBA finals appearances in 1997 and 1998. Russell also played for the Hollywood Fame and Long Beach Breakers of the American Basketball Association (ABA). He finished his career with the Los Angeles Lightning of the International Basketball League (IBA), winning a championship in 2009.
Cyril Scott, English composer, writer, and poet (b. 1879) deaths

Cyril Meir Scott was an English composer, writer, poet, and occultist. He created around four hundred musical compositions including piano, violin, cello concertos, symphonies, and operas. He also wrote around 20 pamphlets and books on occult topics and natural health.
Gerry Dee, Canadian comedian, actor, and screenwriter births

Gerry Dee is a Canadian actor, stand-up comedian, game show host, director, producer, and writer. He is currently the host of Family Feud Canada. He placed third on the fifth season of Last Comic Standing, and he wrote and starred in the sitcom Mr. D, which aired on CBC Television.
Junot Diaz, Dominican-born American novelist, short story writer, and essayist births

Junot Díaz is a Dominican-American writer, creative writing professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and was fiction editor at Boston Review. He also serves on the board of advisers for Freedom University, a volunteer organization in Georgia that provides post-secondary instruction to undocumented immigrants. Central to Díaz's work is the immigrant experience, particularly the Latino immigrant experience.
George Lewis, American clarinet player and composer (b. 1900) deaths

George Lewis was an American jazz clarinetist who achieved his highest profile in the later decades of his life.
Paul McGregor, Australian rugby league player and coach births
Paul McGregor is an Australian professional rugby league coach who was until August 2020, the head coach of the St. George Illawarra Dragons in the NRL, and a former professional rugby league footballer who played as a centre in the 1990s and 2000s.
Tony Dorigo, Australian-English footballer and sportscaster births
Anthony Robert Dorigo is a former professional footballer, sports pundit and co-commentator.
Julie Doucet, Canadian cartoonist and author births

Julie Doucet is a Canadian underground cartoonist and artist, best known for her autobiographical works such as Dirty Plotte and My New York Diary. Her work is concerned with such topics as "sex, violence, menstruation and male/female issues."
Gong Li, Chinese actress births

Gong Li is a Chinese actress. She starred in three of the four Chinese-language films that were nominated for the Academy Award for Best International Feature Film.
Laxman Sivaramakrishnan, Indian cricketer births
Laxman Sivaramakrishnan, popularly known as "Siva" and LS, is a former Indian cricketer and current cricket commentator. During his playing career, he was a right arm leg-spinner. Sivaramakrishnan began his commentary career in a test match between India and Bangladesh on 12 November 2000. He also serves as one of the players’ representatives on the International Cricket Council’s cricket committee.
Nicholas Sparks, American author, screenwriter, and producer births

Nicholas Charles Sparks is an American novelist, screenwriter, and philanthropist. He has published twenty-three novels and two non-fiction books, some of which have been New York Times bestsellers, with over 115 million copies sold worldwide in more than 50 languages.
Winston Benjamin, Antiguan cricketer births
Winston Keithroy Matthew Benjamin is a former Antiguan cricketer who played 21 Tests and 85 One Day Internationals for the West Indies. He is also the father of world champion athlete Rai Benjamin.
Michael McDonald, American comedian, actor, and director births

Michael James McDonald is an American stand-up comedian, actor, screenwriter, and director. He is best known for starring in the sketch comedy show MADtv. McDonald joined the show during the fourth season (1998) and remained in the cast until the end of the thirteenth and penultimate season, having become the longest-tenured cast member.
Bobby Byrne, American baseball and soccer player (b. 1884) deaths
Robert Matthew Byrne was a third baseman in Major League Baseball. From 1907 through 1917, he played for the St. Louis Cardinals (1907–1909), Pittsburgh Pirates (1909–1913), Philadelphia Phillies (1913–1917) and Chicago White Sox (1917). Byrne batted and threw right-handed. He was born in St. Louis, Missouri.
Ólafur Thors, Icelandic lawyer and politician, 8th Prime Minister of Iceland (b. 1892) deaths

Ólafur Tryggvason Thors was an Icelandic politician of the Independence Party, who served five times as prime minister of Iceland.

The prime minister of Iceland is Iceland's head of government. The prime minister is appointed formally by the president and exercises executive authority along with the cabinet subject to parliamentary support.
Henry Maitland Wilson, English field marshal (b. 1881) deaths

Field Marshal Henry Maitland Wilson, 1st Baron Wilson,, also known as Jumbo Wilson, was a senior British Army officer of the 20th century. He saw active service in the Second Boer War and then during the First World War on the Somme and at Passchendaele. During the Second World War he served as General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-in-C) British Troops in Egypt, in which role he launched Operation Compass, attacking Italian forces with considerable success, in December 1940. He went on to be Military Governor of Cyrenaica in February 1941, commanding a Commonwealth expeditionary force to Greece in April 1941 and General Officer Commanding (GOC) British Forces in Palestine and Trans-Jordan in May 1941.
Scott Ian, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Scott Ian is an American musician, best known as the rhythm guitarist and co-founder of the thrash metal band Anthrax. Ian is the guitarist and a founding member of the crossover thrash band Stormtroopers of Death for which he is also the lyricist. He has hosted The Rock Show on VH1 and has appeared on VH1's I Love the... series, Heavy: The Story of Metal, and SuperGroup. Ian is also the rhythm guitarist for the metal band the Damned Things, and played with experimental band Mr. Bungle for seven reunion shows in 2020.
Tyrone Corbin, American basketball player and coach births

Tyrone Kennedy Corbin is an American former basketball player and assistant coach for the Charlotte Hornets. He was first appointed the assistant coach of the Phoenix Suns, then was named the Utah Jazz’s head coach, on February 10, 2011 following the resignation of longtime coach Jerry Sloan. He was also the brief interim head coach of the Sacramento Kings in the 2014–15 season before being replaced by George Karl. Prior to that, Corbin played 16 seasons in the NBA.
Chris Hallam, English-Welsh swimmer and wheelchair racer (d. 2013) births
Christopher "Chris" Alexander Hallam, MBE was a Welsh Paralympian and wheelchair athlete. He competed at four Paralympic Games; Stoke Mandeville, England (1984), Seoul, South Korea (1988), Barcelona, Spain (1992) and Atlanta, United States (1996), as well as two Commonwealth Games; Auckland, New Zealand (1990) and Victoria, British Columbia (1994).
Jennifer Higdon, American composer births

Jennifer Elaine Higdon is an American composer of contemporary classical music. She has received many awards, including the 2010 Pulitzer Prize for Music for her Violin Concerto and three Grammy Award for Best Contemporary Classical Composition for her Percussion Concerto in 2010, Viola Concerto in 2018, and Harp Concerto in 2020. Elected a Member of the American Philosophical Society in 2019, she was a professor of composition at the Curtis Institute of Music from 1994 to 2021.
Rick Aguilera, American baseball player and coach births

Richard Warren Aguilera is an American former professional baseball player and coach. He played in Major League Baseball as a right-handed pitcher from 1985 to 2000. Aguilera won a world championship as a member of the New York Mets in 1986, then won a second world championship as a member of the Minnesota Twins in 1991. He also played for the Boston Red Sox and the Chicago Cubs. In 2008, Aguilera was inducted into the Minnesota Twins Hall of Fame.
Jeremy Heywood, English economist and civil servant (d. 2018) births

Jeremy John Heywood, Baron Heywood of Whitehall, was a British civil servant who served as Cabinet Secretary to David Cameron and Theresa May from 2012 to 2018 and Head of the Home Civil Service from 2014 to 2018. He served as the Principal Private Secretary to Prime Ministers Tony Blair and Gordon Brown from 1999 to 2003 and 2008 to 2010. He also served as Downing Street Chief of Staff and the first Downing Street Permanent Secretary. After he was diagnosed with lung cancer, he took a leave of absence from June 2018, and retired on health grounds on 24 October 2018, receiving a life peerage; he died two weeks later on 4 November 2018.
Nina Li Chi, Hong Kong actress births
Nina Li Chi is a retired Hong Kong actress. She is married to actor Jet Li.
Steve Bruce, English footballer and manager births

Stephen Roger Bruce is an English professional football manager and former player who played as a centre-back. He most recently managed West Bromwich Albion.
Liveris Andritsos, Greek basketball player births
Liveris Andritsos is a retired Greek professional basketball player and coach. At a height of 2.02 m tall, he could play at both the small forward and power forward positions.
Val Kilmer, American actor births

Val Edward Kilmer is an American actor. Originally a stage actor, Kilmer found fame after appearances in comedy films, starting with Top Secret! (1984) and Real Genius (1985), as well as the military action film Top Gun (1986) and the fantasy film Willow (1988).
Phill Kline, American lawyer and politician, Kansas Attorney General births
Phillip D. Kline is a former American attorney who served as a Kansas state legislator, district attorney of Johnson County, and Kansas Attorney General. Kline, a member of the Republican Party, lost re-election as attorney general to Democratic challenger Paul J. Morrison in 2006. Kline was appointed by the Republican County Central Committee to fill the vacancy left Morrison's election as Kansas Attorney General, becoming district attorney of Johnson County on the day he left office as attorney general and essentially switching jobs with Morrison. Kline then ran for a full term as district attorney, but was defeated in the 2008 Republican primary.

The Attorney General of Kansas is a statewide elected official responsible for providing legal services to the state government of Kansas.
Baron Waqa, Nauruan composer and politician, 14th President of Nauru births

Baron Divavesi Waqa is a Nauruan politician who was the 14th President of Nauru from 11 June 2013 until 27 August 2019. He previously served as Minister of Education from 2004 to 2007.

The president of Nauru is elected by Parliament from among its members, and is both the head of state and the head of government of Nauru. Nauru's unicameral Parliament has 19 members, with an electoral term of 3 years. Political parties only play a minor role in Nauru politics, and there have often been periods of instability in the Presidential office. Shifting allegiances among a small number of individuals can lead to frequent changes in the makeup of the government of the day, including the presidential position itself.
Paul Westerberg, American singer-songwriter and guitarist births

Paul Harold Westerberg is an American musician, best known as the lead singer, guitarist, and songwriter for the Replacements. Following the breakup of the Replacements, Westerberg launched a solo career that saw him release three albums on major record labels.
Geoff Marsh, Australian cricketer and coach births

Geoffrey Robert Marsh is a former Australian cricketer, coach and selector. He played 50 Test matches and 117 One Day Internationals for Australia as an opening batsman. As the coach of Australia he was in charge when Australia won the 1999 Cricket World Cup in England. He later coached Zimbabwe (2001–2004) and Sri Lanka (2011–12).
Bebe Neuwirth, American actress and dancer births

Beatrice "Bebe" Jane Neuwirth is an American actress, singer, and dancer. On television, she played Dr. Lilith Sternin, Frasier Crane's wife, on both the TV sitcom Cheers and its spin-off Frasier. The role won her two Emmy Awards. In 2005, Neuwirth was cast as Bureau Chief/ADA Tracey Kibre in the short-lived Law & Order courtroom drama series, Law & Order: Trial by Jury on NBC that ran for 12 episodes. In film, she portrayed Nora Shepherd in the original Jumanji (1995) and Jumanji: The Next Level (2019).
Robert Goodwill, English farmer and politician births

Sir Robert Goodwill is a British Conservative Party politician and farmer serving as Member of Parliament (MP) for Scarborough and Whitby since 2005. He was previously a Member of the European Parliament (MEP) for Yorkshire and the Humber. Goodwill served in Theresa May’s government as Minister of State at the Home Office, the Department for Education and the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs.
Helma Knorscheidt, German shot putter births

Helma Knorscheidt is an East German shot putter.
Steve Rude, American author and illustrator births

Steve Rude is an American comics artist. He is best known as the co-creator of Nexus.
Alex Salmond, Scottish economist and politician, 4th First Minister of Scotland births

Alexander Elliot Anderson Salmond is a Scottish politician and economist who served as First Minister of Scotland from 2007 to 2014. A prominent figure on the Scottish nationalist movement, he has served as leader of the Alba Party since 2021. Salmond was leader of the Scottish National Party (SNP), on two occasions, from 1990 to 2000 and from 2004 to 2014. He served as the party's depute leader from 1987 to 1990.

The first minister of Scotland is the leader of the Scottish Government and keeper of the Great Seal of Scotland. The first minister chairs the Scottish Cabinet and is primarily responsible for the formulation, development and presentation of Scottish Government policy. Additional functions of the first minister include promoting and representing Scotland in an official capacity, at home and abroad.
Hermann Tilke, German racing driver, architect and engineer births

Hermann Tilke is a German engineer, racing driver and circuit designer, who has designed numerous Formula One motor racing circuits.
Jane Badler, American actress births

Jane Badler is an American-Australian actress and singer. She is known for her role as Diana, the main antagonist in NBC's science fiction series V between 1983 and 1985. Badler also appeared in ABC's version of V in 2011, again playing an alien named Diana, who this time is the mother of the series' chief antagonist, Anna. Badler has also become an established nightclub singer in Australia, where she lives, and has released three albums.
Albert Plesman, Dutch businessman, founded KLM (b. 1889) deaths

Albert Plesman was a Dutch pioneer in aviation and the first administrator and later director of the KLM, the oldest airline in the world still operating under its original name. Until his death, he was in charge as CEO for over 35 years and was also on the board of the Dutch airline, which was to become one of the most important airlines in the world under his leadership.
KLM Royal Dutch Airlines, legally Koninklijke Luchtvaart Maatschappij N.V., is the flag carrier airline of the Netherlands. KLM is headquartered in Amstelveen, with its hub at nearby Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. It is part of the Air France–KLM group and a member of the SkyTeam airline alliance. Founded in 1919, KLM is the oldest operating airline in the world, and has 35,488 employees with a fleet of 110 as of 2021. KLM operates scheduled passenger and cargo services to 145 destinations.
Vaughan Jones, New Zealand mathematician and academic (d. 2020) births

Sir Vaughan Frederick Randal Jones was a New Zealand mathematician known for his work on von Neumann algebras and knot polynomials. He was awarded a Fields Medal in 1990.
Jean-Pierre Rives, French rugby player, painter, and sculptor births

Jean-Pierre Rives is a French former rugby union player and visual artist. "A cult figure in France", according to the BBC, he came to epitomise the team's spirit and "ultra-committed, guts-and-glory style of play". He won 59 caps for France – 34 of them as captain – and was inducted into the International Rugby Hall of Fame. After retiring from the sport, Rives concentrated entirely on his art. He is both a painter and a sculptor, and exhibiting regularly at prominent public venues all over the globe. Rives was awarded the Order of the Legion of Honor and the National Order of Merit by the government of France.
Tom Hamilton, American bass player and songwriter births

Thomas William Hamilton is an American musician who serves as the bassist for the hard rock band Aerosmith. He has regularly co-written songs for Aerosmith, including two of the band's biggest successes: "Sweet Emotion" (1975) and "Janie's Got a Gun" (1989). Hamilton occasionally plays guitar, sings backing vocals and on rare occasions, lead vocals. He was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 2001 as a member of Aerosmith.
Kenny Roberts, American motorcycle racer births

Kenneth Leroy Roberts is an American former professional motorcycle racer and racing team owner. In 1978, he became the first American to win a Grand Prix motorcycle racing world championship. He was also a two-time winner of the A.M.A. Grand National Championship. Roberts is one of only four riders in American Motorcyclist Association (AMA) racing history to win the AMA Grand Slam, representing Grand National wins at a mile, half-mile, short-track, TT Steeplechase and road race events.
Murtaza Hasan Chandpuri, Indian Muslim scholar (b. 1868) deaths

Murtaza Hasan Chandpuri (1868-1951) was an Indian Sunni Islamic scholar. He was a disciple of Ashraf Ali Thanwi in the Chishti order of Sufism.
Bob Gilder, American golfer births
Robert Bryan Gilder is an American professional golfer. He won six tournaments on the PGA Tour and currently plays on the Champions Tour, where he has ten wins since joining in 2001.
Inge Helten, German sprinter births
Ingeborg "Inge" Helten is a former athlete from West Germany, who competed mainly in the 100 metres. She was born in Westum, Sinzig, Rhineland-Palatinate.
Cheryl Womack, American businesswoman births

Verna Cheryl Womack is an entrepreneur who founded Kansas City, Missouri-based VCW and National Association of Independent Truckers, Inc. which became a $100 million a year business selling insurance to independent truckers before selling the companies to private equity investors Clayton, Dubilier & Rice. She become a major philanthropist in the Kansas City area. Among her donations was $2 million to the University of Kansas to build Arrocha Ballpark which is named for her father Demostenes Arrocha.
Charles Koechlin, French composer and educator (b. 1867) deaths

Charles-Louis-Eugène Koechlin, commonly known as Charles Koechlin, was a French composer, teacher and musicologist. He was a political radical all his life and a passionate enthusiast for such diverse things as medieval music, The Jungle Book of Rudyard Kipling, Johann Sebastian Bach, film stars, traveling, stereoscopic photography and socialism. He once said: "The artist needs an ivory tower, not as an escape from the world, but as a place where he can view the world and be himself. This tower is for the artist like a lighthouse shining out across the world." Among his better known works is Les Heures persanes, a set of piano pieces based on the novel Vers Ispahan by Pierre Loti and The Seven Stars Symphony, a 7 movement symphony where each movement is themed around a different film star who were popular at the time of the piece's writing (1933).
Ellen Datlow, American anthologist and author births

Ellen Datlow is an American science fiction, fantasy, and horror editor and anthologist. She is a winner of the World Fantasy Award and the Bram Stoker Award.
Flora Gomes, Bissau-Guinean filmmaker births
Flora Gomes is a Bissau-Guinean film director. He was born in Cadique, Guinea-Bissau on 31 December 1949 and after high school in Cuba, he decided to study film at the Instituto Cubano del Arte y la Industria Cinematográficos in Havana.
Susan Shwartz, American author births
Susan Shwartz is an American author.
Rıza Tevfik Bölükbaşı, Turkish philosopher, poet, and politician (b. 1869) deaths

Rıza Tevfik Bey was an Ottoman and later Turkish philosopher, poet, politician of liberal signature and a community leader of the late-19th-century and early-20th-century. A polyglot, he is most remembered in Turkey for being one of the four Ottoman signatories of the disastrous Treaty of Sèvres, for which reason he was included in 1923 among the 150 personae non gratae of Turkey, and he spent 20 years in exile until he was given amnesty by Turkey in 1943.
Raimond Valgre, Estonian pianist and composer (b. 1913) deaths
Raimond Valgre was an Estonian composer and musician, whose songs have become some of the most well known in Estonia. During World War II, Valgre was conscripted into the Red Army and was a member of the orchestra for the 8th Estonian Rifle Corps. It is believed that as a result of his service on the Eastern Front Valgre suffered from alcoholism. His music was banned in 1948 by the Soviet authorities. Raimond Valgre died in an accident on 31 December 1949.
Joe Dallesandro, American actor births

Joseph Angelo D'Allesandro III is an American actor and Warhol superstar. Having also crossed over into mainstream roles such as mobster Lucky Luciano in the film The Cotton Club, Dallesandro was a sex symbol of gay subculture in the 1960s and 1970s, and of several American underground films.
Sandy Jardine, Scottish footballer and manager (d. 2014) births

William "Sandy" Pullar Jardine was a Scottish professional footballer who played for Rangers, Hearts and represented Scotland. He played over 1000 professional games and twice won the Scottish Football Writers Association Player of the Year award. He won several honours with Rangers, including two domestic trebles in 1976 and 1978, and was part of the Rangers team that won the European Cup Winners' Cup in 1972. He won 38 caps for Scotland and played in the 1974 and 1978 World Cups. Jardine was also co-manager of Hearts with Alex MacDonald and later worked for Rangers.
Donna Summer, American singer-songwriter (d. 2012) births

LaDonna Adrian Gaines, known professionally as Donna Summer, was an American singer and songwriter. She gained prominence during the disco era of the 1970s and became known as the "Queen of Disco", while her music gained a global following.
Malcolm Campbell, English racing driver and journalist (b. 1885) deaths

Major Sir Malcolm Campbell was a British racing motorist and motoring journalist. He gained the world speed record on land and on water at various times, using vehicles called Blue Bird, including a 1921 Grand Prix Sunbeam. His son, Donald Campbell, carried on the family tradition by holding both land speed and water speed records.
Burton Cummings, Canadian singer-songwriter and keyboard player births

Burton Lorne Cummings is a Canadian musician, singer, and songwriter. He is best known for leading The Guess Who during that band's most successful period from 1965 to 1975, and for a lengthy solo career.
Rita Lee, Brazilian singer-songwriter, guitarist, and actress births

Rita Lee Jones is a Brazilian rock singer, composer and writer. She is a former member of the Brazilian band Os Mutantes and is a popular figure in Brazilian entertainment, where she is also known for being an animal rights activist and a vegan. She has sold more than 60 million albums worldwide. Her autobiography Rita Lee: Uma Autobiografia was the best-selling non-fiction book of 2017 in Brazil.
Tim Matheson, American actor, director, and producer births

Tim Matheson is an American actor and director. Some of his best-known acting roles include the title character of the 1960s animated Jonny Quest TV series, Eric "Otter" Stratton in the 1978 comedy film National Lampoon's Animal House, and the recurring role of Vice President John Hoynes in the 2000s NBC drama The West Wing, which earned him two Primetime Emmy Award nominations for Outstanding Guest Actor in a Drama Series.
Roy Greenslade, English journalist and academic births

Roy Greenslade is a British author and freelance journalist, and a former professor of journalism. He worked in the UK newspaper industry from the 1960s onwards. As a media commentator, he wrote a daily blog from 2006 to 2018 for The Guardian and a column for London's Evening Standard from 2006 to 2016. Under a pseudonym, Greenslade also wrote for the Sinn Féin newspaper An Phoblacht during the late 1980s whilst also working on Fleet Street. In 2021, it was reported in The Times newspaper, citing an article by Greenslade in the British Journalism Review, that he supported the bombing campaign of the Provisional IRA. Following this revelation, Greenslade resigned as Honorary Visiting Professor at City, University of London.
Bryan Hamilton, Northern Irish footballer and coach births
Bryan Hamilton is a Northern Irish former professional football player and manager. He gained 50 caps for Northern Ireland between 1969 and 1980, and later managed the national team for four years. He later became Technical Director at Antigua Barracuda F.C., which no longer exists, having been dissolved in 2014.
Raphael Kaplinsky, South African international development academic births
Raphael Kaplinsky is professorial fellow, Science Policy Research Unit, and emeritus professorial fellow, Institute of Development Studies, University of Sussex.
Pius Ncube, Zimbabwean archbishop births

Pius Alick Mvundla Ncube served as the Roman Catholic Archbishop of Bulawayo, Zimbabwe, until he resigned on 11 September 2007. Widely known for his human rights advocacy, Ncube was an outspoken critic of former President Robert Mugabe while he was in office.
Lyudmila Pakhomova, Russian ice dancer (d. 1986) births

Lyudmila Alekseyevna Pakhomova was an ice dancer who competed for the Soviet Union. With her husband Alexandr Gorshkov, she was the 1976 Olympic champion, one of the oldest female figure skating Olympic champions.
Cliff Richey, American tennis player births

George Clifford Richey Jr. is an American former amateur and professional tennis player who was active during the 1960s and 1970s. Richey achieved a highest singles ranking of World No. 6 and reached at least the quarterfinal stage of the singles event at all four Grand Slam tournaments.
Eric Robson, Scottish journalist and author births
Eric Bell Robson is a television broadcaster, author and documentary film maker who has lived for most of his life in Cumbria, where he has a sheep farm. For many years he was the main presenter of Brass Tacks.
Nigel Rudd, English businessman, founded Williams Holdings births
Sir Nigel Rudd, is a Fellow of the Institute of Chartered Accountants. In 1982, he founded Williams Holdings, a company which went on to become one of the largest industrial holding companies in the United Kingdom until its demerger in November 2000, creating Chubb plc and Kidde plc. He became the non-executive chairman of Kidde plc until December 2003. He currently presides as chairman of BBA Aviation PLC.

Williams Holdings was a major British conglomerate. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange, and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
Tim Stevens, English bishop births

Timothy John Stevens, is a retired British Anglican bishop. He was Bishop of Dunwich from 1995 to 1999 and was Bishop of Leicester from 1999 to 2015. From 2003 to 2015, he was a member of the House of Lords as a Lord Spiritual and served as Convenor of the Lords Spiritual from 2009 to 2015.
Diane von Fürstenberg, Belgian-American fashion designer births

Diane von Fürstenberg is a Belgian fashion designer best known for her wrap dress. She initially rose to prominence in 1969 when she married into the German princely House of Fürstenberg, as the wife of Prince Egon von Fürstenberg. Following their separation in 1972 and divorce in 1983, she has continued to use his family name.
Connie Willis, American author births

Constance Elaine Trimmer Willis, commonly known as Connie Willis, is an American science fiction and fantasy writer. She has won eleven Hugo Awards and seven Nebula Awards for particular works—more major SF awards than any other writer—most recently the "Best Novel" Hugo and Nebula Awards for Blackout/All Clear (2010). She was inducted by the Science Fiction Hall of Fame in 2009 and the Science Fiction Writers of America named her its 28th SFWA Grand Master in 2011.
Taylor Hackford, American director, producer, and screenwriter births

Taylor Edwin Hackford is an American film director and former president of the Directors Guild of America. He won the Academy Award for Best Live Action Short Film for Teenage Father (1979). Hackford went on to direct a number of highly regarded feature films, most notably An Officer and a Gentleman (1982) and Ray (2004), the latter of which saw him nominated for the Academy Award for Best Director and the Academy Award for Best Picture.
John Denver, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and actor (d. 1997) births

Henry John Deutschendorf Jr., known professionally as John Denver, was an American singer-songwriter, guitarist, actor, activist, and humanitarian whose greatest commercial success was as a solo singer. After traveling and living in numerous locations while growing up in his military family, Denver began his music career with folk music groups during the late 1960s. Starting in the 1970s, he was one of the most popular acoustic artists of the decade and one of its best-selling artists. By 1974, he was one of America's best-selling performers; AllMusic has called Denver "among the most beloved entertainers of his era".
Ben Kingsley, English actor births

Sir Ben Kingsley is an English actor. He has received various accolades throughout his career spanning five decades, including an Academy Award, a British Academy Film Award, a Grammy Award, and two Golden Globe Awards. Kingsley was appointed Knight Bachelor in 2002 for services to the British film industry. In 2010, he was awarded a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame. In 2013, he received the Britannia Award for Worldwide Contribution to Filmed Entertainment.
Pete Quaife, English bass player, author, and artist (d. 2010) births

Peter Alexander Greenlaw Quaife was an English musician, artist and author. He was a founding member and the original bass guitarist for the Kinks, from 1963 until 1969. He also sang backing vocals on some of their records.
Andy Summers, English guitarist, songwriter, and producer births

Andrew James Summers, is an English guitarist who was a member of the rock band the Police. He was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame as a band member in 2003. Summers has recorded solo albums, collaborated with other musicians, composed film scores, and exhibited his photography in galleries.
Alex Ferguson, Scottish footballer and manager births

Sir Alexander Chapman Ferguson is a Scottish former football manager and player, best known for managing Manchester United from 1986 to 2013. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest football managers of all time and has won more trophies than any other manager in the history of football. Ferguson is often credited for valuing youth during his time with Manchester United, particularly in the 1990s with the "Class of '92", who contributed to making the club one of the richest and most successful in the world.
Sarah Miles, English actress births

Sarah Miles is an English actress. She is known for her roles in films The Servant (1963), Blowup (1966), Ryan's Daughter (1970), The Man Who Loved Cat Dancing (1973), White Mischief (1987) and Hope and Glory (1987). For her performance in Ryan's Daughter, Miles received a nomination for the Academy Award for Best Actress.
Mani Neumeier, German drummer births

Mani Neumeier is a German rock musician, free-jazz drummer, artist, and frontman of the German Krautrock-band Guru Guru.
Willye White, American sprinter and long jumper (d. 2007) births

Willye Brown White was an American track and field athlete who took part in five Olympics from 1956 to 1972. She was America's best female long jumper of the time and also competed in the 100 meters sprint. White was a Tennessee State University Tigerbelle under Coach Ed Temple. She was African-American.
Rosalind Cash, American singer and actress (d. 1995) births

Rosalind Theresa Cash was an American actress. Her best-known film role is in the 1971 science-fiction film The Omega Man. Cash also had another notable role as Mary Mae Ward in ABC's General Hospital, a role she portrayed from 1994 until her death in 1995.
Atje Keulen-Deelstra, Dutch speed skater (d. 2013) births

Atje Keulen-Deelstra was a Dutch speed skater, who was a four-time World Allround Champion between the age of 32 and 36.
Avram Hershko, Hungarian-Israeli biochemist and physician, Nobel Prize laureate births

Avram Hershko is a Hungarian-Israeli biochemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2004.

The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation, and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences on proposal of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry which consists of five members elected by the Academy. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death.
Anthony Hopkins, Welsh actor, director, and composer births

Sir Philip Anthony Hopkins is a Welsh actor, director, and producer. One of Britain's most recognisable and prolific actors, he is known for his performances on the screen and stage. Hopkins has received many accolades throughout his career, including two Academy Awards, three British Academy Film Awards, a British Academy Television Award, two Primetime Emmy Awards and a Laurence Olivier Award. He has also received an honorary Golden Globe Award and the BAFTA Fellowship for lifetime achievement from the British Academy of Film and Television Arts. In 1993, he was knighted by Queen Elizabeth II for his services to the arts, and in 2003, he received a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame for his achievements in the motion picture industry.
Barry Hughes, Welsh footballer and manager (d. 2019) births

Barry Hughes was a Welsh professional football player and manager, active primarily in the Netherlands. He played as a defender.
Tess Jaray, Austrian-English painter and educator births

Tess Jaray is a British painter and printmaker. She taught at The Slade School of Fine Art, UCL from 1968 until 1999. Over the last twenty years Jaray has completed a succession of major public art projects. She was made an Honorary Fellow of RIBA in 1995 and a Royal Academician in 2010. Tess Jaray is represented by Karsten Schubert, London.
Miguel de Unamuno, Spanish philosopher, author, and poet (b. 1864) deaths

Miguel de Unamuno y Jugo was a Spanish essayist, novelist, poet, playwright, philosopher, professor of Greek and Classics, and later rector at the University of Salamanca.
Salman of Saudi Arabia, King of Saudi Arabia births

Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud is King of Saudi Arabia, reigning since 2015, and served as Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia from 2015 to 2022. The 25th son of King Abdulaziz, the founder of Saudi Arabia, he assumed the throne on 23 January 2015. Prior to his accession, he was Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia from 16 June 2012 to 23 January 2015. Salman is the 3rd oldest living head of state and the oldest living monarch.
Ameer Muhammad Akram Awan, Indian author, poet, and scholar (d. 2017) births
Ameer Muhammad Akram Awan was an Islamic scholar and spiritual leader of the Naqshbandia Owaisiah order of Sufism. He belonged to Awan tribe. As a mufassir, he authored four exegeses (tafsir) of the Qur'an, including Asrar at-Tanzeel. Awan was dean of the Siqarah Education System and patron of the magazine Al-Murshid and of the Al-Falah Foundation.
Cornelia Clapp, American marine biologist (b. 1849) deaths

Cornelia Maria Clapp was an American zoologist and educator, specializing in marine biology. She earned the first Ph.D. in biology awarded to a woman in the United States from Syracuse University in 1889, and she would earn a second doctoral degree from the University of Chicago in 1896. Clapp was the first female researcher employed at the Marine Biological Laboratory, as well as its first female trustee. She was rated one of the top zoologists in the United States in 1903, and her name was starred in the first five editions of American Men of Science.
Edward Bunker, American author, screenwriter, and actor (d. 2005) births

Edward Heward Bunker was an American author of crime fiction, a screenwriter, convicted felon and an actor. He wrote numerous books, some of which have been adapted into films. He wrote the scripts for—and acted in—Straight Time (1978), Runaway Train (1985) and Animal Factory (2000). He also played a minor role in Reservoir Dogs (1992).
Don James, American football player and coach (d. 2013) births

Donald Earl James was an American football player and coach. He served as the head coach at Kent State University from 1971 to 1974 and at the University of Washington from 1975 to 1992, compiling a career college football record of 178–76–3 (.698).
Felix Rexhausen, German journalist and author (d. 1992) births

Felix Rexhausen was a German journalist, editor and author. As a journalist, he wrote for Kölner Stadt-Anzeiger, Westdeutscher Rundfunk, and the magazines Die Zeit and Der Spiegel.
Bob Shaw, Northern Irish journalist and author (d. 1996) births

Robert Shaw was a science fiction writer and fan from Northern Ireland, noted for his originality and wit. He won the Hugo Award for Best Fan Writer in 1979 and 1980. His short story "Light of Other Days" was a Hugo Award nominee in 1967, as was his novel The Ragged Astronauts in 1987.
Odetta, American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and actress (d. 2008) births

Odetta Holmes, known as Odetta, was an American singer, actress, guitarist, lyricist, and a civil rights activist, often referred to as "The Voice of the Civil Rights Movement". Her musical repertoire consisted largely of American folk music, blues, jazz, and spirituals. An important figure in the American folk music revival of the 1950s and 1960s, she influenced many of the key figures of the folk-revival of that time, including Bob Dylan, Joan Baez, Mavis Staples, and Janis Joplin. In 2011 Time magazine included her recording of "Take This Hammer" on its list of the 100 Greatest Popular Songs, stating that "Rosa Parks was her No. 1 fan, and Martin Luther King Jr. called her the queen of American folk music."
Jaime Escalante, Bolivian-American educator (d. 2010) births

Jaime Alfonso Escalante Gutiérrez was a Bolivian-American educator known for teaching students calculus from 1974 to 1991 at Garfield High School in East Los Angeles. Escalante was the subject of the 1988 film Stand and Deliver, in which he is portrayed by Edward James Olmos.
Mies Bouwman, Dutch television host (d. 2018) births

Maria Antoinette "Mies" Bouwman was a Dutch television presenter.
Peter May, English cricketer (d. 1994) births
Peter Barker Howard May was an English cricketer who played for Surrey County Cricket Club, Cambridge University and England. Already a cricketing prodigy during his school days, May played his entire cricket career as an amateur, and was regarded by many players and fans as England's finest batsman in the post-war era.
Ross Barbour, American pop singer (d. 2011) births
Ross Edwin Barbour was an American singer with the vocal quartet The Four Freshmen.
Tatyana Shmyga, Russian actress and singer (d. 2011) births

Tatyana Ivanovna Shmyga was a Soviet and Russian operetta/musical theatre performer. She went on to act in films as well. She was a People's Artist of the USSR (1978).
Siné, French cartoonist (d. 2016) births

Maurice Sinet, known professionally as Siné, was a French political cartoonist. His work is noted for its anti-capitalism, anti-clericalism, anti-colonialism, anti-semitism, and anarchism.
Veijo Meri, Finnish author and translator (d. 2015) births

Veijo Väinö Valvo Meri was a Finnish writer. Much of his work focuses on war and its absurdity. The work is anti-war and has dark humor.
Valerie Pearl, English historian and academic (d. 2016) births
Valerie Louise Pearl was a British historian who was noted for her work on the English Civil War. She was the second President of New Hall, Cambridge.
Billy Snedden, Australian lawyer and politician, 17th Attorney-General for Australia (d. 1987) births

Sir Billy Mackie Snedden, was an Australian politician who served as the leader of the Liberal Party from 1972 to 1975. He was also a cabinet minister from 1964 to 1972, and Speaker of the House of Representatives from 1976 to 1983.

The Attorney-General for Australia is the First Law Officer of the Crown in right of the Commonwealth of Australia, chief law officer of the Commonwealth of Australia and a minister of state. The attorney-general is usually a member of the Federal Cabinet, but need not be. Under the Constitution, they are appointed by the Governor-General on the advice of the Prime Minister, and serve at the Governor-General's pleasure. In practice, the attorney-general is a party politician and their tenure is determined by political factors. By convention, but not constitutional requirement, the attorney-general is a lawyer by training.
Irina Korschunow, German author and screenwriter (d. 2013) births
Irina Korschunow was a German writer. Her oeuvre comprises short stories, novels theatrical works and film scripts. Born in Stendal, she started her career as a journalist and writer for children's books and young adult literature but focused predominantly on writing novels in her later years since about 1983. She was also a translator.
Sri Lal Sukla, Indian author (d. 2011) births

Shrilal Shukla was a Hindi writer, notable for his satire. He worked as a PCS officer for the state government of Uttar Pradesh, later inducted into the IAS. He has written over 25 books, including Raag Darbari, Makaan, Sooni Ghaati Ka Sooraj, Pehla Padaav and Bisrampur Ka Sant.
Daphne Oram, British composer and electronic musician (d. 2003) births

Daphne Blake Oram was a British composer and electronic musician. She was one of the first British composers to produce electronic sound, and was an early practitioner of musique concrète in the UK. As a co-founder of the BBC Radiophonic Workshop, she was central to the development of British electronic music. Her uncredited scoring work on the 1961 film The Innocents helped to pioneer the electronic soundtrack.
Taylor Mead, American actor and poet (d. 2013) births
Taylor Mead was an American writer, actor and performer. Mead appeared in several of Andy Warhol's underground films filmed at Warhol's Factory, including Tarzan and Jane Regained... Sort of (1963) and Taylor Mead's Ass (1964).
Giannis Dalianidis, Greek actor, director, and screenwriter (d. 2010) births
Giannis Dalianidis was a Greek film director.
Tomás Balduino, Brazilian bishop (d. 2014) births

Tomás Balduíno, O.P. was a diocesan bishop of the Catholic Church in Brazil.
Halina Czerny-Stefańska, Polish pianist and educator (d. 2001) births

Halina Czerny-Stefańska was a Polish pianist.
Luis Zuloaga, Venezuelan baseball player (d. 2013) births

Luis Zuloaga was a Venezuelan professional baseball pitcher.
Boies Penrose, American lawyer and politician (b. 1860) deaths

Boies Penrose was an American lawyer and Republican politician from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Rex Allen, American actor and singer-songwriter (d. 1999) births

Rex Elvie Allen, known as "the Arizona Cowboy", was an American film and television actor, singer and songwriter; he was also the narrator of many Disney nature and Western productions. For his contributions to the film industry, Allen received a motion pictures star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame in 1975, located at 6821 Hollywood Boulevard.
Tommy Byrne, American baseball player, coach, and politician (d. 2007) births

Thomas Joseph Byrne was an American left-handed starting pitcher in Major League Baseball who played for four American League teams from 1943 through 1957, primarily the New York Yankees. He also played for the St. Louis Browns (1951–52), Chicago White Sox (1953) and Washington Senators (1953). Byrne batted and threw left-handed.
Carmen Contreras-Bozak, Puerto Rican-American soldier (d. 2017) births

Tech4 Carmen Contreras-Bozak, was the first Puerto Rican woman to serve in the U.S. Women's Army Corps (WAC) where she served as an interpreter and in numerous administrative positions.
Ray Graves, American football player and coach (d. 2015) births

Samuel Ray Graves was an American college and professional football player and college football coach. He was a native of Tennessee and a graduate of the University of Tennessee, where he was the starting center and team captain for the Volunteers under head coach Robert Neyland. After playing in the National Football League for three seasons, he returned to Tennessee to serve as an assistant football coach, then left for a longer stint as an assistant at Georgia Tech under head coach Bobby Dodd. He was the head football coach at the University of Florida from 1960 until 1969, where he led the Gators to their most successful decade in program history up to that point. While at Florida, he recruited and coached Heisman Trophy-winning quarterback Steve Spurrier, who often praised Graves as a role model and mentor during his own successful coaching career. Graves also served as Florida's athletic director from 1960 until his retirement in 1979.
Evelyn Knight, American singer (d. 2007) births

Evelyn Knight was an American singer of the 1940s and 1950s. Damon Runyon, in one of his newspaper columns, described Knight as "a lissome blonde lassie with a gentle little voice and a face mother would not mind having brought home to her."
Wilfrid Noyce, English mountaineer and author (d. 1962) births

Cuthbert Wilfrid Francis Noyce was an English mountaineer and author. He was a member of the 1953 British Expedition that made the first ascent of Mount Everest.
Sam Ragan, American journalist, author, and poet (d. 1996) births
Samuel Talmadge Ragan was an American journalist, author, poet, and arts advocate from North Carolina.
Mary Logan Reddick, American neuroembryologist (d. 1966) births

Mary Logan Reddick was an American neuroembryologist who earned her PhD from Radcliffe College, Harvard University in 1944. She was a full professor, first at Morehouse College, and then at the University of Atlanta from 1953 to her death. Her doctoral dissertation was on the study of chick embryos, and she went on to do research with time-lapse microscopy in tissue cultures.
John Frost, Indian-English general (d. 1993) births

Major-General John Dutton Frost, was an airborne officer of the British Army best known for being the leader of the small group of British airborne troops that actually arrived at Arnhem bridge during the Battle of Arnhem in Operation Market Garden, in World War II. He was one of the first to join the newly formed Parachute Regiment and served with distinction in many wartime airborne operations, such as in North Africa and Sicily and Italy, until his injury and subsequent capture at Arnhem. He retired from the army in 1968 to become a beef cattle farmer in West Sussex.
Dal Stivens, Australian soldier and author (d. 1997) births
Dallas George "Dal" Stivens was an Australian writer who produced six novels and eight collections of short stories between 1936, when The Tramp and Other Stories was published, and 1976, when his last collection The Unicorn and Other Tales was released.
Carl Dudley, American director, producer, and screenwriter (d. 1973) births
Carl Ward Dudley (1910–1973) was an American film director and producer. He was best known for directing and producing short travelogues.
Enrique Maier, Spanish tennis player (d. 1981) births

Enrique 'Bubi' Maier was a male Spanish tennis player who was mainly active in the 1930s.
Archibald Hoxsey, American pilot (b. 1884) deaths

Archibald Hoxsey was an American aviator who worked for the Wright brothers.
John Moisant, American pilot and engineer (b. 1868) deaths

John Bevins Moisant, known as the "King of Aviators," was an American aviator, aeronautical engineer, flight instructor, businessman, and revolutionary. He was the first pilot to conduct passenger flights over a city (Paris), as well as across the English Channel, from Paris to London. He co-founded an eponymous flying circus, the Moisant International Aviators.
Jonah Jones, American trumpet player and saxophonist (d. 2000) births

Jonah Jones was a jazz trumpeter who created concise versions of jazz and swing and jazz standards that appealed to a mass audience. In the jazz community, he is known for his work with Stuff Smith. He was sometimes referred to as "King Louis II", a reference to Louis Armstrong. Jones started playing alto saxophone at the age of 12 in the Booker T. Washington Community Center band in Louisville, Kentucky, before quickly transitioning to trumpet, where he excelled.
Spencer Trask, American financier and philanthropist (b. 1844) deaths

Spencer Trask was an American financier, philanthropist, and venture capitalist. Beginning in the 1870s, Trask began investing and supporting entrepreneurs, including Thomas Edison's invention of the electric light bulb and his electricity network. In 1896 he reorganized The New York Times, becoming its majority shareholder and chairman.
Simon Wiesenthal, Ukrainian-Austrian Nazi hunter and author (d. 2005) births

Simon Wiesenthal was a Jewish Austrian Holocaust survivor, Nazi hunter, and writer. He studied architecture and was living in Lwów at the outbreak of World War II. He survived the Janowska concentration camp, the Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp, the Gross-Rosen concentration camp, a death march to Chemnitz, Buchenwald, and the Mauthausen concentration camp.
A Nazi hunter is an individual who tracks down and gathers information on alleged former Nazis, or SS members, and Nazi collaborators who were involved in the Holocaust, typically for use at trial on charges of war crimes and crimes against humanity. Prominent Nazi hunters include Simon Wiesenthal, Tuviah Friedman, Serge Klarsfeld, Beate Klarsfeld, Ian Sayer, Yaron Svoray, Elliot Welles, and Efraim Zuroff.
Helen Dodson Prince, American astronomer and academic (d. 2002) births

Helen Dodson Prince was an American astronomer who pioneered work in solar flares at the University of Michigan.
Jule Styne, English-American composer (d. 1994) births

Jule Styne was an English-American songwriter and composer best known for a series of Broadway musicals, including several famous frequently-revived shows that also became successful films: Gypsy, Gentlemen Prefer Blondes, and Funny Girl.
William Heynes, English engineer (d. 1989) births
William Munger Heynes CBE, born in Leamington Spa, was an English automotive engineer.
Lionel Daunais, Canadian singer-songwriter (d. 1982) births

Noël Ferdinand Lionel Daunais, was a French Canadian baritone and composer.
Roy Goodall, English footballer (d. 1982) births
Frederick Roy Goodall was a professional footballer, who played for Huddersfield Town for 16 years and played 25 games for England, 12 as captain.
Karl-August Fagerholm, Finnish politician, valtioneuvos, the Speaker of the Parliament and the Prime Minister of Finland (d. 1984) births

Karl-August Fagerholm was Speaker of Parliament and three times Prime Minister of Finland. Fagerholm became one of the leading politicians of the Social Democrats after the armistice in the Continuation War. As a Scandinavia-oriented Swedish-speaking Finn, he was believed to be more to the taste of the Soviet Union's leadership than his predecessor, Väinö Tanner. Fagerholm's postwar career was, however, marked by fierce opposition from both the Soviet Union and the Communist Party of Finland. He narrowly lost the presidential election to Urho Kekkonen in 1956.
Valtioneuvos is a Finnish title of honor awarded by the President of Finland to elder statesmen. It is one of two titles in the highest class of State of Finland honors. A tax on the titles of 48,400 euros or 12,100 euros must be paid by whoever proposes the title to a holder.

The speaker of the Parliament of Finland, along with two deputy speakers, is elected by Parliament during the first plenary session each year. Speakers are chosen for a year at a time. In addition to their preparing the work in plenary sessions the speakers also play a key role in Parliament's international co-operation, which includes visits by speakers and international delegations as well as participation in numerous interparliamentary organisations.

The prime minister of Finland is the leader of the Finnish Government. The prime minister and their cabinet exercise executive authority in the state. The prime minister is formally ranked third in the protocol after the president of Finland and the speaker of the Parliament. Finland's first prime minister, Pehr Evind Svinhufvud, was appointed on 27 November 1917, just a few days before the country declared independence from Russia.
Nikos Ploumpidis, Greek educator and politician (d. 1954) births
Nikos Ploumpidis was in the leading cadre of the Greek Communist Party during the Second World War and a famous member of the wartime anti-Nazi resistance.
Silvestre Revueltas, Mexican violinist, composer, and conductor (d. 1940) births

Silvestre Revueltas Sánchez was a Mexican composer of classical music, a violinist and a conductor.
Thomas Joannes Stieltjes, Dutch mathematician and academic (b. 1856) deaths

Thomas Joannes Stieltjes was a Dutch mathematician. He was a pioneer in the field of moment problems and contributed to the study of continued fractions. The Thomas Stieltjes Institute for Mathematics at Leiden University, dissolved in 2011, was named after him, as is the Riemann–Stieltjes integral.
Samuel Ajayi Crowther, Nigerian bishop and linguist (b. 1809) deaths

Samuel Ajayi Crowther, was a Nigerian linguist, clergyman, and the first African Anglican bishop of West Africa. Born in Osogun, he and his family were captured by slave raiders when he was about twelve years old. This took place during the Yoruba civil wars, notably the Owu wars of (1821–1829), where his village Osogun was sacked. Ajayi was later on resold to Portuguese slave dealers, where he was put on board to be transported to the New World through the Atlantic.
Pancha Carrasco, Costa Rican soldier (b. 1826) deaths

Pancha Carrasco, born Francisca Carrasco Jiménez, was Costa Rica's first woman in the military. Carrasco is most famous for joining the defending forces at the Battle of Rivas in 1856 with a rifle and a pocketful of bullets. The strength and determination she showed there made her a symbol of national pride and she was later honored with a Costa Rican postage stamp, a Coast Guard vessel, and the creation of the "Pancha Carrasco Police Women's Excellence Award".
Ion Creangă, Romanian author and educator (b. 1837) deaths

Ion Creangă was a Moldavian, later Romanian writer, raconteur and schoolteacher. A main figure in 19th-century Romanian literature, he is best known for his Childhood Memories volume, his novellas and short stories, and his many anecdotes. Creangă's main contribution to fantasy and children's literature includes narratives structured around eponymous protagonists, as well as fairy tales indebted to conventional forms. Widely seen as masterpieces of the Romanian language and local humor, his writings occupy the middle ground between a collection of folkloric sources and an original contribution to a literary realism of rural inspiration. They are accompanied by a set of contributions to erotic literature, collectively known as his "corrosives".
George Kerferd, English-Australian politician, 10th Premier of Victoria (b. 1831) deaths

George Briscoe Kerferd, Australian colonial politician, was the 10th Premier of Victoria.

The premier of Victoria is the head of government in the Australian state of Victoria. The premier is appointed by the governor of Victoria, and is the leader of the political party able to secure a majority in the Victorian Legislative Assembly.
Samson Raphael Hirsch, German rabbi and scholar (b. 1808) deaths

Samson Raphael Hirsch was a German Orthodox rabbi best known as the intellectual founder of the Torah im Derech Eretz school of contemporary Orthodox Judaism. Occasionally termed neo-Orthodoxy, his philosophy, together with that of Azriel Hildesheimer, has had a considerable influence on the development of Orthodox Judaism.
Princess Victoria Adelaide of Schleswig-Holstein (d. 1970) births

Princess Victoria Adelaide of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg was Duchess of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as the consort of Duke Charles Edward from their marriage on 11 October 1905 until his abdication on 14 November 1918. Victoria Adelaide is the maternal grandmother of Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden. She was a niece of German Empress Augusta Victoria.
Bobby Byrne, American baseball and soccer player (d. 1964) births
Robert Matthew Byrne was a third baseman in Major League Baseball. From 1907 through 1917, he played for the St. Louis Cardinals (1907–1909), Pittsburgh Pirates (1909–1913), Philadelphia Phillies (1913–1917) and Chicago White Sox (1917). Byrne batted and threw right-handed. He was born in St. Louis, Missouri.
Mihály Fekete, Hungarian actor, screenwriter, and film director (d. 1960) births

Mihály Fekete was a Hungarian actor, screenwriter and film director.
Max Pechstein, German painter and academic (d. 1955) births

Hermann Max Pechstein was a German expressionist painter and printmaker and a member of the Die Brücke group. He fought on the Western Front during World War I and his art was classified as Degenerate Art by the Nazis. More than 300 paintings were removed from German Museums during the Nazi era.
Fred Beebe, American baseball player and coach (d. 1957) births

Frederick Leonard Beebe was a professional baseball player. He played for the Chicago Cubs, St. Louis Cardinals, Cincinnati Reds, Philadelphia Phillies and Cleveland Indians.
George Marshall, American general and politician, 50th United States Secretary of State, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1959) births

George Catlett Marshall Jr. was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the US Army under Presidents Franklin D. Roosevelt and Harry S. Truman, then served as Secretary of State and Secretary of Defense under Truman. Winston Churchill lauded Marshall as the "organizer of victory" for his leadership of the Allied victory in World War II. After the war, he spent a frustrating year trying and failing to avoid the impending Chinese Civil War. As Secretary of State, Marshall advocated a U.S. economic and political commitment to post-war European recovery, including the Marshall Plan that bore his name. In recognition of this work, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1953.

The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Cabinet, and ranks the first in the U.S. presidential line of succession among Cabinet secretaries.

The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiology or Medicine and Literature. Since March 1901, it has been awarded annually to those who have "done the most or the best work for fraternity between nations, for the abolition or reduction of standing armies and for the holding and promotion of peace congresses".
Elizabeth Arden, Canadian businesswoman, founded Elizabeth Arden, Inc. (d. 1966) births

Elizabeth Arden was a Canadian-American businesswoman who founded what is now Elizabeth Arden, Inc., and built a cosmetics empire in the United States. By 1929, she owned 150 salons in Europe and the United States. Her 1,000 products were being sold in 22 countries. She was the sole owner, and at the peak of her career, she was one of the wealthiest women in the world.

Elizabeth Arden, Inc. is a major American cosmetics, skin care and fragrance company founded by Elizabeth Arden. As of September 7, 2016, the company is a wholly owned subsidiary of Revlon, Inc.
Horacio Quiroga, Uruguayan-Argentinian author, poet, and playwright (d. 1937) births

Horacio Silvestre Quiroga Forteza was a Uruguayan playwright, poet, and short story writer.
Lawrence Beesley, English journalist and author (d. 1967) births
Lawrence Beesley was an English science teacher, journalist and author who was a survivor of the sinking of RMS Titanic.
Gustave Courbet, French-Swiss painter and sculptor (b. 1819) deaths

Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and the Romanticism of the previous generation of visual artists. His independence set an example that was important to later artists, such as the Impressionists and the Cubists. Courbet occupies an important place in 19th-century French painting as an innovator and as an artist willing to make bold social statements through his work.
Catherine Labouré, French nun and saint (b. 1806) deaths

Catherine Labouré was a French member of the Daughters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul and a Marian visionary. She is believed to have relayed the request from the Blessed Virgin Mary to create the famous Miraculous Medal of Our Lady of Graces worn by millions of people around the world. Labouré spent forty years caring for the aged and infirm. For this, she is called the patroness of seniors.
Julius Meier, American businessman and politician, 20th Governor of Oregon (d. 1937) births

Julius L. Meier was an American businessman, civic leader, and politician in the state of Oregon. The son of the Meier & Frank department store founder, he would become a lawyer before entering the family business in Portland. Politically an independent, Meier served a single term as the 20th Governor of Oregon from 1931–1935. He is the only independent to be elected Governor of Oregon.

The governor of Oregon is the head of government of Oregon and serves as the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The title of governor was also applied to the office of Oregon's chief executive during the provisional and U.S. territorial governments.
Konstantin Konik, Estonian surgeon and politician, 19th Estonian Minister of Education (d. 1936) births

Konstantin Konik was an Estonian politician and surgeon who served as a member of the Estonian Salvation Committee.
The Minister of Education and Research is the senior minister at the Ministry of Education and Research in the Estonian Government. The Minister is responsible for administration and development of Estonian educational system as well as for administration and funding of research and development activities on national level.
Fred Marriott, American race car driver (d. 1956) births

Fred Marriott was an American race car driver. In 1906, he set the world land speed record at 127.659 mph (205.5 km/h) at the Daytona Beach Road Course, while driving the Stanley Land Speed Record Car. This garnered Stanley Motor Carriage Company the Dewar Trophy. A crew of four accompanied the car to Daytona, Marriott was chosen to be driver because he was the only bachelor.
Aleksis Kivi, Finnish author and playwright (b. 1834) deaths

Aleksis Kivi was a Finnish author who wrote the first significant novel in the Finnish language, Seitsemän veljestä in 1870. He is also known for his 1864 play Heath Cobblers. Although Kivi was among the very earliest authors of prose and lyrics in Finnish, he is still considered one of the greatest.
Henri Matisse, French painter and sculptor (d. 1954) births

Henri Émile Benoît Matisse was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known primarily as a painter. Matisse is commonly regarded, along with Pablo Picasso, as one of the artists who best helped to define the revolutionary developments in the visual arts throughout the opening decades of the twentieth century, responsible for significant developments in painting and sculpture.
Robert Grant Aitken, American astronomer and academic (d. 1951) births

Robert Grant Aitken was an American astronomer.
Joseph S. Cullinan, American businessman, co-founded Texaco (d. 1937) births

Joseph Stephen Cullinan was a U.S. oil industrialist. Although he was a native of Pennsylvania, his lifetime business endeavors would help shape the early phase of the oil industry in Texas. He founded The Texas Company, which would eventually be known as Texaco Incorporated.
Texaco, Inc. is an American oil brand owned and operated by Chevron Corporation. Its flagship product is its fuel "Texaco with Techron". It also owned the Havoline motor oil brand. Texaco was an independent company until its refining operations merged into Chevron, at which time most of its station franchises were divested to Shell plc through its American division.
King Kelly, American baseball player and manager (d. 1894) births

Michael Joseph "King" Kelly, also commonly known as "$10,000 Kelly", was an American outfielder, catcher, and manager in various professional American baseball leagues including the National League, International Association, Players' League, and the American Association. He spent the majority of his 16-season playing career with the Chicago White Stockings and the Boston Beaneaters. Kelly was a player-manager three times in his career – in 1887 for the Beaneaters, in 1890 leading the Boston Reds to the pennant in the only season of the Players' League's existence, and in 1891 for the Cincinnati Kelly's Killers – before his retirement in 1893. He is also often credited with helping to popularize various strategies as a player such as the hit and run, the hook slide, and the catcher's practice of backing up first base.
Giovanni Pascoli, Italian poet and scholar (d. 1912) births

Giovanni Placido Agostino Pascoli was an Italian poet, classical scholar and an emblematic figure of Italian literature in the late nineteenth century. Alongside Gabriele D'Annunzio, he was one of the greatest Italian decadent poets.
Henry Carter Adams, American economist and academic (d. 1921) births

Henry Carter Adams was a U.S. economist and Professor of Political Economy and finance at the University of Michigan.
Giovanni Boldini, Italian painter (d. 1931) births

Giovanni Boldini was an Italian genre and portrait painter who lived and worked in Paris for most of his career. According to a 1933 article in Time magazine, he was known as the "Master of Swish" because of his flowing style of painting.
Émile Loubet, French lawyer and politician, 7th President of France (d. 1929) births

Émile François Loubet was the 45th Prime Minister of France from February to December 1892 and later President of France from 1899 to 1906.

The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic, is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency is the supreme magistracy of the country, the position is the highest office in France. The powers, functions and duties of prior presidential offices, in addition to their relation with the prime minister and Government of France, have over time differed with the various constitutional documents since the Second Republic.
Queen Kapiolani of Hawaii (d. 1899) births

Kapiʻolani was the queen of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi as the consort of Mōʻī (king) Kalākaua, who reigned from 1874 to 1891 until Mōʻī's death when she became known as the Dowager Queen Kapiʻolani. Deeply interested in the health and welfare of Native Hawaiians, Kapiʻolani established the Kapiʻolani Home for Girls, for the education of the daughters of residents of the Kalaupapa Leprosy Settlement, and the Kapiʻolani Maternity Home, where Hawaiian mothers and newborns could receive care.
Hugh Nelson Scottish-Australian politician, 11th Premier of Queensland (d. 1906) births

Sir Hugh Muir Nelson, was Premier of Queensland from 1893 to 1898.

The premier of Queensland is the head of government in the Australian state of Queensland.
Isma'il Pasha, Egyptian ruler (d. 1895) births

Isma'il Pasha, was the Khedive of Egypt and conqueror of Sudan from 1863 to 1879, when he was removed at the behest of Great Britain. Sharing the ambitious outlook of his grandfather, Muhammad Ali Pasha, he greatly modernized Egypt and Sudan during his reign, investing heavily in industrial and economic development, urbanization, and the expansion of the country's boundaries in Africa.
Alexander Smith, Scottish poet and critic (d. 1867) births

Alexander Smith was a Scottish poet, labelled as one of the Spasmodic School, and essayist.
Jean-Pierre Duport, French cellist (b. 1741) deaths
Jean-Pierre Duport was a cellist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Along with his brother, Jean-Louis Duport, he was active in the musical life of France and Germany. Jean-Pierre was the son of a dancing master, and a student of the founder of the French school of cello playing Martin Berteau (1700?–1771).
George Meade, American general and engineer (d. 1872) births

George Gordon Meade was a United States Army officer and civil engineer best known for decisively defeating Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. He previously fought with distinction in the Second Seminole War and the Mexican–American War. During the Civil War, he served as a Union general, rising from command of a brigade to that of the Army of the Potomac. Earlier in his career, he was an engineer and was involved in the coastal construction of several lighthouses.
Marie d'Agoult, German-French historian and author (d. 1876) births

Marie Cathérine Sophie, Comtesse d'Agoult, was a Franco-German romantic author and historian, known also by her pen name, Daniel Stern.
Jean-François Marmontel, French historian and author (b. 1723) deaths

Jean-François Marmontel was a French historian, writer and a member of the Encyclopédistes movement.
Friedrich Robert Faehlmann, Estonian physician, philologist, and academic (d. 1850) births

Friedrich Robert Faehlmann (Fählmann) was an Estonian writer, medical doctor and philologist active in Livonia, Russian Empire. He was a co-founder of the Learned Estonian Society at the University of Dorpat and its chairman (1843-1850).
Johann Spurzheim, German-American physician and phrenologist (d. 1832) births

Johann Gaspar Spurzheim was a German physician who became one of the chief proponents of phrenology, which was developed c. 1800 by Franz Joseph Gall (1758–1828).
Richard Montgomery, American general (b. 1738) deaths

Richard Montgomery was an Irish soldier who first served in the British Army. He later became a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War, and he is most famous for leading the unsuccessful 1775 invasion of Quebec.
Pierre-Charles Villeneuve, French admiral (d. 1806) births

Pierre-Charles-Jean-Baptiste-Silvestre de Villeneuve was a French naval officer during the Napoleonic Wars. He was in command of the French and the Spanish fleets that were defeated by Nelson at the Battle of Trafalgar.
Charles III Philip, Elector Palatine (b. 1661) deaths

Charles III Philip was Elector Palatine, Count of Palatinate-Neuburg, and Duke of Jülich and Berg from 1716 to 1742. Until 1728 he was also Count of Megen.
Gottfried August Bürger, German poet and academic (d. 1794) births

Gottfried August Bürger was a German poet. His ballads were very popular in Germany. His most noted ballad, Lenore, found an audience beyond readers of the German language in an English and Russian adaptation and a French translation.
Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, English general and politician, 3rd Governor-General of India (d. 1805) births

Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis,, styled Viscount Brome between 1753 and 1762 and known as the Earl Cornwallis between 1762 and 1792, was a British Army general and official. In the United States and the United Kingdom, he is best remembered as one of the leading British generals in the American War of Independence. His surrender in 1781 to a combined American and French force at the siege of Yorktown ended significant hostilities in North America. He later served as a civil and military governor in Ireland, where he helped bring about the Act of Union; and in India, where he helped enact the Cornwallis Code and the Permanent Settlement.

The Governor-General of India was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom and after Indian independence in 1947, the representative of the British monarch. The office was created in 1773, with the title of Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William. The officer had direct control only over Fort William but supervised other East India Company officials in India. Complete authority over all of British territory in the Indian subcontinent was granted in 1833, and the official came to be known as the "Governor-General of India".
Carlo Gimach, Maltese architect, engineer and poet (b. 1651) deaths
Carlo Gimach was a Maltese architect, engineer and poet who was active in the late 17th and early 18th centuries. Throughout his career, he worked in Malta, Portugal and Rome, and he is mostly known for designing Palazzo Carneiro in Valletta, renovating the Monastery of Arouca in Portugal, and restoring the Basilica of St. Anastasia in Rome. He is known to have written a number of poems and other literary works, but these are all lost with the exception of one cantata which he wrote in 1714.
Charles Edward Stuart, Scottish claimant to the throne of England (d. 1788) births

Charles Edward Louis John Sylvester Maria Casimir Stuart was the elder son of James Francis Edward Stuart, grandson of James II and VII, and the Stuart claimant to the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland from 1766 as Charles III. During his lifetime, he was also known as "the Young Pretender" and "the Young Chevalier"; in popular memory, he is known as Bonnie Prince Charlie.
John Flamsteed, English astronomer and academic (b. 1646) deaths

John Flamsteed was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, Catalogus Britannicus, and a star atlas called Atlas Coelestis, both published posthumously. He also made the first recorded observations of Uranus, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a star, and he laid the foundation stone for the Royal Greenwich Observatory.
Arima Yoriyuki, Japanese mathematician and educator (d. 1783) births

Arima Yoriyuki was a Japanese mathematician of the Edo period. He was the lord of Kurume Domain.
Catherine of Braganza (b. 1638) deaths

Catherine of Braganza was Queen of England, Scotland and Ireland during her marriage to King Charles II, which lasted from 21 May 1662 until his death on 6 February 1685. She was the daughter of King John IV of Portugal, who became the first king from the House of Braganza in 1640 after overthrowing the 60–year rule of the Spanish Habsburgs over Portugal and restoring the Portuguese throne which had first been created in 1143. Catherine served as regent of Portugal during the absence of her brother Peter II in 1701 and during 1704–1705, after her return to her homeland as a widow.
Robert Boyle, Anglo-Irish chemist and physicist (b. 1627) deaths

Robert Boyle was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. He is best known for Boyle's law, which describes the inversely proportional relationship between the absolute pressure and volume of a gas, if the temperature is kept constant within a closed system. Among his works, The Sceptical Chymist is seen as a cornerstone book in the field of chemistry. He was a devout and pious Anglican and is noted for his writings in theology.
Dudley North, English merchant and economist (b. 1641) deaths

Sir Dudley North was an English merchant, politician, economist and writer on free trade. He was also a member of the North family.
Giovanni Alfonso Borelli, Italian physiologist and physicist (b. 1608) deaths

Giovanni Alfonso Borelli was a Renaissance Italian physiologist, physicist, and mathematician. He contributed to the modern principle of scientific investigation by continuing Galileo's practice of testing hypotheses against observation. Trained in mathematics, Borelli also made extensive studies of Jupiter's moons, the mechanics of animal locomotion and, in microscopy, of the constituents of blood. He also used microscopy to investigate the stomatal movement of plants, and undertook studies in medicine and geology. During his career, he enjoyed the patronage of Queen Christina of Sweden.
Oliver St John, English judge and politician, Chief Justice of the Common Pleas (b. 1598) deaths

Sir Oliver St John was an English judge and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1640-53. He supported the Parliamentary cause in the English Civil War.

The chief justice of the Common Pleas was the head of the Court of Common Pleas, also known as the Common Bench or Common Place, which was the second-highest common law court in the English legal system until 1875, when it, along with the other two common law courts and the equity and probate courts, became part of the High Court of Justice. As such, the chief justice of the Common Pleas was one of the highest judicial officials in England, behind only the Lord High Chancellor and the Lord Chief Justice of England, who headed the Queen's Bench.
Herman Boerhaave, Dutch botanist and physician (d. 1738) births

Herman Boerhaave was a Dutch botanist, chemist, Christian humanist, and physician of European fame. He is regarded as the founder of clinical teaching and of the modern academic hospital and is sometimes referred to as "the father of physiology," along with Venetian physician Santorio Santorio (1561–1636). Boerhaave introduced the quantitative approach into medicine, along with his pupil Albrecht von Haller (1708–1777) and is best known for demonstrating the relation of symptoms to lesions. He was the first to isolate the chemical urea from urine. He was the first physician to put thermometer measurements to clinical practice. His motto was Simplex sigillum veri: 'Simplicity is the sign of the truth'. He is often hailed as the "Dutch Hippocrates".
Janusz Radziwiłł, Polish–Lithuanian politician (b. 1612) deaths

Prince Janusz Radziwiłł, also known as Janusz the Second or Janusz the Younger was a noble and magnate in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Throughout his life he occupied a number of posts in the state administration, including that of Court Chamberlain of Lithuania, Field Hetman of Lithuania and Grand Hetman of Lithuania. He was also a voivode of Vilna Voivodeship, as well as a starost of Samogitia, Kamieniec, Kazimierz and Sejwy. He was a protector of the Protestant religion in Lithuania and sponsor of many Protestant schools and churches.
Dorgon, Chinese emperor (b. 1612) deaths

Dorgon, was a Manchu prince and regent of the early Qing dynasty. Born in the House of Aisin-Gioro as the 14th son of Nurhaci, Dorgon started his career in military campaigns against the Ming dynasty, Mongols and Koreans during the reign of his eighth brother, Hong Taiji, who succeeded their father.
Christian, Count of Waldeck-Wildungen, German count (b. 1585) deaths

Count Christian of Waldeck-Wildungen, German: Christian Graf von Waldeck-Wildungen, official titles: Graf zu Waldeck und Pyrmont, was since 1588 Count of Waldeck-Eisenberg and after the division with his brother in 1607 Count of Waldeck-Wildungen. He founded the new cadet branch of Waldeck-Wildungen and is the progenitor of the princes of Waldeck and Pyrmont.
Ludolph van Ceulen, German-Dutch mathematician and academic (b. 1540) deaths

Ludolph van Ceulen was a German-Dutch mathematician from Hildesheim. He emigrated to the Netherlands.
Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba, Spanish general and politician, 24th Governor of the Duchy of Milan (d. 1645) births

Gonzalo Andrés Domingo Fernández de Córdoba was one of the main Spanish military leaders during the Eighty Years' War,[?] Thirty Years' War, and the War of the Mantuan Succession.
The governor of Milan ruled the Duchy of Milan as a representative of the Holy Roman Emperor (1535–1556), the King of Spain (1556–1706) and the Archduke of Austria (1706–1796) and (1799–1800). The first governor was appointed after the death of the last duke of the House of Sforza, Francesco II.
Thomas Erastus, Swiss physician and theologian (b. 1524) deaths

Thomas Erastus was a Swiss physician and Calvinist theologian. He wrote 100 theses in which he argued that the sins committed by Christians should be punished by the State, and that the Church should not withhold sacraments as a form of punishment. They were published in 1589, after his death, with the title Explicatio gravissimae quaestionis. His name was later applied to Erastianism.
Pierino Belli, Italian commander and jurist (b. 1502) deaths
Pierino Belli was an Italian soldier and jurist.
Emperor Go-Yōzei of Japan, (d. 1617) births

Emperor Go-Yōzei was the 107th Emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. Go-Yōzei's reign spanned the years 1586 through to his abdication in 1611, corresponding to the transition between the Azuchi–Momoyama period and the Edo period.
Shimazu Tadayoshi, Japanese daimyō (b. 1493) deaths

Shimazu Tadayoshi was a daimyō of Satsuma Province during Japan's Sengoku period. He was born into the Mimasaka Shimazu family (伊作島津家), which was part of the Shimazu clan, but after his father Shimazu Yoshihisa died, his mother married Shimazu Unkyu of another branch family, the Soshū (相州家). Tadayoshi thus came to represent two families within the larger Shimazu clan.
Simon Forman, English occultist and astrologer (d. 1611) births

Simon Forman was an Elizabethan astrologer, occultist and herbalist active in London during the reigns of Queen Elizabeth I and James I of England. His reputation, however, was severely tarnished after his death when he was implicated in the plot to kill Sir Thomas Overbury. Astrologers continued to revere him, while writers from Ben Jonson to Nathaniel Hawthorne came to characterize him as either a fool or an evil magician in league with the Devil.
Henry I, Duke of Guise (d. 1588) births

Henry I, Prince of Joinville, Duke of Guise, Count of Eu, sometimes called Le Balafré ('Scarface'), was the eldest son of Francis, Duke of Guise, and Anna d'Este. His maternal grandparents were Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara, and Renée of France. Through his maternal grandfather, he was a descendant of Lucrezia Borgia and Pope Alexander VI.
John Radcliffe, English politician (d. 1568) births
Sir John Radcliffe, was the son of Robert Radcliffe, 1st Earl of Sussex, and his third wife, Mary Arundell.
William Skeffington, English-Irish politician, Lord Deputy of Ireland (b. 1465) deaths

Sir William Skeffington was an English knight who served as Lord Deputy of Ireland.
The Lord Deputy was the representative of the monarch and head of the Irish executive under English rule, during the Lordship of Ireland and then the Kingdom of Ireland. He deputised prior to 1523 for the Viceroy of Ireland. The plural form is Lords Deputy.
Andreas Vesalius, Belgian anatomist, physician, and author (d. 1564) births

Andreas Vesalius was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem. Vesalius is often referred to as the founder of modern human anatomy. He was born in Brussels, which was then part of the Habsburg Netherlands. He was a professor at the University of Padua (1537–1542) and later became Imperial physician at the court of Emperor Charles V.
Bianca Maria Sforza, Holy Roman Empress (b. 1472) deaths

Bianca Maria Sforza was Queen of Germany and Italy, and Empress of the Holy Roman Empire as the third spouse of Maximilian I. She was the eldest legitimate daughter of Duke Galeazzo Maria Sforza of Milan by his second wife, Bona of Savoy.
Beatrice of Portugal, Duchess of Savoy (d. 1538) births

Infanta Beatrice of Portugal was a Portuguese princess by birth and Duchess of Savoy by marriage to Charles III, Duke of Savoy. She was the ruling countess of Asti from 1531 to 1538.
Eleonora Gonzaga, Duchess of Urbino (d. 1570) births

Eleonora Gonzaga, Duchess of Urbino was Duchess and sometime regent of Urbino by marriage to Francesco Maria I della Rovere, duke of Urbino.
Jacques Cartier, French navigator and explorer (d. 1557) births

Jacques Cartier was a French-Breton maritime explorer for France. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, which he named "The Country of Canadas" after the Iroquoian names for the two big settlements he saw at Stadacona and at Hochelaga.
Richard Neville, 5th Earl of Salisbury, English politician, Lord Chancellor of the United Kingdom (b. 1400) deaths

Richard Neville, 5th Earl of Salisbury was an English nobleman and magnate based in northern England who became a key supporter of the House of York during the early years of the Wars of the Roses. He was the father of Richard Neville, 16th Earl of Warwick, the "Kingmaker".

The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. The lord chancellor is appointed by the sovereign on the advice of the prime minister. Prior to their Union into the Kingdom of Great Britain, there were separate lord chancellors for the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland; there were lord chancellors of Ireland until 1922.
Margaret Holland, English noblewoman (b. 1385) deaths

Margaret Holland was a medieval English noblewoman. She was a daughter of Thomas Holland, 2nd Earl of Kent, who was the son of Joan "the Fair Maid of Kent". Margaret's mother was Alice FitzAlan, daughter of Richard FitzAlan, 10th Earl of Arundel and Eleanor of Lancaster.
Thomas Beaufort, Duke of Exeter (b. 1377) deaths

Thomas Beaufort, Duke of Exeter was an English military commander during the Hundred Years' War, and briefly Chancellor of England. He was the third of the four children born to John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster, and his mistress Katherine Swynford. To overcome their problematic parentage, his parents were married in 1396, and he and his siblings were legitimated in 1390 and again in 1397. He married the daughter of Sir Thomas Neville of Hornby, Margaret Neville, who bore him one son, Henry Beaufort. However, the child died young.
Johanna of Bavaria, Queen of Bohemia (b. c. 1362) deaths

Joanna of Bavaria, a member of the House of Wittelsbach, was German queen from 1376 and Queen of Bohemia from 1378 until her death, by her marriage with the Luxembourg king Wenceslaus.
John Wycliffe, English philosopher, theologian, and translator (b. 1331) deaths

John Wycliffe was an English scholastic philosopher, theologian, biblical translator, reformer, Catholic priest, and a seminary professor at the University of Oxford. He became an influential dissident within the Catholic priesthood during the 14th century and is considered an important predecessor to Protestantism. Wycliffe questioned the privileged status of the clergy, who had bolstered their powerful role in England, and the luxury and pomp of local parishes and their ceremonies.
Pope Callixtus III (d. 1458) births

Pope Callixtus III, born Alfonso de Borgia, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 April 1455 to his death in August 1458. Borgia spent his early career as a professor of law at the University of Lleida; he later served as a diplomat for the kings of Aragon. He became a tutor for King Alfonso V's illegitimate son Ferdinand. After arranging a reconciliation between Alfonso and Pope Martin V, Borgia was made Bishop of Valencia. In 1444, Pope Eugene IV named him a cardinal, and Borgia became a member of the Roman Curia. During the siege of Belgrade (1456), Callixtus initiated the custom that bells be rung at midday to remind the faithful to pray for the crusaders. The tradition of the Angelus noon bell still exists in most Catholic Churches to this day. He was also responsible for the retrial of Joan of Arc that saw her vindicated. He appointed two nephews as cardinals, one of whom became Pope Alexander VI. He is the last pope to date to take on the pontifical name "Callixtus".
Frederick III, Duke of Lorraine (b. 1238) deaths

Frederick III was the Duke of Lorraine from 1251 to his death. He was the only son and successor of Matthias II and Catherine of Limburg.
Margaret, Countess of Anjou (b. 1273) deaths

Margaret of Anjou was Countess of Anjou and Maine in her own right and Countess of Valois, Alençon and Perche by marriage. Margaret's father was King Charles II of Naples, whilst her husband was Charles, Count of Valois, and her older brother was Saint Louis of Toulouse; her nephew was King Charles I of Hungary.
Humphrey de Bohun, 3rd Earl of Hereford, English politician, Lord High Constable of England (b. 1249) deaths

Humphrey (VI) de Bohun, 3rd Earl of Hereford and 2nd Earl of Essex, was an English nobleman known primarily for his opposition to King Edward I over the Confirmatio Cartarum. He was also an active participant in the Welsh Wars and maintained for several years a private feud with the earl of Gloucester. His father, Humphrey (V) de Bohun, fought on the side of the rebellious barons in the Barons' War. When Humphrey (V) predeceased his father, Humphrey (VI) became heir to his grandfather, Humphrey (IV). At Humphrey (IV)'s death in 1275, Humphrey (VI) inherited the earldoms of Hereford and Essex. He also inherited major possessions in the Welsh Marches from his mother, Eleanor de Braose.

The Lord High Constable of England is the seventh of the Great Officers of State, ranking beneath the Lord Great Chamberlain and above the Earl Marshal. This office is now called out of abeyance only for coronations. The Lord High Constable was originally the commander of the royal armies and the Master of the Horse. He was also, in conjunction with the Earl Marshal, president of the court of chivalry or court of honour. In feudal times, martial law was administered in the court of the Lord High Constable.
Leopold V, Duke of Austria (b. 1157) deaths

Leopold V, known as the Virtuous was a member of the House of Babenberg who reigned as Duke of Austria from 1177 and Duke of Styria from 1192 until his death. The Georgenberg Pact resulted in Leopold being enfeoffed with Styria by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in 1193, which would lead to the eventual creation of modern Austria. Leopold was also known for his involvement in the Third Crusade where he fought in the Siege of Acre in 1191.
Ottokar III of Styria (b. 1124) deaths

Ottokar III was Margrave of Styria from 1129 until 1164.
Ahmad Maymandi, Persian statesman, vizier of the Ghaznavid Empire deaths
Abuʾl-Ḥasan al-Qāsim Aḥmad ibn Ḥasan Maymandī, better known as Ahmad Maymandi, and also known by his honorific title of Shams al-Kufat, was a Persian vizier of the Ghaznavid ruler Mahmud of Ghazni and the latter's son Mas'ud I of Ghazni.
The Ghaznavid dynasty was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic mamluk origin, ruling, at its greatest extent, large parts of Persia, Khorasan, much of Transoxiana and the northwest Indian subcontinent from 977 to 1186. The dynasty was founded by Sabuktigin upon his succession to the rule of Ghazna after the death of his father-in-law, Alp Tigin, who was an ex-general of the Samanid Empire from Balkh, north of the Hindu Kush in Greater Khorasan.
Ibn Hawshab, founder of the Isma'ili community in Yemen deaths
Abu'l-Qāsim al-Ḥasan ibn Faraj ibn Ḥawshab ibn Zādān al-Najjār al-Kūfī, better known simply as Ibn Ḥawshab, or by his honorific of Manṣūr al-Yaman, was a senior Isma'ili missionary from the environs of Kufa. In cooperation with Ali ibn al-Fadl al-Jayshani, he established the Isma'ili creed in Yemen and conquered much of that country in the 890s and 900s in the name of the Isma'ili imam, Abdallah al-Mahdi, who at the time was still in hiding. After al-Mahdi proclaimed himself publicly in Ifriqiya in 909 and established the Fatimid Caliphate, Ibn al-Fadl turned against him and forced Ibn Hawshab to a subordinate position. Ibn Hawshab's life is known from an autobiography he wrote, while later Isma'ili tradition ascribes two theological treatises to him.

Isma'ilism is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelver Shia, who accept Musa al-Kadhim, the younger brother of Isma'il, as the true Imām.
Muhammad ibn al-Qasim, Umayyad general (d. 715) births

Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqāfī was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh, inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His military exploits led to the establishment of the Islamic province of Sindh, and the takeover of the region from the Sindhi Brahman dynasty and its ruler, Raja Dahir, who was subsequently decapitated with his head sent to al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf in Basra. With the capture of the then-capital of Aror by Arab forces, Muhammad ibn al-Qasim became the first Muslim to have successfully captured Hindu land, which marked the beginning of Muslim rule in India.
Li Shiji, Chinese general (b. 594) deaths

Li Shiji, courtesy name Maogong, posthumously known as Duke Zhenwu of Ying, was a Chinese military general and politician who lived in the early Tang dynasty. His original family name was Xú, but he was later given the family name of the Tang imperial clan, Li, by Emperor Gaozu, the Tang dynasty's founding emperor. Later, during the reign of Emperor Gaozong, Li Shiji was known as Li Ji to avoid naming taboo because the personal name of Emperor Gaozong's predecessor, Emperor Taizong, had the same Chinese character "Shi". Li Shiji is also referred to as Xu Maogong and Xu Ji in the historical novels Shuo Tang and Sui Tang Yanyi.
Pope Sylvester I deaths

Pope Sylvester I was the bishop of Rome from 31 January 314 until his death. He filled the see of Rome at an important era in the history of the Western Church, yet very little is known of him. The accounts of his pontificate preserved in the seventh- or eighth-century Liber Pontificalis contain little more than a record of the gifts said to have been conferred on the church by Constantine I, although it does say that he was the son of a Roman named Rufinus. His feast is celebrated as Saint Sylvester's Day, on 31 December in Western Christianity, and on 2 January in Eastern Christianity.
Commodus, Roman emperor (b. 161) deaths

Commodus was a Roman emperor who ruled from 177 to 192. He served jointly with his father Marcus Aurelius from 176 until the latter's death in 180, and thereafter he reigned alone until his assassination. His reign is commonly thought of as marking the end of a golden period of peace in the history of the Roman Empire, known as the Pax Romana.
Quintus Fabius Maximus, consul suffectus deaths
Quintus Fabius Maximus was a general and politician of the late Roman Republic who became suffect consul in 45 BC.
Christian feast day: Pope Sylvester I (Catholic Church)

Pope Sylvester I was the bishop of Rome from 31 January 314 until his death. He filled the see of Rome at an important era in the history of the Western Church, yet very little is known of him. The accounts of his pontificate preserved in the seventh- or eighth-century Liber Pontificalis contain little more than a record of the gifts said to have been conferred on the church by Constantine I, although it does say that he was the son of a Roman named Rufinus. His feast is celebrated as Saint Sylvester's Day, on 31 December in Western Christianity, and on 2 January in Eastern Christianity.

The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2019. As the world's oldest and largest continuously functioning international institution, it has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. The church consists of 24 sui iuris churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state.
Christian feast day: December 31 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)

December 30 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar - January 1
International Solidarity Day of Azerbaijanis (Azerbaijan)
International Solidarity Day of Azerbaijanis is an annual public holiday in Azerbaijan celebrating the worldwide solidarity and unity of Azerbaijanis. The day was inspired by the dismantling of border fences between Soviet Azerbaijan and Iran in December 1989 and the collapse of the Berlin Wall in the same year.

Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city.
New Year's Eve (International observance), and its related observances: First Night (United States)

First Night is a North American artistic and cultural celebration on New Year's Eve, taking place from afternoon until midnight. Some cities have all their events during the celebration outside, but some cities have events that are hosted indoors by organizations in the city, especially clustered in the local historic downtown which are easily walkable to each other, such as churches and theaters. The celebration is family-friendly and alcohol-free, serving as an alternative to conventional adult New Year's parties that are abundant with alcohol. Since it happens on New Year's Eve, First Night celebrations are actually held on the last night of the old year. First Night celebrates a community's local culture, often featuring music, dance, comedy, art, fireworks and, in some cities, ice sculptures and parades.

The United States of America, commonly known as the United States or America, is a country in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. It is the third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. It has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 331 million, it is the most populous country in North America and the third most populous in the world. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City.
New Year's Eve (International observance), and its related observances: Last Day of the Year or Bisperás ng Bagong Taón, special holiday between Rizal Day and New Year's Day (Philippines)

Public holidays in the Philippines are of two types, regular holidays and special non-working days.

Rizal Day is a Philippine national holiday commemorating life and works of José Rizal, a national hero of the Philippines. It is celebrated every December 30, the anniversary of Rizal's 1896 execution at Bagumbayan in Manila.

New Year's Day is a festival observed in most of the world on 1 January, the first day of the year in the modern Gregorian calendar. 1 January is also New Year's Day on the Julian calendar, but this is not the same day as the Gregorian one. Whilst most solar calendars begin the year regularly at or near the northern winter solstice, cultures that observe a lunisolar or lunar calendar celebrate their New Year at less fixed points relative to the solar year.

The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is situated in the western Pacific Ocean and consists of around 7,641 islands that are broadly categorized under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the southwest. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. The Philippines covers an area of 300,000 km2 (120,000 sq mi) and, as of 2021, it had a population of around 109 million people, making it the world's thirteenth-most populous country. The Philippines has diverse ethnicities and cultures throughout its islands. Manila is the country's capital, while the largest city is Quezon City; both lie within the urban area of Metro Manila.
New Year's Eve (International observance), and its related observances: Novy God Eve (Russia)

Novy God is the Russian phrase for "New Year", and also designates the Russian New Year's Eve and New Year's Day celebration.

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering 17,098,246 square kilometres (6,601,670 sq mi), and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan.
New Year's Eve (International observance), and its related observances: Ōmisoka (Japan)

Ōmisoka (大晦日) or ōtsugomori (大晦) is a Japanese traditional celebration on the last day of the year. Traditionally, it was held on the final day of the 12th lunar month. With Japan's switch to using the Gregorian calendar at the beginning of the Meiji era, December 31 is now used for the celebration.

Japan is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering 377,975 square kilometers (145,937 sq mi); the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto.
New Year's Eve (International observance), and its related observances: The first day of Hogmanay or "Auld Year's Night" (Scotland)

Hogmanay is the Scots word for the last day of the old year and is synonymous with the celebration of the New Year in the Scottish manner. It is normally followed by further celebration on the morning of New Year's Day or in some cases, 2 January—a Scottish bank holiday.

Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a 96-mile (154-kilometre) border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands.
The seventh of the Twelve Days of Christmas (Western Christianity)

The Twelve Days of Christmas, also known as Twelvetide, is a festive Christian season celebrating the Nativity of Jesus. In some Western ecclesiastical traditions, "Christmas Day" is considered the "First Day of Christmas" and the Twelve Days are 25 December to 5 January, inclusive, with 6 January being a "thirteenth day" in some traditions and languages. However, 6 January is sometimes considered Twelfth Day/Twelfth Night with the Twelve Days "of" Christmas actually after Christmas Day from 26 December to 6 January. For many Christian denominations—for example, the Anglican Communion and Lutheran Church—the Twelve Days are identical to Christmastide, but for others, e.g. the Roman Catholic Church, Christmastide lasts longer than the Twelve Days of Christmas.

Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity. Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic Church, Independent Catholicism and Restorationism.
The sixth and penultimate day of Kwanzaa (United States)
Penult is a linguistics term for the second to last syllable of a word. It is an abbreviation of penultimate, which describes the next-to-last item in a series. The penult follows the antepenult and precedes the ultima. For example, the main stress falls on the penult in such English words as banána, and Mississíppi, and just about all words ending in –ic such as músic, frántic, and phonétic. Occasionally, "penult" refers to the last word but one of a sentence.

Kwanzaa is an annual celebration of African-American culture from December 26 to January 1, culminating in a communal feast called Karamu, usually on the sixth day. It was created by activist Maulana Karenga, based on African harvest festival traditions from various parts of West and Southeast Africa. Kwanzaa was first celebrated in 1966.